Pass Cisco CCNP Enterprise Certification Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


350-401 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 728 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 31, 2026
- Training Course 196 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 636 Pages

350-401 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 728 Questions & Answers
Last update: Jan 31, 2026 - Training Course 196 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 636 Pages
Purchase Individually

Premium File

Training Course

Study Guide
350-401 Exam - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
| Download Free 350-401 Exam Questions |
|---|
Cisco CCNP Enterprise Certification Practice Test Questions and Answers, Cisco CCNP Enterprise Certification Exam Dumps
All Cisco CCNP Enterprise certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are prepared by industry experts. Cisco CCNP Enterprise certification practice test questions and answers, exam dumps, study guide and training courses help candidates to study and pass hassle-free!
Navigating the New Era of Cisco CCNP Enterprise Networking
The landscape of enterprise networking has undergone tremendous transformation in recent years, driven by cloud adoption, software-defined networking, and automation. Cisco's CCNP Enterprise certification represents a comprehensive framework for network professionals seeking to master these modern networking paradigms. This credential validates expertise in implementing and troubleshooting enterprise networks, including advanced routing, switching, and wireless technologies. Network engineers pursuing this certification gain skills that position them at the forefront of digital transformation initiatives across organizations of all sizes. The certification path emphasizes hands-on experience with real-world scenarios, ensuring that certified professionals can immediately apply their knowledge to solve complex networking challenges.
Much like professionals pursuing Azure administrator expertise to advance their cloud careers, CCNP Enterprise candidates invest significant time mastering technologies that define modern IT infrastructure. The certification requires passing two exams: a core exam covering enterprise infrastructure and a concentration exam in a specialized area. This structure allows candidates to demonstrate broad knowledge while developing deep expertise in specific technologies aligned with their career goals. The core exam encompasses routing protocols, switching technologies, wireless connectivity, network security, automation, and virtualization. Concentration options include advanced routing, software-defined access, wireless design, and automation, enabling professionals to tailor their certification to match industry demands and personal interests.
Mastering Core Infrastructure Components for Enterprise Success
The CCNP Enterprise core exam, designated 350-401 ENCOR, forms the foundation of the certification path by testing comprehensive understanding of enterprise infrastructure implementation and operation. This exam covers routing technologies including EIGRP, OSPF, and BGP, requiring candidates to design, implement, and troubleshoot complex routing scenarios across diverse network topologies. Switching technologies represent another critical domain, encompassing VLANs, spanning tree protocols, EtherChannel, and first-hop redundancy protocols that ensure network availability. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in configuring and troubleshooting these technologies while understanding their interaction within larger network designs. The exam also addresses wireless principles, including RF fundamentals, wireless security, and integration with wired infrastructure.
Network professionals who achieve this certification experience career benefits comparable to those earning transformative Azure credentials in cloud computing. The ENCOR exam uniquely combines traditional networking knowledge with emerging technologies, reflecting the hybrid nature of modern enterprise networks. Infrastructure services covered include DHCP, DNS, NAT, and NTP, which remain essential despite the evolution toward software-defined architectures. Network assurance topics require understanding of logging, SNMP, NetFlow, and other monitoring technologies that provide visibility into network performance and security. Virtualization concepts including virtual routing and forwarding, overlay protocols, and network functions virtualization prepare candidates for cloud-integrated environments where physical and virtual networks coexist seamlessly.
Implementing Advanced Routing Protocols Across Complex Topologies
Advanced routing represents a cornerstone of enterprise networking, enabling efficient traffic forwarding across complex topologies that span multiple sites, cloud platforms, and service provider connections. EIGRP implementation requires understanding of metric calculations, neighbor relationships, route summarization, and troubleshooting techniques that resolve common configuration errors. OSPF knowledge extends to multi-area designs, LSA types, path selection criteria, and optimization strategies that minimize convergence time while conserving bandwidth. BGP mastery proves essential for organizations with multiple internet connections or private WAN services, demanding expertise in path attributes, route filtering, and policy implementation that controls traffic flows according to business requirements. These routing protocols form the backbone of enterprise connectivity, making their proper implementation critical to network performance and reliability.
The depth of knowledge required mirrors the comprehensive understanding needed in database administration roles where multiple interconnected systems must work harmoniously. Route redistribution between different protocols creates opportunities for routing loops and suboptimal path selection if not carefully implemented with appropriate filtering and metric manipulation. Advanced features like route maps, prefix lists, and policy-based routing allow granular control over traffic patterns, enabling network architects to implement sophisticated traffic engineering strategies. Troubleshooting routing issues requires systematic approaches that examine neighbor adjacencies, route advertisements, path selection, and forwarding plane behavior. Successful candidates develop mental models of how routing protocols operate, enabling them to quickly diagnose problems and implement effective solutions under pressure.
Designing Resilient Switching Architectures for Business Continuity
Enterprise switching architectures must deliver high availability, performance, and scalability while remaining manageable as networks grow in complexity. Spanning Tree Protocol and its variants prevent Layer 2 loops while enabling redundant paths that activate when primary links fail, requiring careful planning of root bridge placement and port costs. VLAN design balances security isolation with administrative overhead, grouping devices logically while considering traffic patterns and broadcast domain sizes. Trunking protocols carry multiple VLANs across interconnecting links, with configuration errors causing connectivity failures that can be challenging to diagnose. EtherChannel aggregates multiple physical links into logical bundles, increasing bandwidth and providing redundancy through load distribution algorithms.
Understanding the investment required for professional advancement parallels considerations in security certification planning where candidates evaluate time and financial commitments. First-hop redundancy protocols like HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP ensure that default gateway failures don't disrupt end-user connectivity, with each protocol offering different features regarding load sharing and preemption. Switch stacking and chassis aggregation technologies simplify management by presenting multiple physical switches as a single logical device with unified configuration. Quality of Service mechanisms prioritize critical traffic during congestion, implementing classification, marking, queuing, and shaping policies that align network behavior with business priorities. Security features including port security, DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection, and IP Source Guard protect against common Layer 2 attacks that can compromise network integrity.
Integrating Wireless Networks Within Converged Enterprise Infrastructures
Wireless networking has evolved from a convenience feature to a critical infrastructure component supporting mobile devices, IoT sensors, and location services. Understanding RF fundamentals helps network designers select appropriate channel plans, power levels, and antenna types that provide coverage without creating interference. Wireless LAN controllers centralize management and policy enforcement across distributed access points, implementing seamless roaming and load balancing that enhance user experience. Security mechanisms have progressed from easily-cracked WEP to robust WPA3 with Protected Management Frames and enhanced cryptographic algorithms. Enterprise deployments typically use 802.1X authentication with RADIUS servers, enabling per-user access control and dynamic VLAN assignment based on credentials.
The rapidly evolving security landscape in wireless networking mirrors developments in cybersecurity certification tracks where professionals must stay current with emerging threats. Wireless site surveys identify optimal access point placement, considering building materials, interference sources, and capacity requirements that vary by location and usage patterns. Troubleshooting wireless issues requires understanding of association processes, authentication flows, and client behaviors that differ across device types and operating systems. Guest access solutions balance security requirements with user convenience, often employing web authentication portals and traffic segregation. Integration with wired infrastructure involves careful VLAN mapping, QoS consistency, and security policy alignment ensuring that wireless clients receive appropriate access regardless of connection method.
Automating Network Operations Through Modern DevOps Practices
Network automation represents a paradigm shift from manual configuration to programmatic infrastructure management, reducing errors while accelerating deployment cycles. Cisco's automation strategy encompasses multiple approaches including configuration management tools, APIs, and domain-specific languages that enable infrastructure-as-code practices. NETCONF and RESTCONF APIs provide standardized interfaces for programmatic device interaction, allowing scripts and automation platforms to query configurations and make changes without screen-scraping CLI output. Model-driven programmability using YANG data models ensures consistency and validation, with tools like NETCONF and gNMI providing transport mechanisms. Python emerges as the preferred language for network automation, offering extensive libraries and community support that simplifies common tasks.
Staying current with evolving certification landscapes parallels challenges in navigating updated Azure pathways where technologies advance rapidly. Ansible, Puppet, and Chef represent configuration management platforms that treat network devices as infrastructure-to-be-managed rather than manually configured, enabling consistent deployments across hundreds or thousands of devices. Version control systems like Git track configuration changes over time, providing rollback capabilities and audit trails that enhance accountability. CI/CD pipelines automate testing and deployment of network changes, with validation stages catching errors before they impact production environments. Intent-based networking platforms like Cisco DNA Center abstract low-level configuration details into business policies, translating high-level intentions into device-specific configurations while maintaining consistency across diverse hardware.
Securing Enterprise Networks Against Evolving Cyber Threats
Network security extends beyond firewalls and access lists to encompass comprehensive defense-in-depth strategies that address threats at multiple layers. Access control lists remain fundamental tools for traffic filtering, requiring careful design that balances security with operational requirements and troubleshooting access. Zone-based firewalls improve upon traditional stateful inspection by defining security zones and policies governing inter-zone traffic, providing more granular control than interface-based ACLs. VPN technologies secure remote access and site-to-site connectivity, with IPsec and SSL/TLS providing different tradeoffs between security strength, client requirements, and performance impact. Network segmentation limits breach impact by containing compromised systems within trust boundaries, preventing lateral movement that can escalate minor incidents into major data breaches.
The breadth of security knowledge required mirrors comprehensive coverage in leading cybersecurity certifications where professionals master multiple security domains. Identity services like 802.1X port-based network access control authenticate users and devices before granting network access, enforcing policies based on credentials rather than just IP addresses or MAC addresses. TrustSec technology extends security segmentation through scalable group tags that travel with traffic regardless of physical location, enabling consistent policy enforcement across wired, wireless, and VPN connections. Threat intelligence integration allows network devices to block communications with known malicious IP addresses and domains, reducing the attack surface. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments identify weaknesses before adversaries exploit them, with remediation prioritized based on risk exposure and business impact.
Optimizing Network Performance Through Intelligent Traffic Management
Quality of Service mechanisms ensure that critical applications receive necessary bandwidth and low latency even during network congestion periods. Classification identifies traffic types through various means including IP precedence, DSCP markings, access lists, or deep packet inspection that examines application-layer protocols. Marking applies QoS values to packets at network ingress points, with trust boundaries defining where existing markings are honored versus remarked according to local policy. Queuing strategies determine how different traffic classes share output interfaces during congestion, with mechanisms like Low Latency Queuing protecting real-time applications from delays caused by bulk data transfers. Policing and shaping control traffic rates, either dropping excess traffic or buffering it for later transmission, with the choice between approaches depending on downstream equipment capabilities and application tolerance for delay versus loss.
Effective time management during certification preparation parallels principles in productivity optimization strategies where focused effort yields better results than scattered studying. Congestion avoidance mechanisms like Weighted Random Early Detection drop packets before queues fill completely, signaling senders to reduce transmission rates before congestion becomes severe. Call Admission Control prevents voice and video systems from accepting more sessions than the network can support with acceptable quality, maintaining experience for existing calls rather than degrading service for all users. Bandwidth reservation protocols like RSVP establish resource guarantees for specific flows, though these prove less common in enterprise networks than DiffServ approaches. Performance monitoring through NetFlow analysis reveals actual traffic patterns, enabling QoS policy refinement based on empirical data rather than assumptions about application behavior.
Preparing Effectively for CCNP Enterprise Certification Examinations
Successful certification requires strategic preparation that balances theoretical study with hands-on practice, as the exams test both knowledge and practical troubleshooting skills. Official Cisco learning resources including instructor-led training, self-paced digital courses, and comprehensive study guides provide authoritative content aligned with exam objectives. Practice labs allow candidates to configure and troubleshoot technologies in simulated environments, developing muscle memory for common tasks and troubleshooting sequences. Third-party resources supplement official materials with alternative explanations and diverse practice questions, though candidates should verify content accuracy against current exam blueprints. Study groups provide accountability and diverse perspectives, with members teaching concepts to each other in ways that reinforce understanding.
Awareness of questionable preparation materials parallels concerns in ethical exam preparation approaches where shortcuts undermine genuine learning. Time management during preparation involves creating realistic study schedules that accommodate work and personal commitments while ensuring adequate coverage of all exam topics. Diagnostic assessments identify knowledge gaps early in the preparation process, allowing focused study on weak areas rather than spending equal time on topics already mastered. Spaced repetition techniques improve long-term retention by reviewing material at increasing intervals, preventing the forgetting that occurs when cramming everything shortly before the exam. Practice exams simulate the testing experience, building stamina for the actual exam duration while identifying areas needing additional review based on performance patterns.
Applying Enterprise Networking Skills to Consultant Opportunities
CCNP Enterprise certified professionals possess skills that translate directly to consulting roles where organizations need expert guidance on network design, implementation, and optimization. Consultants assess client environments, identifying improvement opportunities in areas like routing protocol optimization, security posture, redundancy implementation, and capacity planning. Project planning skills prove essential for scoping engagements accurately, managing client expectations, and delivering results within budget and timeline constraints. Communication abilities allow consultants to translate technical concepts into business terms that resonate with decision-makers who control project funding. Documentation practices ensure that clients can maintain solutions after consultant departure, with clear diagrams, configuration templates, and operational procedures.
The transition into consulting parallels career development approaches in business consulting pathways where technical expertise combines with client management skills. Troubleshooting expertise becomes particularly valuable during crisis situations where rapid problem resolution minimizes business impact, with consultants often called during outages that internal teams cannot resolve. Vendor-neutral perspectives help clients make technology decisions based on requirements rather than familiarity, though CCNP certification obviously indicates Cisco expertise that naturally influences recommendations. Staying current with technology trends allows consultants to guide clients toward solutions with longevity rather than implementing soon-to-be-obsolete approaches. Building professional networks through industry associations, certification communities, and client relationships generates referrals that sustain consulting practices during periods between major projects.
Crafting Compelling Proposals for Network Infrastructure Projects
Network infrastructure projects require detailed proposals that convince stakeholders to approve funding for equipment, services, and implementation efforts. Effective proposals begin with clear problem statements that establish why the current situation is inadequate, using metrics and business impact to quantify pain points. Proposed solutions explain how specific technologies and approaches address identified problems, with enough technical detail to demonstrate expertise while remaining accessible to non-technical reviewers. Cost-benefit analysis shows projected returns on investment, considering both hard savings from efficiency improvements and soft benefits like enhanced user productivity or improved security posture. Implementation plans outline project phases, resource requirements, timeline estimates, and risk mitigation strategies that build confidence in successful delivery.
Creating persuasive proposal documents draws upon skills similar to those required for business proposal development where technical and business perspectives merge. Network diagrams visualize proposed architectures, showing how components interconnect and data flows through the infrastructure. Equipment lists detail specific models and quantities, with justification for selections based on performance requirements, budget constraints, and operational considerations. Migration strategies explain how transitions from current to future state will occur with minimal business disruption, addressing stakeholder concerns about downtime or temporary performance degradation. Post-implementation support plans describe how the organization will maintain and operate new infrastructure, including training requirements, documentation deliverables, and ongoing vendor support arrangements.
Leading Network Teams Through Infrastructure Transformation Initiatives
Network infrastructure projects require leadership that guides teams through complex changes while maintaining daily operations and addressing unexpected challenges. Effective leaders establish clear visions that help team members understand how their individual contributions support broader organizational objectives. Communication skills become critical during change initiatives, with leaders providing regular updates to stakeholders at all levels using language appropriate to each audience. Conflict resolution addresses disagreements about technical approaches, resource allocation, or project priorities before they escalate into team dysfunction. Mentoring develops team capabilities over time, with senior members sharing knowledge that accelerates junior staff progression while building organizational resilience against key person dependencies.
Leadership capabilities required for infrastructure projects parallel competencies in essential leadership frameworks where influencing without authority proves crucial. Delegation balances workload across team members according to skills and development needs, avoiding bottlenecks created when leaders try controlling all decisions. Risk management identifies potential project derailers early, implementing mitigation strategies before problems materialize and impact timelines. Change management addresses the human side of infrastructure transitions, recognizing that technical excellence alone cannot ensure adoption of new systems and processes. Celebration of milestones maintains morale during long projects, acknowledging progress and individual contributions that might otherwise go unrecognized.
Embracing Agile Methodologies for Network Project Execution
Agile approaches originally developed for software projects increasingly influence network infrastructure initiatives, bringing iterative development and continuous feedback to traditionally waterfall-dominated domains. Sprint-based execution delivers functionality incrementally rather than waiting for complete solutions, allowing early user feedback that guides subsequent development. Daily standups maintain team coordination and surface impediments quickly, preventing small issues from growing into project delays. Retrospectives after each sprint identify process improvements, with teams evolving their practices based on experience rather than rigidly following predetermined plans. Product backlogs prioritize work based on business value, ensuring that teams always address highest-impact items first.
The cultural shift toward agile thinking parallels principles in agile value frameworks emphasizing collaboration over rigid processes. User stories translate technical requirements into business outcomes, helping teams maintain focus on value delivery rather than getting lost in implementation details. Continuous integration practices applied to network automation ensure that configuration changes integrate cleanly with existing infrastructure, catching conflicts early when they are easier to resolve. Sprint demos showcase completed work to stakeholders, building trust through visible progress while gathering feedback that shapes upcoming priorities. Agile scaling frameworks help larger network teams coordinate work across multiple groups, maintaining agility benefits despite organizational complexity.
Adapting Network Practices to Disciplined Agile Frameworks
Disciplined Agile extends basic agile principles with additional governance and scaling guidance particularly relevant to enterprise networking environments. Context-sensitive approaches acknowledge that no single process fits all situations, with teams selecting practices appropriate to their specific constraints and goals. Risk-value delivery balances aggressive innovation against stability requirements, recognizing that production networks cannot tolerate the experimentation that might benefit development projects. Lifecycle flexibility accommodates different project types, from exploratory proofs-of-concept through production deployments and ongoing operational support. Enterprise awareness ensures that team decisions consider broader organizational context rather than optimizing for local benefits that create system-level problems.
Understanding disciplined approaches to agility connects to comprehensive frameworks in disciplined agile methodologies where structure supports rather than constrains flexibility. Consumable solutions emphasize delivering working infrastructure that users can actually adopt rather than technically perfect implementations that prove too complex for operational teams to maintain. Tactical scaling addresses the reality that network infrastructure projects often involve multiple teams across different locations and time zones, requiring coordination mechanisms beyond what small co-located teams need. Organizational optimization recognizes that improving individual team performance may degrade overall outcomes if teams pursue conflicting objectives, encouraging system-level thinking about performance optimization.
Prioritizing Network Infrastructure Improvements Strategically
Network environments accumulate technical debt and improvement opportunities faster than teams can address them, requiring prioritization frameworks that ensure resources focus on highest-value activities. Business value assessment considers how different improvements impact organizational objectives, whether through cost reduction, revenue enablement, risk mitigation, or user experience enhancement. Technical risk evaluation identifies which infrastructure components pose greatest threats to stability, security, or performance if not addressed. Dependency analysis reveals which improvements unlock subsequent capabilities, influencing sequencing decisions that maximize cumulative value delivery. Cost estimates inform prioritization by revealing which improvements deliver best value relative to required investment.
Systematic prioritization approaches draw from methodologies in agile prioritization techniques where competing demands exceed available capacity. Weighted scoring combines multiple criteria into composite scores that support objective comparison across diverse improvement candidates. MoSCoW classification divides potential work into must-have, should-have, could-have, and won't-have categories that focus initial efforts on absolute requirements. Kano analysis distinguishes between basic expectations that cause dissatisfaction if unmet, performance factors that provide proportional satisfaction, and delighters that exceed expectations and drive enthusiasm. Continuous reprioritization acknowledges that circumstances change, with regular backlog refinement ensuring that priorities reflect current rather than historical realities.
Navigating Remote Work Realities in Network Operations
The shift toward distributed work arrangements has transformed network operations, with teams managing infrastructure remotely and supporting users connecting from diverse locations. VPN capacity planning ensures that remote access infrastructure handles user loads, with considerations for bandwidth, authentication throughput, and license restrictions. Collaboration tools enable distributed teams to work effectively despite physical separation, with screen sharing, remote control, and persistent chat channels supporting complex troubleshooting sessions. Security implications of remote access demand careful consideration, balancing usability against protection requirements through multi-factor authentication, endpoint compliance checking, and traffic inspection. Home network variables introduce troubleshooting complexity, with ISP issues, consumer-grade equipment, and wireless interference creating problems outside organizational control.
The transformation of work arrangements parallels broader trends in freelance workforce evolution where location independence reshapes career possibilities. Asynchronous communication becomes essential when team members work different hours across time zones, with documentation and recorded explanations replacing real-time conversations. Cloud-based management platforms enable infrastructure administration from anywhere with internet connectivity, reducing reliance on physical presence in data centers. Remote hands services provide physical access when needed for tasks like cable replacement or hardware troubleshooting that cannot occur remotely. Building team cohesion across distance requires intentional effort through virtual social events and periodic in-person gatherings that strengthen relationships frayed by constant video meetings.
Grounding Network Skills in Computer Engineering Fundamentals
Deep networking expertise builds upon computer engineering foundations that explain how systems operate at fundamental levels. Binary number systems underpin IP addressing, subnet masking, and wildcard masks that network engineers manipulate daily. Boolean logic appears in access control lists, routing policies, and automation scripts that implement decision trees. Computer architecture knowledge illuminates how network processors handle packet forwarding, with concepts like pipelining and parallel processing explaining performance characteristics. Operating systems understanding reveals how end hosts interact with networks through TCP/IP stacks, sockets, and device drivers that translate application requests into network traffic.
Foundational knowledge provides context for advanced networking concepts, similar to how computer engineering principles support diverse technical specializations. Data structures like trees and graphs model network topologies, with algorithms like shortest path finding directly applicable to routing protocol operation. Probability and statistics inform capacity planning, performance analysis, and troubleshooting decisions based on imperfect information. Physics concepts explain signal propagation, attenuation, and interference that affect both wired and wireless networks. Understanding these fundamentals enables network engineers to reason about new technologies rather than merely memorizing vendor-specific implementation details.
Expanding Skills Through Complementary Cloud Networking Certifications
Modern enterprise networks increasingly integrate with cloud platforms, creating demand for professionals who understand both traditional networking and cloud-specific paradigms. Cloud networking concepts including virtual networks, load balancers, and software-defined perimeters complement on-premises expertise that CCNP Enterprise provides. Multi-cloud strategies require understanding how different providers implement networking, with variations in terminology, capabilities, and pricing models affecting architecture decisions. Hybrid connectivity solutions like dedicated connections and encrypted tunnels bridge on-premises and cloud environments, with proper design ensuring security, performance, and cost optimization. Network automation skills transfer directly to cloud infrastructure-as-code practices, with similar tools and languages managing resources across environments.
Expanding expertise into cloud domains parallels learning approaches in complimentary platform education where free resources build capabilities. Cloud security models differ from on-premises approaches, with shared responsibility boundaries requiring careful understanding to avoid gaps where neither customer nor provider implements necessary controls. Performance optimization in cloud environments involves different techniques than traditional networks, with provider-specific features for traffic acceleration, caching, and global distribution. Cost management becomes explicit concern in cloud networking where bandwidth and processing incur direct charges rather than being absorbed into overall infrastructure costs. Certifications like AWS Advanced Networking or Azure Network Engineer Associate complement CCNP Enterprise by validating cloud-specific skills that enhance career flexibility.
Strategizing Certification Pathways for Long-Term Career Growth
Professional development requires strategic thinking about certification sequences that build upon each other while maintaining relevance to career goals. Foundation certifications establish breadth across networking domains before specialization, with CCNA providing prerequisites for CCNP Enterprise. Concentration exam selection aligns certification with career direction, whether toward design roles, automation specialization, or wireless focus. Timing decisions balance immediate job requirements against long-term skill development, with some professionals pursuing certifications before role changes while others wait for employer support. Recertification requirements maintain currency through continuing education, with paths including new exams, training participation, or professional contributions.
Understanding testing strategies parallels approaches in standardized assessment preparation where informed decisions optimize outcomes. Complementary certifications from other vendors broaden perspective beyond single-vendor approaches, with multi-vendor expertise increasingly valuable as organizations adopt best-of-breed strategies. Security certifications add capabilities that enhance networking roles, addressing the convergence of network and security operations in many organizations. Automation and programming credentials formalize DevOps skills that differentiate modern network engineers from traditional CLI-focused practitioners. Regular skill assessment through practice exams and lab exercises reveals knowledge gaps before they become career limiters, enabling proactive learning rather than reactive scrambling when capabilities prove insufficient.
Optimizing Exam Preparation Through Targeted Study Resources
Effective exam preparation requires quality resources that align with current exam objectives while matching individual learning preferences. Official Cisco Press publications provide comprehensive coverage authored by subject matter experts with direct exam development involvement. Video courses offer dynamic explanations with demonstrations that illuminate concepts challenging to grasp through text alone. Hands-on labs build practical skills that exam simulations assess, with platforms ranging from physical equipment to virtual environments. Practice exams identify weak areas while building familiarity with question formats and time management requirements. Study guides synthesize information into focused formats emphasizing key concepts and common pitfalls.
Selecting appropriate study materials parallels resource evaluation in test preparation planning where quality matters more than quantity. Community resources including forums, study groups, and social media provide peer support and diverse perspectives that enrich understanding. Vendor documentation offers authoritative references for configuration syntax and feature capabilities, though dense technical writing requires persistence to extract relevant information. Webinars and workshops provide structured learning with opportunities for questions that clarify confusion. Creating personal reference materials through note-taking and documentation summarizes learning in formats optimized for individual retention patterns. Regular review sessions prevent forgetting through spaced repetition that moves information from short-term to long-term memory.
Architecting Scalable Database-Driven Network Management Platforms
Network management platforms increasingly rely on sophisticated database architectures to store device configurations, performance metrics, and historical data enabling trend analysis. Time-series databases optimize storage and retrieval of network telemetry collected at regular intervals, with compression and aggregation strategies managing data volume growth. Relational databases maintain inventory information, user accounts, and policy definitions that drive configuration automation. NoSQL databases handle unstructured data like syslogs and trap messages that don't fit predetermined schemas. Database selection considers query patterns, scaling requirements, consistency needs, and operational complexity, with different data types often requiring different database technologies within comprehensive management platforms.
Database integration skills prove valuable across technical domains, similar to expertise in database certification programs where professionals master data management fundamentals. Normalization principles reduce data redundancy while maintaining referential integrity, though denormalization sometimes improves query performance for read-heavy workloads. Indexing strategies accelerate searches through large datasets, with careful design balancing query speed against write performance and storage overhead. Backup and recovery procedures protect against data loss from hardware failures, software bugs, or operational errors. Performance tuning addresses query optimization, connection pooling, and caching strategies that maintain responsiveness as data volumes grow. Integration APIs allow management platforms to exchange data with other systems, creating unified views across diverse tools.
Meeting Regulatory Compliance in Financial Network Infrastructure
Financial services organizations face stringent regulatory requirements that influence network design, implementation, and operation across all infrastructure components. Data protection regulations mandate encryption for sensitive information both in transit and at rest, with key management processes ensuring cryptographic controls remain effective. Audit logging captures administrative actions and security events, with log retention periods and tamper-resistance mechanisms satisfying evidence requirements. Network segmentation isolates systems processing different data sensitivity levels, preventing unauthorized access through defense-in-depth approaches. Disaster recovery capabilities must meet specific recovery time and recovery point objectives, with regular testing validating that documented procedures work under pressure.
Navigating complex regulatory frameworks parallels challenges in compliance certification contexts where professionals master industry-specific requirements. Change management processes document and approve infrastructure modifications before implementation, creating audit trails that regulators review during examinations. Vulnerability management programs identify and remediate security weaknesses on timelines proportional to risk severity, with compensating controls implemented when immediate patching proves impractical. Third-party risk management extends security requirements to vendors and service providers with network access, through contractual obligations and periodic assessments. Incident response plans define procedures for detecting, analyzing, containing, and recovering from security events, with communication protocols addressing regulatory notification requirements.
Implementing Next-Generation Firewall Technologies
Next-generation firewalls extend traditional packet filtering with application awareness, intrusion prevention, and advanced threat protection capabilities. Application identification classifies traffic based on behavioral analysis rather than just port numbers, enabling policies that block Facebook while allowing Salesforce even though both use HTTPS. User identity integration ties access policies to authenticated users rather than IP addresses, maintaining security as users move between locations and devices. Intrusion prevention systems inspect traffic for attack signatures and anomalous behaviors, blocking threats before they reach protected systems. URL filtering prevents access to malicious and inappropriate websites, with categories and reputation scores enabling flexible policy implementation.
Advanced security capabilities reflect evolving threat landscapes that demand defense-in-depth, similar to comprehensive protection in security certification curricula covering modern threats. Sandboxing analyzes suspicious files in isolated environments before allowing delivery, detecting zero-day malware that signature-based scanning misses. SSL inspection decrypts and inspects encrypted traffic, preventing attackers from hiding malicious payloads in HTTPS streams though privacy and performance considerations require careful implementation. Threat intelligence integration provides real-time information about emerging threats, with automatic policy updates blocking newly-identified attack sources. High availability configurations ensure that firewall failures don't create security gaps or connectivity outages, with stateful failover maintaining session continuity during device transitions.
Validating Professional Competency Through Standardized Assessments
Professional competency validation through standardized testing ensures that certified individuals meet consistent knowledge standards regardless of how they acquired skills. Question design focuses on practical scenarios requiring application of knowledge rather than rote memorization of facts, with distractors based on common misconceptions that incomplete understanding might produce. Performance-based testing components require actual configuration and troubleshooting rather than just selecting correct answers from multiple choices. Adaptive testing adjusts difficulty based on response patterns, efficiently assessing competency while minimizing test duration. Cut score determination through psychometric analysis establishes passing thresholds that represent minimum competence, with periodic review ensuring standards remain current as knowledge requirements evolve.
Assessment methodologies balance validity and reliability concerns, paralleling considerations in workforce skills testing where accurate evaluation matters. Beta testing with subject matter experts identifies questions with technical errors, ambiguous wording, or multiple defensible answers before release to candidates. Statistical analysis reveals question performance characteristics including difficulty levels and discrimination indices showing how well each question separates high performers from low performers. Security measures prevent unauthorized content disclosure through non-disclosure agreements, test center monitoring, and item rotation across exam forms. Accommodations address candidate needs related to disabilities, ensuring that tests measure competency rather than unrelated factors while maintaining validity and fairness.
Assessing Workplace Skills Relevant to Network Engineering
Network engineering requires diverse workplace skills beyond pure technical knowledge, including problem-solving abilities, communication effectiveness, and learning agility. Applied mathematics enables subnet calculations, bandwidth estimations, and statistical analysis of performance metrics. Reading comprehension allows understanding of vendor documentation, RFC specifications, and technical articles explaining new concepts. Listening skills facilitate requirements gathering through stakeholder interviews and troubleshooting through customer problem descriptions. Writing abilities support documentation creation, including network diagrams, configuration standards, and post-incident reports.
Comprehensive skill assessment approaches parallel methodologies in workplace competency evaluation measuring practical abilities. Teamwork capabilities enable collaboration on large projects where individual contributors must coordinate efforts toward shared objectives. Critical thinking supports troubleshooting processes that systematically eliminate potential causes until root problems are identified. Time management allows juggling multiple priorities from routine maintenance through emergency response without dropping critical tasks. Adaptability helps navigate technology changes that continuously reshape networking landscapes, with willingness to abandon outdated approaches when superior alternatives emerge. Ethical decision-making guides choices when pressures tempt shortcuts that could compromise security or reliability.
Applying Enterprise Architecture Frameworks to Network Design
Enterprise architecture frameworks provide structured approaches to aligning IT infrastructure with business objectives, goals, and processes. TOGAF methodologies guide architecture development through phased processes including preliminary framework establishment, architecture vision creation, business architecture documentation, information systems architecture design, technology architecture specification, opportunities and solutions identification, migration planning, implementation governance, and architecture change management. Architecture Development Method iterates through these phases, refining designs based on stakeholder feedback and constraint discovery. Building blocks represent reusable components at different abstraction levels, from foundational technology services through common systems to business capabilities.
Structured architecture approaches bring discipline to complex initiatives, similar to frameworks in enterprise architecture certification validating systematic design capabilities. Architecture principles establish guidelines that drive decisions throughout development, addressing concerns like interoperability, security, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Stakeholder management ensures that architecture considers diverse perspectives from executives through operations teams, balancing competing requirements through transparent tradeoff analysis. Gap analysis compares current state to target state, revealing transformation requirements including new capabilities to develop and existing systems to retire. Architecture governance establishes decision rights and review processes that maintain architectural integrity as implementation teams make detailed choices.
Protecting Business Continuity Through Backup and Recovery
Data protection strategies ensure that organizations can recover from disasters, equipment failures, and human errors that could otherwise cause permanent information loss. Backup methodologies including full, incremental, and differential approaches balance storage consumption against recovery time and complexity. Retention policies determine how long backup copies persist before deletion, with considerations for operational recovery needs, compliance requirements, and storage costs. Off-site replication protects against site-wide disasters like fires or floods that could destroy both primary systems and local backups. Testing validates that backup procedures actually work and that recovery objectives are achievable, with documentation addressing gaps before real disasters occur.
Comprehensive data protection parallels systematic approaches in backup certification programs where professionals master recovery technologies. Recovery point objectives define acceptable data loss in terms of time, with frequent backups minimizing loss but consuming more resources. Recovery time objectives establish how quickly systems must return to operation, influencing technology selections around backup formats, restore procedures, and infrastructure redundancy. Immutable backups prevent ransomware from encrypting or deleting recovery copies, with air-gapped systems providing additional protection. Cloud-based backup services offer scalable storage and geographic distribution, though bandwidth and egress costs require analysis.
Managing Multi-Cloud Network Architectures
Organizations increasingly deploy workloads across multiple cloud providers, creating complex networking requirements that span diverse platforms with different capabilities and terminology. Inter-cloud connectivity options include VPN tunnels over public internet, dedicated circuits through interconnection providers, and cloud provider peering services with private high-bandwidth links. Routing considerations address how to direct traffic between clouds efficiently while maintaining desired failover behaviors and traffic engineering policies. Security controls must protect data traversing between clouds while enabling necessary flows, with consistent policy implementation despite platform differences. Cost management requires understanding each provider's networking pricing models, with architecture decisions significantly impacting ongoing expenses.
Multi-cloud expertise demands platform-specific knowledge combined with vendor-neutral design principles, similar to skills in cloud management certification paths addressing heterogeneous environments. Workload placement decisions consider data gravity, regulatory requirements, pricing differences, and capability availability across providers. Network abstraction layers provide unified management interfaces across clouds, simplifying operations though introducing dependencies on abstraction tools. Monitoring distributed applications requires correlation across provider-specific observability platforms, with third-party tools often providing unified visibility. Disaster recovery strategies leverage multi-cloud deployments for resilience, with careful planning ensuring that regional failures don't impact backup sites.
Deploying Cloud Foundation Infrastructure Services
Cloud foundation services provide building blocks upon which organizations construct application environments and deploy workloads. Identity and access management establishes authentication and authorization frameworks controlling resource access, with integration to existing corporate directories maintaining unified user management. Networking services create isolated environments for workload deployment, with features like VPNs, load balancing, and DNS built into platforms. Storage services offer object, file, and block storage options with varying performance, durability, and cost characteristics. Compute services range from virtual machines through containers to serverless functions, each appropriate for different application architectures.
Foundation service mastery enables rapid capability delivery, paralleling skills validated through infrastructure certification programs covering platform essentials. Automation capabilities including infrastructure-as-code tools allow programmatic resource provisioning that ensures consistency while maintaining change tracking through version control. Monitoring and logging services provide visibility into resource utilization, application performance, and security events. Cost management tools track spending across services and teams, with budgets and alerts preventing bill shock. Security services including encryption, key management, and compliance tools protect workloads and data. Understanding these foundation services enables architects to design solutions leveraging cloud capabilities rather than recreating existing data center patterns.
Implementing Data Center Networking Technologies
Modern data center networks employ spine-leaf architectures that eliminate traditional three-tier designs' oversubscription and bottlenecks. Leaf switches connect to servers and storage, providing high-bandwidth low-latency access to workloads. Spine switches interconnect leaves, enabling any-to-any communication at full line rate. VXLAN overlays create logical networks across physical infrastructure, enabling flexible workload placement unconstrained by VLAN limitations. EVPN control planes distribute reachability information, supporting features like multi-tenancy, mobility, and distributed gateways.
Data center networking expertise addresses unique scale and performance requirements, similar to specializations in data center certification tracks validating facility-specific knowledge. East-west traffic patterns dominate modern data centers as microservices architectures create extensive server-to-server communication. Network virtualization separates logical topologies from physical infrastructure, enabling operational independence and multi-tenancy. Converged infrastructure integrates networking with compute and storage, simplifying deployment and management of integrated stacks. Hybrid cloud integration extends data center networks into public clouds, with consistent policies across locations despite infrastructure differences.
Orchestrating Professional-Level Network Infrastructure
Professional-grade network infrastructure requires sophisticated orchestration balancing performance, reliability, and operational efficiency across distributed environments. Software-defined networking controllers centralize policy definition while distributing enforcement to network devices, separating control planes from forwarding planes. Intent-based networking translates business policies into device configurations automatically, maintaining desired states through continuous validation and remediation. Analytics platforms process telemetry from across infrastructure, identifying trends and anomalies that inform capacity planning and troubleshooting. Automation frameworks execute common tasks through workflows that reduce manual effort while improving consistency.
Infrastructure orchestration capabilities reflect modern operational approaches, paralleling expertise in professional infrastructure certifications validating advanced implementations. Closed-loop automation responds to detected conditions without human intervention, like automatically scaling capacity when utilization exceeds thresholds. Workflow engines coordinate multi-step processes spanning devices and systems, with error handling that ensures partial failures don't leave infrastructure in inconsistent states. Integration platforms connect networking tools with broader IT service management, enabling unified operations across traditionally siloed domains. Template-based provisioning accelerates deployment of new sites and services, encoding organizational standards that new infrastructure inherits automatically.
Managing Contemporary Data Center Operations
Contemporary data center operations balance competing demands for agility, reliability, and cost optimization in environments supporting business-critical workloads. Change management processes govern infrastructure modifications, balancing risk mitigation against speed demands from business stakeholders. Capacity planning anticipates future resource needs based on growth projections and seasonality patterns, with procurement lead times influencing how far ahead planning must occur. Performance monitoring tracks resource utilization and application behavior, identifying degradation before it impacts users. Incident management coordinates response to problems, from initial detection through root cause analysis and preventative measures implementation.
Operational excellence in complex environments demands disciplined practices, similar to frameworks in operations management certifications emphasizing process maturity. Vendor management maintains relationships with equipment suppliers and service providers, negotiating contracts and managing support escalations. Documentation practices capture infrastructure designs, operational procedures, and institutional knowledge that enables team members to support environments effectively. Training programs develop team capabilities, addressing both new hire onboarding and continuous skill development for existing staff. Security operations integrate with broader infrastructure management, monitoring for threats while ensuring that security controls don't unnecessarily impede legitimate activities.
Designing Advanced ICM Infrastructure Components
Infrastructure and Cloud Management platforms provide unified interfaces for administering resources across heterogeneous environments including on-premises data centers, private clouds, and public cloud services. Policy-based provisioning translates service catalogs into deployed infrastructure, with approval workflows ensuring that requests meet organizational standards before execution. Lifecycle management automates patching, upgrades, and decommissioning according to defined policies and schedules. Cost optimization features identify underutilized resources and recommend rightsizing or termination, with chargeback capabilities allocating expenses to consuming teams.
Comprehensive management capabilities simplify operations at scale, paralleling solutions in infrastructure administration certifications covering unified management. Self-service portals enable users to provision approved resources without IT intervention, accelerating delivery while maintaining governance. Configuration management maintains desired states through drift detection and automatic remediation. Compliance monitoring validates that deployed resources adhere to security baselines and regulatory requirements, with reporting for audit purposes. Integration with existing tools leverages investments in monitoring, ticketing, and configuration management rather than requiring wholesale replacement.
Implementing Modern Management Solutions
Modern management solutions address the complexity of hybrid and multi-cloud environments where workloads span traditional infrastructure and cloud platforms. Unified dashboards provide visibility across heterogeneous resources, aggregating metrics and alerts into consolidated views. AI-enhanced analytics detect anomalies and predict potential issues before they impact operations, with machine learning models that improve through experience. Remediation automation responds to detected problems without human intervention when appropriate, escalating complex issues requiring judgment. Mobile applications enable infrastructure management from anywhere, with responsive interfaces optimized for different device form factors.
Comprehensive management platforms deliver operational efficiency, similar to capabilities in management certification programs validating solution expertise. Role-based access control ensures that users can perform necessary functions without excessive privileges that create security risks. Multi-tenancy supports managed service providers serving multiple clients from shared infrastructure, with logical isolation preventing customers from accessing each other's environments. Extensibility through APIs and plugins allows customization for organization-specific requirements not addressed by out-of-box functionality. Migration tools simplify transitions from legacy management platforms, with data import and integration capabilities that reduce cutover risks.
Administering Contemporary Infrastructure Platforms
Contemporary infrastructure platforms abstract underlying hardware through virtualization layers that provide flexibility, efficiency, and standardization benefits. Hypervisor management includes host configuration, resource allocation, and networking integration that create foundations for virtual machine deployment. Storage tiering balances performance and cost by placing frequently-accessed data on fast media while moving cold data to economical storage. Distributed resource scheduling optimizes workload placement across cluster members, balancing loads while respecting affinity and anti-affinity rules. High availability features protect against hardware failures through automatic workload migration to surviving hosts.
Platform administration expertise enables effective resource utilization, paralleling skills in infrastructure platform certifications covering operational capabilities. Template libraries standardize virtual machine configurations, ensuring consistent deployments that incorporate security hardening and monitoring agents. Snapshot management provides point-in-time recovery capabilities, though overuse degrades performance and consumes storage. Resource pools allocate CPU and memory guarantees to prioritized workloads while allowing less critical systems to share excess capacity. Performance monitoring identifies resource contention, oversized virtual machines, and opportunities for consolidation that improve efficiency.
Orchestrating Network Services Delivery
Network services orchestration automates service delivery across multi-vendor infrastructure, transforming manual processes into automated workflows that reduce deployment time from weeks to hours. Service catalogs present approved offerings to consumers, abstracting complex infrastructure into consumable services described by business-relevant characteristics. Workflow engines coordinate provisioning across networking, compute, storage, and security systems, with error handling that ensures consistency. Template-based deployment encodes organizational standards that new services inherit, improving consistency while reducing configuration errors. APIs enable integration with ITSM platforms, creating unified service delivery experiences across traditionally separate domains.
Service delivery automation transforms operations, similar to capabilities in service orchestration certifications addressing modern delivery models. Resource allocation considers capacity, policy constraints, and placement requirements when deciding where to deploy workloads. Configuration management maintains desired states through continuous monitoring and drift remediation, preventing manual changes that violate established standards. Change scheduling coordinates deployments during maintenance windows, with rollback capabilities enabling recovery from problematic changes. Analytics track service delivery metrics including time-to-provision, successful first-time deployments, and customer satisfaction that inform continuous improvement.
Managing Advanced Service Platform Operations
Advanced service platforms support complex workloads requiring sophisticated networking, storage, and compute capabilities coordinated through centralized management. Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple service instances, improving performance and availability while enabling rolling upgrades without downtime. Auto-scaling adjusts capacity automatically based on demand, optimizing cost by running only necessary resources. Service mesh technologies manage service-to-service communication in microservices architectures, handling retry logic, circuit breaking, and traffic routing independently from application code. Monitoring platforms collect metrics, logs, and traces from distributed services, correlating data to provide end-to-end visibility.
Platform management at scale demands automation and standardization, paralleling operational approaches in platform operations certifications emphasizing production environments. Container orchestration platforms schedule containerized workloads across clusters, managing placement, health checking, and resource allocation. Persistent storage solutions address stateful application requirements in ephemeral container environments, with volume plugins supporting diverse storage backends. Network policies control traffic between services, implementing zero-trust security models where every connection requires explicit authorization. GitOps practices manage platform configuration through version-controlled declarations, with automated reconciliation ensuring running state matches desired state.
Implementing Horizon Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
Virtual desktop infrastructure centralizes desktop computing in data centers while delivering experiences to endpoint devices including thin clients, tablets, and repurposed PCs. Connection brokering matches users to desktop resources based on entitlements and availability, with load balancing across pools that optimize resource utilization. Protocol optimization reduces bandwidth consumption and latency impact, enabling acceptable performance even over constrained connections. Persona management maintains user settings and data across sessions, whether accessing the same desktop repeatedly or using non-persistent desktops that reset between sessions. Application delivery separates application access from full desktop provisioning, enabling just-in-time delivery of specific tools.
VDI implementations require careful planning balancing user experience against infrastructure costs, similar to considerations in desktop virtualization certifications addressing workspace technologies. Storage performance significantly impacts boot storms and login times, with caching and tiering strategies managing I/O demands. Graphics acceleration through virtual GPUs enables CAD and video applications that would otherwise require physical workstations. Security benefits include centralized data storage that prevents sensitive information from residing on easily-lost endpoint devices. Disaster recovery simplifies through server-side backups compared to distributed endpoint protection. Print management redirects output from virtual desktops to local printers without complex driver installations.
Administering Modern Workspace Technologies
Modern workspace technologies deliver applications and desktops as services accessed from any device, creating flexible work environments that support hybrid models combining office and remote workers. Application layering separates operating systems, applications, and user data into independent layers that compose dynamically, reducing image management complexity. User environment management maintains consistent experiences across delivery methods whether accessing local desktops, virtual desktops, or published applications. Profile management solutions persist settings and data while users roam between physical and virtual environments. Monitoring platforms track user experience metrics including logon duration, application responsiveness, and session quality that inform infrastructure optimization.
Workspace administration balances user productivity demands against IT management complexity, paralleling expertise in workspace management certifications covering end-user computing. Policy engines enforce security controls including multi-factor authentication, context-aware access, and data loss prevention without degrading user experience. Application catalog services provide self-service access to approved tools, reducing IT ticket volumes while maintaining governance. Performance analytics identify problematic applications and infrastructure bottlenecks that affect productivity. Cost optimization through rightsizing, power management, and lifecycle management reduces total cost of ownership while maintaining service quality.
Managing vSphere Virtualization Infrastructure
vSphere provides enterprise-grade virtualization foundations that power private clouds and on-premises infrastructure with high performance, availability, and operational efficiency. Distributed switches simplify network management across clustered hosts, with consistent configurations and centralized monitoring. Storage policies define service levels that infrastructure automatically satisfies through intelligent placement and caching. vMotion enables live migration of running virtual machines between hosts without downtime, supporting workload balancing and maintenance activities. Fault tolerance creates continuous availability through synchronous replication between primary and secondary instances that take over instantaneously upon failure.
Virtualization platform expertise enables efficient infrastructure operations, similar to skills in virtualization certifications validating platform administration. Resource scheduling algorithms optimize workload placement considering CPU, memory, storage, and network requirements alongside affinity rules and reservations. Snapshot technology provides recovery points for virtual machines, though performance impacts limit production usage to short-term purposes. Template libraries standardize virtual machine configurations with organization-approved security hardening and applications. Automation through APIs and tools like PowerCLI enables infrastructure-as-code practices that improve consistency while accelerating deployments.
Integrating Digital Workspace Platforms
Digital workspace platforms unify access to applications, data, and services regardless of location or device, creating consistent productive environments for distributed workforces. Single sign-on eliminates authentication friction by enabling one set of credentials to access multiple applications across cloud and on-premises systems. Conditional access policies adapt security controls based on user identity, device posture, network location, and risk signals detected through behavioral analytics. Productivity applications including email, file sharing, and collaboration tools integrate into cohesive experiences. Mobile device management extends workspace policies to smartphones and tablets, balancing security against personal privacy on BYOD devices.
Unified workspace delivery addresses modern work patterns, paralleling solutions in workspace platform certifications covering integrated environments. Application delivery mechanisms range from full virtual desktops through published applications to SaaS services, with appropriate methods selected based on application characteristics and user requirements. Profile management maintains consistent user experiences as workers move between devices and connection methods. Analytics platforms track adoption, identify training needs, and quantify productivity improvements attributed to workspace initiatives. Endpoint security ensures that devices accessing corporate resources meet minimum security standards before allowing connections.
Deploying Next-Generation Workspace Solutions
Next-generation workspace solutions leverage cloud services, AI capabilities, and modern endpoints to deliver superior experiences compared to traditional desktop computing. Cloud-hosted virtual desktops reduce on-premises infrastructure requirements while providing global delivery that follows users across locations. AI-powered assistance helps users accomplish tasks through natural language interactions rather than navigating complex menus. Contextual security continuously evaluates risk and adapts controls accordingly rather than applying static policies that treat all situations identically. Progressive web applications deliver capabilities through browsers without client software installation requirements.
Modern workspace approaches transform how organizations deliver computing capabilities, similar to innovations in workspace solution certifications addressing contemporary platforms. Biometric authentication improves security while eliminating password frustrations, using fingerprints or facial recognition that can't be forgotten or stolen. Unified endpoint management handles traditional PCs alongside mobile devices through single consoles, reducing administrative overhead. Automation handles routine tasks like application updates and security patching without user intervention, maintaining currency while minimizing disruptions. Analytics provide insights into workspace utilization patterns that inform technology investments and support optimization.
Managing Contemporary Workspace Infrastructure
Contemporary workspace infrastructure balances user experience demands against cost containment and security requirements across hybrid environments mixing physical and virtual resources. Profile management solutions maintain settings and data consistency as users move between delivery methods including physical desktops, virtual desktops, and published applications. Tiered storage architectures place frequently-accessed data on high-performance media while archiving cold data to economical storage. Network optimization prioritizes interactive traffic over background activities, maintaining acceptable responsiveness during congestion. Monitoring platforms track user experience metrics from login duration through application responsiveness that quantify service quality.
Infrastructure management expertise ensures productive workspace delivery, paralleling capabilities in infrastructure management certifications covering operational platforms. Capacity planning anticipates resource requirements based on user growth and seasonal patterns, with procurement aligned to lead times. High availability designs eliminate single points of failure through redundancy and automatic failover. Disaster recovery capabilities enable rapid restoration following site failures, with RTO and RPO targets driving technology selections. Security controls including network segmentation, endpoint protection, and data encryption protect against threats while enabling necessary access and collaboration.
Administering Established vSphere Platforms
Established vSphere platforms require ongoing administration maintaining performance, security, and availability while accommodating growth and technology refresh cycles. Host management includes patching, firmware updates, and hardware maintenance that keep infrastructure current while minimizing downtime. Virtual machine lifecycle processes handle provisioning, cloning, migration, and decommissioning through defined workflows. Resource optimization identifies oversized virtual machines, idle workloads, and opportunities for consolidation that improve efficiency. Backup integration protects virtual machines through automated processes with retention policies meeting recovery and compliance requirements.
Platform administration sustains operational environments, similar to expertise in virtualization platform certifications validating maintenance capabilities. Permissions management controls who can perform administrative functions across the environment, with role-based access ensuring least-privilege principles. Monitoring alerts administrators to performance degradation, capacity constraints, and potential failures before they impact production workloads. License management tracks entitlement consumption ensuring compliance while optimizing costs through appropriate edition selection. Documentation captures infrastructure designs, operational procedures, and troubleshooting guides that enable teams to support environments effectively.
Operating Modern Virtual Infrastructure
Modern virtual infrastructure operations leverage automation, analytics, and integration with broader IT service management to deliver reliable services efficiently. Automated remediation responds to detected issues without human intervention when appropriate, like restarting failed services or migrating workloads from degraded hosts. Predictive analytics identify trends that forecast future problems, enabling proactive intervention before incidents occur. Capacity management continuously optimizes resource allocation across competing workloads, balancing performance against cost. Integration with ITSM platforms creates unified operational experiences where infrastructure incidents flow into service desk workflows.
Operational excellence in virtual environments demands sophisticated tooling and processes, paralleling approaches in infrastructure operations certifications emphasizing service delivery. Performance baselines establish normal behavior patterns that anomaly detection uses to identify deviations requiring investigation. Change management coordinates infrastructure modifications with broader service delivery, ensuring that network, storage, and compute changes occur in coordinated fashion. Cost allocation tracks resource consumption by department, application, or project enabling chargeback or showback. Security operations integrate vulnerability management, compliance monitoring, and incident response into infrastructure management rather than treating security as separate concern.
Maintaining Production Virtual Environments
Production virtual environments require disciplined maintenance balancing stability requirements against needs for currency and improvement. Patching procedures address vulnerabilities and bugs while minimizing downtime through rolling updates and testing in non-production environments first. Capacity additions scale infrastructure in controlled fashion, integrating new hosts into clusters with validation before enabling production workloads. Version upgrades follow deliberate schedules considering feature benefits against disruption risks, with rollback plans addressing potential complications. Hardware refresh cycles replace aging equipment before failures occur, with migration processes moving workloads to new infrastructure seamlessly.
Maintenance discipline prevents degradation while enabling improvement, similar to approaches in production environment certifications emphasizing operational stability. Documentation updates track infrastructure changes ensuring that records accurately reflect current state rather than initial deployment. Training keeps teams current with new features and best practices as platforms evolve. Performance tuning optimizes configurations based on actual workload characteristics observed through monitoring. Security hardening addresses emerging threats through configuration adjustments and additional controls layered onto existing infrastructure.
Advancing Skills Through SharePoint Development
SharePoint development skills complement network engineering expertise in organizations building collaboration platforms requiring both infrastructure and application capabilities. Custom web parts extend SharePoint functionality delivering organization-specific features unavailable in out-of-box platform capabilities. Workflow automation handles business processes like document approval or expense reporting through no-code or low-code tools. List customization creates tailored data structures and forms meeting specific business requirements. Search configuration optimizes content discovery through managed properties, query rules, and result sources.
Development capabilities broaden career options beyond pure infrastructure, similar to versatility in application development certifications addressing platform customization. Client-side development using frameworks like SharePoint Framework creates responsive experiences that work across desktop and mobile devices. Backend development through Azure Functions or custom APIs extends SharePoint with external data integration and complex processing. Migration projects modernize legacy SharePoint implementations or transition to SharePoint Online, requiring expertise in content migration, customization remediation, and user adoption. Governance frameworks establish standards for site creation, permission management, and content lifecycle that maintain platform usability as adoption grows.
Creating Modern Applications for Mobile Platforms
Modern application development increasingly targets mobile and web platforms rather than traditional desktop applications, creating opportunities for network professionals to expand into development. Progressive web apps deliver native-like experiences through browsers, eliminating app store distribution while maintaining cross-platform compatibility. Responsive design ensures acceptable experiences across device sizes from smartphones through tablets to desktops. Offline capabilities enable continued functionality without connectivity, synchronizing changes once connections restore. Push notifications engage users with timely information, though requiring careful consideration to avoid notification fatigue.
Mobile development skills complement infrastructure knowledge, paralleling expertise in mobile application certifications addressing contemporary platforms. Backend services provide APIs that mobile applications consume, with considerations for security, performance, and version compatibility as apps evolve. Application lifecycle management handles version distribution, crash reporting, and analytics that inform feature prioritization. Performance optimization addresses battery consumption, bandwidth usage, and responsiveness constraints more stringent than desktop development. Testing across device variations and OS versions ensures quality despite platform fragmentation.
Implementing SharePoint Server Solutions
SharePoint Server provides on-premises collaboration platforms for organizations maintaining data center infrastructure rather than adopting cloud-hosted services. Farm architecture determines topology including server roles, service applications, and database design that balance performance against complexity. Service application configuration enables capabilities like search, managed metadata, user profiles, and business connectivity services that deliver SharePoint functionality. Content database management handles growth through database sizing, attachment limits, and archiving strategies. Authentication integration connects SharePoint with Active Directory or SAML identity providers.
On-premises collaboration platforms require specialized expertise, similar to skills in server solution certifications validating platform implementations. High availability designs eliminate single points of failure through SQL clustering, load-balanced web front ends, and distributed cache redundancy. Disaster recovery procedures protect against data loss through backup strategies, farm rebuilds, and content recovery capabilities. Performance optimization addresses query tuning, output caching, and BLOB storage that maintain acceptable response times as content volumes grow. Governance frameworks establish policies around site provisioning, permission inheritance, and content lifecycle.
Architecting Cloud Solutions on Azure Platform
Azure cloud architecture requires understanding of platform capabilities, pricing models, and design patterns that differ substantially from on-premises infrastructure. Compute options span virtual machines, container instances, Kubernetes clusters, and serverless functions with different tradeoffs between control and operational burden. Storage services provide blob, file, queue, and table storage optimized for different access patterns. Networking features create isolated environments with VPN connectivity, load balancing, and application gateways. Identity integration extends Active Directory into cloud with synchronization and federated authentication.
Cloud architecture expertise opens opportunities beyond traditional networking, similar to breadth in Azure specialist certifications covering platform capabilities. Well-Architected Framework guidance addresses reliability, security, cost optimization, operational excellence, and performance efficiency through design principles and implementation best practices. Infrastructure-as-code tools like ARM templates or Terraform enable repeatable deployments with version control and testing. Monitoring and alerting through Azure Monitor, Application Insights, and Log Analytics provide visibility into application performance and resource utilization. Cost management features track spending and optimize resource sizing, reservations, and deletion of unused resources.
Conclusion
The comprehensive exploration of Cisco CCNP Enterprise networking reveals the breadth and depth required for modern enterprise network engineering success. From foundational routing and switching concepts through advanced automation and security implementations to emerging technologies like SD-WAN and cloud integration, the certification validates expertise across the full spectrum of enterprise networking responsibilities. The curriculum's evolution reflects industry transformation toward software-defined infrastructure, automation-centric operations, and cloud-integrated architectures that characterize contemporary enterprise networks. Professionals pursuing this certification position themselves at the intersection of traditional networking and emerging technologies, maintaining relevance as the industry continues evolving.
Career development opportunities expand significantly with CCNP Enterprise certification, from network engineering roles through architecture positions to consulting opportunities. Organizations increasingly seek professionals who can design comprehensive solutions rather than just implementing predefined designs. Architecture roles require strategic thinking about how networks support business objectives alongside technical expertise in solution design. Consulting enables working with diverse clients across industries, solving varied challenges while commanding premium billing rates. Technical leadership positions leverage networking expertise while developing team management and mentoring capabilities that multiply individual contributor impact through team development.
Complementary certifications enhance CCNP Enterprise value through additional capabilities in related domains. Security certifications add depth in threat protection and compliance that aligns with network security responsibilities. Cloud certifications validate expertise in specific platforms like AWS or Azure that complement on-premises knowledge. Automation certifications formalize programming and DevOps skills increasingly expected of network professionals. Project management credentials address the leadership and coordination aspects of large infrastructure initiatives. This certification stacking approach creates unique professional profiles combining multiple expertise areas that few individuals possess.
Continuous learning extends beyond initial certification achievement through recertification requirements and ongoing skill development addressing emerging technologies. Cisco's recertification policies encourage ongoing education rather than treating certification as permanent credential requiring no maintenance. Technology evolution demands that network professionals continuously expand knowledge as new protocols, platforms, and approaches emerge. Industry involvement through conferences, user groups, and online communities provides exposure to diverse perspectives and emerging trends. Laboratory experimentation with new technologies builds hands-on familiarity before they become mainstream expectations.
The investment required for CCNP Enterprise certification preparation pays dividends throughout networking careers through enhanced capabilities, improved career prospects, and increased compensation potential. Time invested in study and lab practice builds knowledge that remains valuable for years despite specific technology changes. Financial costs including training materials, practice labs, and examination fees represent small investments compared to salary increases that certification enables. The discipline developed through certification pursuit transfers to other challenges requiring sustained effort toward distant goals. Certification achievement builds confidence in ability to master complex technical domains through dedicated study.
Ultimately, CCNP Enterprise certification represents more than credential acquisition—it validates comprehensive enterprise networking expertise enabling professionals to design, implement, and troubleshoot complex networks supporting organizational missions. The knowledge gained through preparation creates the foundation for career-long success as networking continues evolving through technological innovation and changing business requirements. Certified professionals join communities of accomplished practitioners worldwide, creating networking opportunities and peer relationships that extend beyond individual organizations. The certification signals to employers, colleagues, and clients that professionals have demonstrated expertise through rigorous examination rather than merely claiming capabilities. This validation creates opportunities that might otherwise remain inaccessible despite actual knowledge levels.
For professionals embarking on CCNP Enterprise certification journeys, approaching preparation systematically with clear goals, structured study plans, and adequate hands-on practice maximizes success probability while building deep expertise. Understanding that certification represents milestones in longer learning careers rather than destinations prevents complacency after achievement. Balancing breadth across certification domains with depth in concentration areas creates versatile professionals who can address diverse challenges. Maintaining currency through ongoing learning ensures that hard-won expertise remains relevant despite rapid industry evolution. The comprehensive framework presented across these three parts provides a roadmap for successful certification achievement and long-term career development in enterprise networking.
CCNP Enterprise certification practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE files format by real users. Study and pass Cisco CCNP Enterprise certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are the best available resource to help students pass at the first attempt.

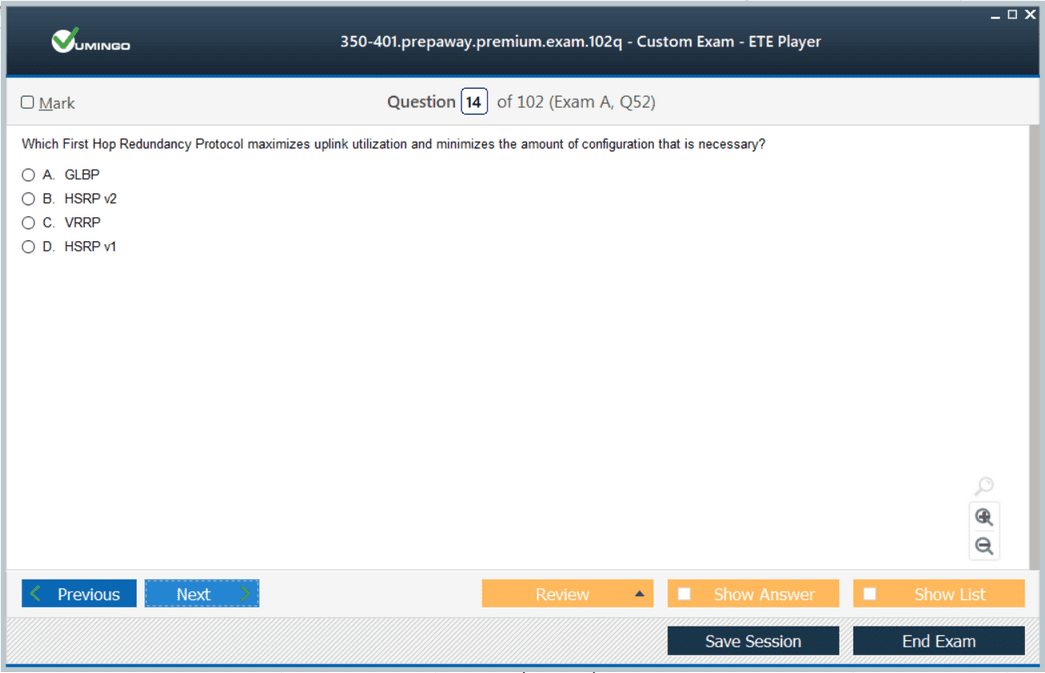
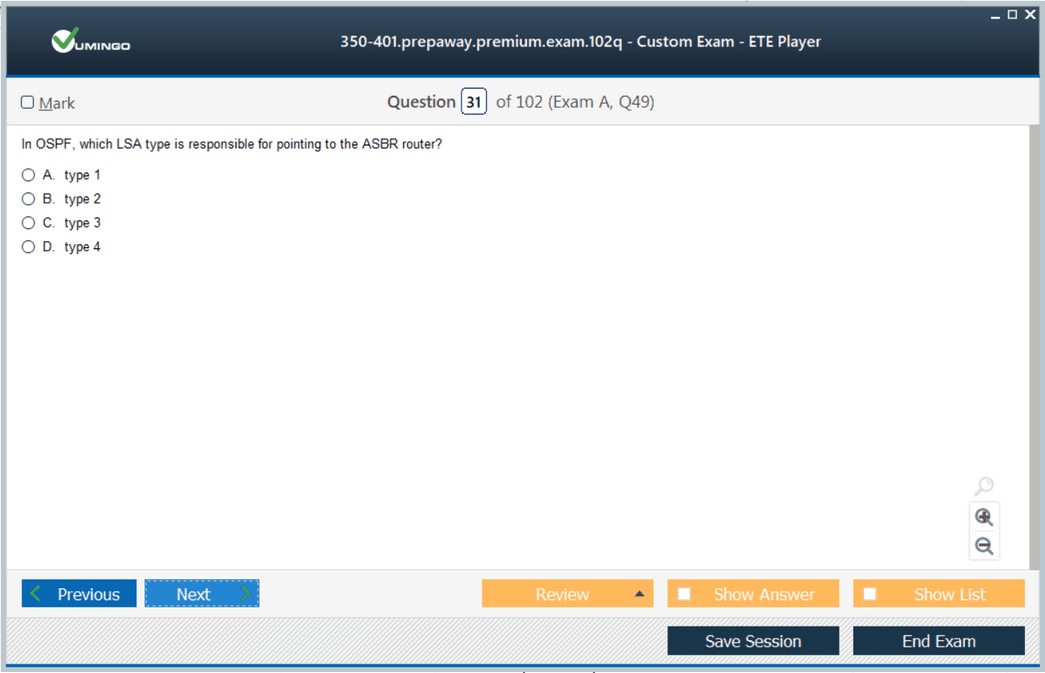
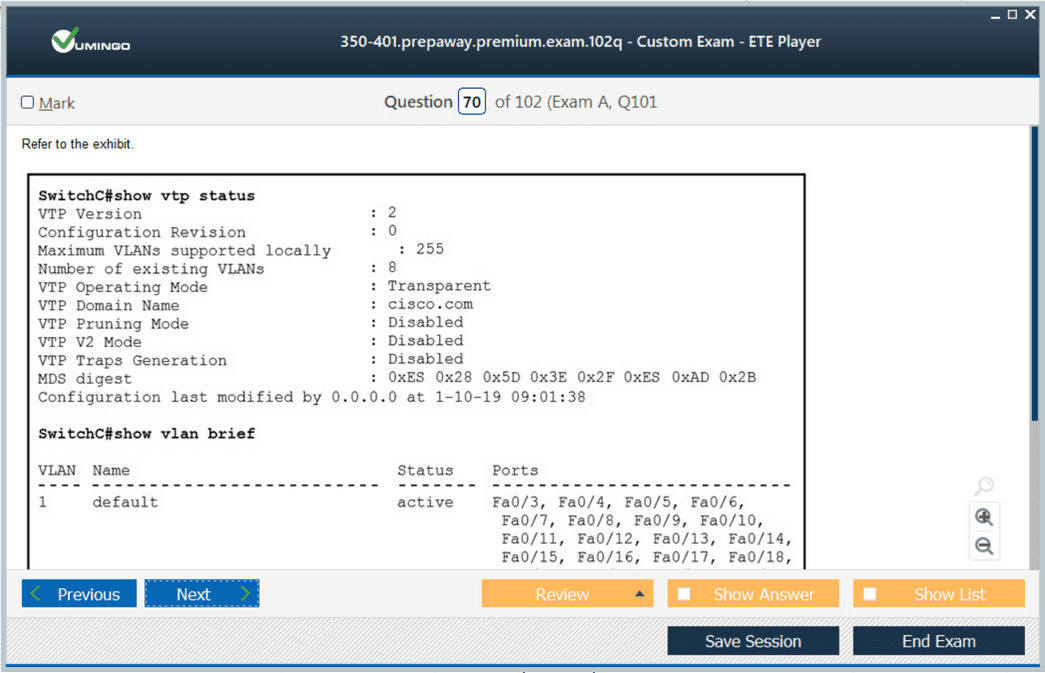








Can I purchase just 350-401 and 300-410 Bundle ?
Thanks