- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- MB2-712 Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2016 Customization and Configuration Dumps
Pass Microsoft MCP MB2-712 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


MB2-712 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 90 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 15, 2026
- Training Course 44 Video Lectures
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.
All Microsoft MCP MB2-712 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the MB2-712 Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2016 Customization and Configuration practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Exploring MB2-712: Key Skills for Dynamics CRM Customization and Configuration
The MB2-712 exam evaluates a professional’s capability to customize and configure Microsoft Dynamics CRM environments effectively. The focus is on practical skills that ensure administrators can tailor entities, fields, relationships, and processes to meet organizational requirements. Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in managing entity structures, configuring field properties, implementing relationships, and controlling data through status and status reason mechanisms. The exam emphasizes real-world application, requiring candidates to handle complex configurations while ensuring system integrity and data consistency.
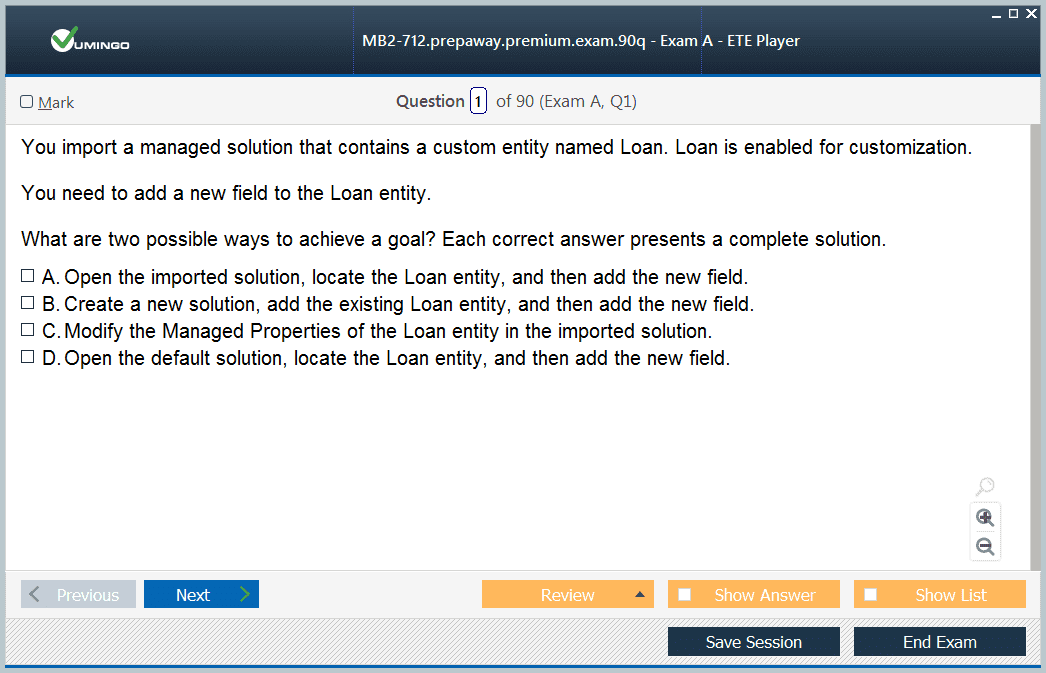
Entity Management and Ownership
A strong understanding of entity management is fundamental for MB2-712. Entities represent the core data structures within Dynamics CRM, and each can be either system-defined or custom-created to suit specific business needs. Candidates must understand entity ownership, including user-owned and organization-owned entities, as this impacts record security, access, and sharing. Entity properties, such as primary fields, display names, and customizable options, require careful configuration to ensure consistency and usability across the CRM system. Administrators must also recognize system entities like accounts, contacts, leads, and opportunities, understanding their unique behaviors and constraints compared to custom entities.
Configuring Fields and Field Properties
Fields are critical in capturing and storing relevant information within entities. MB2-712 tests the candidate’s ability to configure field types, field behavior, and properties effectively. This includes creating text, number, date, and lookup fields, as well as defining calculated and rollup fields for automated computations. Global option sets allow standardized selections across multiple entities, ensuring consistency and ease of reporting. Alternate keys are used to enforce uniqueness in key fields, preventing duplicate records and enhancing data quality. Field-level security ensures that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized users, while default values and requirement levels govern data completeness. Proper configuration of fields directly influences the quality of data and the efficiency of workflows within the CRM system.
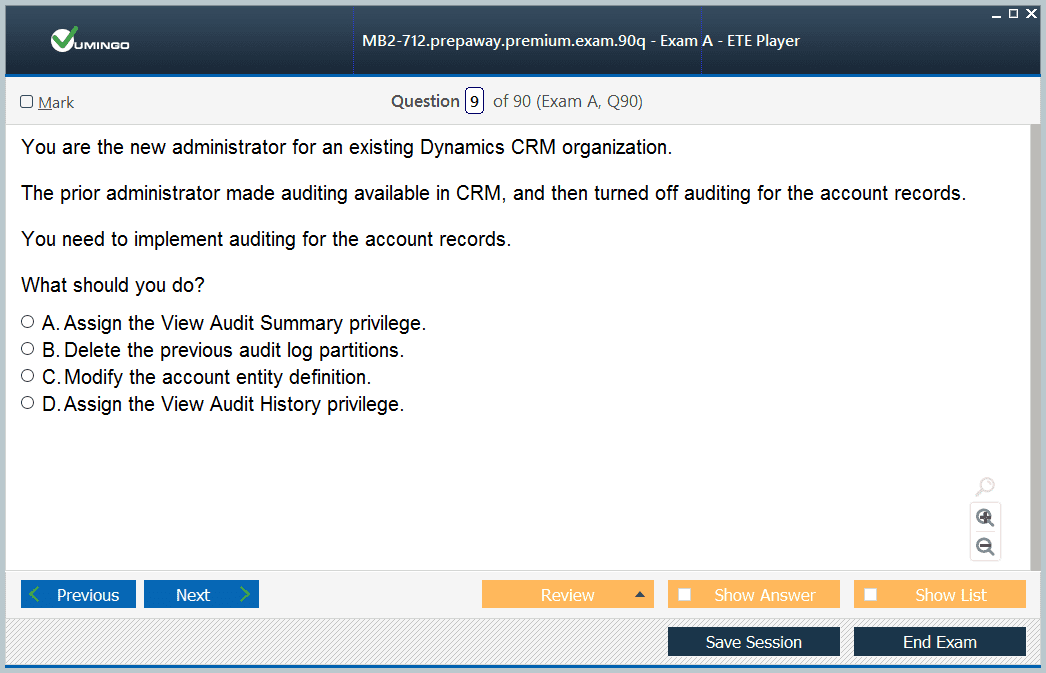
Status and Status Reason Management
Every entity in Dynamics CRM has a status field, often referred to as statecode, which indicates the current condition of a record. For custom entities, the standard states are active and inactive, with inactive records being read-only but capable of reactivation if needed. System entities like leads, opportunities, and cases have more complex state models. Leads can be open or qualified, opportunities may be open, won, or lost, and cases have states such as active or resolved. While the status field itself cannot be altered, candidates are tested on their ability to customize the associated status reason options. Status reasons provide granular context, such as distinguishing between a lead that is disqualified due to lack of interest versus an unreachable contact. Administrators can rename default status reasons, add new options, and ensure that these options accurately reflect organizational processes.
Configuring Status Reason Transitions
Status reason transitions define valid progressions between the different reasons associated with a status. For custom entities, administrators can configure the flow of status reasons to enforce logical record lifecycles. For example, an issue management system might move from logged to reviewed, then to accepted or rejected, and finally to resolved. Transition rules prevent records from moving backward inappropriately, such as returning an accepted issue to a logged state. Understanding and configuring these transitions is critical for maintaining data integrity, supporting workflow automation, and ensuring that business processes are adhered to consistently.
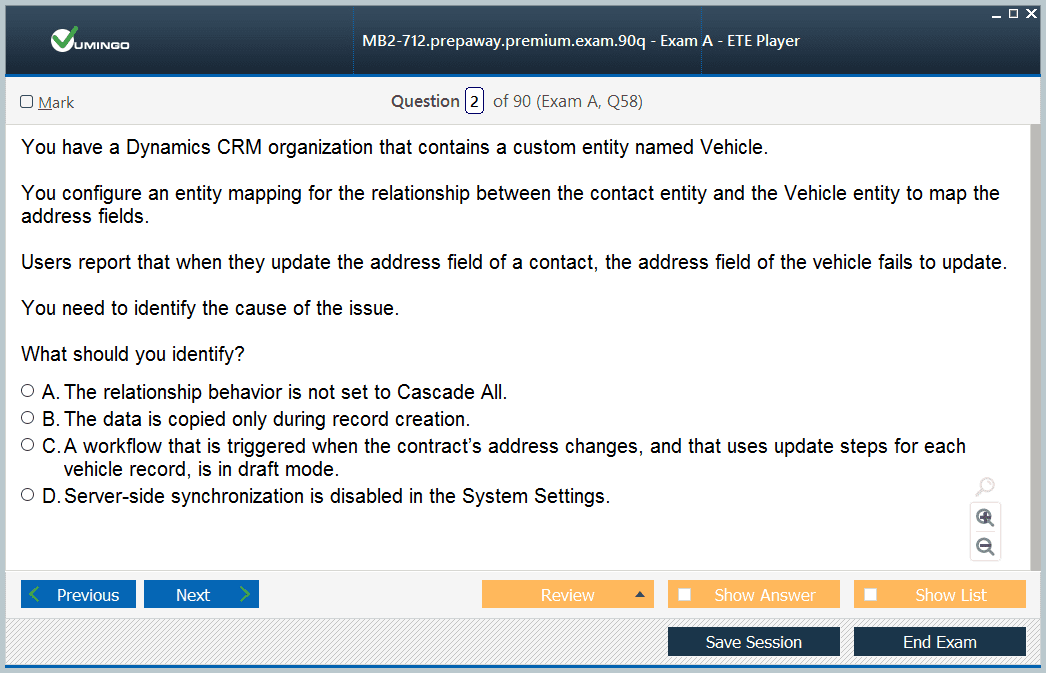
Implementing Entity Relationships
Relationships in Dynamics CRM define how data connects across entities, which is a key focus area in MB2-712. Understanding one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many relationships allows administrators to model real-world business interactions effectively. Cascading rules determine how operations on a parent record, such as deletion or reassignment, affect related child records. Hierarchical data structures support parent-child relationships, enabling organizations to manage complex reporting and visibility requirements. Entity mapping allows automatic transfer of data between related entities, ensuring data consistency across processes. Connections and connection roles enable non-hierarchical associations, allowing flexible relationships between records that support advanced business scenarios.
Field Calculations and Rollups
Calculated fields in Dynamics CRM allow administrators to define formulas that automatically derive values based on other fields within the same entity or related entities. Rollup fields aggregate data, such as summing the total value of associated opportunities or counting related cases. Proper use of calculated and rollup fields reduces manual data entry, ensures accuracy, and supports analytical reporting. Candidates are tested on creating these fields, configuring the appropriate aggregation logic, and ensuring that the calculations update correctly in real-time or on demand.
Global Option Sets and Alternate Keys
Global option sets standardize choices across multiple entities, which helps maintain consistency and simplifies reporting. They reduce errors by enforcing uniform selections for fields such as status, priority, or category. Alternate keys enforce data uniqueness on key fields, ensuring that duplicate records are not created. Understanding when and how to implement alternate keys is essential for maintaining data integrity, especially in systems where duplicate prevention is a priority.
Security and Data Access
Field-level security, entity ownership, and access controls are core topics for MB2-712. Administrators must ensure that sensitive information is only available to authorized personnel while enabling collaboration and visibility where appropriate. Security roles define permissions for entities, fields, and records, while business units and teams support organizational hierarchy and access distribution. Proper security configuration safeguards data, supports compliance requirements, and ensures that users have the right level of access to perform their tasks efficiently.
Managing System and Custom Entities
System entities have built-in behaviors and limitations, while custom entities provide flexibility to meet specific organizational requirements. Candidates must understand the differences, including which fields can be customized, which behaviors are fixed, and how custom entities can be extended with additional fields, relationships, and business rules. This knowledge allows administrators to create tailored solutions without compromising the stability of core CRM functionality.
Connections and Connection Roles
Connections enable non-hierarchical relationships between records, allowing organizations to represent flexible associations beyond parent-child structures. Connection roles define the type of relationship, such as advisor, partner, or competitor. This feature is important for capturing business networks, managing collaborative relationships, and supporting processes that require complex interactions across multiple entities. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to configure connections and assign roles appropriately to reflect organizational relationships.
Business Rules and Process Enforcement
Business rules enforce logic at the field or entity level without requiring custom code. They can validate data, set default values, show or hide fields, and trigger actions based on specific conditions. Configuring business rules correctly ensures consistency, reduces errors, and enhances user experience. Candidates are expected to understand how to implement these rules to enforce organizational policies and streamline processes across the CRM system.
MB2-712 emphasizes the ability to configure Dynamics CRM systems to align with organizational processes while maintaining data integrity and security. Candidates must master entity management, field customization, status and status reason configuration, relationships, and access controls. Understanding calculated fields, rollup fields, global option sets, and alternate keys enhances system functionality and reliability. Implementing connection roles, business rules, and status reason transitions ensures structured workflows and logical progression of records. Comprehensive knowledge of these topics equips candidates to design and manage Dynamics CRM environments effectively, meeting both business requirements and technical standards.
Advanced Field Configuration and Data Types
Candidates preparing for the MB2-712 exam must develop a comprehensive understanding of field configuration in Dynamics CRM. Each field within an entity can have specific data types such as text, number, date, lookup, or option set. Understanding how each type behaves and interacts with other components is critical for designing functional and scalable solutions. Calculated fields and rollup fields extend the system’s capabilities by performing dynamic calculations or aggregating data across related records. Proper configuration ensures data accuracy, reduces manual work, and enables advanced reporting and analytics. Field-level security controls ensure sensitive data is accessible only to authorized users, supporting compliance and confidentiality requirements.
Complex Entity Relationships
Entity relationships form the backbone of relational data structures in Dynamics CRM. MB2-712 candidates must demonstrate proficiency in creating and managing one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many relationships. Each relationship type has implications for data consistency, cascading behaviors, and workflow automation. Cascading rules determine how actions on parent records, such as deletion or updates, affect associated child records. Hierarchical relationships provide visibility into nested data structures, while entity mapping ensures synchronization of key attributes between related records. Mastery of relationships enables administrators to model complex business scenarios effectively and maintain integrity across multiple interconnected entities.
Status Management in Depth
Status fields indicate the current state of a record and are essential for workflow and reporting. Custom entities typically include active and inactive states, with inactive records rendered read-only but capable of reactivation. System entities such as leads, opportunities, and cases have specialized states aligned with their operational lifecycle. Understanding how these status fields influence record behavior is essential for effective CRM management. Although the status field cannot be customized, candidates can configure status reasons, which provide additional context for each state. This allows organizations to track progress, define workflow rules, and capture nuanced information relevant to decision-making.
Status Reason Customization and Transitions
Status reasons enhance workflow control by defining specific conditions associated with a record’s state. Candidates must know how to rename default status reasons, add new options, and configure valid transitions between reasons. For example, an issue in a project management context may progress from logged to reviewed, then accepted or rejected, and finally resolved if accepted. Preventing improper transitions, such as moving an accepted issue back to logged, maintains data integrity and ensures adherence to business rules. Properly configured status reason transitions help enforce logical record progression, supporting automation and structured workflows within Dynamics CRM.
Business Rules Implementation
Business rules in Dynamics CRM allow administrators to enforce logic at the entity or field level without custom code. They can validate user input, set default values, display or hide fields, and trigger actions based on conditions. Effective use of business rules ensures consistent data entry, reduces errors, and enhances system usability. Candidates preparing for MB2-712 must demonstrate the ability to design, implement, and manage business rules to enforce organizational policies, guide user behavior, and maintain data quality.
Connection Roles and Networking Entities
Connections in Dynamics CRM provide a flexible way to represent relationships between records outside hierarchical structures. Each connection uses a defined connection role to specify the type of relationship, such as advisor, partner, or competitor. Understanding how to configure connections and assign roles allows organizations to capture complex networks and associations that may not fit standard parent-child relationships. Proper use of connection roles supports advanced reporting, analytical processes, and holistic understanding of business interactions.
Data Quality and Alternate Keys
Maintaining data quality is a critical focus for MB2-712. Alternate keys allow administrators to enforce uniqueness on selected fields, preventing duplicate records and ensuring the integrity of business-critical information. Proper configuration of alternate keys is essential in environments where data duplication can compromise reporting accuracy, workflow efficiency, and decision-making. Combining alternate keys with validation rules and business rules supports a structured, reliable CRM environment.
Field-Level Security and Access Control
Candidates must understand how to implement field-level security to protect sensitive data. Security roles define which users or teams can create, read, update, or delete specific fields within an entity. Entity ownership, combined with business unit structures and team hierarchies, further defines access permissions. Mastery of access control ensures compliance with organizational policies, maintains confidentiality, and allows collaborative workflows without compromising sensitive information.
System Entities versus Custom Entities
System entities have predefined behaviors and constraints that cannot be altered, while custom entities provide flexibility to align with unique business processes. Understanding the differences is essential for proper configuration and avoiding conflicts within the system. MB2-712 candidates must be capable of extending custom entities with additional fields, relationships, and rules while integrating them effectively with system entities. This ensures that the overall system operates cohesively while meeting specific organizational requirements.
Practical Workflow Management
Workflow management is an essential aspect of Dynamics CRM customization. Candidates must configure entities, fields, and relationships to support automated processes that reduce manual intervention and ensure consistency. Workflow automation can include updating field values, sending notifications, or initiating tasks based on record changes. Properly configured workflows maintain process consistency, support business objectives, and enhance operational efficiency.
Advanced Rollup Field Configuration
Rollup fields aggregate data across related records, such as calculating total sales, summing open cases, or determining average values. Candidates must understand how to configure rollup fields, including setting aggregation criteria, filtering data, and scheduling updates. Mastery of rollup fields enhances reporting, supports decision-making, and reduces the need for manual calculations.
Global Option Sets and Standardization
Global option sets allow administrators to maintain standardized selections across multiple entities, improving data consistency and simplifying reporting. Candidates preparing for MB2-712 must understand how to create, modify, and apply global option sets effectively. Standardized options reduce errors, streamline data entry, and ensure that multiple entities use consistent terminologies for similar values.
Scenario-Based Problem Solving
The MB2-712 exam includes scenario-based tasks that test candidates’ ability to apply knowledge in practical situations. These scenarios require configuring entities, fields, relationships, and status reason transitions to meet specific business requirements. Scenario-based practice prepares candidates for real-world challenges, enhancing problem-solving abilities and ensuring they can manage complex CRM environments effectively.
MB2-712 tests advanced customization and configuration capabilities in Dynamics CRM. Candidates must demonstrate expertise in managing entities, configuring fields, defining relationships, enforcing business rules, and controlling data access. Mastery of status and status reason management, workflow configuration, connection roles, alternate keys, rollup fields, and global option sets ensures that administrators can create efficient, reliable, and scalable CRM environments. These skills support organizational workflows, enhance data integrity, and enable professionals to implement solutions that meet business needs effectively.
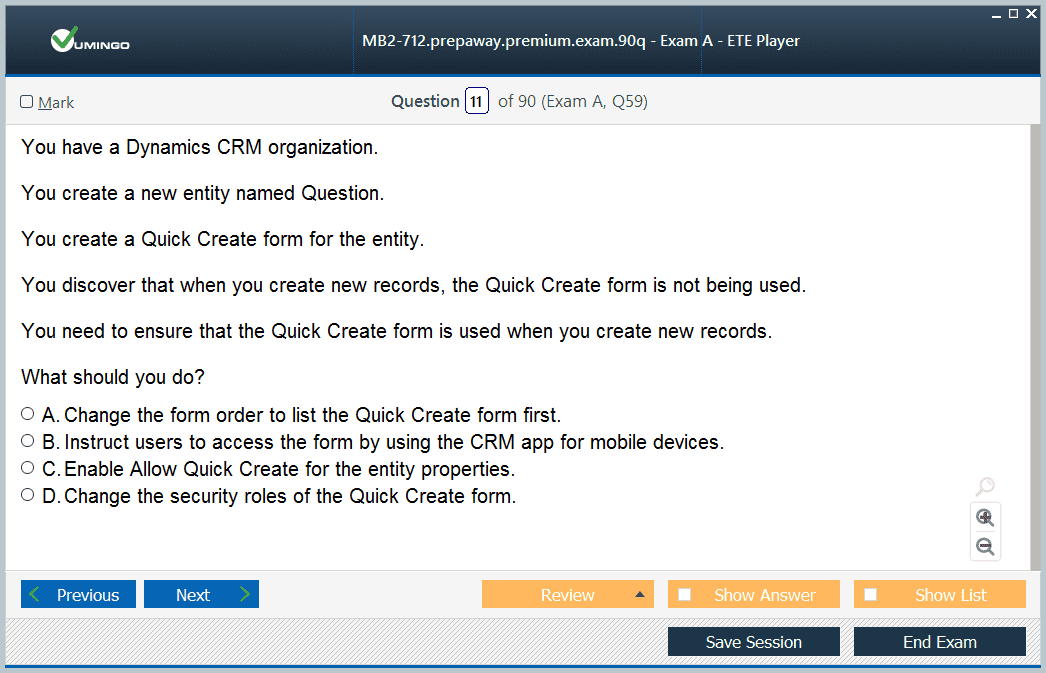
Customizing Forms and Views
In the MB2-712 exam, understanding how to customize forms and views is essential. Forms control how users interact with entity data and provide a structured interface for data entry and review. Candidates are expected to configure multiple forms per entity, including main forms, quick create forms, and card forms. Each form type serves a specific purpose, such as simplifying data entry or providing an overview of key information. Views display collections of records and can be customized to filter, sort, and group data based on business requirements. Knowledge of both forms and views allows administrators to create efficient user experiences that align with organizational workflows.
Implementing Business Process Flows
Business process flows guide users through standard procedures, ensuring consistency and compliance across operations. MB2-712 candidates must know how to design, configure, and manage these flows to support entity lifecycles. Business process flows can be applied to system or custom entities, guiding users through steps such as qualification, review, approval, or resolution. Each stage can include required fields and automated actions to enforce policies. Proper configuration of business process flows reduces errors, supports productivity, and ensures that records progress logically according to organizational procedures.
Advanced Relationship Management
Beyond basic entity relationships, candidates must demonstrate proficiency in configuring hierarchical relationships, connections, and mapping. Hierarchical relationships provide insights into parent-child structures, enabling reporting on aggregated data and facilitating management oversight. Connection roles allow entities to be associated in flexible ways that are not hierarchical, supporting scenarios like advisory relationships, partnerships, or collaborative tasks. Mapping fields between related entities ensures that critical data flows accurately across associated records, supporting synchronization and reducing manual entry. Mastery of these advanced relationship features is critical for maintaining data integrity and supporting complex business scenarios.
Utilizing Calculated and Rollup Fields
Calculated and rollup fields extend Dynamics CRM functionality by performing dynamic computations without custom code. Calculated fields derive values based on formulas using fields from the same entity or related entities, while rollup fields aggregate data from child records to provide insights at the parent level. Candidates must know how to configure these fields, including defining the calculation logic, selecting aggregation criteria, and managing update schedules. Proper use of calculated and rollup fields enhances reporting capabilities, supports business analysis, and minimizes manual calculations.
Configuring Global Option Sets and Field Behavior
Global option sets standardize selections across multiple entities, promoting consistency and simplifying reporting. Candidates are tested on creating and applying these option sets effectively, ensuring that fields across entities use uniform terminology. Additionally, understanding field behavior, including required levels, default values, and field-level security, is essential for ensuring that data entry aligns with organizational policies. Proper configuration of fields and option sets ensures high-quality data and reduces errors in operational processes.
Security and Access Management
MB2-712 emphasizes the importance of securing data while enabling collaboration. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to configure entity and field-level security, define roles, and manage access through ownership and business units. Security configurations determine who can create, read, update, or delete records and fields, ensuring sensitive information is protected. Access control also involves managing team and user hierarchies, supporting collaboration while maintaining compliance. Mastery of security principles ensures that users have the correct level of access to perform tasks efficiently without compromising data integrity.
Status and Status Reason Transitions
Status and status reason configuration plays a key role in record lifecycle management. While the status field indicates the primary state of a record, status reasons provide additional granularity to describe why a record is in a given state. Candidates must understand how to configure custom status reasons, rename default options, and define valid transitions to enforce logical record progression. This ensures that records follow business rules consistently, prevents inappropriate backtracking, and supports automated workflows. Configuring transitions accurately enhances operational control and ensures structured processing of records.
Business Rules and Workflow Automation
Business rules provide a no-code method to enforce data integrity, automate actions, and guide user input. MB2-712 candidates must understand how to design rules that validate data, set default values, trigger actions, and show or hide fields based on conditions. These rules complement workflows by enforcing logic at the entity or field level in real time. Workflow automation can include triggering tasks, updating records, sending notifications, and integrating processes across entities. Mastery of these tools ensures efficient, consistent, and compliant operations within Dynamics CRM.
Customizing Dashboards and Reports
Dashboards and reports provide critical insights into CRM data. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to create and configure dashboards that display key metrics, charts, and lists in a meaningful way. Reports can be customized to aggregate, filter, and present data for analysis or operational decision-making. Knowledge of how to configure dashboards and reports, including selecting visualizations, defining filters, and integrating data from multiple entities, is essential for providing actionable insights to users and management.
Practical Application Scenarios
The MB2-712 exam tests candidates on practical scenarios that replicate real-world challenges. These scenarios require configuring entities, fields, relationships, forms, views, business process flows, and workflows to meet specific business requirements. Candidates must demonstrate problem-solving skills, the ability to apply customization best practices, and adherence to organizational policies. Practicing scenario-based exercises helps candidates develop proficiency in designing and managing CRM environments effectively, ensuring readiness for both the exam and practical implementation.
Maintaining Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is a critical focus for MB2-712. Candidates must understand how to implement validation rules, enforce alternate keys, manage duplicate detection, and configure data consistency mechanisms. Properly managing data integrity ensures accurate reporting, reduces errors, and supports effective business decision-making. Administrators who master these aspects can design CRM systems that operate reliably and meet organizational requirements.
Integration and Connectivity
Although customization is the primary focus, MB2-712 also requires understanding how entities and configurations integrate with other systems. Integration points may involve importing and exporting data, connecting with external services, and ensuring that custom entities and relationships align with broader organizational workflows. Candidates must know how to configure mappings, maintain data consistency, and support seamless communication across integrated systems.
MB2-712 evaluates advanced knowledge of Dynamics CRM customization and configuration. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in managing entities, configuring fields, implementing relationships, and securing data. Mastery of status and status reason management, business rules, workflows, dashboards, and reports ensures that CRM environments operate efficiently and effectively. Additional focus on data integrity, calculated and rollup fields, global option sets, and integration enables administrators to deliver scalable, reliable, and compliant solutions. Developing these skills prepares professionals to meet complex organizational requirements and manage robust CRM deployments successfully.
Custom Entity Design and Lifecycle
In preparing for the MB2-712 exam, a deep understanding of custom entity design is crucial. Custom entities allow organizations to model business-specific data that is not covered by system entities. Candidates must know how to create entities with appropriate primary fields, ownership types, and entity properties. Designing custom entities requires consideration of their interaction with existing entities, security, data integrity, and workflow processes. Custom entities also involve configuring forms, views, and field-level customizations to support efficient data entry and reporting. Administrators must understand how these entities progress through their lifecycle, including status management, status reasons, and valid transitions between states.
Field Configuration and Advanced Properties
Fields are central to capturing and managing data within Dynamics CRM. Candidates must demonstrate mastery in configuring various field types, including text, numeric, date, lookup, and option sets. Advanced field properties, such as calculated fields and rollup fields, allow automated calculations and aggregations that reduce manual input. Global option sets provide standardized choices across multiple entities, enhancing consistency in data entry. Alternate keys are implemented to enforce uniqueness, preventing duplicate records. Understanding these field configurations ensures that data remains accurate, structured, and reliable while supporting complex business processes.
Status and Status Reason Management
Every record in Dynamics CRM has a status field representing its state. Custom entities typically have active and inactive states, while system entities may have more nuanced states reflecting business processes, such as open, won, or lost for opportunities. The MB2-712 exam requires candidates to understand how to configure status reasons, which provide additional context for each state. Status reasons can be renamed, new options added, and transitions defined to enforce logical record progressions. Proper configuration of status and status reasons ensures data integrity, supports automated workflows, and aligns CRM behavior with organizational rules.
Implementing Relationships and Cascading Behavior
Relationships define how data is interconnected across entities. MB2-712 candidates must be proficient in configuring one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many relationships. Cascading behaviors determine how operations on a parent record, such as deletion or reassignment, affect child records. Hierarchical relationships provide insights into parent-child data structures, which are critical for reporting and management oversight. Entity mapping ensures that key fields synchronize between related records, reducing manual entry errors. Properly managing relationships ensures data consistency, supports automation, and enables complex reporting and analysis.
Business Rules and Workflow Logic
Business rules enforce logic without requiring custom code. Candidates must configure rules to validate data, set default values, hide or show fields, and trigger actions based on conditions. Workflows extend automation capabilities, allowing updates to records, notifications, or task assignments triggered by entity events. Mastery of business rules and workflows ensures consistent application of business processes, reduces errors, and enhances productivity. Proper configuration of these tools is essential for maintaining compliance with organizational policies and supporting structured operations.
Connection Roles and Non-Hierarchical Relationships
Connections allow entities to be related in ways that are not hierarchical, supporting flexible associations such as partnerships, advisory roles, or collaborative tasks. Candidates must understand how to define connection roles and assign them to entities appropriately. Connection roles capture complex business relationships, enable accurate reporting, and support analytical tasks by providing visibility into non-linear associations between records. This knowledge is essential for modeling real-world interactions that extend beyond standard parent-child relationships.
Calculated and Rollup Fields
Calculated fields perform real-time computations based on other fields within the same entity or related entities. Rollup fields aggregate data from related records, such as summing total sales or counting active cases. MB2-712 candidates must understand how to create these fields, define their formulas or aggregation criteria, and ensure they update correctly. Effective use of calculated and rollup fields improves reporting accuracy, reduces manual work, and supports strategic business decisions.
Form and View Customization
Forms and views control how users interact with data in Dynamics CRM. Candidates must configure multiple forms per entity to support different scenarios, such as quick entry, detailed review, or mobile access. Views filter, group, and sort records, providing actionable insights and enabling efficient workflow management. Mastery of forms and views ensures that users can access relevant data quickly, enter information accurately, and follow organizational procedures effectively.
Data Integrity and Duplicate Prevention
Maintaining data integrity is critical for effective CRM management. Candidates must implement alternate keys, validation rules, and duplicate detection mechanisms to ensure accurate and consistent data. Proper configuration reduces errors, supports reporting, and ensures that workflows operate reliably. Understanding how to enforce data integrity through entity, field, and relationship configurations is a key component of MB2-712 preparation.
Security and Access Controls
Security in Dynamics CRM encompasses entity-level, field-level, and record-level controls. Candidates must configure security roles, ownership, business units, and teams to ensure appropriate access to data. Proper security configuration protects sensitive information, supports compliance, and allows collaboration where appropriate. Mastery of security concepts ensures that users have the access necessary to perform their tasks efficiently without compromising data protection.
Business Process Flows
Business process flows guide users through defined sequences of actions within an entity. MB2-712 candidates must design and implement flows that reflect organizational procedures, including required fields and automated actions at each stage. These flows standardize user actions, ensure process consistency, and provide visibility into record progress. Effective business process flows enhance operational efficiency and reduce errors in task execution.
Reporting and Dashboards
Dashboards and reports provide visual representations of CRM data for analysis and decision-making. Candidates must configure dashboards to display charts, metrics, and lists that provide insights into business performance. Reports aggregate and filter data, supporting strategic planning and operational oversight. Mastery of dashboards and reports ensures that stakeholders receive timely, accurate information to make informed decisions.
Integration Considerations
While MB2-712 focuses on customization, candidates must also understand how entities interact with external systems. Integration may include data imports, exports, and synchronization with other business applications. Proper configuration ensures data consistency, supports workflows, and allows seamless communication across platforms. Understanding integration points enhances the CRM’s value as a central hub for business operations.
Scenario-Based Problem Solving
The exam includes scenario-based tasks that require applying knowledge to real-world situations. Candidates must configure entities, fields, relationships, business rules, and workflows to meet specific business requirements. Scenario-based practice develops problem-solving skills, reinforces best practices, and prepares candidates to implement functional, efficient, and compliant CRM environments.
MB2-712 evaluates a candidate’s ability to customize and configure Dynamics CRM to meet complex business needs. Mastery of entity design, field configuration, status and status reason management, relationships, business rules, workflows, connection roles, calculated and rollup fields, forms, views, security, and reporting is essential. Candidates who develop these skills can create CRM environments that support efficient processes, maintain data integrity, enable automation, and provide actionable insights, positioning them as proficient administrators capable of managing advanced Dynamics CRM implementations.
Automating Processes with Workflows
In preparation for the MB2-712 exam, candidates must develop a strong understanding of workflows and how they can automate repetitive tasks within Dynamics CRM. Workflows are designed to execute actions automatically based on defined triggers, such as record creation, updates, or deletion. They can update fields, assign records, send notifications, or even initiate custom processes. Proper workflow design ensures consistency in data management, reduces human error, and aligns operational processes with organizational policies. Candidates must know how to configure sequential and parallel workflows, understand the implications of synchronous and asynchronous execution, and manage error handling to maintain reliable automation across entities.
Implementing Advanced Business Rules
Business rules provide administrators with a method to enforce logic at the entity or field level without writing custom code. MB2-712 candidates must be proficient in designing rules that dynamically validate data, calculate values, show or hide fields, and trigger other system actions. These rules are evaluated in real time, guiding user input and ensuring compliance with organizational requirements. Knowledge of how business rules interact with workflows and other automated processes is critical for designing a seamless and efficient CRM environment.
Managing Entity Ownership and Security
Ownership and security are core elements of Dynamics CRM customization. Each entity can be configured with user, team, or organization-level ownership, determining who can access, update, or delete records. MB2-712 candidates must understand how security roles, business units, and team hierarchies interact to control access to entities and fields. Proper configuration ensures sensitive data is protected while allowing collaboration and task execution within defined boundaries. Candidates must also understand how ownership impacts workflow execution and reporting visibility across different levels of the organization.
Optimizing Forms and User Experience
Forms are the primary interface through which users interact with entity data. Candidates must be able to customize main forms, quick create forms, and card forms to enhance usability and efficiency. Understanding how to organize sections, tabs, and sub-grids allows for intuitive navigation and data entry. Configuring form scripts and events can add dynamic behaviors, ensuring users are guided through the correct data input processes. Optimized forms improve user adoption, reduce errors, and enable quicker completion of tasks.
Customizing Views for Efficient Data Access
Views display collections of records and can be tailored to meet specific reporting and operational needs. MB2-712 candidates must configure system and personal views, applying filters, sorting, grouping, and conditional formatting. Views support decision-making by allowing users to quickly access relevant data sets. Knowledge of how to manage public and personal views, along with applying advanced filters and linked entity conditions, ensures that users can efficiently retrieve and act on information within Dynamics CRM.
Advanced Relationship Management
Complex business scenarios often require advanced relationship configurations beyond basic one-to-many or many-to-many relationships. Hierarchical relationships allow visibility into organizational structures, while connections enable flexible associations between unrelated entities. Candidates must understand how to configure relationship behaviors, cascading actions, and mapping of key fields. Proper management of relationships ensures data integrity, enables accurate reporting, and supports complex processes such as lead qualification, opportunity management, and case resolution.
Calculated and Rollup Field Mastery
Calculated fields perform automatic computations using existing entity fields, enabling dynamic values without manual input. Rollup fields aggregate data from related child records, providing summaries such as total opportunities, average sales, or case counts. MB2-712 candidates must know how to define calculation logic, manage update schedules, and ensure accuracy. Mastery of these fields supports enhanced reporting, improved data analysis, and streamlined decision-making by providing real-time insights into critical business metrics.
Global Option Sets and Standardization
Standardizing data entry across multiple entities is critical for maintaining consistency. Global option sets allow administrators to define a single set of selectable values applicable across multiple fields and entities. Candidates must understand how to create, modify, and deploy global option sets effectively. Standardization reduces errors, facilitates reporting, and ensures uniform terminology is used across the organization, supporting clearer analysis and communication.
Status and Status Reason Configuration
Every entity record has a status field representing its current state, while status reasons provide additional context. Candidates must understand how to configure custom status reasons, define valid transitions, and maintain logical progression of records. For example, a lead may move from new to contacted, qualified, or disqualified. Proper configuration prevents improper status changes, supports automated processes, and ensures that records reflect actual business scenarios accurately.
Implementing Business Process Flows
Business process flows guide users through structured procedures, ensuring consistency in handling records. Candidates must design flows with defined stages, required fields, and automated actions to align with organizational workflows. These flows apply to system and custom entities and support tasks such as opportunity management, case resolution, and project tracking. Effective business process flows enhance user adherence to processes, reduce errors, and provide a framework for consistent data capture and management.
Data Integrity and Duplicate Management
Maintaining data quality is essential for accurate reporting and operational efficiency. MB2-712 candidates must configure alternate keys, validation rules, and duplicate detection to prevent redundant or incorrect records. Implementing these mechanisms ensures that workflows, automation, and reporting rely on consistent, trustworthy data. Proper data integrity measures also enhance user confidence and improve decision-making processes.
Reporting and Dashboards Configuration
Dashboards provide visual insights into CRM data, while reports offer detailed analysis of entity information. Candidates must configure dashboards to include charts, lists, and metrics relevant to organizational goals. Reports should aggregate, filter, and display data across multiple entities to provide actionable insights. Mastery of dashboards and reports allows users and management to monitor performance, track key indicators, and make informed decisions based on real-time CRM data.
Scenario-Based Customization and Practical Skills
MB2-712 emphasizes applying knowledge to practical scenarios. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to configure entities, fields, relationships, workflows, business rules, forms, views, and dashboards to meet specific requirements. Scenario-based practice develops critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and readiness to implement CRM solutions that are both efficient and aligned with organizational objectives.
Integration and System Interoperability
While the focus is on customization, MB2-712 also requires an understanding of integration with external systems. Candidates should know how to map fields, synchronize data, and ensure that custom configurations maintain consistency across connected systems. This knowledge supports seamless operation of Dynamics CRM as a central platform for business operations, enabling effective data flow and unified processes.
The MB2-712 exam evaluates advanced skills in customizing and configuring Dynamics CRM. Key competencies include entity management, field configuration, relationships, status and status reason management, workflows, business rules, forms and views, security, dashboards, and integration. Mastery of these areas ensures administrators can build reliable, scalable, and efficient CRM environments. Developing proficiency across these domains enables professionals to manage complex processes, maintain data integrity, automate workflows, and provide actionable insights, making them capable of delivering robust CRM solutions that meet organizational needs.
Conclusion
Achieving proficiency in Dynamics CRM customization and configuration through the MB2-712 exam demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of how to design, implement, and manage complex CRM systems. The exam evaluates candidates on advanced administrative and technical skills required to configure entities, fields, relationships, business process flows, and automation tools within Dynamics CRM. Mastery of these areas equips professionals with the ability to create CRM solutions that align with organizational goals, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure data integrity.
A critical aspect of MB2-712 is the ability to design custom entities and configure their lifecycle. Understanding entity ownership, primary fields, and entity properties is fundamental to creating structures that support both system and business-specific requirements. Candidates must also manage field-level customizations, including calculated fields, rollup fields, and global option sets, which allow for automated computations and standardized data entry. Proper configuration of these elements ensures consistent, accurate data that supports reporting, analytics, and decision-making.
Managing status and status reasons is another essential competency. While the primary status field governs the overall state of a record, status reasons provide additional granularity and context. Candidates must configure valid transitions between status reasons, ensuring that records progress logically through their lifecycle. This functionality supports structured workflows, prevents inconsistencies, and provides clarity in operational processes. Advanced understanding of hierarchical relationships, entity mappings, and connection roles further allows administrators to model complex business interactions, enabling accurate reporting and data synchronization across entities.
Business process flows, workflows, and business rules are key components for enforcing organizational policies and automating processes. Business process flows guide users through structured procedures, ensuring consistency and compliance, while workflows automate repetitive actions and maintain efficiency. Business rules provide dynamic logic at the field or entity level, validating data and driving automated behaviors without custom code. Mastery of these automation tools allows CRM administrators to design solutions that reduce errors, increase productivity, and support operational objectives effectively.
Security and access management play a significant role in MB2-712 competencies. Candidates must configure security roles, ownership hierarchies, and field-level access to protect sensitive information while enabling collaboration. Proper security configuration ensures that users can access the data required for their roles without compromising confidentiality or compliance. This knowledge is critical for maintaining robust CRM environments that are secure, scalable, and capable of supporting diverse business processes.
Forms, views, dashboards, and reports are essential for presenting data effectively and supporting user adoption. Candidates must understand how to customize forms to improve usability, configure views for efficient data access, and design dashboards and reports that provide actionable insights. These tools enhance decision-making, enable operational transparency, and allow users to interact with the CRM system in a structured, intuitive manner.
Finally, MB2-712 also requires an understanding of integration and interoperability with external systems. Administrators must ensure that data flows seamlessly between Dynamics CRM and other business applications, maintaining consistency and supporting end-to-end processes. Knowledge of integration considerations further expands the value of the CRM platform as a central hub for organizational operations.
In conclusion, the MB2-712 exam assesses a candidate’s ability to deliver comprehensive, reliable, and scalable CRM solutions. It tests practical skills in entity design, field configuration, relationship management, automation, security, reporting, and integration. Professionals who master these competencies are equipped to manage complex Dynamics CRM environments, enforce business rules, optimize user experience, and maintain data integrity. Successfully achieving this certification validates advanced technical expertise, preparing administrators to implement efficient, compliant, and data-driven CRM solutions that enhance organizational performance and support strategic business goals.
Microsoft MCP MB2-712 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass MB2-712 Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2016 Customization and Configuration certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MO-300 - Microsoft PowerPoint (PowerPoint and PowerPoint 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
Purchase MB2-712 Exam Training Products Individually


Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the MB2-712 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the MB2-712 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the MB2-712 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The MB2-712 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the MB2-712 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for MB2-712. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the MB2-712 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my MB2-712 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the MB2-712 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed MB2-712 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!