- Home
- Cisco Certifications
- 350-401 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR) Dumps
Pass Cisco ENCOR 350-401 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


350-401 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 728 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 31, 2026
- Training Course 196 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 636 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Cisco ENCOR 350-401 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 350-401 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR) practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Demystify The Foundations Of Enterprise Network Architecture (350-401)
The 350-401 exam demands a strong grasp of modern enterprise network design. This includes understanding hierarchical architecture models such as access, distribution, and core layers, and why they are used to ensure performance, modularity, and fault isolation.
A well-designed architecture minimizes bottlenecks and enables scalability. The hierarchical model supports segmentation and easy policy enforcement. For example, placing access controls closer to the access layer improves response time and reduces unnecessary traffic across the network.
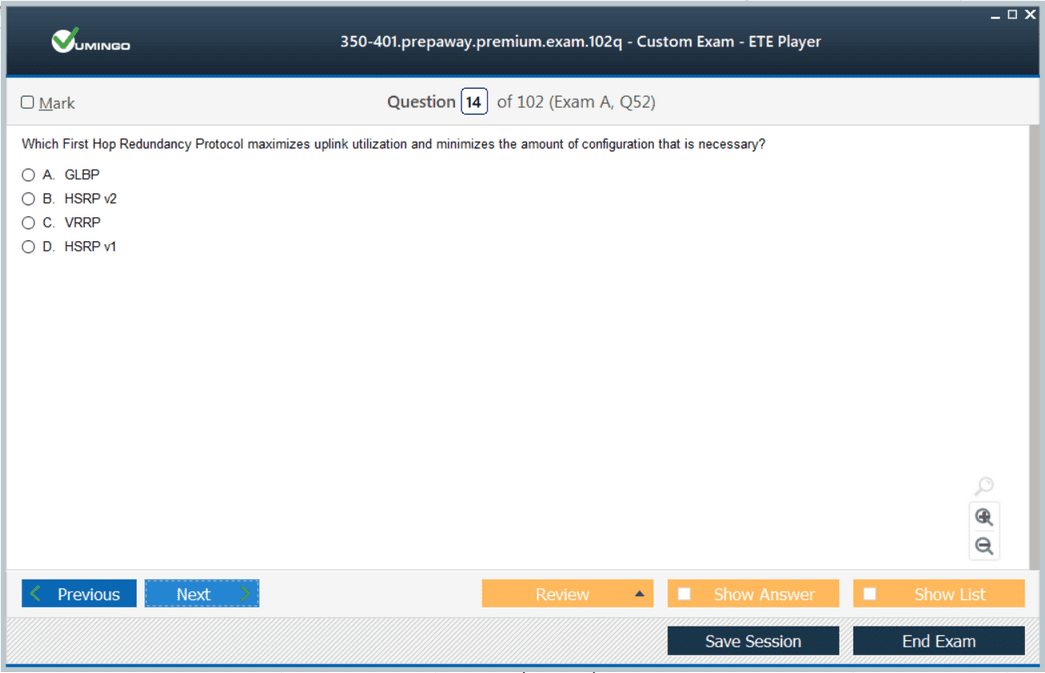
In enterprise settings, redundancy is key. High availability is achieved through redundant power supplies, links, and protocols like HSRP and VRRP. Engineers preparing for this exam should analyze failure scenarios, understand spanning tree behavior, and know when to use technologies like EtherChannel or StackWise.
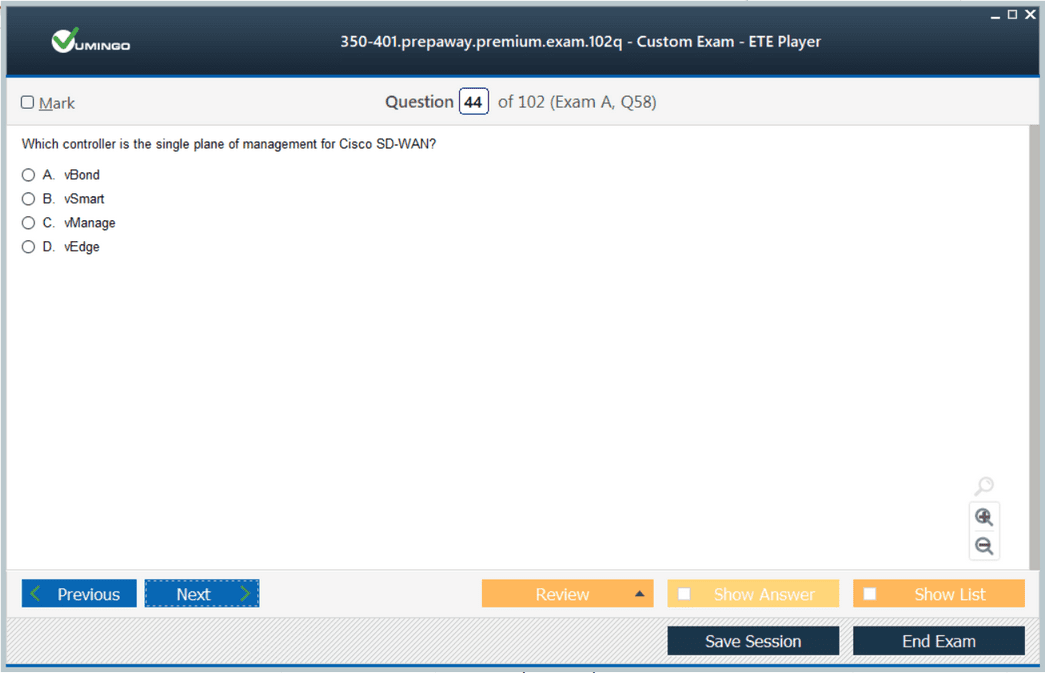
Overlaying traditional architectures are software-defined networks. These networks use centralized control and policy enforcement, often through controllers. While preparing for the exam, it is essential to learn how a controller interacts with the data plane and how it enables automation and faster troubleshooting.
Exploring Virtualization In The Enterprise
Virtualization is a cornerstone of modern IT. The 350-401 exam includes virtualization at both the network and compute layers. Network engineers must understand concepts like VRFs, VLANs, hypervisor-based switching, and overlay tunnels such as VXLAN.
Virtual routing and forwarding allows multiple instances of a routing table on a single router. This means different tenants or departments can share the same hardware while maintaining isolated networks. Similarly, VLANs segment Layer 2 networks and limit broadcast domains.
VXLAN is a technology that extends Layer 2 over Layer 3. It supports large-scale segmentation and is often used in data center environments. Network engineers should understand how VXLAN uses multicast or unicast-based transport and how control plane mechanisms like EVPN enhance functionality.
At the compute level, virtualization abstracts hardware using hypervisors. Each virtual machine has its own network interface, managed by virtual switches. Knowledge of how these switches interact with physical networks is important. Misconfigurations at this layer can lead to performance degradation or security gaps.
Building Robust Layer 2 And Layer 3 Infrastructure
Layer 2 and 3 concepts are foundational for enterprise networks. The exam requires more than memorizing commands—it asks for understanding real-world deployment issues. For example, engineers should know how to configure and troubleshoot STP variants like RSTP and MST, and why loop prevention is critical.
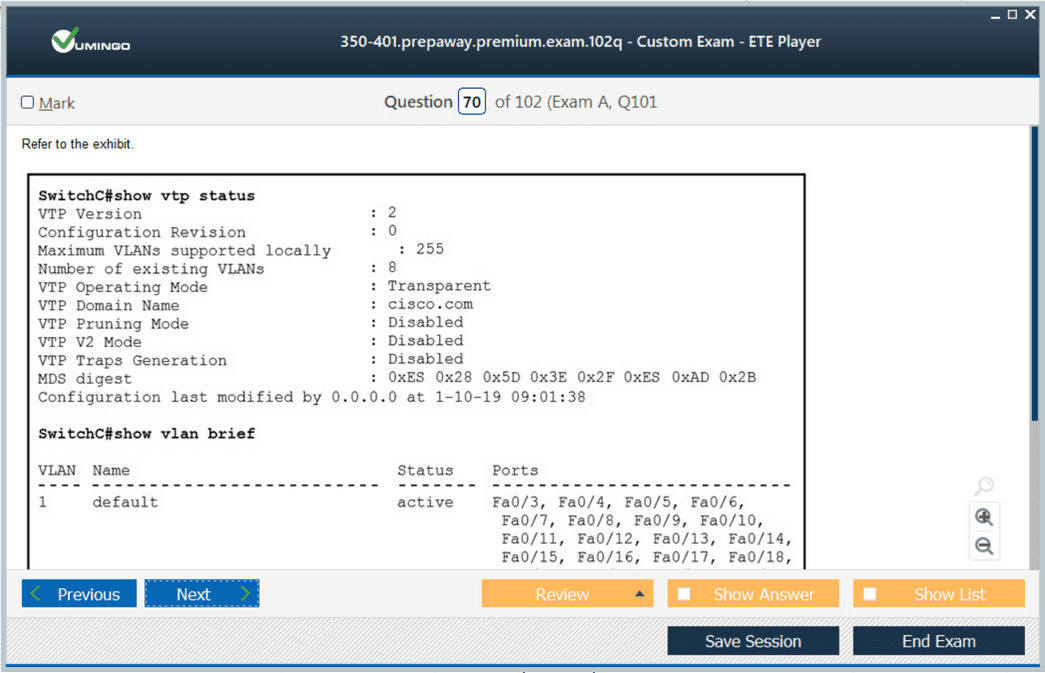
Layer 2 network designs must limit broadcast domains. Excessive broadcast traffic can cause performance issues and mask configuration errors. Using VLANs effectively allows better control over traffic and policy enforcement.
At Layer 3, engineers must design efficient IP addressing schemes. Using VLSM and summarization reduces the size of routing tables and simplifies troubleshooting. Understanding route redistribution, administrative distances, and metric manipulation is essential.
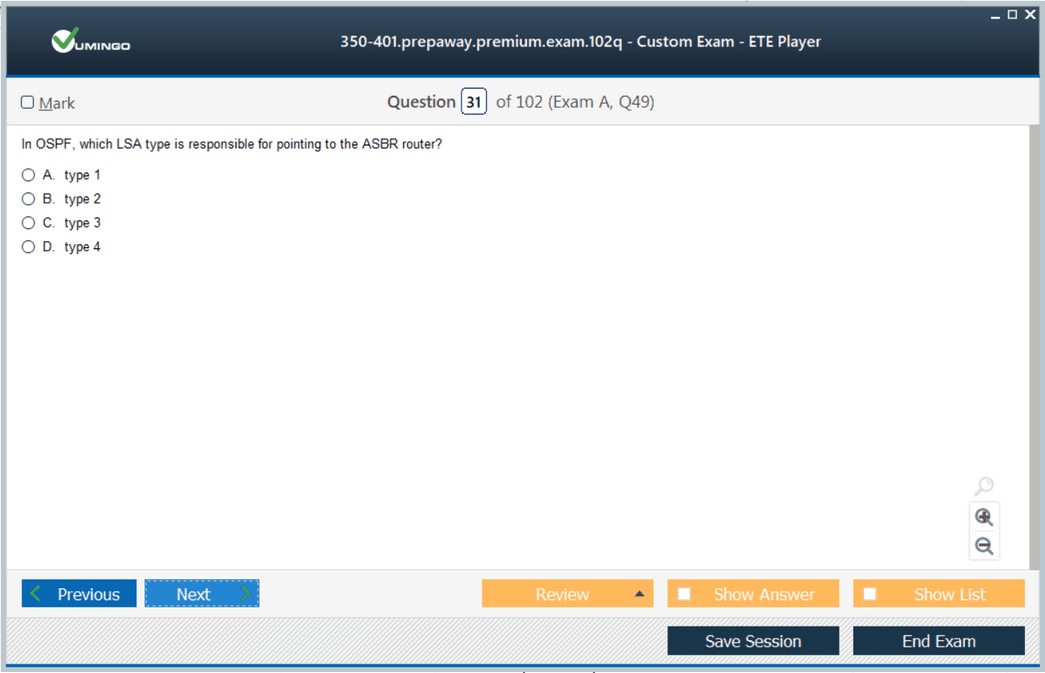
Protocols like OSPF and EIGRP are often tested in this exam. For OSPF, engineers should focus on neighbor formation, area design, and LSA types. For EIGRP, understanding DUAL and feasible successors is crucial. These details help in both planning and troubleshooting.
The exam also tests IPv6 knowledge. Dual-stack configurations, transition techniques like tunneling and NAT64, and address assignment methods should be thoroughly understood. IPv6 introduces new challenges, and awareness of those challenges is part of mastering the infrastructure domain.
Implementing Network Assurance And Monitoring
Network assurance is about maintaining performance, detecting anomalies, and resolving issues before they impact users. The 350-401 exam covers both manual and automated monitoring techniques.
SNMP is one of the most traditional methods for monitoring. Engineers should understand the differences between SNMPv2 and SNMPv3, especially around security features. Knowing how to configure SNMP agents and collectors is expected.
NetFlow and IPFIX provide visibility into traffic patterns. These tools are invaluable for capacity planning and identifying unusual behavior. The exam may test how to interpret flow data to detect DoS attacks or network misuse.
Syslog is another important tool. Properly configured logging helps trace configuration changes and pinpoint failures. Engineers should understand how to set severity levels and filter messages to reduce noise.
Automation is increasingly used to maintain network assurance. Scripts written in Python or tools like Ansible can automate tasks such as configuration backups, validation, or even real-time fault responses. Understanding the basics of automation frameworks helps engineers remain effective in dynamic environments.
Telemetry pushes monitoring to a new level by streaming data to collectors. It offers real-time insight into metrics such as interface errors, CPU usage, or protocol state changes. Unlike polling-based systems, telemetry allows faster detection and response to issues.
Managing Device And Data Plane Security
Enterprise networks must be secured at multiple layers. The exam evaluates understanding of both device-level and network-level security controls.
Device hardening is the first step. This includes disabling unused services, using secure management protocols like SSH, and implementing role-based access control. Engineers should also be familiar with local and centralized authentication methods like TACACS+.
At the data plane level, segmentation is key. VLANs, private VLANs, and VRFs help enforce logical separation. Access control lists provide fine-grained control over traffic, allowing or denying based on source, destination, or protocol.
Control plane policing protects routers and switches from malformed or excessive control traffic. For example, protecting OSPF routers from spoofed hello packets requires proper authentication and rate limiting.
Understanding how to secure Layer 2 is also important. Techniques such as DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, and port security prevent common attacks like spoofing or man-in-the-middle. Engineers should understand how these mechanisms interact and when to apply them.
AAA integration with RADIUS or TACACS+ enables consistent user management. It’s not just about authentication, but also authorization and accounting. Exam candidates should know how to troubleshoot common issues like failed logins or inconsistent privilege levels.
Exploring Wireless Architectures And Deployment Models
Wireless networking plays a critical role in enterprise networks. The 350-401 exam expects familiarity with both centralized and distributed wireless deployments, as well as cloud-managed wireless models.
In a centralized model, wireless LAN controllers (WLCs) manage all access points. This model simplifies configuration and monitoring, as policies are centrally pushed to all devices. It also enables better control over radio frequency optimization, load balancing, and client roaming.
A distributed model allows each access point to operate independently. While this model works in small environments or remote branches, it does not scale well. Engineers should understand the trade-offs between simplicity and control.
Cloud-managed wireless solutions are also gaining popularity. These models use cloud-hosted platforms to manage devices without the need for on-premises controllers. While convenient, they require robust connectivity and may introduce security considerations.
When preparing for the exam, understanding concepts like SSID broadcasting, radio frequency channels, signal-to-noise ratio, and client roaming behavior is essential. Engineers should be able to troubleshoot coverage issues and avoid co-channel interference through proper channel planning.
Securing Wireless Communications
Wireless networks are more vulnerable than wired networks due to the open nature of radio frequencies. The exam tests knowledge of securing wireless communications using protocols such as WPA2, WPA3, and 802.1X.
WPA2 with AES encryption has been widely adopted, but WPA3 introduces enhancements such as SAE (Simultaneous Authentication of Equals), which mitigates dictionary attacks. Understanding the evolution of wireless security helps in designing future-proof deployments.
802.1X enables port-based access control using a RADIUS server. Devices must authenticate before gaining access to the network. Engineers should understand how the supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server interact during this process.
Wireless intrusion detection and prevention systems (WIDS/WIPS) monitor for rogue access points, denial-of-service attempts, and spoofing. A well-secured deployment includes both proactive configurations and reactive detection tools.
Advanced Routing Techniques
The 350-401 exam includes advanced routing topics that go beyond basic protocol configurations. Engineers must understand how to design scalable, efficient, and redundant routing topologies.
Route summarization helps reduce the size of routing tables and limits the propagation of network changes. In protocols like OSPF, summarization is done at the area boundary. In EIGRP, summarization can occur at any interface.
Understanding route redistribution is another key skill. When multiple routing protocols coexist, redistribution enables sharing of routes between them. However, improper redistribution can lead to routing loops or suboptimal paths. Engineers should be able to use filtering and route maps to control this behavior.
Path control involves manipulating routing decisions using administrative distance, metrics, or policy-based routing. For example, if a link has lower bandwidth but higher reliability, engineers may prefer it for certain traffic classes.
BGP, although not covered in extreme depth, is part of the exam. Candidates should know how BGP forms neighbor relationships, how route advertisements are controlled using prefix lists and route maps, and how BGP path selection works using attributes like weight and local preference.
Implementing Multicast Routing
Multicast routing is used for efficiently delivering data to multiple recipients. The 350-401 exam tests knowledge of concepts such as PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast), IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol), and multicast distribution trees.
PIM Sparse Mode is commonly used in large-scale networks. It creates a shared tree rooted at a rendezvous point. Engineers should know how to configure RP mapping, understand source and shared trees, and optimize transitions.
IGMP operates between hosts and routers. IGMPv2 and IGMPv3 are most common in enterprise networks. Understanding how multicast receivers signal their interest and how routers manage group membership is important.
Multicast requires proper Layer 2 configuration. For instance, using IGMP snooping ensures that multicast traffic is only sent to interested hosts. Without it, multicast traffic behaves like a broadcast, consuming unnecessary bandwidth.
Fundamentals Of Network Programmability
Network programmability changes how infrastructure is configured and managed. The exam emphasizes understanding controller-based architectures and basic automation concepts.
Controllers such as SDN controllers or enterprise automation platforms provide a centralized way to manage network policies. Unlike traditional CLI-based management, controllers offer an abstraction layer that simplifies operations.
Northbound APIs connect applications to the controller. They allow developers to create custom monitoring or configuration tools. Southbound APIs connect the controller to the network devices using protocols like NETCONF, RESTCONF, or proprietary options.
The exam may include questions about interpreting RESTful API responses. Engineers should know how to issue basic GET, POST, and PUT requests and understand JSON structures. Python is often used for scripting against APIs, and familiarity with data parsing techniques like Python dictionaries is helpful.
Leveraging Configuration Management Tools
Configuration management tools help enforce consistent configurations across the network. While the exam does not focus deeply on specific tools, engineers must understand their role and operation.
Tools like Ansible or Puppet use templates and variables to create repeatable configurations. This reduces human error and enables quick rollback in case of failure. Playbooks define the desired state of devices, and the tools ensure that state is maintained.
Using these tools requires device support for APIs or SSH access. Engineers should know how to integrate inventory files, manage credentials securely, and interpret logs to detect failures.
The concept of idempotence is central to configuration management. An operation should not make changes if the desired state already exists. This ensures that repeated runs of a script do not disrupt the network.
Working With Model-Driven Telemetry
Model-driven telemetry offers a modern approach to network monitoring. Unlike polling methods like SNMP, telemetry pushes real-time data from network devices to collectors.
YANG models define the data structure. Engineers preparing for the exam should understand the role of YANG, how it is used to standardize data models, and why it improves interoperability.
Data is streamed using protocols like gRPC or NETCONF. Subscriptions are created to monitor specific metrics, such as CPU load or interface errors. The data can be used for analytics, automation triggers, or visual dashboards.
Understanding how to configure telemetry, interpret exported data, and troubleshoot delivery issues is important for managing modern enterprise networks.
Zero Trust And Segmentation Strategies
The concept of zero trust is increasingly relevant in enterprise environments. It assumes that no device or user should be automatically trusted, even inside the network perimeter.
Network segmentation is a key component of zero trust. Engineers can implement segmentation using VLANs, VRFs, and firewalls. Microsegmentation takes it further by enforcing policies at the host level.
Access control policies must be dynamic and context-aware. For example, a user’s role, device posture, and location can influence what resources they can access. Engineers should understand how network access control systems integrate with directories and authentication services.
Policy enforcement points can be at switches, firewalls, or access points. Knowing where to place these controls for maximum effectiveness is a design skill emphasized in the exam.
Cloud Integration And Enterprise Connectivity
Enterprise networks increasingly connect to cloud environments. The 350-401 exam includes concepts related to hybrid connectivity, security considerations, and cloud architecture impacts on routing.
Engineers should understand how site-to-cloud VPNs, direct connections, or SD-WAN are used to connect branch offices to cloud resources. Each option has trade-offs in latency, security, and cost.
Cloud architectures can shift traffic patterns. Instead of data center-centric traffic, cloud applications introduce east-west and internet-bound flows. Engineers must adapt their routing and firewall designs accordingly.
DNS, DHCP, and IPAM services must also extend to cloud environments. Understanding how to coordinate address spaces between on-premises and cloud is crucial to avoid conflicts.
Understanding Infrastructure Security Principles
Infrastructure security is one of the most critical domains in the 350-401 exam. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data across the network infrastructure. Security must be embedded in every layer—from endpoint devices to core switches.
Engineers should understand how to segment traffic using access control lists and how to enforce policies at various points in the network. Zone-based firewalls, traffic filtering, and control-plane policing are methods used to protect the infrastructure.
A secure network design also involves protecting against common attacks such as MAC flooding, DHCP starvation, and ARP spoofing. The exam requires familiarity with mitigation techniques such as dynamic ARP inspection, DHCP snooping, and port security.
Layer 2 security threats are particularly dangerous due to their ability to disrupt the local network. Engineers must know how to configure switch features to detect anomalies and prevent attacks.
Control plane security ensures that the routing infrastructure is not disrupted by rogue protocols or malformed packets. Features such as routing protocol authentication, infrastructure ACLs, and control plane policing help maintain router stability.
Device Hardening Best Practices
Device hardening refers to the process of securing network devices against unauthorized access or configuration changes. This includes switches, routers, wireless controllers, and firewalls.
The exam expects familiarity with both physical and logical security techniques. Physical security involves protecting access to console ports and securing device locations. Logical security focuses on securing remote access, limiting management protocols, and using role-based access control.
Using SSH instead of Telnet, disabling unused services, and enforcing strong password policies are baseline practices. Engineers should also limit the number of login attempts and set timeouts for idle sessions.
Role-based access control ensures that users only have permissions necessary for their roles. For example, an auditor may have read-only access, while a network engineer may have full configuration access. This prevents accidental or malicious changes.
Syslog, SNMP, and NetFlow provide monitoring capabilities but must be configured securely. Encrypting communication and restricting access to these tools prevents data leakage and misuse.
Configuration backups and version control are also part of device hardening. Engineers should automate backup procedures and store configurations in secure locations. If a compromise occurs, this allows for a fast and reliable recovery.
Access Control Models And Implementation
Access control models define how users and devices gain access to network resources. In enterprise networks, access control must be both granular and dynamic.
The 350-401 exam emphasizes models like 802.1X authentication, MAC authentication bypass, and web authentication. These mechanisms provide layered protection depending on device capabilities.
802.1X uses RADIUS servers to authenticate users before they are granted access to the network. This process involves a supplicant (client device), authenticator (switch or wireless controller), and authentication server.
MAC authentication bypass is used for devices that do not support 802.1X, such as printers. Web authentication redirects unauthenticated users to a captive portal. Engineers should know when to use each method and how to implement fallback strategies.
Centralized identity services integrate with directory servers to enforce access control based on user attributes. Policies can be location-aware or time-based. Understanding the flow of authentication requests and policy evaluation is vital.
Guest access and BYOD introduce unique challenges. Segregated VLANs, time-limited access, and posture assessment ensure that non-corporate devices do not compromise the internal network.
Quality Of Service Design And Deployment
Quality of Service ensures that critical applications receive the bandwidth and priority needed for optimal performance. The 350-401 exam includes multiple QoS models and how they are applied across the network.
The primary QoS models include best-effort, differentiated services, and integrated services. In most enterprise networks, the differentiated services model (DiffServ) is used due to its scalability.
Traffic classification identifies the type of application or flow. This is often based on port numbers, access control lists, or deep packet inspection. Once classified, traffic is marked using Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCP) at Layer 3.
Traffic is then queued and scheduled based on its priority. Techniques like weighted fair queuing, low latency queuing, and class-based weighted fair queuing help manage congestion. Engineers should understand how each queueing strategy affects delay-sensitive traffic such as voice or video.
Policing and shaping control the rate at which traffic is transmitted. Policing drops excess packets, while shaping buffers them for future transmission. Understanding when to apply each technique depends on network design and service-level agreements.
Trust boundaries must be defined clearly. Typically, traffic markings are trusted only at the network edge. All other devices either reclassify or ignore external markings to prevent abuse.
Network Address Translation And Services
Network Address Translation plays a key role in conserving IP addresses and providing privacy. The 350-401 exam includes NAT types, configuration practices, and use cases.
Static NAT provides a one-to-one mapping between internal and public addresses. It is used when a device must be reachable from the outside using a fixed address, such as for web or mail servers.
Dynamic NAT uses a pool of public addresses and assigns them as needed. Once the pool is exhausted, new connections are blocked. Engineers must monitor NAT pool usage and plan accordingly.
Port Address Translation (PAT), often called NAT overload, maps multiple internal addresses to a single public IP using port numbers. This is the most commonly used NAT method for outbound internet traffic.
NAT has limitations, especially with applications that embed IP information in payloads. Engineers should be familiar with NAT traversal techniques and Application Layer Gateways that resolve these issues.
Other services tested in the exam include DHCP and DNS. DHCP assigns IP addresses dynamically and must be configured with proper lease times, exclusion ranges, and default gateways. DNS translates hostnames into IP addresses and should be redundant and fast.
Understanding how these services integrate with network policies and security features helps ensure a seamless user experience.
Virtualization And Network Function Virtualization
Virtualization changes how network devices and services are deployed. The 350-401 exam explores both server virtualization and network function virtualization.
Server virtualization uses hypervisors to host multiple virtual machines on a single physical server. Engineers should understand the role of Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors and how resource sharing is managed.
Virtual machines used for routers, firewalls, or load balancers are examples of network function virtualization. These virtual appliances provide flexibility in deployment and scaling.
Virtual switches connect virtual machines and integrate with physical networks. Engineers must configure VLANs, trunks, and port groups to manage traffic effectively. Understanding how virtual networking differs from physical networking is essential.
Overlay networks use tunneling protocols like VXLAN to connect distributed virtual environments. This allows for scalable segmentation across data centers. Engineers should understand the basics of encapsulation and how it affects MTU sizes and latency.
Cloud environments often use virtualization and overlays extensively. Familiarity with these concepts prepares engineers for hybrid network designs.
Monitoring And Managing Network Devices
Monitoring ensures the health and performance of the network. The exam includes traditional tools like SNMP, Syslog, and NetFlow, as well as model-driven telemetry.
SNMP allows centralized monitoring using management information bases (MIBs). Engineers should know how to configure SNMP communities, versions, and traps. SNMPv3 provides encryption and authentication.
Syslog provides event logging and is used to track configuration changes, errors, and access attempts. Logs should be forwarded to a central server and include timestamps for proper correlation.
NetFlow captures traffic flow data and is used for capacity planning, security analysis, and troubleshooting. Engineers should understand how to configure flow exporters and collectors.
Model-driven telemetry differs from polling by pushing updates in real time. It uses structured data models like YANG and streaming protocols such as gRPC. This enables more scalable and accurate monitoring.
Automated monitoring tools can trigger alerts and even initiate scripts to resolve issues. This reduces downtime and allows for proactive maintenance.
Device Management Strategies
Device management involves maintaining configurations, software versions, and uptime. The 350-401 exam includes concepts related to centralized and decentralized management.
Configuration management tools like Ansible or scripts using REST APIs allow for repeatable and consistent changes. Engineers should understand the benefits of automation and how to implement idempotent scripts.
Version control helps track changes over time. Engineers should maintain changelogs and review configurations before deploying. Backup procedures ensure configurations can be restored after failures.
Device lifecycle management includes regular software upgrades, hardware audits, and policy compliance. Keeping devices updated reduces vulnerabilities and ensures compatibility with new features.
Redundancy strategies such as hot standby and failover configurations improve availability. Engineers must design networks to handle device failures without service disruption.
Out-of-band management provides access to devices even when the primary network is unavailable. Engineers should deploy terminal servers or dedicated management links to critical infrastructure.
Understanding Network Security Architecture
Security in enterprise networks is more than just firewalls and passwords. The 350-401 exam emphasizes how security policies are integrated into network design. Engineers must understand how security zones, segmentation, trust boundaries, and access controls are applied at multiple layers.
A secure architecture starts with defining trust zones such as internal, DMZ, guest, and cloud segments. Each zone has unique access restrictions. Firewalls and access control lists control the flow of traffic between zones.
Identity-based policies are enforced through mechanisms like 802.1X, MAC filtering, or integration with directory services. Context-aware firewalls evaluate user, device, and application data to make more intelligent decisions.
Intrusion detection and prevention systems are deployed at key ingress and egress points. These systems inspect traffic for known attack signatures and anomalies. Engineers must understand how traffic is mirrored, analyzed, and acted upon.
Secure remote access uses encrypted VPNs and multi-factor authentication. Split tunneling, endpoint posture checks, and session logging are critical design considerations in environments with remote users.
Implementing Identity-Based Access Control
Controlling who accesses the network and what they can do is essential. The 350-401 exam covers concepts around identity and access control, including authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
Authentication verifies user identity using credentials such as passwords, certificates, or biometrics. Authorization determines what the user is allowed to access based on policies. Accounting logs all user activities for audit and troubleshooting.
Network devices often integrate with central identity stores such as RADIUS or TACACS+ servers. These systems manage policy enforcement and role assignments.
Access control can be static, based on VLAN or IP, or dynamic using downloadable ACLs. Engineers must be familiar with how policy enforcement points receive and apply these controls.
Guest network access is another area of focus. Captive portals allow users to authenticate before receiving network access. Engineers should understand the configuration flow and security implications of guest solutions.
Final Words
Preparing for the 350-401 ENCOR exam is a journey that demands a strong grasp of both foundational networking principles and emerging technologies. It challenges professionals to think beyond simple configurations and dive deeper into the why and how of enterprise-level network design, security, automation, and troubleshooting.
This certification is not just about passing an exam—it reflects a broader shift in networking. Today’s engineers are expected to manage increasingly complex environments that span on-premises infrastructure, cloud services, and software-defined solutions. As such, the knowledge gained while studying for the 350-401 exam equips you not only with the skills to operate a modern network but also to evolve with the field as technologies and business needs change.
Hands-on practice is essential. Simulated labs, real-world configurations, and working through scenarios will help solidify abstract concepts. It’s also valuable to understand how different parts of the network interact, whether it's routing protocols converging after a link failure, or security mechanisms responding to a threat.
Time spent studying this material builds a mindset that emphasizes both precision and adaptability—key qualities for any successful network engineer. In practice, this means being able to troubleshoot quickly, plan scalable architectures, and implement secure, automated, and resilient designs.
The 350-401 ENCOR certification is more than a milestone—it is a foundation for further growth in enterprise networking roles. It prepares you for advanced certifications and, more importantly, for solving the real challenges that today’s networks face. Whether your goal is to strengthen your existing role or move toward a higher-level architecture or automation position, this exam plays a critical part in that path. Commit to the process, invest time in your understanding, and your efforts will open doors to new and exciting opportunities.
Cisco ENCOR 350-401 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 350-401 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR) certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- 200-301 - Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- 350-401 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
- 350-701 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies
- 300-410 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
- 300-715 - Implementing and Configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine (300-715 SISE)
- 350-601 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Data Center Core Technologies (DCCOR)
- 350-801 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies (CLCOR)
- 300-420 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)
- 300-425 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-425 ENWLSD)
- 300-415 - Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)
- 200-901 - DevNet Associate (DEVASC)
- 200-201 - Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS)
- 300-710 - Securing Networks with Cisco Firewalls
- 820-605 - Cisco Customer Success Manager (CSM)
- 350-901 - Developing Applications using Cisco Core Platforms and APIs (DEVCOR)
- 300-620 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (DCACI)
- 350-501 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR)
- 400-007 - Cisco Certified Design Expert
- 300-730 - Implementing Secure Solutions with Virtual Private Networks (SVPN 300-730)
- 300-430 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-430 ENWLSI)
- 300-435 - Automating Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)
- 500-220 - Cisco Meraki Solutions Specialist
- 100-150 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking
- 300-810 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Applications (CLICA)
- 300-820 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Cloud and Edge Solutions
- 350-201 - Performing CyberOps Using Core Security Technologies (CBRCOR)
- 700-805 - Cisco Renewals Manager (CRM)
- 300-735 - Automating Cisco Security Solutions (SAUTO)
- 300-815 - Implementing Cisco Advanced Call Control and Mobility Services (CLASSM)
- 300-745 - Designing Cisco Security Infrastructure
- 300-610 - Designing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure for Traditional and AI Workloads
- 300-510 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions (SPRI)
- 300-440 - Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)
- 300-720 - Securing Email with Cisco Email Security Appliance (300-720 SESA)
- 100-140 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) IT Support
- 300-910 - Implementing DevOps Solutions and Practices using Cisco Platforms (DEVOPS)
- 700-250 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Sales
- 300-725 - Securing the Web with Cisco Web Security Appliance (300-725 SWSA)
- 300-215 - Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR)
- 300-835 - Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO)
- 500-442 - Administering Cisco Contact Center Enterprise
- 300-445 - Designing and Implementing Enterprise Network Assurance
- 300-635 - Automating Cisco Data Center Solutions (DCAUTO)
- 300-515 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider VPN Services (SPVI)
- 700-750 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Engineer
- 700-240 - Cisco Environmental Sustainability Overview
- 700-245 - Environmental Sustainability Practice-Building
- 700-150 - Introduction to Cisco Sales (ICS)
- 800-150 - Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians
- 100-490 - Cisco Certified Technician Routing & Switching (RSTECH)
- 300-615 - Troubleshooting Cisco Data Center Infrastructure (DCIT)
- 300-630 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure - Advanced
- 500-560 - Cisco Networking: On-Premise and Cloud Solutions (OCSE)
- 500-444 - Cisco Contact Center Enterprise Implementation and Troubleshooting (CCEIT)
Purchase 350-401 Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Cisco certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 350-401 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Cisco certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 350-401 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 350-401 preparation materials for the Cisco certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 350-401 materials for the Cisco certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 350-401 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Cisco certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 350-401. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 350-401 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 350-401 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Cisco certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 350-401 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 350-401 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!