- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- AI-900 Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals Dumps
Pass Microsoft Azure AI AI-900 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


AI-900 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 303 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 04, 2026
- Training Course 85 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 391 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Microsoft Azure AI AI-900 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the AI-900 Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
AI-900 Exam Success as a Non-Technical Professional: Step-by-Step Guide
The Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals certification, known as AI-900, represents an accessible entry point into artificial intelligence for professionals without extensive technical backgrounds. This certification validates foundational knowledge of machine learning and artificial intelligence concepts, along with related Microsoft Azure services. Non-technical professionals including business analysts, project managers, marketing specialists, and sales executives find this certification valuable for understanding AI capabilities and communicating effectively with technical teams. The exam does not require coding skills or deep mathematical knowledge, making it approachable for individuals from diverse professional backgrounds seeking to enhance their AI literacy and career prospects.
Understanding the certification landscape helps non-technical professionals position the AI-900 within broader career development strategies. Similar to how professionals evaluate whether CISSP recognition spans globally, individuals should understand that AI-900 certification carries Microsoft's brand recognition across industries worldwide. The certification demonstrates commitment to professional development and signals to employers that you possess foundational AI knowledge applicable across business functions. The relatively modest time investment required for AI-900 preparation makes it an efficient way to build AI competency without disrupting existing work responsibilities. Organizations increasingly value employees who understand AI concepts and can identify opportunities for AI implementation within their business domains.
Demystifying Artificial Intelligence Concepts for Business Professionals
Artificial intelligence encompasses various technologies that enable machines to perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, including recognizing patterns, making decisions, and understanding natural language. For non-technical professionals, grasping these fundamental concepts provides the foundation for exam success and practical business application. Machine learning represents a subset of AI where systems learn from data without explicit programming for every scenario. Deep learning, a specialized form of machine learning, uses neural networks inspired by human brain structure to process complex patterns in large datasets. Understanding these hierarchical relationships helps clarify the AI landscape and how different technologies complement each other.
The AI-900 exam assesses understanding of practical AI applications rather than theoretical mathematics or programming implementation. Candidates should focus on recognizing appropriate use cases for different AI technologies, understanding capabilities and limitations, and identifying ethical considerations. Much like professionals considering whether CISSP difficulty matches expectations, AI-900 candidates should approach preparation strategically by focusing on conceptual understanding rather than technical implementation details. Real-world examples help solidify abstract concepts, so relating AI principles to familiar applications like virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and spam filters enhances retention. The exam emphasizes practical knowledge that business professionals can apply when evaluating AI solutions or collaborating with data science teams on AI projects.
Machine Learning Fundamentals Explained Without Complex Mathematics
Machine learning enables computers to improve their performance on tasks through experience rather than explicit programming. For non-technical professionals, understanding the three main types of machine learning suffices for AI-900 success. Supervised learning uses labeled training data where the desired output is known, allowing systems to learn relationships between inputs and outputs. Unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data without predetermined categories or outcomes. Reinforcement learning trains models through trial and error, rewarding desired behaviors and penalizing undesired ones. Each approach suits different business problems, and recognizing appropriate applications demonstrates practical AI knowledge.
The model training process involves feeding data to algorithms that identify patterns and relationships, then testing the model's performance on new data. Non-technical candidates need not understand the mathematical calculations but should grasp that models require sufficient quality training data to perform well. Understanding concepts like overfitting, where models perform well on training data but poorly on new data, demonstrates practical awareness. Similar to how professionals assess whether cybersecurity careers offer worthwhile returns, evaluating AI project feasibility requires understanding data requirements and realistic performance expectations. Model evaluation metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall measure performance from different perspectives, helping business stakeholders assess whether models meet requirements. The iterative nature of machine learning means models improve through refinement and additional training data.
Computer Vision Applications in Modern Business Scenarios
Computer vision enables machines to derive meaningful information from digital images and videos, automating tasks that previously required human visual interpretation. Common applications include facial recognition systems, quality control inspection in manufacturing, medical image analysis, and autonomous vehicle navigation. For AI-900 preparation, non-technical professionals should understand how computer vision works at a conceptual level, including image classification that assigns labels to entire images, object detection that identifies and locates multiple objects within images, and semantic segmentation that classifies each pixel in an image. These capabilities enable diverse business applications across industries from retail to healthcare to agriculture.
Azure Computer Vision services provide pre-built models that businesses can use without developing custom solutions, lowering barriers to adoption. Understanding when to use custom vision models versus pre-built services demonstrates practical knowledge valued in the examination. Non-technical professionals benefit from recognizing that computer vision projects require significant labeled image data for training custom models. Much like understanding CISSP domain foundations in security, grasping computer vision fundamentals enables professionals to identify appropriate use cases and communicate requirements effectively. Optical character recognition represents a specialized computer vision application that extracts text from images, enabling document digitization and automated data entry. Understanding these capabilities helps business professionals envision applications within their specific domains.
Natural Language Processing Capabilities and Business Use Cases
Natural language processing enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in meaningful ways. Common applications include sentiment analysis that determines emotional tone in text, language translation, chatbots and virtual assistants, and text summarization. For non-technical professionals preparing for AI-900, understanding these application categories and their business value proves more important than knowing specific algorithms or implementation details. Key concepts include tokenization that breaks text into individual words or phrases, entity recognition that identifies people, places, organizations, and other significant items in text, and language understanding that extracts meaning and intent from user inputs.
Azure provides several natural language processing services including Text Analytics for sentiment analysis and key phrase extraction, Translator for multilingual content, and Language Understanding for building conversational AI applications. Understanding when each service applies and what capabilities it provides demonstrates the practical knowledge assessed in AI-900. Non-technical candidates should recognize that NLP models require training data in relevant languages and domains to perform well. Similar to how professionals explore information security analyst career paths, understanding NLP capabilities enables identifying automation opportunities within communication-intensive business processes. Speech recognition and text-to-speech technologies extend NLP capabilities to voice interfaces, enabling hands-free interactions and accessibility features. Conversational AI combines multiple NLP capabilities to create sophisticated chatbots and virtual agents that handle customer service inquiries and routine transactions.
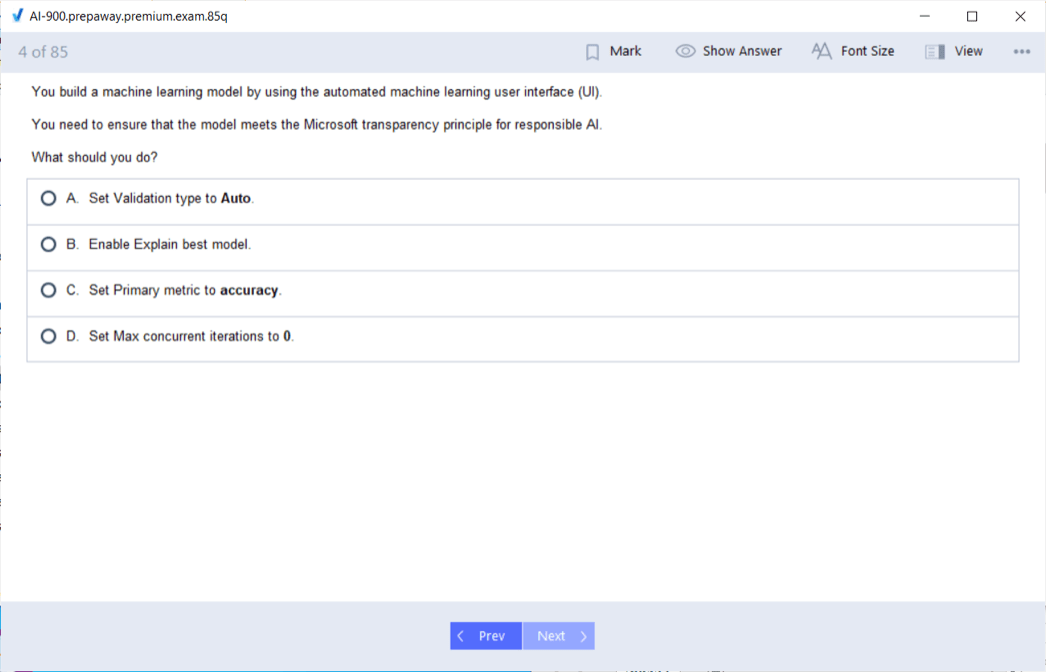
Responsible AI Principles and Ethical Considerations
Microsoft emphasizes six principles for responsible AI development and deployment: fairness, reliability and safety, privacy and security, inclusiveness, transparency, and accountability. Understanding these principles represents crucial knowledge for AI-900 success and practical AI implementation. Fairness ensures AI systems treat all people equitably without discriminating based on race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics. Reliability and safety mean AI systems perform consistently and safely across diverse conditions, with appropriate safeguards against harmful outputs. Privacy and security protect sensitive data used to train and operate AI systems, maintaining confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access.
Inclusiveness ensures AI systems work well for people with diverse backgrounds, abilities, and circumstances, designing for accessibility from the outset. Transparency means making AI systems understandable to users, explaining how they work and what data they use. Accountability establishes clear responsibility for AI system outcomes and provides mechanisms for addressing problems. Much like professionals navigating CISSP certification paths, AI-900 candidates must understand how principles translate into practice through impact assessments, bias testing, and ongoing monitoring. Real-world examples of AI failures, such as biased hiring systems or discriminatory credit decisions, illustrate why these principles matter. Understanding how to implement responsible AI practices through diverse training data, regular audits, and human oversight demonstrates practical application knowledge. The examination includes scenario-based questions assessing how candidates would apply responsible AI principles to specific situations.
Azure AI Services Overview for Business Decision Makers
Microsoft Azure provides numerous pre-built AI services enabling organizations to implement AI capabilities without building models from scratch. These services fall into several categories including vision services for image analysis, speech services for voice interaction, language services for text understanding, and decision services for personalized recommendations. Understanding the service portfolio and when to use each service demonstrates practical knowledge valuable for AI-900 success. Cognitive Services represent Azure's collection of pre-trained AI models accessible through APIs, allowing developers to add AI capabilities to applications with minimal machine learning expertise. Azure Machine Learning provides a complete platform for building, training, and deploying custom machine learning models when pre-built services don't meet specific requirements.
Bot Services enable creating conversational AI experiences across multiple channels including websites, mobile apps, and messaging platforms. Form Recognizer extracts structured data from documents, automating data entry and document processing workflows. Understanding these services at a conceptual level, including their inputs, outputs, and appropriate use cases, prepares candidates for exam questions about selecting appropriate Azure services for specific scenarios. Similar to mastering software development security in CISSP, understanding Azure AI services requires knowing when each tool applies and how they integrate into broader solutions. Candidates need not memorize detailed API specifications but should understand service capabilities, limitations, and pricing models. Hands-on experimentation with Azure AI services through free trial subscriptions significantly enhances conceptual understanding and retention. Microsoft Learn provides free, guided learning paths specifically designed for AI-900 preparation, complete with hands-on exercises in the Azure portal.
Conversational AI and Chatbot Implementation Strategies
Conversational AI enables natural language interactions between humans and computer systems through chatbots, virtual agents, and voice assistants. Modern conversational AI combines natural language understanding, dialog management, and natural language generation to create engaging user experiences. For non-technical professionals, understanding the components of conversational AI systems and their business applications provides practical knowledge applicable across industries. Intent recognition identifies what users want to accomplish through their messages, while entity extraction captures specific details like dates, locations, and product names. Dialog management maintains conversation context and determines appropriate system responses based on conversation history and business logic.
Azure Bot Service and Language Understanding work together to create sophisticated conversational AI solutions without requiring extensive programming knowledge. Understanding when conversational AI provides value, such as handling routine customer inquiries, guiding users through processes, or collecting information, helps business professionals identify implementation opportunities. Recognizing limitations including difficulty handling complex, multi-turn conversations or understanding nuanced language prevents unrealistic expectations. Much like understanding core IT security principles, grasping conversational AI fundamentals enables effective collaboration with technical teams implementing these solutions. Conversational AI requires ongoing refinement based on actual user interactions, analyzing conversation logs to identify gaps and improve responses. Multichannel deployment capabilities allow deploying chatbots across websites, mobile apps, Microsoft Teams, and other platforms from a single bot implementation. Understanding these concepts prepares candidates for AI-900 questions about conversational AI architecture and appropriate applications.
Knowledge Mining and Intelligent Search Solutions
Knowledge mining extracts insights from large volumes of unstructured content including documents, images, and databases, making information discoverable and actionable. Azure Cognitive Search combines traditional search capabilities with AI enrichment that extracts entities, identifies key phrases, translates languages, and recognizes sentiment within documents. For non-technical professionals, understanding how knowledge mining transforms raw content into structured, searchable information demonstrates practical AI application knowledge. The process typically involves ingesting content from diverse sources, applying AI skills to enrich and structure the content, and indexing the enriched content for search and analysis. Common business applications include enterprise search solutions, compliance and legal document review, customer service knowledge bases, and competitive intelligence gathering.
Built-in AI skills handle common enrichment tasks like language detection, key phrase extraction, and entity recognition, while custom skills enable domain-specific processing. Understanding the knowledge mining pipeline from content ingestion through enrichment to searchable index prepares candidates for exam questions about solution architecture. Non-technical professionals should recognize that knowledge mining provides value when organizations have significant volumes of unstructured content containing valuable information difficult to access through manual review. Similar to how professionals pursue top cybersecurity certifications for career advancement, understanding knowledge mining capabilities positions professionals to lead digital transformation initiatives. The technology enables compliance teams to quickly identify relevant documents during investigations, customer service representatives to find accurate answers quickly, and analysts to discover trends across large document collections. Azure Cognitive Search provides scalability to handle enterprise-scale content volumes while maintaining fast query response times. Understanding these capabilities at a conceptual level prepares candidates for scenario-based exam questions about appropriate knowledge mining applications.
Practical Study Strategies for Non-Technical Exam Preparation
Effective AI-900 preparation for non-technical professionals requires strategic study approaches emphasizing conceptual understanding over technical implementation. Microsoft Learn provides free, comprehensive learning paths specifically designed for AI-900, structured as self-paced modules covering all exam objectives. These interactive modules include text explanations, videos, knowledge checks, and hands-on exercises in the Azure portal, accommodating diverse learning styles. Supplementing official Microsoft content with third-party courses, books, and practice exams provides multiple perspectives and reinforces concepts through repetition. Creating a structured study plan allocating specific time daily or weekly to exam preparation maintains consistent progress and prevents last-minute cramming.
Active learning techniques including summarizing key concepts in your own words, teaching material to others, and relating AI concepts to familiar business scenarios enhance retention significantly more than passive reading. Joining online study groups or forums connects candidates with peers sharing similar goals, providing motivation, support, and opportunities to discuss challenging concepts. Much like how professionals transform careers through EC-Council certifications, strategic preparation enables non-technical professionals to achieve AI-900 success efficiently. Hands-on practice with Azure AI services proves invaluable for solidifying theoretical knowledge, and Microsoft provides free Azure subscriptions including credits for experimenting with AI services. Taking practice exams under timed conditions builds familiarity with question formats and identifies knowledge gaps requiring additional study. Reviewing incorrect practice exam answers thoroughly, understanding why you missed questions and studying related concepts, transforms mistakes into learning opportunities. Scheduling the actual exam creates accountability and provides a concrete goal motivating consistent preparation effort.
Hands-On Azure Portal Exploration for Practical Learning
While AI-900 doesn't require hands-on Azure experience, practical exploration significantly enhances conceptual understanding and retention. Creating a free Azure account provides access to many AI services without credit card requirements, enabling experimentation without financial risk. Starting with pre-built demos and tutorials guides initial exploration, gradually building confidence before attempting independent projects. Vision services offer particularly accessible starting points, allowing uploads of your own images to test object detection, face recognition, and image description capabilities. Seeing AI services in action transforms abstract concepts into concrete experiences, making exam preparation more engaging and memorable.
Language services provide another approachable entry point, testing sentiment analysis on sample text, translating content between languages, and experimenting with key phrase extraction. Following step-by-step tutorials from Microsoft Learn guides hands-on exercises aligned with exam objectives, ensuring productive experimentation. Understanding service configuration options, input requirements, and output formats through direct interaction prepares candidates for exam questions about service capabilities. Similar to how professionals master network security examination strategies, hands-on practice builds intuitive understanding surpassing theoretical study alone. Documenting your experiments including screenshots, observations, and lessons learned creates personalized reference materials useful during final exam review. Comparing results from different AI services applied to the same input illustrates relative strengths and appropriate use cases for each service. Hands-on experience also demystifies Azure, building general cloud platform familiarity valuable beyond AI-900 certification.
Data Analytics Fundamentals Supporting AI Implementations
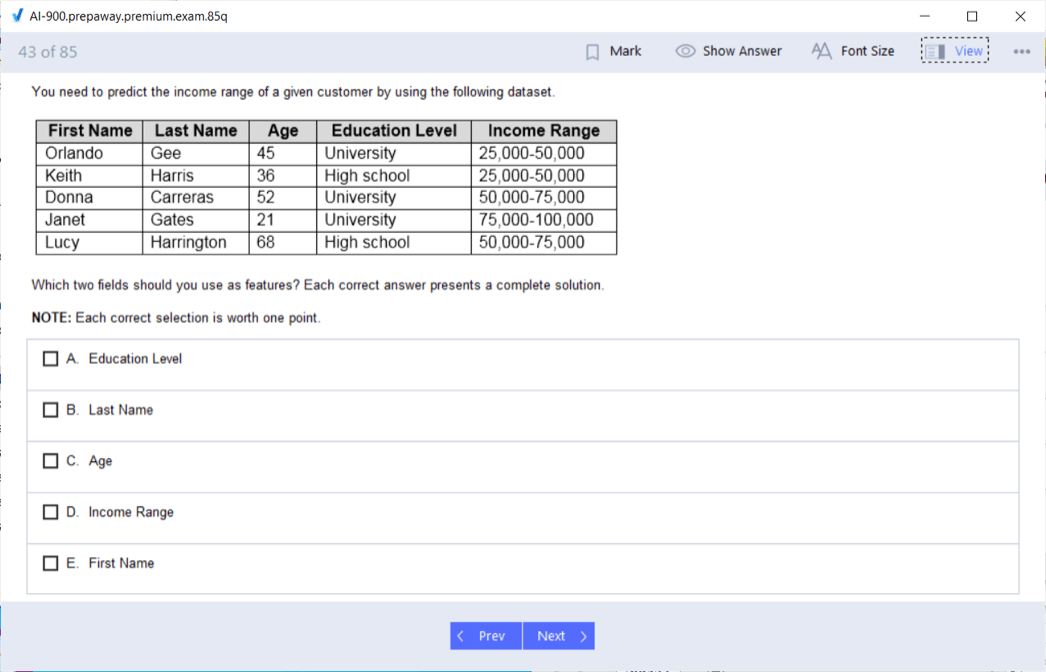
Understanding basic data concepts provides essential context for AI and machine learning discussions. Data exists in structured formats like databases and spreadsheets, semi-structured formats like JSON and XML, and unstructured formats including text documents, images, and videos. AI models typically require significant data for training, and data quality directly impacts model performance. Recognizing that "garbage in, garbage out" applies to AI emphasizes the importance of high-quality training data. Data preparation including cleaning, formatting, and labeling often represents the most time-consuming aspect of AI projects, requiring significant resources before model training begins.
Understanding data privacy and governance becomes increasingly important as organizations implement AI solutions processing sensitive information. Regulations like GDPR impose requirements for data handling, storage, and processing that affect AI implementations. Non-technical professionals should understand concepts like data classification, access controls, and audit logging at a conceptual level. Much like understanding website analytics differences, grasping data fundamentals enables informed business decisions about AI projects. Data storage options in Azure include relational databases for structured data, Cosmos DB for globally distributed data, and Blob Storage for unstructured content like images and documents. Understanding when each storage type applies demonstrates practical knowledge valuable for AI-900 and real-world implementations. The exam includes questions about appropriate data storage choices for different AI scenarios, requiring conceptual understanding of storage options and their characteristics.
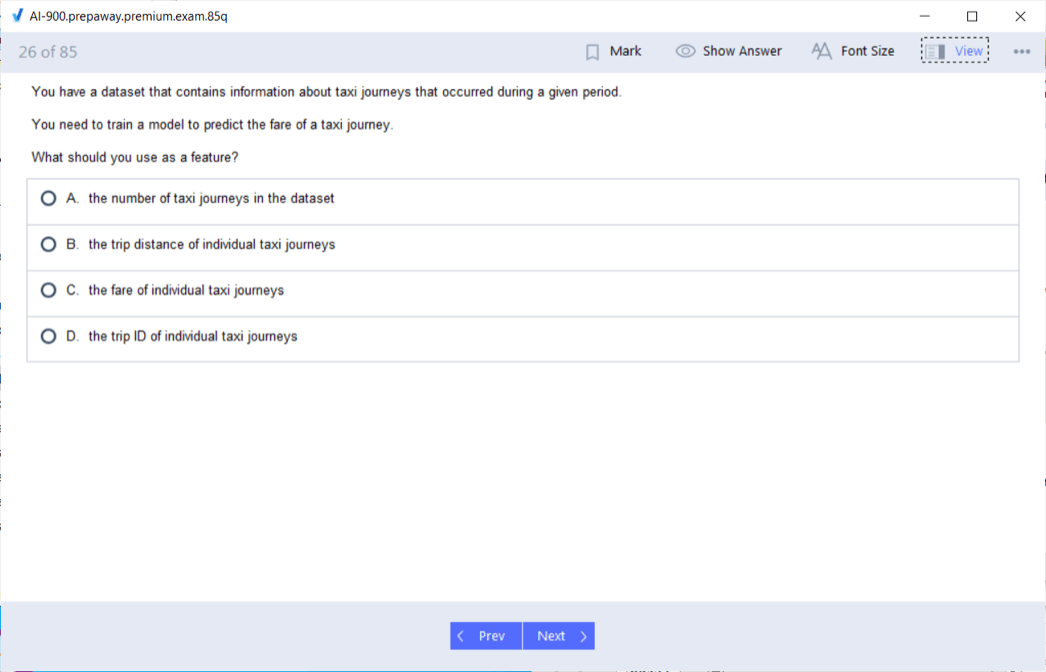
Model Training and Evaluation Concepts for Business Stakeholders
Model training involves feeding data to machine learning algorithms that identify patterns and relationships, iteratively adjusting internal parameters to improve performance. Non-technical professionals need not understand mathematics but should grasp that training requires computational resources and time, particularly for complex models and large datasets. The training process produces a trained model that can make predictions on new data, and model quality depends heavily on training data quality and quantity. Understanding the distinction between training, validation, and test data sets helps business stakeholders appreciate the rigor required for proper model development. Training data teaches the model, validation data guides refinement during training, and test data provides unbiased performance assessment.
Model evaluation metrics quantify performance from different perspectives, and understanding these metrics enables informed discussions about whether models meet business requirements. Accuracy measures the percentage of correct predictions overall, while precision measures what percentage of positive predictions were actually correct, and recall measures what percentage of actual positives were correctly identified. Different business scenarios prioritize different metrics based on the relative costs of false positives versus false negatives. Similar to strategies for conquering AI fundamentals examinations, understanding evaluation concepts requires focusing on practical interpretation rather than mathematical calculation. Confusion matrices visualize model performance across different classes, helping identify specific areas where models struggle. Model performance varies across different datasets and real-world conditions, requiring ongoing monitoring and potential retraining as data distributions change over time. Understanding these concepts enables business professionals to set realistic expectations, interpret technical team reports, and make informed decisions about AI project investments.
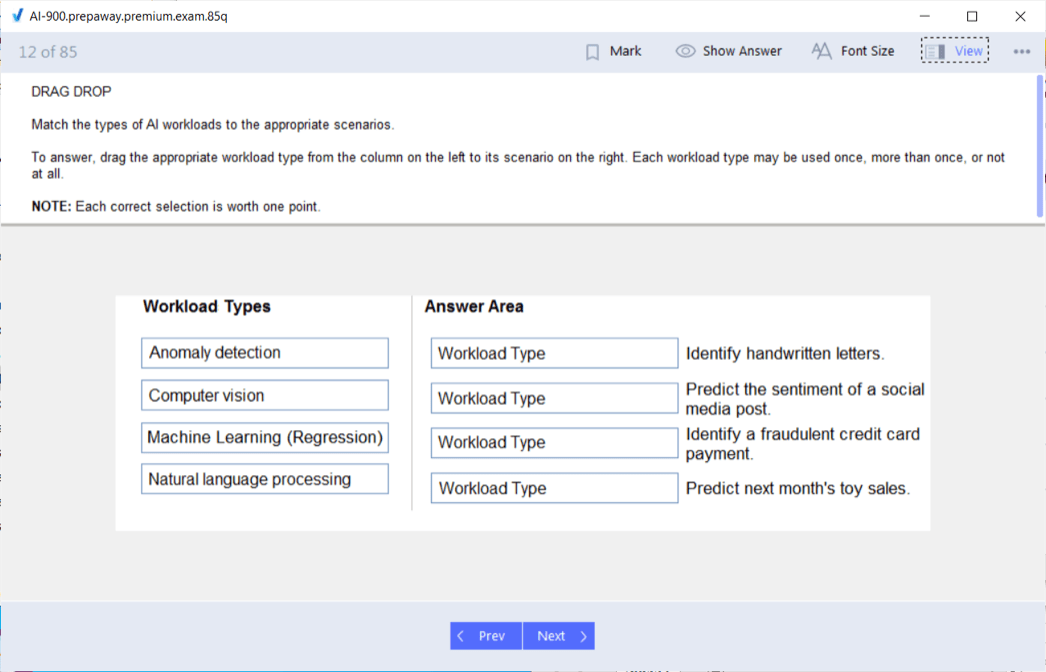
AI Workload Classification and Appropriate Solution Selection
The AI-900 exam assesses ability to identify appropriate AI solutions for specific business scenarios, requiring understanding of different AI workload types and their characteristics. Computer vision workloads analyze visual content, appropriate for scenarios like quality control inspection, inventory management through image analysis, and security surveillance. Natural language processing workloads handle text and speech, suitable for customer service chatbots, document analysis, and sentiment monitoring across social media. Predictive analytics workloads forecast future outcomes based on historical patterns, applicable to demand forecasting, customer churn prediction, and maintenance scheduling. Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns indicating potential problems, valuable for fraud detection, equipment failure prediction, and network security monitoring.
Recommendation systems suggest relevant products, content, or actions based on user preferences and behaviors, powering personalized shopping experiences and content discovery. Understanding these workload categories and recognizing appropriate applications demonstrates practical knowledge central to AI-900 success. Exam questions present business scenarios requiring candidates to identify the most appropriate AI workload type and corresponding Azure services. Much like understanding ServiceNow CSA examination foundations, recognizing patterns across scenarios enables systematic solution selection. Non-technical professionals should practice analyzing business problems to identify underlying AI requirements, matching requirements to appropriate workload types and services. Some scenarios require combining multiple AI capabilities, such as conversational AI that incorporates both natural language understanding and knowledge mining to provide comprehensive customer support. Understanding how different AI services integrate to create complete solutions demonstrates advanced comprehension valuable professionally beyond certification success.
Certification Value Proposition for Career Advancement
AI-900 certification provides non-technical professionals with validated credentials demonstrating AI literacy increasingly valued across industries. As organizations integrate AI into business processes, employees who understand AI capabilities and limitations become valuable assets. The certification signals to employers that you've invested in professional development and possess foundational knowledge enabling effective collaboration with technical teams. Unlike more advanced certifications requiring technical prerequisites, AI-900 remains accessible while still providing meaningful credential value. The relatively modest preparation time investment yields significant returns through enhanced resume credentials, expanded job opportunities, and confidence in AI-related discussions.
Many organizations pursuing digital transformation initiatives value employees who combine domain expertise with AI awareness, creating opportunities for certified professionals to lead AI adoption within their business areas. The certification prepares professionals to identify AI implementation opportunities, evaluate vendor solutions, and contribute meaningfully to AI project planning and oversight. Similar to benefits from SMAC certification achievement, AI-900 credentials differentiate professionals in competitive job markets. The knowledge gained through preparation applies immediately in current roles, enabling professionals to contribute AI-informed perspectives during strategy discussions and project planning. Beyond immediate career benefits, the certification provides foundation for pursuing more advanced Azure certifications as interest and experience grow. Understanding AI fundamentals positions professionals to take advantage of emerging opportunities as AI adoption accelerates across industries and job functions. The certification also demonstrates adaptability and commitment to continuous learning, characteristics employers value increasingly in rapidly evolving business environments.
Exam Registration Process and Test-Taking Strategies
Registering for AI-900 through Microsoft's certification portal involves creating a Microsoft certification profile, scheduling an exam appointment through Pearson VUE, and paying the examination fee. Microsoft frequently offers discounts and promotions reducing certification costs, and Microsoft Ignite and Build conferences typically include free exam vouchers for attendees. Online proctored exams provide flexibility to test from home or office, while testing center options suit candidates preferring formal testing environments. Scheduling exams several weeks in advance creates accountability and motivation during preparation while allowing flexibility to reschedule if necessary. Understanding exam logistics including duration, question count, and passing score reduces test-day anxiety and allows appropriate time allocation.
The AI-900 exam includes various question types including multiple choice, drag-and-drop, and scenario-based questions requiring analysis of business situations. Reading questions carefully and identifying key requirements before reviewing answer options prevents common mistakes from misunderstanding scenarios. Elimination strategies help narrow options when you're uncertain, improving probability of correct responses. Time management proves crucial, pacing yourself to ensure adequate attention to all questions without rushing through sections. Similar to approaches for career advancement through certification, strategic test-taking maximizes performance. Flagging difficult questions for review after completing items you can answer confidently prevents getting stuck and maintains momentum. Taking advantage of scheduled breaks during longer exams helps maintain focus and prevents fatigue-related mistakes. Remaining calm when encountering unfamiliar questions prevents anxiety from cascading and impairing performance on subsequent items. Trusting your preparation and initial instincts often proves more reliable than second-guessing answers repeatedly. Understanding that passing requires demonstrating competency across multiple domains rather than perfection on every question reduces pressure and enables confident performance.
Marketing Applications of AI Knowledge in Digital Campaigns
AI-900 knowledge applies directly to marketing professionals seeking to leverage AI capabilities for campaign optimization, customer insights, and content personalization. Understanding natural language processing enables evaluating sentiment analysis tools that monitor brand perception across social media and review sites. Computer vision capabilities support visual content analysis, identifying how brand imagery appears across digital channels and analyzing competitor visual strategies. Predictive analytics inform customer segmentation, lifetime value prediction, and churn risk identification, enabling targeted retention campaigns. Recommendation systems power personalized product suggestions and content recommendations that improve customer engagement and conversion rates.
Conversational AI enhances customer experience through intelligent chatbots that answer questions, guide purchasing decisions, and provide 24/7 support. Marketing automation platforms increasingly incorporate AI for send-time optimization, subject line generation, and content personalization. Understanding these capabilities enables marketing professionals to evaluate vendor solutions critically, set realistic expectations, and identify high-value AI implementation opportunities. Similar to mastering social media marketing terminology, understanding AI concepts enables effective communication with technical teams and vendors. AI-powered analytics tools reveal customer journey patterns, attribution insights, and campaign performance drivers that inform strategy optimization. Natural language generation tools assist content creation, generating product descriptions, social media posts, and email variations at scale. Understanding AI capabilities and limitations helps marketing professionals identify tasks suitable for automation versus those requiring human creativity and judgment. The strategic advantage comes from combining marketing domain expertise with AI awareness, identifying opportunities others might miss and leading successful AI adoption initiatives.
Academic Test Preparation Parallels and Study Methodology
Preparing for AI-900 shares methodological similarities with academic test preparation, where systematic study approaches yield superior results compared to cramming. Creating detailed study schedules that allocate specific times to different exam domains ensures comprehensive coverage of all topics. Breaking complex topics into manageable chunks prevents overwhelm and enables steady progress through material. Spaced repetition, reviewing material at increasing intervals, significantly enhances long-term retention compared to massed practice. Active recall through practice questions and self-testing strengthens memory more effectively than passive rereading of materials.
Understanding personal learning preferences and adapting study methods accordingly maximizes efficiency and retention. Visual learners benefit from diagrams, flowcharts, and video content, while reading/writing learners prefer text-based materials and note-taking. Similar to strategies in ACT math preparation resources, identifying optimal study approaches accelerates AI-900 preparation. Auditory learners gain value from recorded lectures, podcasts, and discussing concepts with study partners. Kinesthetic learners benefit most from hands-on Azure portal experimentation and interactive exercises. Maintaining consistent study schedules builds momentum and prevents knowledge decay between sessions. Setting specific, measurable goals for each study session provides direction and enables tracking progress toward certification readiness. Creating summary sheets or mind maps consolidates information and provides quick reference materials for final review before the exam. Understanding the examination blueprint and weighting of different topics enables strategic time allocation, focusing more effort on heavily weighted domains.
Mathematics and Science Test Success Mindsets Applied to AI-900
Non-technical professionals may feel intimidated by AI concepts, similar to anxiety some experience with mathematics or science examinations. However, AI-900 requires conceptual understanding rather than mathematical calculation or programming skills. Adopting growth mindsets that view challenges as learning opportunities rather than evidence of inadequacy proves essential for success. Breaking down complex AI concepts into simpler components makes intimidating topics manageable, similar to how complex math problems yield to systematic problem-solving approaches. Recognizing that everyone starts as a beginner and expertise develops through consistent effort and practice builds confidence.
Analogies relating AI concepts to familiar experiences enhance understanding and retention. For example, machine learning resembles how children learn through examples, while neural networks mirror how interconnected brain neurons process information. Understanding fundamental concepts thoroughly before advancing to complex topics prevents knowledge gaps that undermine later learning. Similar to mastering ASVAB mathematics comprehensively, systematic AI-900 preparation builds cumulative knowledge where each concept supports understanding subsequent material. Embracing mistakes as learning opportunities rather than failures creates positive learning environments where growth flourishes. Seeking help when stuck, whether through online forums, study groups, or mentors, prevents frustration from derailing progress. Celebrating small victories and progress milestones maintains motivation throughout preparation journeys. Understanding that certification demonstrates baseline competency rather than complete mastery reduces pressure and enables enjoyable learning experiences. The knowledge gained provides foundations for continuous learning as AI technologies evolve and your expertise deepens through practical application.
Chemistry and Life Sciences Analogies for AI Concepts
Drawing analogies between AI concepts and familiar scientific principles helps non-technical professionals grasp abstract ideas. Machine learning model training resembles chemistry experiments where specific inputs yield predictable outputs, and understanding relationships requires systematic testing. Data features in machine learning correspond to variables in scientific experiments, where identifying relevant factors determines success. Overfitting resembles memorizing specific examples rather than understanding underlying principles, performing well on familiar material but failing with novel situations. Transfer learning mirrors how scientific knowledge from one domain applies to related areas, leveraging existing understanding to accelerate new learning.
Neural network layers resemble biological systems where specialized components perform specific functions, combining to create complex capabilities exceeding individual component abilities. Activation functions in neural networks determine whether signals propagate forward, similar to how threshold levels in biological systems determine whether reactions proceed. Similar to mastering organic chemistry MCAT concepts, understanding AI fundamentals requires grasping relationships between components rather than memorizing isolated facts. Ensemble methods combining multiple models resemble how biological redundancy improves system reliability and performance. Understanding AI through scientific analogies makes abstract concepts concrete, enhancing comprehension and retention for non-technical professionals. These conceptual frameworks provide mental models supporting deeper understanding beyond surface-level memorization. The scientific method's emphasis on hypothesis testing, observation, and iterative refinement parallels machine learning development cycles. Recognizing these parallels helps professionals from scientific backgrounds leverage existing mental models when learning AI concepts.
Strategic Preparation Methods and Comprehensive Domain Coverage
Structured preparation strategies distinguish successful AI-900 candidates from those who struggle despite adequate study time. Creating comprehensive study plans that map Microsoft's official exam objectives to specific learning resources ensures complete coverage without gaps. The exam outline published by Microsoft details all topics assessed, providing authoritative guidance for preparation focus. Allocating study time proportionally to domain weights maximizes efficiency by emphasizing heavily tested areas while ensuring adequate coverage of all topics. Breaking the multi-week or multi-month preparation journey into smaller milestones creates achievable targets that maintain motivation and enable progress tracking.
Study environments significantly influence learning effectiveness, with quiet, dedicated spaces minimizing distractions and enabling focused concentration. Consistency in study location and times builds routines that trigger mental readiness for learning. Digital distractions including social media, email, and messaging represent common productivity killers, and silencing notifications during study sessions preserves focus. Much like professionals pursuing blockchain certification credentials, AI-900 candidates benefit from eliminating interruptions during dedicated preparation time. Pomodoro techniques alternating focused study intervals with short breaks maintain mental freshness and prevent fatigue. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, and proper nutrition support cognitive function and memory consolidation essential for effective learning. Balancing study with work responsibilities and personal commitments requires realistic planning that accounts for available time and energy. Setting boundaries around study time communicates importance to family and colleagues, reducing interruptions and enabling productive sessions.
AI Workload Recognition Through Pattern Analysis Methods
Developing systematic approaches to analyzing business scenarios and identifying appropriate AI solutions represents crucial exam competency. Pattern recognition across multiple practice scenarios builds intuitive understanding that enables quick, accurate solution identification during the examination. Computer vision scenarios typically involve analyzing visual content including images, videos, or both, with outcomes like classification, detection, or recognition. Natural language processing scenarios feature text or speech inputs requiring understanding, generation, translation, or sentiment analysis. Predictive scenarios involve forecasting future outcomes based on historical patterns, while anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns deviating from established norms.
Recommendation scenarios suggest items, content, or actions based on user preferences and behaviors. Practicing with diverse scenarios covering different industries and applications builds versatile solution-matching capabilities. Creating decision trees or flowcharts that systematically narrow solution options based on scenario characteristics provides structured problem-solving frameworks. Understanding common indicator words and phrases that signal specific workload types accelerates scenario analysis under time pressure. Similar to approaches used in proxy server certification preparations, systematic analysis methods enable confident solution selection. Reviewing incorrect practice question responses thoroughly, understanding why chosen answers were wrong and why correct answers fit better, transforms mistakes into valuable learning experiences. Building personal scenario libraries with diverse examples for each AI workload type creates customized study resources reflecting your understanding. Discussing scenarios with study partners or online communities exposes different analytical perspectives and deepens comprehension.
Automation and Intelligent Process Implementation Knowledge
Understanding how AI enables intelligent automation provides practical knowledge applicable across business functions and industries. Robotic process automation combined with cognitive capabilities creates intelligent automation that handles complex, judgment-based tasks beyond simple rule-based workflows. Document processing automation leveraging AI extracts data from forms, invoices, receipts, and other structured documents, eliminating manual data entry. Natural language understanding enables automating customer inquiry routing, identifying intent and extracting relevant information to direct requests appropriately. Intelligent automation opportunities exist across functions including finance, human resources, customer service, and operations.
Business process improvement through AI requires understanding current process pain points, identifying automation opportunities, and realistically assessing AI readiness and potential value. Change management considerations including employee training, process redesign, and cultural adaptation determine automation initiative success. Similar to expertise developed through Blue Prism automation certifications, understanding intelligent automation principles enables identifying high-value implementation opportunities. AI-powered automation performs best on high-volume, repetitive tasks with consistent patterns, while complex, highly variable tasks still require human judgment. Understanding this distinction prevents unrealistic expectations and ensures appropriate task selection for automation. Monitoring automated process performance and continuously optimizing based on results ensures sustained value and improvement over time. The exam includes scenarios requiring identification of appropriate automation opportunities and matching business requirements to Azure AI capabilities enabling intelligent automation.
Programming Concepts for Non-Developers Supporting AI Understanding
While AI-900 doesn't require programming skills, understanding basic programming concepts helps grasp how AI services integrate into applications. APIs represent interfaces enabling communication between different software systems, allowing applications to use AI services through standardized requests and responses. REST APIs represent a common approach where applications send HTTP requests to AI services and receive results, enabling integration across programming languages and platforms. Understanding that APIs abstract implementation complexity, allowing use of sophisticated AI capabilities without understanding underlying algorithms, demystifies AI integration. JSON format commonly structures data in API requests and responses, organizing information in human-readable text format.
Software development kits provide pre-built code libraries simplifying AI service integration in specific programming languages including Python, C#, JavaScript, and Java. Understanding that SDKs handle low-level communication details, allowing developers to focus on business logic rather than API mechanics, explains their value. Much like how C++ Institute certifications validate programming expertise, AI-900 assesses conceptual understanding enabling effective collaboration with development teams. Authentication and authorization mechanisms ensure only permitted applications and users access AI services, protecting resources and data. Understanding these security concepts at a high level demonstrates awareness of practical implementation considerations. Rate limiting controls how frequently applications can call AI services, preventing abuse and managing costs. Understanding these operational concepts enables realistic planning around AI service consumption and associated expenses. The exam may include questions about appropriate integration approaches for different scenarios, requiring basic understanding of how applications consume AI services.
Enterprise Software Integration and AI Adoption Strategies
Large organizations typically maintain complex software ecosystems requiring careful consideration when introducing AI capabilities. Integration strategies determine how AI services connect with existing systems including customer relationship management platforms, enterprise resource planning systems, and custom applications. Understanding that modern AI services typically offer API-based integration enabling connection from virtually any platform demonstrates practical deployment knowledge. Cloud-first strategies leverage Azure AI services without on-premises infrastructure requirements, accelerating deployment and reducing maintenance burden. Hybrid approaches combine cloud AI services with on-premises systems, addressing data residency requirements and network constraints.
Change management represents critical success factors for AI adoption, requiring stakeholder engagement, clear communication about changes and benefits, and comprehensive training for affected users. Pilot programs testing AI solutions with limited scope before organization-wide deployment reduce risk and enable refinement based on real-world feedback. Similar to strategies in CA Technologies enterprise certifications, successful AI adoption requires balancing innovation with organizational readiness. Governance frameworks establish policies, standards, and approval processes ensuring responsible AI deployment aligned with organizational values and regulatory requirements. Understanding that successful AI adoption requires attention to organizational and process dimensions beyond technical implementation demonstrates mature perspective valuable professionally. The exam includes scenarios requiring consideration of organizational factors when recommending AI solutions, assessing not just technical fit but practical deployment feasibility.
Financial Services Applications and Regulatory Compliance Awareness
Financial services organizations face unique AI implementation considerations including strict regulatory requirements, high security and privacy standards, and risk management imperatives. AI applications in finance span fraud detection identifying suspicious transactions, credit risk assessment evaluating loan applicants, algorithmic trading executing market transactions, and customer service automation handling routine inquiries. Understanding these applications and their business value provides context for exam questions about appropriate AI workload selection. Regulatory compliance requirements including explainability, auditability, and bias prevention influence AI solution design and deployment. Model risk management practices ensure AI systems making consequential decisions undergo appropriate validation, monitoring, and governance.
Data privacy regulations including GDPR impose requirements for personal data handling that affect AI implementations processing customer information. Understanding that financial services AI applications require extra rigor around testing, documentation, and ongoing monitoring demonstrates industry awareness. Similar to knowledge required for Canadian Securities Institute credentials, understanding financial services AI applications requires grasping both capabilities and constraints. Customer trust considerations mean financial institutions must balance AI-driven efficiency with transparency and maintaining human oversight for sensitive decisions. Anti-money laundering and know-your-customer requirements create specific AI use cases around transaction monitoring and identity verification. Understanding these domain-specific applications helps candidates recognize appropriate solutions in finance-related exam scenarios. The responsible AI principles of transparency, fairness, and accountability prove particularly important in financial services contexts given the consequential nature of financial decisions.
Healthcare AI Applications and HIPAA Compliance Considerations
Healthcare presents compelling AI opportunities balanced against stringent privacy requirements and patient safety concerns. Medical imaging analysis assists radiologists in detecting anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, improving diagnostic accuracy and speed. Predictive analytics identifies patients at risk for specific conditions, enabling preventive interventions and personalized treatment plans. Natural language processing extracts insights from clinical notes, research literature, and patient feedback, structuring unstructured medical information. Drug discovery and development leverage AI to identify promising compounds, predict molecular behavior, and optimize clinical trial designs. Virtual health assistants provide patients with medication reminders, answer health questions, and triage symptoms to determine appropriate care levels.
HIPAA regulations protect patient health information, imposing strict requirements for data security, access controls, and audit logging that affect AI implementations. Understanding that healthcare AI must comply with privacy regulations while delivering clinical value demonstrates awareness of practical deployment challenges. Similar to competencies assessed in CBIC certification examinations, healthcare AI knowledge requires understanding domain-specific requirements. AI model validation in healthcare requires clinical evidence demonstrating safety and effectiveness, often involving regulatory approval processes. Understanding that healthcare AI augments rather than replaces clinical judgment, with human oversight remaining essential for patient care decisions, prevents unrealistic expectations. Bias in healthcare AI can perpetuate health disparities if training data doesn't represent diverse populations, making fairness testing particularly critical. The exam may include healthcare scenarios requiring identification of appropriate AI applications while recognizing regulatory and safety constraints specific to medical contexts.
Cybersecurity Foundations Supporting AI Security Awareness
AI systems themselves require protection against security threats including adversarial attacks, data poisoning, and model theft. Understanding basic cybersecurity principles provides context for AI security considerations assessed in AI-900. Confidentiality ensures sensitive data used in AI systems remains protected from unauthorized access. Integrity ensures AI models and training data remain unaltered by malicious actors. Availability ensures AI services remain accessible when needed. These principles apply specifically to AI contexts where model tampering or training data manipulation can compromise system behavior.
Authentication verifies identity of users and systems accessing AI services, while authorization determines what authenticated entities can do. Encryption protects data in transit and at rest, preventing interception or unauthorized access to training data and model parameters. Similar to foundations in CompTIA Security Plus credentials, AI security awareness requires understanding how general security principles apply to AI-specific contexts. Adversarial machine learning attacks attempt to fool AI models through carefully crafted inputs designed to trigger incorrect outputs. Data poisoning introduces malicious data during training to compromise model behavior. Understanding these AI-specific threats demonstrates advanced security awareness. The exam may include questions about appropriate security controls for AI systems, requiring basic cybersecurity knowledge application to AI scenarios. Model interpretability and explainability support security by enabling detection of unexpected model behaviors that might indicate compromise.
Information Security Management and AI Governance Frameworks
Organizations implementing AI require governance frameworks ensuring responsible development, deployment, and operation aligned with organizational values and regulatory requirements. AI governance includes policies defining acceptable AI use cases, approval processes for AI initiatives, and standards for data quality, model validation, and ongoing monitoring. Understanding that governance provides necessary oversight without stifling innovation requires balancing control with flexibility. Risk assessment processes evaluate potential harms from AI systems before deployment, considering impacts on individuals, organizations, and society. Impact assessments specifically examine fairness, bias, privacy, security, and other responsible AI dimensions.
AI ethics committees or review boards provide multidisciplinary oversight for high-stakes AI applications, incorporating diverse perspectives including legal, ethical, technical, and domain expert viewpoints. Incident response procedures address AI system failures or unintended behaviors, establishing clear escalation paths and remediation processes. Similar to frameworks in ISM certification programs, AI governance structures provide systematic approaches to managing AI-related risks and opportunities. Documentation requirements ensure AI systems maintain records of training data, model development decisions, validation results, and operational performance supporting accountability and auditability. Understanding these governance concepts demonstrates mature perspective on AI implementation extending beyond technical capabilities to organizational and societal considerations. The exam assesses understanding of responsible AI principles and how governance mechanisms support their implementation in practice.
Ethical Hacking and AI Security Testing Methodologies
AI systems face unique security challenges requiring specialized testing approaches. Adversarial testing evaluates model robustness against maliciously crafted inputs designed to trigger incorrect outputs. Penetration testing of AI services identifies vulnerabilities in APIs, authentication mechanisms, and access controls. Red team exercises simulate sophisticated attacks against AI systems to identify weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. Understanding these security testing approaches demonstrates awareness that AI systems require validation beyond functional testing. Model privacy testing ensures AI systems don't inadvertently reveal sensitive training data through their outputs or behaviors.
Bias testing evaluates whether AI models perform equitably across different demographic groups, identifying potentially discriminatory patterns before deployment. Robustness testing validates model performance across diverse inputs including edge cases and unusual scenarios not well-represented in training data. Similar to methodologies in CEH certification preparation, AI security testing requires systematic approaches to identifying vulnerabilities. Explainability testing verifies that AI systems can provide understandable rationales for their decisions, supporting transparency requirements. Performance testing under various load conditions ensures AI services maintain acceptable response times and throughput at scale. Understanding these testing dimensions demonstrates a comprehensive view of AI quality assurance extending beyond basic functional validation. The exam may include scenarios requiring identification of appropriate testing and validation approaches for different AI applications and risk levels.
Financial Industry Examinations and Professional Standards Parallels
Professional certification programs across industries share common characteristics with AI-900 including standardized knowledge assessment, ongoing education requirements, and ethical standards. Financial services professionals pursuing securities licenses understand the value of validated credentials demonstrating competency to employers and regulators. Understanding AI-900 as part of the professional credentialing ecosystem helps contextualize its value and requirements. Study discipline required for professional examinations transfers across domains, with systematic preparation approaches yielding success regardless of specific content. Time management skills, test-taking strategies, and stress management techniques apply universally across professional certification examinations.
Much like how Series 6 examinations validate investment product knowledge, AI-900 validates AI foundational competency. The structured learning process preparing for professional certifications builds valuable study habits and self-discipline applicable throughout careers. Understanding examination formats, question types, and scoring approaches enables strategic preparation focusing on high-value knowledge areas. Creating personal study materials including flashcards, summary notes, and practice questions reinforces learning while building customized review resources. Maintaining perspective that certification exams test baseline competency rather than complete mastery reduces anxiety and enables confident performance. The professional credibility gained through certification transcends specific exam content, signaling commitment to professional development and continuous learning valued across industries.
Securities and Investment Knowledge Systematic Acquisition
Investment professionals building expertise through progressive certification levels demonstrate how systematic knowledge acquisition supports career advancement. Starting with foundational certifications and progressively pursuing advanced credentials mirrors effective AI learning pathways. Understanding AI-900 as foundation for potential future Azure AI certifications provides long-term perspective on professional development. The knowledge hierarchy where foundational concepts support advanced topics applies across domains from finance to technology. Ensuring solid grasp of fundamentals before advancing prevents knowledge gaps undermining later learning.
Much like preparation for Series 63 state securities examinations, AI-900 success requires understanding both broad concepts and specific details. Active recall through practice questions strengthens retention more effectively than passive review, a principle applying universally across professional certification preparation. Spaced repetition reviewing material at increasing intervals combats forgetting and supports long-term retention essential for applying knowledge professionally beyond examination success. The discipline developed through professional certification preparation including goal-setting, time management, and persistence builds character and capabilities valuable throughout careers. Understanding that initial certification represents beginning of continuous learning journey rather than endpoint maintains growth mindset supporting ongoing professional development.
Comprehensive Securities Expertise and Advanced Credential Pathways
Advanced professional credentials requiring extensive preparation demonstrate how significant knowledge domains yield to systematic study approaches. The breadth of knowledge required for comprehensive securities credentials parallels Azure certification pathways where foundational certifications support specialization. Understanding AI-900 as entry point to Azure AI specialty certifications provides context for considering long-term professional development trajectories. The compound returns on foundational knowledge investments become apparent as later learning builds upon solid bases. Ensuring thorough understanding rather than superficial familiarity with fundamentals pays dividends throughout professional journeys.
Similar to preparation requirements for Series 7 general securities examinations, comprehensive AI certification pathways require sustained commitment and strategic preparation. Study strategies scaling across small and large knowledge domains share common principles including active learning, spaced repetition, and practice testing. The mental stamina developed through extensive examination preparation serves professionals well in demanding career contexts requiring sustained focus and complex problem-solving. Understanding that challenging preparation processes build valuable capabilities beyond specific content knowledge provides motivation during difficult study periods. The credential recognition and professional opportunities following successful certification validate the investment and open doors to continued growth.
Financial Industry Entry and Foundational Credential Value
Entry-level professional credentials provide accessible pathways into industries while demonstrating commitment and baseline competency to potential employers. The relatively modest preparation requirements for foundational certifications enable career transitions and skill development without excessive time investments. Understanding AI-900 as accessible credential for non-technical professionals parallels entry-level certifications across industries. The confidence gained through certification success creates momentum supporting pursuit of more advanced credentials and professional challenges. Starting with achievable goals builds success patterns and self-efficacy supporting ambitious long-term objectives.
Much like how SIE examination preparation introduces securities industry fundamentals, AI-900 introduces AI concepts without requiring extensive prerequisites. The broad applicability of foundational knowledge across specializations provides flexibility in career direction while building common understanding. Understanding industry terminology, concepts, and frameworks through foundational certifications enables effective communication with colleagues and productive contributions to team efforts. The professional network developed through certification communities provides ongoing support, learning opportunities, and potential career connections. Celebrating certification achievement while maintaining perspective that it represents one milestone in ongoing professional development maintains balanced outlook supporting sustained growth.
Network Security and Access Control Fundamentals
AI systems require robust security controls protecting against unauthorized access and misuse. Network security principles including firewalls, intrusion detection, and secure communication protocols apply to AI service deployments. Understanding that AI services deployed in cloud environments inherit cloud platform security capabilities while requiring additional application-level controls demonstrates layered security awareness. Access control mechanisms ensure only authorized users and applications interact with AI services, preventing unauthorized usage and associated costs. Role-based access control assigns permissions based on job functions, implementing least privilege principles where users receive minimum access necessary for their responsibilities.
Multi-factor authentication strengthens identity verification beyond passwords alone, reducing risk of unauthorized access from compromised credentials. Encryption protects data transmitted to and from AI services, preventing interception of sensitive information. Similar to concepts in FortiGate access control certifications, AI security requires understanding how various controls combine to create comprehensive protection. Audit logging records AI service access and usage, supporting security monitoring, compliance validation, and incident investigation. Understanding these security fundamentals enables informed discussions about AI deployment security and appropriate control selection. The exam may include questions about appropriate security measures for different AI deployment scenarios, requiring basic security knowledge application. Vulnerability management processes identify and remediate security weaknesses in AI services and their integration with enterprise systems.
Advanced Preparation Techniques and Professional Application
Transitioning from theoretical knowledge to practical application represents the final preparation phase before the AI-900 examination. Intensive practice with scenario-based questions builds pattern recognition and decision-making speed essential for success under time pressure. Creating personal question banks from study materials and online resources provides unlimited practice opportunities. Reviewing not just correct answers but understanding why other options were incorrect deepens comprehension and prevents similar mistakes during actual examination. Simulated full-length exams under timed conditions build stamina and familiarity with examination experience, reducing anxiety on test day.
Identifying weak knowledge areas through practice exam performance enables targeted final review focusing on topics needing reinforcement. Teaching AI concepts to colleagues, friends, or online communities solidifies understanding while identifying knowledge gaps revealed through teaching difficulties. Much like preparing for FortiAnalyzer administration examinations, final AI-900 preparation emphasizes application over memorization. Creating summary sheets consolidating key concepts, Azure service capabilities, and decision frameworks provides concise review materials for final preparation days. Maintaining physical and mental health through adequate sleep, regular exercise, and stress management supports optimal cognitive performance during examination. Visualization techniques imagining successful examination completion builds confidence and reduces test anxiety. The final preparation week should emphasize review and confidence building rather than introducing new topics that might create confusion.
Network Security Analytics and Threat Detection Concepts
AI enhances cybersecurity through automated threat detection, behavior analysis, and incident response. Security information and event management systems increasingly incorporate machine learning for anomaly detection identifying unusual patterns indicating potential security incidents. Understanding how AI analyzes network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify threats demonstrates practical security application knowledge. Behavioral analytics establish baselines for normal activity then flag deviations potentially indicating compromised accounts or malicious insider activity. Automated threat intelligence processing helps security teams stay current with emerging threats and vulnerabilities across vast information sources.
AI-powered security orchestration and automated response systems execute predefined actions when specific threats are detected, accelerating incident response and reducing impact. Understanding these applications demonstrates how AI enhances security operations beyond just detection to include response capabilities. Similar to expertise in FortiAnalyzer analytics certifications, understanding security AI applications requires grasping both detection and analysis capabilities. Phishing detection leverages natural language processing and computer vision to identify fraudulent emails and websites attempting to steal credentials or install malware. Malware analysis uses AI to identify malicious code patterns and behaviors distinguishing threats from legitimate software. Understanding these specific security AI applications provides context for exam scenarios involving cybersecurity use cases. The exam may include questions requiring identification of appropriate AI capabilities for specific security challenges.
Advanced Network Analytics and Performance Monitoring
AI transforms network operations through predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and capacity planning. Network performance monitoring systems use machine learning to establish normal behavior baselines then detect degradation before users experience service impact. Predictive analytics forecast network capacity needs based on usage trends, enabling proactive infrastructure scaling. Automated troubleshooting systems analyze symptoms, consult knowledge bases, and recommend remediation steps accelerating problem resolution. Understanding these applications demonstrates how AI enhances IT operations, relevant knowledge for AI-900 scenarios involving operational use cases.
Root cause analysis leveraging AI correlates events across multiple systems identifying underlying issues causing symptoms, distinguishing symptoms from causes. Network optimization uses AI to adjust routing, load balancing, and resource allocation maximizing performance and reliability. Similar to competencies in advanced FortiAnalyzer examinations, understanding network analytics requires grasping how AI processes operational data to generate insights. User experience monitoring combines application performance data, network metrics, and device information providing holistic views of service quality. Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns indicating potential problems before they cause outages or performance degradation. Understanding these operational AI applications helps candidates recognize appropriate solutions in infrastructure management scenarios. The exam includes questions about applying AI to IT operations challenges requiring understanding of monitoring, analytics, and automation capabilities.
Cloud Infrastructure and Containerization Basics
Modern AI services increasingly deploy using container technologies enabling portability, scalability, and efficient resource utilization. Understanding containerization basics helps grasp how AI services are packaged and deployed. Containers bundle applications and dependencies into portable units running consistently across different environments. Orchestration platforms manage container deployment, scaling, and networking across clusters of servers. Understanding these concepts at a high level provides context for how AI services achieve scalability and reliability. Serverless computing abstracts infrastructure management further, allowing code execution without provisioning or managing servers.
Microservices architectures decompose applications into small, independent services communicating through APIs, an approach commonly used for AI-powered applications. Understanding that modern applications combine multiple specialized services rather than monolithic designs explains how AI capabilities integrate with broader solutions. Similar to cloud infrastructure knowledge in FortiGate certification programs, AI-900 candidates benefit from basic cloud deployment understanding. Scaling capabilities enable AI services to handle varying loads, automatically adding resources during high demand and reducing them during low usage. High availability designs ensure AI services remain accessible despite individual component failures through redundancy and failover mechanisms. Understanding these infrastructure concepts enables informed discussions about AI deployment options and their implications for performance, cost, and reliability.
Firewall and Network Security Advanced Administration
Network security controls protect AI services from unauthorized access and attacks. Firewalls filter network traffic based on security rules, controlling communication between AI services and other systems. Understanding firewall concepts including allow and deny rules, stateful inspection, and application-layer filtering demonstrates security awareness. Network segmentation isolates AI services from other systems limiting potential attack spread if one component is compromised. Virtual private networks enable secure remote access to AI services over public networks through encryption.
Intrusion detection and prevention systems monitor network traffic for malicious patterns, alerting security teams or automatically blocking suspicious activity. Much like advanced security knowledge in FortiGate administrator certifications, understanding network security controls provides context for AI service protection. Web application firewalls specifically protect applications from common attacks including SQL injection and cross-site scripting. Understanding these security technologies enables appropriate security recommendations when AI services require internet accessibility or handle sensitive data. The exam may include scenarios requiring selection of appropriate security controls for different AI deployment contexts. Defense in depth approaches layer multiple security controls ensuring comprehensive protection rather than relying on single mechanisms.
Anti-Money Laundering and Financial Crime Prevention
AI transforms financial crime prevention through sophisticated transaction monitoring, behavior analysis, and risk assessment. Traditional rule-based systems generate excessive false positives requiring manual review, while AI-powered systems more accurately distinguish legitimate transactions from suspicious activity. Behavior analytics establish normal patterns for each customer, identifying anomalies that might indicate money laundering, fraud, or other financial crimes. Network analysis reveals hidden relationships between entities suggesting coordinated criminal activity invisible when examining individual transactions or accounts.
Natural language processing analyzes unstructured data including news articles, social media, and legal filings identifying reputational risks and potential regulatory violations. Understanding these applications demonstrates how AI addresses complex regulatory compliance challenges. Similar to expertise in anti-money laundering specialist certifications, understanding financial crime AI applications requires grasping both detection capabilities and regulatory context. Customer due diligence processes use AI to automate identity verification, screen against sanctions lists, and assess customer risk levels. Transaction monitoring systems analyze payments in real-time flagging suspicious patterns for investigation. Understanding these specific applications helps candidates recognize appropriate AI solutions in financial crime prevention scenarios. The responsible AI principles of fairness, transparency, and accountability prove particularly important in financial crime prevention given potential impacts on individuals and institutions.
Advanced Cloud Networking and Hybrid Connectivity
Modern AI deployments often involve hybrid architectures combining cloud services with on-premises systems. Understanding hybrid connectivity options including VPNs, dedicated connections, and SD-WAN enables appropriate architecture selection for different scenarios. Latency considerations affect real-time AI applications requiring fast response times, favoring cloud deployments near users or edge computing approaches. Bandwidth requirements vary significantly across AI workloads, with computer vision applications processing images and videos requiring more capacity than text-based natural language processing. Understanding these technical factors enables informed deployment decisions balancing performance requirements against cost and complexity.
Data residency and sovereignty requirements may mandate keeping certain data within specific geographic regions, influencing where AI services are deployed and how they connect with data sources. Similar to networking expertise in AWS advanced networking certifications, understanding hybrid cloud connectivity provides context for AI deployment options. Content delivery networks accelerate AI service access by caching responses near users, improving performance for geographically distributed user bases. Network performance monitoring ensures connectivity between components meets requirements, identifying and resolving bottlenecks. Understanding these networking concepts enables appropriate infrastructure recommendations supporting AI service deployment. The exam may include scenarios requiring consideration of deployment location, connectivity options, and network performance requirements when recommending AI solutions.
Big Data Analytics Foundations Supporting AI Implementations
AI and machine learning build upon big data foundations where large datasets are collected, stored, processed, and analyzed. Understanding basic big data concepts provides context for AI data requirements and capabilities. Data lakes store vast amounts of raw data in native formats, providing flexible repositories for AI model training. Data warehouses structure data for analysis and reporting, organizing information to support specific analytical queries. Understanding differences between these storage approaches helps match data management strategies to AI requirements.
Data processing frameworks enable transforming, cleaning, and aggregating large datasets preparing them for AI model training. Batch processing handles large data volumes over extended periods, suitable for AI training jobs that don't require real-time processing. Stream processing analyzes data as it arrives enabling real-time insights and actions. Similar to expertise in AWS big data specialty certifications, understanding data management concepts supports AI implementation discussions. Data catalogs inventory available datasets, documenting contents, structure, and access requirements supporting data discovery for AI projects. Data quality tools identify and remediate issues ensuring AI models train on accurate, complete information. Understanding these big data foundations enables informed discussions about data readiness for AI implementations and appropriate data management practices.
Cloud Fundamentals and Service Model Comprehension
Understanding basic cloud computing concepts provides essential context for Azure AI services. Infrastructure as a Service provides virtualized computing resources enabling deployment flexibility while requiring infrastructure management. Platform as a Service abstracts infrastructure management, providing development platforms and managed services including databases, web hosting, and AI capabilities. Software as a Service delivers complete applications via internet without requiring installation or maintenance. Azure AI services typically follow PaaS models, abstracting AI implementation complexity while providing configurable capabilities.
Cloud advantages including scalability, pay-per-use pricing, global accessibility, and rapid deployment explain why AI services increasingly deploy in cloud environments. Understanding that cloud services eliminate large upfront infrastructure investments, converting capital expenses to operational costs, explains cloud financial advantages. Similar to foundations in AWS cloud practitioner certifications, basic cloud understanding supports AI service comprehension. Shared responsibility models define which security and operational responsibilities cloud providers handle versus customer responsibilities. Understanding this division clarifies that while cloud providers secure underlying infrastructure, customers remain responsible for appropriate service configuration and access controls. The exam assumes basic cloud familiarity and may include questions about appropriate cloud deployment models and responsibility divisions for different AI scenarios.
Updated Cloud Fundamentals and Latest Service Offerings
Cloud platforms continuously evolve with new services, features, and capabilities. Staying current with latest offerings ensures understanding of current best practices and available options. Azure regularly introduces new AI services and enhances existing ones with additional capabilities. Understanding that certification exam content updates periodically to reflect service evolution motivates staying current even after initial certification. Microsoft Learn and Azure updates documentation provide authoritative information about new and changed services. Following official Microsoft blogs and announcements helps track significant changes affecting exam content.
Understanding that cloud certifications have expiration periods and require recertification ensures professionals maintain current knowledge throughout careers. Much like updated content in revised cloud practitioner examinations, AI-900 exam content refreshes to reflect Azure platform evolution. Preview features provide early access to new capabilities before general availability, offering learning opportunities for professionals seeking cutting-edge knowledge. Understanding service lifecycle stages including preview, general availability, and deprecation helps set appropriate expectations about maturity and support levels. The exam focuses on generally available services but may reference preview features becoming mainstream. Maintaining cloud platform awareness beyond certification examination content supports professional effectiveness and positions professionals to leverage new capabilities as they emerge.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence Integration
AI enhances traditional business intelligence by automating insight generation, identifying patterns humans might miss, and enabling predictive capabilities. Understanding how AI complements analytics helps identify appropriate application opportunities. Automated insight discovery analyzes data identifying notable patterns, trends, and anomalies without requiring explicit queries. Natural language query interfaces enable business users to ask questions conversationally without learning query languages or understanding data structures. Visual analytics platforms increasingly incorporate AI recommendations suggesting relevant visualizations and highlighting significant patterns.
Predictive analytics forecast future outcomes based on historical patterns, supporting proactive decision-making. Prescriptive analytics go further recommending specific actions to achieve desired outcomes. Similar to analytics expertise in AWS data analytics certifications, understanding how AI enhances analytics demonstrates practical application knowledge. Real-time analytics process data as it arrives enabling immediate insights and actions, valuable for time-sensitive decisions. Understanding these analytics concepts and how AI enhances traditional approaches helps identify appropriate solutions in business intelligence scenarios. The exam may include questions about applying AI to analytics challenges requiring understanding of different analytics types and their business applications.
Data Engineering Foundations and Pipeline Development
AI models require data pipelines ingesting, transforming, and delivering data for training and inference. Understanding basic data engineering concepts provides context for AI data requirements. Extract, transform, load processes move data from source systems, apply transformations, and load into target destinations. Data transformation includes cleaning, formatting, enriching, and aggregating data preparing it for analysis or AI model training. Data validation ensures quality and completeness, preventing poor-quality data from degrading AI model performance.
Automation of data pipelines enables reliable, scheduled data movement without manual intervention. Much like engineering expertise in AWS data engineer certifications, understanding data pipeline concepts supports AI implementation discussions. Data lineage tracks data origin and transformations applied, supporting debugging, compliance, and understanding what data underlies AI model predictions. Monitoring data pipelines identifies failures and performance issues ensuring reliable data availability for AI systems. Understanding these data engineering fundamentals enables appropriate discussions about data readiness and pipeline requirements for AI projects. The exam may include scenarios requiring understanding of how data reaches AI services and appropriate data preparation approaches.
Database Concepts Supporting AI Data Storage
Databases provide persistent storage for data used in AI applications. Understanding basic database concepts helps grasp data management for AI. Relational databases organize data in structured tables with defined schemas, suitable for structured business data. NoSQL databases support flexible schemas accommodating diverse data types including documents, key-value pairs, and graphs. Understanding when each database type applies supports appropriate storage selection for AI data. Database performance considerations including indexing, query optimization, and scalability affect AI application responsiveness.
Data backup and recovery protect against data loss ensuring business continuity when problems occur. Much like database expertise in AWS database specialty certifications, understanding database fundamentals supports AI data management discussions. Database security controls protect sensitive data through encryption, access controls, and audit logging. Understanding these security measures enables appropriate recommendations for AI applications handling sensitive information. The exam may include questions about appropriate database selections for different AI scenarios requiring basic database knowledge. Understanding that AI applications may use multiple database types, selecting appropriate storage for different data types and access patterns, demonstrates architectural awareness.
Software Development Lifecycle and AI Integration
AI capabilities increasingly integrate into applications during development rather than as separate systems. Understanding basic software development lifecycle concepts provides context for AI integration. Requirements gathering identifies what AI capabilities applications need and how users will interact with them. Design phases determine how AI services integrate with application architecture and other components. Development implements AI integration using APIs, SDKs, and developer tools. Testing validates AI functionality and performance ensuring requirements are met.
Deployment makes AI-enabled applications available to users through appropriate infrastructure. Similar to development knowledge in AWS developer certifications, understanding development lifecycle supports AI integration discussions. Maintenance and updates ensure AI integrations continue functioning as services evolve and business needs change. Understanding these development phases helps business stakeholders participate effectively in AI application projects. The exam may include questions about when and how AI capabilities integrate into applications requiring basic development lifecycle awareness. Agile development methodologies emphasize iterative development and continuous feedback, well-suited to AI projects where requirements may evolve as capabilities are understood. Understanding that AI integration follows established software engineering practices rather than requiring completely different approaches demystifies AI development.
DevOps Practices and Continuous AI Improvement
DevOps practices emphasizing automation, continuous integration, and continuous deployment apply to AI systems supporting rapid iteration and improvement. Understanding basic DevOps concepts provides context for AI operations. Continuous integration automatically builds and tests AI models and their integrations as code changes. Continuous deployment automatically releases validated changes to production enabling rapid feature delivery. Infrastructure as code defines infrastructure through versioned configuration files enabling consistent, repeatable deployments.
Monitoring and logging provide visibility into AI system performance and behavior supporting troubleshooting and optimization. Similar to DevOps expertise in AWS DevOps certifications, understanding DevOps practices supports AI operations discussions. Automated testing validates AI functionality and performance preventing regressions when updates are deployed. Version control tracks changes to AI code, models, and configurations supporting rollback and collaboration. Understanding these DevOps practices enables discussions about AI system reliability, update frequency, and operational maturity. The exam may include questions about maintaining and improving AI systems over time requiring basic DevOps concept awareness. Treating AI models as code subject to version control, testing, and deployment automation represents best practices increasingly adopted as AI matures.
Conclusion
The comprehensive journey through AI-900 preparation reveals how non-technical professionals can successfully master AI fundamentals through strategic preparation. The certification validates knowledge spanning AI workload types, machine learning concepts, Azure AI services, and responsible AI principles, providing well-rounded AI literacy applicable across industries and roles. Success requires moving beyond memorization to conceptual understanding enabling application of principles to diverse scenarios. The hands-on exploration recommended throughout preparation transforms abstract concepts into concrete understanding while building confidence with Azure technologies.
Non-technical professionals bring valuable perspectives to AI implementations through deep domain knowledge, business acumen, and understanding of organizational dynamics. Combining these existing strengths with AI literacy gained through certification creates powerful capabilities enabling leadership of AI adoption initiatives within business domains. The strategic preparation approaches detailed including structured study plans, active learning techniques, and practice-based assessment apply broadly to professional certification pursuits beyond AI-900. The discipline and study skills developed through certification preparation serve professionals throughout careers as continuous learning becomes increasingly essential.
The career value of AI-900 certification extends beyond the credential itself to include enhanced AI conversations with technical teams, ability to identify AI implementation opportunities, and confidence evaluating vendor solutions critically. As AI adoption accelerates across industries, professionals who understand capabilities and limitations position themselves as valuable contributors to digital transformation initiatives. The foundation provided by AI-900 supports potential pursuit of more advanced Azure AI certifications as experience and interest grow, creating pathways for continued specialization.
Understanding AI concepts empowers professionals to envision applications within their specific domains that technically-focused individuals might miss, as domain expertise reveals nuances and opportunities invisible to outsiders. The responsible AI principles emphasized throughout preparation ensure certified professionals appreciate not just what AI can do but how to implement it ethically and responsibly. This balanced perspective proves increasingly valuable as organizations grapple with AI governance, fairness, and transparency challenges.
The practical applications of AI knowledge span marketing through customer insights and personalization, operations through process automation and predictive maintenance, finance through fraud detection and risk assessment, healthcare through diagnostic support and treatment personalization, and virtually every other business function. Professionals who can bridge business needs with AI capabilities become invaluable facilitators of innovation and efficiency improvements. The certification journey, while focused on Microsoft Azure specifically, builds transferable AI literacy applicable across cloud platforms and AI vendors.
Looking forward, AI technologies will continue evolving with new capabilities, applications, and best practices emerging regularly. The foundational knowledge from AI-900 provides bases for understanding these innovations as they develop. Maintaining currency through continuous learning, experimentation with new services, and engagement with AI communities ensures sustained professional relevance. The investment in AI-900 certification represents not an endpoint but the beginning of ongoing AI learning journeys that will span careers.
The confidence gained through certification success extends beyond AI into broader professional contexts, demonstrating to oneself and others the capacity to master new domains through dedicated effort. This self-efficacy supports ambitious career goals and willingness to take on challenging new responsibilities. The systematic problem-solving approaches developed through AI study transfer to other professional challenges, enhancing overall effectiveness.
Ultimately, AI-900 certification empowers non-technical professionals to participate fully in the AI revolution transforming businesses and society. Rather than remaining passive observers or blindly accepting vendor claims, certified professionals can engage critically, ask informed questions, and drive responsible AI adoption aligned with organizational values and business objectives. This capability proves invaluable as AI transitions from emerging technology to mainstream business tools. The knowledge, skills, and credentials gained through AI-900 preparation position professionals for success in increasingly AI-enabled work environments while contributing positively to responsible AI advancement.
Microsoft Azure AI AI-900 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass AI-900 Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-388 - Introduction to Programming Using Java
- MB-900 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
Purchase AI-900 Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the AI-900 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the AI-900 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the AI-900 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The AI-900 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the AI-900 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for AI-900. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the AI-900 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my AI-900 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the AI-900 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed AI-900 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!