- Home
- Cisco Certifications
- 300-410 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) Dumps
Pass Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


300-410 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 408 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 04, 2026
- Training Course 129 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 2569 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 300-410 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Cisco ENARSI Exam Prep: Enterprise Advanced Routing & Services (300-410)
The 300-410 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services exam is a specialized and rigorous assessment that forms an essential step in achieving the CCNP Enterprise certification. The exam tests the capability of network professionals to configure, implement, and troubleshoot complex enterprise networks, with a strong emphasis on Layer 3 routing, VPN technologies, infrastructure security, and network services. Unlike entry-level certifications, ENARSI demands not only theoretical understanding but also practical, hands-on experience, requiring candidates to solve real-world network problems. It is designed for professionals who already have a foundational understanding of networking principles and are looking to advance into roles that involve designing and maintaining large-scale enterprise networks.
The structure of the exam reflects its focus on advanced networking concepts. Candidates are expected to interpret network topologies, analyze routing behavior, and implement solutions that address scalability, reliability, and security. Multiple-choice questions, simulations, and drag-and-drop exercises test both knowledge and problem-solving ability, ensuring that certified individuals are capable of applying their skills in operational environments. The exam typically lasts ninety minutes and includes approximately fifty-five to sixty-five questions, covering diverse topics that require deep technical comprehension. Although there are no formal prerequisites, it is generally recommended that candidates possess knowledge equivalent to the CCNA certification, including familiarity with IP addressing, subnetting, VLANs, and basic routing concepts.
Achieving success in the ENARSI exam is not simply about memorizing commands or protocols. It requires understanding the principles behind enterprise network design, the interaction between various routing protocols, and the implications of deploying advanced services such as VPNs and Quality of Service mechanisms. It is also essential to grasp the nuances of network troubleshooting, as many exam questions are scenario-based and simulate real operational challenges. Candidates must be able to analyze network diagrams, identify anomalies, and implement corrective actions efficiently. This depth of knowledge ensures that certified professionals are capable of handling the complexity inherent in large enterprise environments, where routing decisions and network policies directly impact business continuity.
The ENARSI exam is broadly divided into four core domains: Layer 3 technologies, VPN technologies, infrastructure security, and infrastructure services. Each domain focuses on critical aspects of enterprise networking. Layer 3 technologies cover dynamic and static routing protocols and emphasize understanding network behavior under different configurations. VPN technologies examine secure connectivity for remote users and branch offices. Infrastructure security involves securing network devices, managing access control, and preventing attacks that can compromise network operations. Infrastructure services cover automation, monitoring, and performance optimization to ensure a network operates efficiently. Mastery of these domains not only facilitates exam success but also equips professionals with the skills required to design, maintain, and troubleshoot enterprise networks effectively.
Layer 3 Routing Technologies Overview
Layer 3 technologies are central to the ENARSI exam because routing forms the backbone of enterprise networks. Routing is the process by which data packets are directed from a source to a destination across interconnected networks. In enterprise environments, Layer 3 routing ensures optimal path selection, redundancy, and resilience, which are critical for maintaining connectivity between various offices, data centers, and cloud environments. The ENARSI exam tests a candidate’s ability to implement, manage, and troubleshoot routing protocols in complex topologies, often with overlapping networks, multiple route redistribution scenarios, and interdependent routing policies.
Routing protocols in the enterprise environment are categorized broadly into distance vector and link-state protocols. Distance vector protocols, such as Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), rely on the distance or cost to determine the best path and periodically share routing tables with neighbors. Link-state protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), maintain a complete topology map of the network, allowing routers to compute optimal paths using the shortest path first algorithm. Each protocol has distinct advantages and trade-offs in terms of convergence speed, scalability, and administrative complexity. Candidates are expected to understand these characteristics, identify scenarios in which one protocol is preferable over another, and implement advanced configurations to optimize performance.
In addition to internal routing protocols, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a critical component of enterprise networking. BGP is an external routing protocol used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems, which are separate administrative domains on the internet or within large organizations. The ENARSI exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to configure BGP for enterprise WAN connectivity, including route filtering, route maps, path selection, and policy-based routing. Understanding the behavior of BGP, such as how attributes like local preference, AS path, and MED influence routing decisions, is essential for maintaining efficient and secure network communication. Candidates must also be able to troubleshoot issues such as route flapping, prefix inconsistencies, and asymmetric routing, which can have significant operational consequences.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
EIGRP is an advanced distance vector protocol that combines features of traditional distance vector and link-state protocols, earning the designation of an advanced distance vector or hybrid protocol. In enterprise networks, EIGRP is widely used due to its rapid convergence, scalability, and ability to support multiple network layer protocols. The ENARSI exam tests candidates on EIGRP concepts such as topology tables, feasible successors, split horizon, and route summarization. Understanding how EIGRP calculates the composite metric based on bandwidth, delay, load, and reliability is critical for designing networks that meet performance requirements.
EIGRP supports features such as stub routing, which restricts unnecessary route advertisements from branch offices to prevent suboptimal routing and reduce network overhead. Candidates must understand the configuration of stub routers, including different stub options such as connected, static, and summary routes. Troubleshooting EIGRP involves analyzing neighbor relationships, detecting stuck-in-active routes, and resolving issues related to metric calculation or misconfigured network statements. Additionally, EIGRP’s support for unequal-cost load balancing allows network engineers to distribute traffic efficiently across multiple paths, which is a key skill evaluated in the exam.
Understanding the interactions between EIGRP and other routing protocols is also essential. In environments where EIGRP coexists with OSPF or BGP, proper route redistribution techniques must be applied to ensure consistent routing information while preventing loops and maintaining policy requirements. Candidates must be able to configure route maps, distribute lists, and tag routes to control how routes are shared between protocols. This knowledge ensures that the enterprise network remains stable and efficient even as multiple protocols operate simultaneously, which is often a focus area in scenario-based exam questions.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that provides fast convergence and scalability in large enterprise networks. It is commonly deployed in hierarchical network designs where backbone and area segmentation improve efficiency and reduce routing overhead. The ENARSI exam evaluates candidates on OSPF implementation, including configuring OSPFv2 for IPv4, OSPFv3 for IPv6, virtual links, route summarization, and redistribution with other protocols. Understanding the concept of areas, including backbone (area 0) and non-backbone areas, is fundamental to ensuring proper routing and preventing loops within the network.
OSPF routers maintain a link-state database that represents the network topology. Each router computes the shortest path to all destinations using the Dijkstra algorithm. Candidates must be able to interpret OSPF link-state advertisements (LSAs) and identify issues related to adjacency formation, mismatched network types, or authentication failures. Advanced OSPF topics such as route filtering, area types (stub, totally stubby, NSSA), and virtual links are included in the exam to assess a candidate’s ability to design scalable and fault-tolerant networks. Troubleshooting OSPF involves examining neighbor relationships, verifying LSDB consistency, and analyzing route selection, all of which are skills critical to enterprise network operations.
Redistribution between OSPF and other routing protocols is a common scenario in multi-protocol networks. Candidates must understand how to configure redistribution while controlling the propagation of routes using route maps, metrics, and tagging. Misconfiguration can lead to routing loops, suboptimal paths, or black holes, making proper implementation a key focus of the ENARSI exam. Additionally, understanding OSPF path types, including intra-area, inter-area, and external routes, is necessary for optimizing routing decisions and ensuring efficient network performance.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
BGP is an exterior gateway protocol that plays a vital role in connecting enterprise networks to external networks or multiple sites within large organizations. It is designed to handle routing between autonomous systems, supporting policy-based routing and extensive scalability. The ENARSI exam evaluates candidates on BGP implementation, including establishing eBGP and iBGP sessions, configuring route reflectors, applying route filtering, and manipulating path selection using attributes such as local preference, weight, MED, and AS path.
BGP differs from interior routing protocols in that it relies on policies and attributes to influence routing decisions rather than calculating the shortest path based on metrics. Candidates must understand how to configure BGP peering, apply prefix lists and route maps, and troubleshoot common issues such as session failures, route flapping, or policy conflicts. Enterprise WAN scenarios often involve complex BGP topologies, requiring engineers to implement scalable designs using route reflectors, confederations, and peer groups. These advanced configurations are crucial for managing routing efficiently in large-scale networks and are a primary focus of the ENARSI exam.
In addition to connectivity, BGP provides mechanisms for redundancy and traffic optimization. Properly configuring BGP ensures high availability and optimal path selection across multiple links, preventing outages and minimizing latency. Candidates are expected to understand BGP behavior in the context of route aggregation, filtering, and redistribution with internal protocols. Troubleshooting exercises in the exam may present scenarios where multiple autonomous systems interact, requiring the candidate to analyze route tables, debug BGP sessions, and implement corrective actions to maintain consistent connectivity across the enterprise network.
Advanced Routing Troubleshooting
A significant portion of the ENARSI exam tests practical troubleshooting skills. Enterprise networks are dynamic, and routing issues can arise from misconfigurations, hardware failures, or protocol interactions. Candidates are expected to diagnose and resolve problems using command-line tools, configuration verification, and logical analysis. Understanding the common causes of routing failures, such as interface mismatches, administrative distance conflicts, or incorrect network statements, is essential. Additionally, candidates must be familiar with commands to verify routing tables, neighbor relationships, and protocol states, allowing them to quickly identify and correct anomalies.
Scenario-based questions may simulate real-world conditions such as route redistribution errors, asymmetrical routing, or suboptimal path selection. Effective troubleshooting requires a deep understanding of protocol behavior, as well as the ability to anticipate the impact of configuration changes. Candidates must also consider the effects of redundant links, load balancing, and route filtering when resolving issues. The ability to apply both analytical and hands-on skills ensures that certified professionals can maintain the stability and performance of complex enterprise networks under operational conditions.
Layer 3 routing is not merely about connectivity; it also involves optimizing network performance, ensuring redundancy, and maintaining security. Advanced routing techniques, including policy-based routing, route filtering, summarization, and redistribution, are essential for designing efficient and resilient networks. Candidates must integrate these techniques seamlessly, considering both immediate operational requirements and long-term scalability. This level of expertise is what differentiates CCNP Enterprise-certified professionals from those with more basic networking knowledge, emphasizing the value of the ENARSI certification in professional career development.
VPN Technologies in Enterprise Networks
Virtual Private Networks are an essential component of modern enterprise networking, providing secure connectivity between remote sites, branch offices, and mobile users. The 300-410 ENARSI exam emphasizes the implementation, configuration, and troubleshooting of VPN technologies as a critical skill for network professionals. VPNs enable organizations to maintain secure communication channels over untrusted networks, such as the internet, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Understanding VPN technologies involves knowledge of encryption methods, tunneling protocols, authentication mechanisms, and integration with routing protocols.
There are several types of VPNs relevant to enterprise networks, each serving a distinct purpose. Site-to-site VPNs provide connectivity between fixed locations, enabling branch offices to access resources at the main data center securely. Remote access VPNs allow individual users to connect to the corporate network from anywhere in the world. Multipoint VPNs, such as Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN), offer scalable solutions for connecting multiple sites dynamically without requiring static configurations for every possible link. Network engineers must be familiar with these different approaches, understanding their benefits, limitations, and appropriate deployment scenarios.
The underlying technologies for VPNs include Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) and GRE tunneling. IPsec provides authentication, integrity, and encryption of IP packets, ensuring that data transmitted over untrusted networks cannot be intercepted or altered. GRE, or Generic Routing Encapsulation, allows the creation of tunnels that carry packets of various protocols between endpoints. In enterprise environments, these technologies are often combined to deliver secure, routable tunnels that integrate seamlessly with existing routing protocols such as OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP. Understanding how to implement, verify, and troubleshoot these technologies is crucial for achieving certification and operational competence.
Site-to-Site VPNs
Site-to-site VPNs are typically used to connect branch offices or remote data centers to a central corporate network. They operate by establishing a secure tunnel between two endpoints, often over the public internet. IPsec is the most commonly used protocol for securing these tunnels, providing encryption for confidentiality, authentication for verifying identities, and integrity checks to prevent data tampering. Candidates for the ENARSI exam must understand the components of IPsec, including the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol, security associations, and the configuration of Phase 1 and Phase 2 settings.
IKE Phase 1 establishes a secure, authenticated communication channel between VPN endpoints. During this phase, the peers negotiate encryption algorithms, authentication methods, and keys to protect subsequent exchanges. Phase 2 establishes the actual IPsec tunnel for data transmission, negotiating parameters such as the encryption algorithm, hash algorithm, and lifetime of the security association. Understanding the sequence and interdependencies of these phases is critical, as misconfiguration can result in tunnel failure or insecure communication.
Advanced site-to-site VPN configurations involve integrating routing protocols within the tunnel, enabling dynamic routing across encrypted links. This requires understanding how routing updates propagate through IPsec tunnels, potential issues with packet fragmentation, and the impact of NAT on VPN traffic. Candidates must also be capable of troubleshooting connectivity issues by examining tunnel status, analyzing security associations, and verifying route propagation to ensure consistent and reliable communication between sites.
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
Dynamic Multipoint VPN is an evolution of traditional VPN technology that addresses the scalability challenges of large enterprise networks with multiple sites. In conventional site-to-site VPNs, establishing a full mesh requires configuring tunnels for every possible pair of sites, which becomes cumbersome as the number of locations increases. DMVPN simplifies this by using a combination of multipoint GRE tunnels, NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol), and IPsec to allow dynamic, on-demand connections between sites without preconfiguring every tunnel.
DMVPN operates in multiple phases. Phase 1 involves a hub-and-spoke topology where all traffic flows through a central hub. Phase 2 allows spoke-to-spoke tunnels to be established dynamically as needed, reducing latency and improving efficiency. Phase 3 introduces enhanced routing capabilities, including support for summarization and NHRP redirection, which optimizes traffic flow in large-scale networks. Candidates must understand the differences between these phases, how to configure NHRP mappings, and how routing protocols interact with dynamically created tunnels.
Troubleshooting DMVPN requires familiarity with its components and behavior under different conditions. Network engineers must verify tunnel creation, check NHRP registrations, and ensure that IPsec policies are applied consistently. Understanding the interaction between routing protocols and DMVPN is essential, as misconfiguration can result in routing loops, unreachable networks, or suboptimal traffic paths. The ENARSI exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to implement and resolve such complex configurations, reflecting real-world scenarios where scalable, dynamic VPNs are required.
MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a technology widely deployed in enterprise WANs to provide scalable and efficient routing over shared infrastructure. MPLS Layer 3 VPNs extend MPLS capabilities by allowing multiple customer networks to operate independently over a shared service provider backbone while maintaining separation and security. This is accomplished by assigning unique route distinguishers and route targets to each customer, enabling overlapping IP address spaces and policy-based routing.
In MPLS L3 VPNs, provider edge (PE) routers maintain VPN routing tables for each customer, while provider (P) routers simply forward labeled packets without inspecting their contents. This separation allows service providers to scale their networks efficiently while providing secure, isolated connectivity for multiple organizations. Candidates must understand the configuration of MPLS L3 VPNs, including VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding), import/export route targets, and integration with BGP for distributing VPN routes.
Troubleshooting MPLS VPNs involves examining label bindings, route advertisements, and PE-to-PE connectivity. Candidates must be able to diagnose issues such as label mismatches, route leaking between VRFs, and connectivity failures caused by misconfigured BGP sessions. Understanding the interaction between MPLS and underlying routing protocols, as well as the implications of route aggregation and summarization, is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable VPN operation. This level of expertise is a critical component of the ENARSI exam, which emphasizes real-world problem-solving skills in complex network environments.
Integration of VPNs with Routing Protocols
A critical aspect of VPN implementation is the integration with dynamic routing protocols. Enterprise networks often rely on OSPF, EIGRP, or BGP to provide redundancy and optimal path selection, even over encrypted tunnels. Candidates must understand how to redistribute routes between VPN-connected sites and the main network, ensuring that routing information propagates correctly without causing loops or inconsistencies. Policy-based routing may be required to direct specific traffic through tunnels based on business requirements, and understanding its configuration and impact is essential for maintaining network performance and reliability.
Troubleshooting routing over VPNs requires analyzing route propagation, examining routing tables, and verifying tunnel status. Issues such as routing black holes, asymmetric paths, and route flapping can arise if VPN tunnels are misconfigured or if routing policies conflict. Candidates must be proficient in using command-line tools to monitor tunnels, analyze routing behavior, and implement corrective actions. This practical knowledge ensures that enterprise networks remain robust, secure, and highly available, reflecting the skill set required for certification and professional roles.
Security Considerations in VPN Deployment
Security is inherent to the design and operation of VPNs. Encryption, authentication, and integrity mechanisms must be properly configured to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. IPsec protocols provide a range of encryption algorithms, hash functions, and key exchange methods that candidates must understand and configure appropriately. Authentication can be performed using pre-shared keys or digital certificates, each with implications for scalability and management. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method is essential for designing secure VPNs that meet enterprise requirements.
Beyond encryption, candidates must consider operational security practices, including access control lists, firewall integration, and monitoring of VPN activity. Detecting anomalies such as unexpected tunnel drops, unauthorized connections, or degraded performance is critical for maintaining network integrity. Candidates are expected to develop a methodology for troubleshooting security-related VPN issues while ensuring that legitimate traffic continues to flow uninterrupted. This comprehensive approach reflects the depth of understanding required for advanced enterprise networking roles and the ENARSI exam.
Troubleshooting Advanced VPN Scenarios
The ENARSI exam evaluates candidates’ ability to solve complex problems that arise in VPN environments. These scenarios may involve multiple VPN technologies, dynamic routing interactions, and multi-site connectivity challenges. Candidates must be capable of identifying the root cause of connectivity issues, whether it is related to IPsec policies, GRE tunneling, NHRP resolution, or routing inconsistencies. Troubleshooting requires a methodical approach, leveraging command-line diagnostics, traffic analysis, and knowledge of protocol behavior to resolve issues efficiently.
Real-world enterprise networks often present unexpected conditions, such as link failures, route flapping, or overlapping IP address spaces. Candidates must understand how to implement solutions that maintain connectivity while minimizing impact on performance and security. This involves configuring redundancy mechanisms, adjusting routing metrics, and ensuring that VPN tunnels remain stable under varying traffic loads. Mastery of these skills is critical for both exam success and professional competence, as enterprise networks demand reliability, scalability, and security.
Performance Optimization in VPN Networks
Performance is a key consideration in VPN deployment. Encrypted tunnels can introduce overhead, latency, and jitter, which may affect applications such as voice and video. Candidates must understand how to monitor VPN performance using tools such as SNMP, NetFlow, and packet captures. Quality of Service (QoS) policies may be applied to prioritize critical traffic, ensuring that business applications operate efficiently even over congested links. Optimizing VPN performance requires a combination of proper configuration, monitoring, and proactive adjustment to network conditions.
Scalability is another critical factor, particularly in large enterprise networks with numerous remote sites. DMVPN and MPLS L3 VPNs offer mechanisms to scale connectivity efficiently, but candidates must understand how to plan capacity, configure routing, and manage tunnel endpoints. Ensuring that VPN solutions can handle growth without degradation in performance or security is a hallmark of advanced networking expertise. The ENARSI exam tests the candidate’s ability to design and implement such solutions, reflecting the practical knowledge required in enterprise environments.
Infrastructure Security in Enterprise Networks
Infrastructure security is a fundamental component of enterprise networking, encompassing the policies, protocols, and configurations required to protect network devices, maintain data integrity, and ensure operational continuity. Modern enterprise networks are increasingly complex, combining physical and virtualized devices, cloud connectivity, and remote user access. This complexity increases the attack surface, making security an essential consideration in network design and operations. The 300-410 ENARSI exam emphasizes a deep understanding of infrastructure security, requiring candidates to implement, configure, and troubleshoot security mechanisms across enterprise networks.
Infrastructure security in enterprise networks involves multiple layers, starting with device hardening, which ensures that network devices such as routers and switches are protected against unauthorized access and configuration changes. Device hardening includes enforcing strong authentication methods, controlling access to management interfaces, and applying security patches and updates. In addition to hardening, candidates must understand the application of access control lists, control plane policing, and other security mechanisms that protect the network from malicious traffic, denial-of-service attacks, and configuration errors.
Effective network security begins with robust authentication and authorization practices. Secure management protocols, such as SSH for command-line access and SNMPv3 for monitoring, replace insecure protocols that transmit sensitive information in clear text. Candidates must understand the configuration and implications of these protocols, including key management, authentication methods, and role-based access control. Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) services are used to centralize user management and enforce policies consistently across devices. Implementing AAA with RADIUS or TACACS+ provides fine-grained control over who can access devices, what actions they can perform, and the ability to log and audit those actions for compliance purposes.
Device Hardening and Secure Management
Device hardening involves several steps that reduce the likelihood of compromise. First, default accounts, passwords, and services must be disabled or changed, as they represent a common attack vector. Candidates must understand how to disable unnecessary services, restrict protocol access, and configure device banners to deter unauthorized access. In addition, configuration files must be protected, and changes monitored to ensure that only authorized personnel can modify critical network settings.
Secure management protocols are essential for protecting network operations. SSH provides encrypted terminal access, preventing credential interception and command injection. SNMPv3 adds authentication and encryption to network monitoring, ensuring that sensitive information about device performance and configuration is protected. Candidates must understand the differences between SNMP versions, including security features and limitations, and implement them appropriately to safeguard enterprise networks.
Regular device audits and configuration reviews are part of maintaining infrastructure security. Network engineers must ensure that configurations comply with organizational policies, identify potential vulnerabilities, and remediate them before they can be exploited. These practices are critical for exam scenarios that simulate security breaches, configuration errors, or unauthorized access attempts, emphasizing the importance of proactive security measures.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Access control lists are a core mechanism for controlling traffic within enterprise networks. ACLs define rules that permit or deny traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports. Candidates must understand how to configure standard, extended, and named ACLs, applying them to interfaces, lines, and routing processes to enforce security policies. ACLs can be used to restrict management access, segment networks, and prevent the propagation of unwanted traffic across routing boundaries.
Implementing ACLs effectively requires understanding the order of evaluation, the implicit deny at the end of the list, and the impact on routing and network performance. Candidates must also consider how ACLs interact with routing protocols, VPN tunnels, and network services, ensuring that legitimate traffic is allowed while malicious or unnecessary traffic is blocked. Troubleshooting ACLs involves analyzing packet flows, verifying rule placement, and ensuring that configurations match intended security policies, which is frequently tested in scenario-based questions on the ENARSI exam.
Advanced ACL strategies include using time-based ACLs, reflexive ACLs, and object groups to simplify policy management while maintaining security. Time-based ACLs allow administrators to enforce policies only during specific periods, which can be useful for restricting access to maintenance windows or temporary services. Reflexive ACLs provide dynamic filtering for session-based traffic, enhancing security while allowing legitimate connections. Object groups simplify configuration by allowing multiple addresses, ports, or protocols to be grouped under a single ACL entry, improving readability and manageability in complex networks.
Control Plane Policing (CoPP)
Control plane policing is a mechanism used to protect the control plane of network devices from excessive or malicious traffic that can disrupt operations. The control plane handles routing updates, management traffic, and other critical functions, making it a target for attacks such as distributed denial-of-service. Candidates must understand how to configure CoPP to classify and limit traffic to the control plane, ensuring that legitimate management and routing traffic is prioritized while potentially harmful traffic is rate-limited or dropped.
CoPP policies are applied using class maps and policy maps, specifying match criteria and actions for traffic. Candidates must be familiar with common CoPP configurations, including the differentiation between normal operational traffic and potential attack traffic. The ability to monitor CoPP behavior using network diagnostics and logs is essential for maintaining network availability and performance. Troubleshooting scenarios may present unexpected spikes in control plane traffic, requiring candidates to analyze and adjust CoPP policies to prevent network degradation or outages.
Network Device Security Features
Modern enterprise devices include built-in security features that complement ACLs and CoPP. These include features such as port security, DHCP snooping, IP source guard, and Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI). Port security limits access to physical interfaces based on MAC addresses, preventing unauthorized devices from connecting to the network. DHCP snooping ensures that only legitimate DHCP servers can assign addresses, protecting against rogue servers. IP source guard prevents IP spoofing, and DAI protects against ARP spoofing attacks. Candidates must understand the configuration, operational impact, and troubleshooting of these features, as they are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the enterprise network.
Device security also involves protecting against common network attacks, including SYN floods, ICMP floods, and malformed packet attacks. Candidates must be familiar with rate-limiting, traffic filtering, and anomaly detection techniques to mitigate these threats. Understanding the interaction between security features and normal network operations is essential, as overly restrictive configurations can inadvertently block legitimate traffic or degrade performance.
AAA Implementation and Best Practices
AAA services provide a centralized method for managing authentication, authorization, and accounting across multiple devices in an enterprise network. Candidates must understand the architecture and configuration of AAA using RADIUS or TACACS+, including defining user roles, command authorization, and accounting for audit purposes. Proper implementation ensures that users have the appropriate level of access, changes are logged for accountability, and unauthorized attempts are detected and mitigated.
Best practices for AAA include using secure communication channels between network devices and authentication servers, implementing redundancy for high availability, and regularly reviewing logs for unusual activity. Integration with directory services, such as LDAP or Active Directory, allows consistent user management across multiple systems. Troubleshooting AAA involves verifying connectivity to servers, analyzing authentication failures, and ensuring that authorization policies are correctly applied, which is frequently tested in the ENARSI exam.
Infrastructure Security Troubleshooting
The ability to troubleshoot infrastructure security issues is critical for network professionals. Scenarios may involve misconfigured ACLs, incorrect CoPP policies, failed AAA authentication, or unauthorized device access. Candidates must apply systematic diagnostic methods, including examining configuration files, verifying interface status, reviewing logs, and using protocol-specific commands. Understanding how different security mechanisms interact is essential, as a misconfiguration in one area can have cascading effects on other network functions.
Scenario-based troubleshooting in the exam often simulates real-world challenges, such as detecting and mitigating attacks, restoring device accessibility after a configuration error, or ensuring continuity of service during a security event. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to analyze, isolate, and resolve problems efficiently while maintaining compliance with organizational security policies.
Security Policy Design and Implementation
Beyond individual security mechanisms, candidates must understand how to design and implement comprehensive network security policies. This includes defining acceptable use, segmenting networks to contain threats, enforcing encryption and authentication, and integrating monitoring and alerting mechanisms. Effective security policies balance protection with operational efficiency, ensuring that security measures do not unnecessarily impede legitimate business activities. Candidates are expected to apply these principles in both theoretical and practical scenarios, demonstrating the ability to plan, implement, and maintain secure enterprise networks.
Policy design also involves considering redundancy, failover, and disaster recovery. Security measures must remain effective even during network failures or high-traffic events. Candidates must understand how to deploy redundant authentication servers, configure high-availability mechanisms for CoPP and ACLs, and ensure that critical network services continue operating under adverse conditions. This holistic understanding of security is a key differentiator for advanced networking professionals and a primary focus of the ENARSI exam.
Monitoring and Maintaining Network Security
Ongoing monitoring is essential to maintaining enterprise network security. Candidates must understand how to implement logging, alerting, and auditing mechanisms to detect potential threats, performance degradation, or configuration errors. Tools such as syslog servers, SNMP monitoring, and network analyzers provide visibility into device behavior and network traffic. Regular audits and reviews ensure that security policies remain aligned with organizational requirements and evolving threat landscapes.
Maintaining network security also involves patch management, vulnerability assessment, and compliance checks. Candidates must understand the procedures for applying firmware updates, addressing known vulnerabilities, and ensuring that network devices adhere to internal and regulatory standards. These practices help prevent exploitation of known weaknesses and maintain the integrity of the enterprise network, reflecting the comprehensive approach to security emphasized in the ENARSI exam.
Security Integration with Routing and VPNs
Infrastructure security is not limited to standalone mechanisms; it must integrate seamlessly with routing protocols and VPN technologies. Security policies must protect routing updates, prevent unauthorized redistribution, and secure control plane communications. Similarly, VPN tunnels must enforce encryption, authentication, and access control to ensure secure connectivity between sites. Candidates must understand how to implement security consistently across these domains, ensuring that routing, VPNs, and device configurations collectively maintain a resilient and protected network environment.
Troubleshooting integrated security scenarios requires analyzing interactions between routing, tunneling, and device protections. Candidates must be able to identify the source of connectivity issues, misapplied security rules, or performance bottlenecks, applying corrective actions without compromising network integrity. This level of expertise ensures that enterprise networks remain both secure and operationally efficient, reflecting the advanced skills assessed in the ENARSI exam.
Infrastructure Services in Enterprise Networks
Infrastructure services in enterprise networks encompass the set of features and technologies that ensure the network operates efficiently, reliably, and securely. These services are critical for supporting business applications, optimizing performance, and enabling automation and monitoring. The 300-410 ENARSI exam evaluates candidates on their understanding and implementation of these services, including Quality of Service (QoS), network automation, and monitoring tools, all of which are essential for maintaining high-performance, scalable enterprise networks. These services complement routing, VPNs, and security mechanisms, ensuring that the network supports organizational objectives while remaining resilient and manageable.
Infrastructure services integrate deeply with Layer 3 routing, VPNs, and security policies. They enhance operational visibility, provide proactive troubleshooting capabilities, and enable consistent policy enforcement across devices. Implementing these services requires a clear understanding of how different technologies interact, as well as practical experience with configuration and management tools. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to design, deploy, and troubleshoot these services in complex environments where multiple technologies coexist and interoperate.
Network Automation
Network automation refers to the use of software tools, scripts, and programmable interfaces to manage network configurations, deploy services, and monitor operations with minimal human intervention. Automation reduces the likelihood of configuration errors, accelerates deployment, and ensures consistent application of policies across multiple devices. In modern enterprise networks, where configurations are complex and dynamic, automation has become a critical skill for network engineers and is emphasized in the ENARSI exam.
Automation in enterprise networks often leverages protocols such as NETCONF, REST APIs, and scripting languages like Python. NETCONF allows for programmatic configuration of network devices, providing a standardized interface for retrieving and applying configurations. REST APIs enable external applications to interact with devices, retrieve telemetry, and make real-time adjustments to network operations. Python scripts are commonly used to automate repetitive tasks, validate configurations, and orchestrate network changes across multiple devices. Candidates must understand how these tools work, how to implement them securely, and how to troubleshoot automation scripts in case of failures.
Automation also extends to configuration templates, version control, and continuous integration workflows. Using configuration templates ensures that devices are provisioned consistently, reducing the risk of human error. Version control allows teams to track changes, revert to previous configurations, and maintain an audit trail, which is critical for compliance and troubleshooting. Continuous integration practices integrate automated testing of configurations before deployment, ensuring that changes do not introduce network instability or security vulnerabilities.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service is an essential infrastructure service that ensures critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth, latency, and priority to function effectively. In enterprise networks, voice over IP (VoIP), video conferencing, and business-critical applications rely on predictable network performance. The ENARSI exam tests candidates on QoS concepts, configuration, and troubleshooting, including traffic classification, marking, queuing, shaping, and policing.
Traffic classification is the first step in QoS implementation, where packets are identified and categorized based on criteria such as IP addresses, protocols, application types, or DSCP values. Candidates must understand how to configure classification rules to differentiate between high-priority and best-effort traffic. Marking allows the network to signal the priority of packets as they traverse devices, ensuring consistent handling across multiple hops. Understanding how to apply DSCP values or IP precedence is essential for maintaining QoS policies end-to-end.
Queuing mechanisms determine how packets are buffered and transmitted during periods of congestion. Common queuing strategies include priority queuing, weighted fair queuing, and custom queuing. Candidates must understand the behavior of each mechanism, how to configure queues for different traffic classes, and how queuing interacts with shaping and policing policies. Shaping smooths traffic by delaying bursts to conform to a defined bandwidth profile, while policing enforces strict limits by dropping or remarking excess traffic. Understanding when to use shaping versus policing is critical for ensuring performance without causing unintended disruptions to critical applications.
Advanced QoS configurations often involve hierarchical policies that combine multiple classes and service levels. Candidates must be able to design QoS hierarchies that prioritize voice, video, and critical data while maintaining fair access for other traffic. Troubleshooting QoS requires analyzing congestion points, monitoring queue depths, verifying marking policies, and using tools such as traffic analyzers or SNMP to confirm that policies are applied correctly. Mastery of QoS ensures that enterprise networks deliver consistent performance and reliability for time-sensitive applications.
Network Monitoring
Network monitoring is the practice of continuously observing the state and performance of network devices and traffic flows to detect anomalies, optimize operations, and support troubleshooting. Effective monitoring provides visibility into device health, interface utilization, routing behavior, and application performance. The ENARSI exam evaluates candidates on the use of monitoring protocols, tools, and techniques to maintain a resilient and high-performing network.
Monitoring protocols include SNMP, NetFlow, and streaming telemetry. SNMP provides a standardized method for collecting device metrics, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, interface statistics, and error rates. Understanding SNMP versions, community strings, and security considerations is essential for ensuring that monitoring data is reliable and secure. NetFlow and IPFIX provide detailed information on traffic flows, enabling analysis of bandwidth usage, application behavior, and potential security threats. Streaming telemetry provides real-time monitoring of device state, delivering granular data directly to collectors for analysis, often used in conjunction with automation systems for proactive network management.
Monitoring also involves setting thresholds and generating alerts for abnormal conditions, such as interface errors, CPU spikes, link congestion, or routing instability. Candidates must understand how to configure alerts, interpret logs, and respond to potential issues before they escalate into outages. Effective monitoring is not limited to device-level metrics; it also includes end-to-end performance assessment, correlating network data with application behavior to ensure service quality and user satisfaction.
Troubleshooting Infrastructure Services
The ability to troubleshoot infrastructure services is a key skill tested in the ENARSI exam. Candidates must analyze and resolve issues related to QoS, automation, and monitoring tools while maintaining overall network stability. Troubleshooting begins with understanding the expected behavior, identifying deviations, and systematically isolating potential causes. Tools such as ping, traceroute, SNMP queries, NetFlow analysis, packet captures, and device logs provide visibility into network operations and assist in pinpointing the source of problems.
Common issues with QoS include misclassified traffic, incorrect queue assignment, or conflicting policies that disrupt prioritization. Candidates must be able to examine device configurations, verify markings and class assignments, and ensure that shaping or policing policies align with design objectives. Automation issues may arise from syntax errors in scripts, misconfigured API endpoints, or incomplete device responses. Understanding how to debug automation workflows and verify successful configuration deployment is essential for maintaining operational continuity.
Monitoring-related troubleshooting involves verifying sensor accuracy, ensuring proper data collection, and addressing gaps in coverage or alerting. Candidates must correlate device-level metrics with network events to identify root causes of performance degradation. This often requires an understanding of interdependencies between routing, VPNs, QoS, and security mechanisms, highlighting the integrated nature of infrastructure services. Mastery of troubleshooting ensures that enterprise networks remain operational, resilient, and efficient.
Integration of Automation and Monitoring
Network automation and monitoring are complementary services that enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Automated scripts can collect monitoring data, analyze trends, and make configuration adjustments proactively to prevent performance degradation or outages. Candidates must understand how to integrate automation with monitoring tools, designing workflows that trigger corrective actions based on predefined thresholds or anomalies.
For example, automation can be used to adjust QoS policies dynamically based on observed traffic patterns, reroute traffic in response to congestion, or apply configuration changes to maintain compliance with security policies. Monitoring data provides the feedback necessary to validate these changes, ensuring that automation actions achieve the desired outcome without unintended consequences. Understanding this integration is critical for the ENARSI exam, as it reflects the practical requirements of modern enterprise networks where scalability and proactive management are essential.
Advanced Infrastructure Services Scenarios
The ENARSI exam often presents complex scenarios involving multiple infrastructure services. Candidates may encounter networks with high-density traffic, multiple VPN connections, advanced routing, and security policies operating simultaneously. Successfully managing such networks requires a holistic understanding of how services interact, how configurations affect performance, and how to troubleshoot issues effectively.
Scenario-based questions may simulate traffic congestion affecting critical applications, automation scripts failing to deploy configurations correctly, or monitoring alerts indicating potential outages. Candidates must analyze these situations, identify root causes, and implement solutions while maintaining network stability. This requires integrating knowledge of routing protocols, VPN connectivity, QoS policies, automation workflows, and monitoring data to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Planning and Implementing Infrastructure Services
Effective implementation of infrastructure services requires careful planning. Candidates must consider network topology, application requirements, traffic patterns, device capabilities, and security policies when designing automation, QoS, and monitoring solutions. Planning involves defining objectives, identifying dependencies, configuring devices consistently, and validating the implementation through testing and verification.
Implementation also includes documenting configurations, establishing rollback procedures, and ensuring that changes are applied consistently across devices. Automation templates, standardized QoS policies, and monitoring baselines contribute to repeatability, reliability, and maintainability of infrastructure services. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to plan, deploy, and verify these services in complex enterprise networks, reflecting the practical skills assessed by the ENARSI exam.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Infrastructure services are not static; networks evolve over time, and services must adapt to changing requirements. Continuous monitoring, performance analysis, and feedback loops enable network engineers to optimize QoS policies, refine automation scripts, and enhance monitoring capabilities. Candidates must understand the importance of iterative improvements, leveraging operational data to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or security gaps.
Optimization may involve adjusting queue assignments for new applications, expanding monitoring coverage to include newly deployed devices, or updating automation workflows to accommodate network growth. Continuous improvement ensures that enterprise networks remain efficient, reliable, and capable of supporting evolving business needs. This proactive approach aligns with the advanced knowledge expected of candidates taking the 300-410 ENARSI exam.
Advanced Troubleshooting in Enterprise Networks
Advanced troubleshooting is a critical skill for enterprise network engineers, and it forms a major component of the 300-410 ENARSI exam. Enterprise networks are complex, often involving multiple routing protocols, VPN connections, security policies, and infrastructure services operating simultaneously. Troubleshooting in such environments requires a systematic methodology, deep understanding of protocol behavior, and the ability to analyze the interplay between different technologies. Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in diagnosing and resolving issues efficiently while minimizing operational impact.
The first step in advanced troubleshooting is problem identification. Engineers must collect information about the symptoms, such as connectivity loss, high latency, packet drops, or routing inconsistencies. This often involves examining device logs, monitoring tools, and network telemetry to understand the scope and nature of the problem. A structured approach ensures that the underlying cause is identified rather than simply treating superficial symptoms, which can prevent recurring issues and network instability.
Once a problem is identified, isolation is critical. This step involves narrowing down the affected segments, devices, or services. Techniques include using traceroute to identify path disruptions, ping tests to verify connectivity, and examining routing tables to detect anomalies in route propagation. Candidates must understand how to analyze Layer 2 and Layer 3 behavior, considering both device-level issues and broader network interactions. Effective isolation often requires understanding the normal operation of protocols such as OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, MPLS, and VPN technologies, as well as the effects of security mechanisms like ACLs and CoPP.
Troubleshooting Routing Protocols
Routing protocol troubleshooting is a core skill for ENARSI candidates. Issues can arise due to misconfigurations, protocol interactions, or hardware limitations. Common problems include incorrect network statements, mismatched area configurations, route redistribution errors, and unstable neighbor relationships. Candidates must be able to interpret routing tables, protocol adjacency states, and route advertisements to identify the root cause of connectivity problems.
For OSPF, troubleshooting may involve verifying area assignments, checking link-state databases, and analyzing LSAs for inconsistencies. Problems such as stuck-in-active routes or misconfigured virtual links can disrupt routing and require careful analysis. EIGRP troubleshooting involves examining neighbor relationships, feasibility conditions, and metric calculations. Misconfigured stub routers, improper summarization, or missing network statements can prevent proper route propagation. Understanding how EIGRP calculates its composite metric is essential for detecting suboptimal paths or unreachable networks.
BGP troubleshooting involves examining neighbor sessions, route advertisements, path attributes, and policy configurations. Common issues include session failures due to authentication mismatches, route filtering errors, and incorrect path selection caused by local preference, AS path, or MED misconfigurations. Candidates must understand the implications of route reflectors, confederations, and route redistribution between BGP and internal protocols. Troubleshooting BGP requires a methodical approach to identify whether problems are related to policy, connectivity, or route propagation.
Advanced troubleshooting often involves multi-protocol environments where redistribution between different routing protocols is necessary. Misconfigured redistribution can cause routing loops, black holes, or inconsistent reachability. Candidates must understand route maps, route tagging, and filtering techniques to control the flow of routing information. This ensures that routes are propagated correctly while preventing conflicts between protocols.
Troubleshooting VPN Connectivity
VPN technologies, including site-to-site IPsec, DMVPN, and MPLS L3 VPNs, present unique challenges in troubleshooting. Connectivity problems can arise due to misconfigured tunnel parameters, authentication failures, encryption mismatches, or routing issues within the VPN. Candidates must understand the sequence of tunnel establishment, including IKE Phase 1 and Phase 2 for IPsec, NHRP resolution for DMVPN, and VRF configuration for MPLS VPNs.
Troubleshooting site-to-site VPNs involves verifying tunnel status, examining security associations, and ensuring that routing updates are correctly propagated across the encrypted link. Issues such as incorrect phase lifetimes, mismatched transform sets, or NAT interference can prevent tunnel establishment. Candidates must be able to diagnose these issues using command-line tools, logs, and packet captures.
DMVPN troubleshooting requires understanding the hub-and-spoke topology, NHRP resolution, and routing integration. Problems may include dynamic tunnel creation failures, misconfigured spoke-to-spoke connectivity, or route propagation errors. Candidates must analyze NHRP registrations, IPsec security associations, and routing table entries to ensure dynamic connectivity functions as intended. MPLS L3 VPN troubleshooting involves examining VRF tables, route targets, and PE-to-PE BGP sessions to identify misconfigurations that prevent connectivity between customer sites.
Troubleshooting Security Mechanisms
Infrastructure security mechanisms can also introduce issues that impact network performance or connectivity. Misconfigured ACLs, CoPP policies, or AAA configurations can prevent legitimate traffic from flowing or block management access. Candidates must understand how to verify ACL placement, evaluate policy rules, and analyze control plane traffic to detect problems.
CoPP troubleshooting involves examining policy maps and class maps applied to the control plane, ensuring that critical routing updates and management traffic are prioritized while unwanted traffic is limited. AAA troubleshooting includes verifying authentication and authorization flows, ensuring connectivity to RADIUS or TACACS+ servers, and analyzing logs for failed access attempts. Security-related issues often manifest as intermittent connectivity problems or selective reachability failures, requiring candidates to correlate multiple pieces of evidence to resolve the root cause.
Advanced troubleshooting scenarios may involve interactions between security mechanisms and routing protocols or VPN tunnels. For example, an ACL applied to an interface may inadvertently block OSPF neighbor updates, or CoPP policies may rate-limit BGP messages, causing session flaps. Candidates must understand the dependencies between security features and operational network services to identify and resolve these complex issues.
Multi-Protocol Network Integration
Enterprise networks often deploy multiple routing protocols simultaneously, integrating internal protocols like OSPF and EIGRP with external protocols like BGP, and combining these with VPN connectivity. This multi-protocol environment presents challenges in configuration, route redistribution, and policy enforcement. Candidates must understand how to integrate these protocols effectively while maintaining scalability, security, and performance.
Route redistribution is a critical aspect of multi-protocol integration. Misconfigured redistribution can cause loops, reachability issues, or inconsistent routing. Candidates must be able to apply route maps, tagging, and filtering to control how routes are advertised between protocols. They must also understand administrative distance and its effect on route selection, ensuring that preferred paths are selected correctly when multiple protocols provide overlapping routes.
Integration also involves managing policy consistency across routing protocols, VPNs, and security mechanisms. For example, traffic routed over a VPN must comply with QoS policies, security restrictions, and routing preferences. Candidates must understand how to configure policies at the edge and core of the network, ensuring consistent behavior and predictable outcomes. Troubleshooting multi-protocol integration often requires correlating information from multiple devices, protocols, and services to identify the source of an issue.
Complex Scenario Management
The ENARSI exam emphasizes complex scenario-based problem-solving, reflecting real-world enterprise environments. Candidates may encounter scenarios with overlapping routing protocols, multiple VPNs, advanced security policies, and infrastructure services operating concurrently. Successfully managing these scenarios requires the ability to analyze the network holistically, anticipate interactions, and implement solutions that maintain operational stability.
Scenario management begins with network documentation and baseline understanding. Candidates must be able to interpret topology diagrams, routing tables, device configurations, and monitoring outputs to understand the expected network behavior. They must then identify deviations from expected behavior, hypothesize potential causes, and test their assumptions systematically. Effective scenario management combines analytical reasoning with practical hands-on troubleshooting skills.
In these scenarios, candidates must prioritize actions based on impact and urgency. For example, resolving a BGP session failure that affects multiple sites may take precedence over an isolated ACL misconfiguration. Understanding the operational impact of each issue allows engineers to make informed decisions, maintain service continuity, and prevent cascading failures. The ENARSI exam tests these decision-making skills, evaluating candidates’ ability to manage complex, high-stakes situations effectively.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Successful troubleshooting and scenario management rely on a variety of diagnostic tools and techniques. Candidates must be proficient in using command-line utilities, monitoring tools, packet analyzers, and logging mechanisms to collect and interpret data. Tools such as ping, traceroute, show commands, debug commands, SNMP queries, and NetFlow analysis provide visibility into network operations and help isolate problems.
Packet capture analysis is particularly important for understanding traffic behavior, protocol interactions, and tunnel operation. Candidates must be able to interpret headers, payloads, and protocol exchanges to identify anomalies or misconfigurations. Combining these techniques with protocol-specific knowledge allows engineers to diagnose complex problems that span multiple layers of the network stack.
Advanced troubleshooting also involves understanding timing and sequence issues, such as route convergence delays, tunnel establishment sequences, and failover events. Candidates must correlate events across devices and protocols to reconstruct the sequence of occurrences, which is essential for identifying root causes and implementing corrective actions.
Best Practices for Advanced Troubleshooting
Effective advanced troubleshooting requires a structured methodology, deep technical knowledge, and practical experience. Candidates should adopt a systematic approach: gather information, isolate the problem, analyze root causes, implement corrective actions, and verify resolution. Maintaining detailed documentation, including configuration changes, monitoring outputs, and test results, supports repeatability and accountability.
Understanding dependencies and interactions between network components is critical. Troubleshooting one area in isolation may fail to address issues caused by interconnected systems. Candidates must consider routing, security, VPNs, and infrastructure services collectively, ensuring that solutions are comprehensive and do not introduce new problems. Scenario-based exercises in the ENARSI exam reflect this holistic approach, testing candidates’ ability to manage complex, multi-faceted network environments.
Continuous learning and hands-on practice are essential for mastering advanced troubleshooting. Familiarity with enterprise topologies, multiple routing protocols, VPN technologies, and infrastructure services develops intuition for recognizing patterns, predicting issues, and implementing effective solutions. This practical expertise is critical for both exam success and real-world professional competence.
Exam Preparation Strategies for 300-410 ENARSI
Preparing for the 300-410 ENARSI exam requires a disciplined and structured approach, combining theoretical understanding, hands-on practice, and scenario-based problem-solving. Unlike entry-level exams, ENARSI evaluates advanced knowledge across routing protocols, VPN technologies, infrastructure security, and infrastructure services. Candidates must demonstrate not only memorization but also practical competence and troubleshooting skills in complex network environments. A systematic preparation strategy maximizes the chances of success and ensures mastery of concepts that are applicable in real-world enterprise networks.
The first step in preparation is to thoroughly understand the exam blueprint. The blueprint defines the domains, subtopics, and weighting of each area, providing insight into where candidates should focus their efforts. The primary domains include Layer 3 routing technologies, VPN technologies, infrastructure security, and infrastructure services. Candidates should assess their current knowledge in each domain, identifying strengths and areas that require additional study. Creating a detailed study plan based on this self-assessment ensures balanced preparation and prevents neglect of critical topics.
Hands-on practice is a cornerstone of ENARSI preparation. Configuring routers and switches in lab environments helps candidates internalize concepts and understand the practical behavior of protocols and services. Simulating real-world scenarios, such as route redistribution, VPN tunneling, QoS configuration, and security implementation, enhances troubleshooting skills and builds confidence. Candidates should aim to practice with equipment or virtual labs that closely replicate enterprise network environments, as this prepares them for the scenario-based nature of the exam.
Simulation exercises are particularly valuable because the ENARSI exam emphasizes problem-solving rather than simple recall. Candidates may be presented with scenarios where network reachability, performance, or security is compromised, requiring diagnosis and corrective action. These simulations test the ability to apply knowledge under pressure, integrating multiple concepts simultaneously. Practicing these exercises helps candidates develop systematic troubleshooting methodologies, learn to correlate symptoms with underlying causes, and verify solutions efficiently.
Time Management and Study Techniques
Effective time management is essential for exam preparation. Candidates should allocate dedicated study sessions for each domain, focusing on challenging areas while periodically reviewing previously studied topics to reinforce retention. Breaking down complex concepts into smaller, manageable sections aids comprehension and prevents burnout. For example, focusing on specific aspects of OSPF, such as area types or virtual links, before moving on to redistribution and route filtering, ensures mastery of foundational knowledge.
Active learning techniques, such as summarizing concepts in one’s own words, creating network diagrams, and teaching concepts to peers, improve retention and understanding. Candidates should also document configuration examples, troubleshooting steps, and common pitfalls encountered during practice labs. This personalized reference material becomes invaluable during final review sessions and reinforces hands-on learning. Reviewing real-world deployment examples and network architectures provides context, helping candidates understand why specific design choices and configurations are used in enterprise environments.
Time management during the exam itself is equally important. The ENARSI exam typically includes 55–65 questions to be completed in 90 minutes, including multiple-choice, simulation, and drag-and-drop formats. Candidates should practice answering questions within a set time frame, prioritizing simulations that require multiple steps and careful analysis. Developing the ability to quickly identify the focus of each question and allocate time accordingly ensures that all items are addressed without rushing or leaving questions unanswered.
Integrating Routing, VPN, and Security Concepts
A key aspect of ENARSI success is the ability to integrate multiple concepts into cohesive solutions. Enterprise networks are interconnected ecosystems where routing protocols, VPN technologies, and security mechanisms interact continuously. Candidates must understand how changes in one domain impact others, and how to design configurations that balance performance, security, and scalability. For example, implementing a DMVPN solution requires knowledge of NHRP, IPsec, dynamic routing, and QoS to ensure secure, efficient, and resilient connectivity.
Integration extends to security considerations as well. Applying ACLs to restrict access may affect routing updates, VPN traffic, or management connectivity. Understanding these interactions is essential for both troubleshooting and configuration design. Candidates must be able to anticipate the effects of routing redistribution, VPN topology changes, and QoS policies on overall network performance and stability. Mastery of integrated problem-solving reflects the depth of expertise expected for certification and real-world enterprise network management.
Candidates should also practice multi-device scenarios, where the interplay of routing protocols, VPNs, security policies, and infrastructure services creates complex operational challenges. These exercises develop the analytical and procedural skills needed to address real-world network issues, enhancing confidence and readiness for the exam.
Real-World Deployment Considerations
Beyond exam preparation, understanding real-world deployment considerations is crucial for enterprise network engineers. Networks must be designed for scalability, redundancy, security, and performance. Candidates should consider factors such as device placement, link redundancy, failover mechanisms, and capacity planning. Deploying routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP requires careful design of areas, summarization, route policies, and redistribution strategies to optimize convergence and minimize complexity.
VPN deployment also demands careful planning. Site-to-site IPsec tunnels, DMVPN architectures, and MPLS Layer 3 VPNs must be configured with attention to security, routing, and scalability. Real-world deployments may involve overlapping IP address spaces, multiple service provider links, and dynamic traffic patterns, all of which require thorough planning and testing. Candidates must understand the operational impact of design choices, including how encryption, routing, and QoS policies affect performance and reliability.
Infrastructure security in deployment involves layered defense strategies. Device hardening, ACLs, CoPP, AAA, port security, and monitoring must be implemented consistently across all network segments. Candidates should understand the operational implications of these security measures, including management access, troubleshooting complexity, and compliance requirements. Designing secure yet manageable networks is a key skill assessed by the ENARSI exam.
Infrastructure services, including QoS, automation, and monitoring, must be integrated into network designs from the outset. QoS policies should be applied to prioritize critical traffic, automation workflows implemented to maintain consistency, and monitoring tools configured to provide visibility and alerts. Candidates must consider how these services interact with routing, VPNs, and security, ensuring that the network supports business objectives while remaining resilient and efficient.
Scenario-Based Practice and Problem-Solving
Scenario-based practice is essential for consolidating knowledge and preparing for the ENARSI exam. Candidates should simulate complex enterprise environments with multiple routing protocols, VPN tunnels, QoS policies, and security mechanisms in place. Practice should involve both configuration and troubleshooting exercises, replicating the kinds of problems that may appear on the exam. This approach develops the ability to analyze symptoms, correlate issues, and implement solutions in a structured and efficient manner.
Practicing with real-world-inspired scenarios also develops strategic thinking. Candidates must evaluate the impact of each configuration choice, anticipate potential conflicts between services, and prioritize corrective actions based on operational importance. These exercises foster a mindset aligned with enterprise network management, where decisions have cascading effects and must be made with consideration for both technical and business implications.
Documentation and review of practice scenarios enhance learning. Candidates should record configuration steps, troubleshooting methodologies, and lessons learned. Reviewing these notes reinforces understanding, identifies recurring challenges, and builds a reference library for final exam preparation. Scenario-based practice not only improves technical competence but also cultivates the analytical and decision-making skills essential for successful network engineering.
Final Preparation and Review Strategies
In the final stages of exam preparation, candidates should focus on consolidation and reinforcement of key concepts. Reviewing configuration examples, troubleshooting methodologies, and scenario resolutions ensures that knowledge is fresh and accessible under exam conditions. Practicing timed simulations helps candidates refine their approach, improve efficiency, and develop confidence in handling complex, multi-step problems.
Active recall techniques, such as mentally walking through configuration steps, predicting outcomes of routing changes, or explaining VPN establishment sequences, reinforce understanding. Candidates should also review areas of difficulty, using practice labs and diagnostic exercises to address knowledge gaps. Final review should emphasize the integration of concepts, ensuring that routing, VPNs, security, and infrastructure services are understood as interconnected components rather than isolated topics.
Mental preparation and exam strategy are also important. Candidates should maintain focus, manage stress, and approach each question methodically. Simulations should be prioritized, and time allocated based on complexity. Developing a systematic approach to interpreting scenarios, analyzing symptoms, and applying solutions ensures efficiency and accuracy under exam conditions.
Integration of All Concepts
The ultimate goal of ENARSI preparation is the integration of all networking concepts into cohesive operational competence. Candidates must understand how Layer 3 routing protocols interact with VPN technologies, security mechanisms, infrastructure services, and automation tools. Mastery of this integration ensures that the network functions optimally, is secure, scalable, and resilient, and can be managed efficiently.
In practical terms, integration involves designing routing policies that support VPN connectivity, applying ACLs and CoPP without disrupting routing or services, implementing QoS to prioritize critical applications over VPN tunnels, and using automation and monitoring to maintain network consistency and performance. Candidates must also be able to troubleshoot multi-faceted issues that arise when these components interact, applying systematic methodologies to resolve problems while maintaining service continuity.
Understanding integration at this level prepares candidates not only for the exam but also for professional roles where advanced enterprise network management is required. It reflects the depth of knowledge expected for CCNP Enterprise certification, emphasizing both technical competence and operational insight.
Continuous Learning and Professional Growth
Finally, preparation for ENARSI should be viewed as part of continuous professional development. Networking technologies evolve rapidly, with new protocols, automation tools, and security threats emerging regularly. Candidates who embrace continuous learning, hands-on experimentation, and real-world application of concepts develop the skills necessary to manage enterprise networks effectively throughout their careers.
Continuous learning involves staying informed about new developments, practicing with updated technologies, and refining troubleshooting and design skills. Candidates who cultivate this mindset gain not only certification success but also long-term professional competence, adaptability, and the ability to design and maintain networks that meet evolving organizational needs.
Final Thoughts
The 300-410 ENARSI exam represents a pivotal step in the development of advanced networking expertise. Unlike entry-level certifications, it emphasizes not just knowledge of protocols and configurations but also the ability to design, troubleshoot, and optimize complex enterprise networks. Success requires a combination of conceptual understanding, hands-on experience, and problem-solving skills that reflect real-world network operations. Candidates who approach the exam with structured preparation, disciplined practice, and scenario-based learning are well-positioned to master the material and demonstrate professional competence.
Mastery of routing protocols, VPN technologies, infrastructure security, and services such as QoS, automation, and monitoring is essential. Beyond passing the exam, these skills translate directly into improved network performance, security, and reliability in operational environments. Real-world deployment considerations, including scalability, redundancy, and integration of multiple services, are as important as theoretical knowledge, reinforcing the value of hands-on experience and lab practice.
Troubleshooting is a recurring theme in ENARSI. The exam tests the ability to analyze symptoms, isolate problems, and implement solutions efficiently, often in multi-protocol, multi-service scenarios. Developing a systematic methodology for troubleshooting, coupled with familiarity with diagnostic tools and monitoring techniques, is critical for both exam success and practical network management.
Ultimately, ENARSI is not just about passing a test—it is about cultivating the skills and mindset required for advanced enterprise networking. It encourages candidates to think holistically, integrate multiple technologies, and anticipate how network design choices affect performance, security, and scalability. Achieving the CCNP Enterprise certification validates these abilities, signaling readiness for complex, high-responsibility roles in network engineering.
Continuous learning remains vital. Networking technologies evolve rapidly, and staying current with emerging protocols, security practices, and automation tools ensures that knowledge remains relevant and applicable. Candidates who combine rigorous study, hands-on practice, and ongoing professional development not only succeed on the ENARSI exam but also build a foundation for long-term career growth and technical excellence in enterprise networking.
In essence, the ENARSI exam is a gateway to mastering advanced network design, deployment, and troubleshooting, fostering expertise that extends far beyond certification into real-world network engineering success.
Cisco CCNP Enterprise 300-410 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 300-410 Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- 200-301 - Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- 350-401 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
- 350-701 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies
- 300-410 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
- 300-715 - Implementing and Configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine (300-715 SISE)
- 350-801 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies (CLCOR)
- 350-601 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Data Center Core Technologies (DCCOR)
- 300-420 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)
- 300-425 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-425 ENWLSD)
- 300-415 - Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)
- 300-710 - Securing Networks with Cisco Firewalls
- 200-901 - DevNet Associate (DEVASC)
- 820-605 - Cisco Customer Success Manager (CSM)
- 200-201 - Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS)
- 300-620 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (DCACI)
- 350-901 - Developing Applications using Cisco Core Platforms and APIs (DEVCOR)
- 350-501 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR)
- 400-007 - Cisco Certified Design Expert
- 300-730 - Implementing Secure Solutions with Virtual Private Networks (SVPN 300-730)
- 300-430 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-430 ENWLSI)
- 500-220 - Cisco Meraki Solutions Specialist
- 300-435 - Automating Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)
- 300-810 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Applications (CLICA)
- 350-201 - Performing CyberOps Using Core Security Technologies (CBRCOR)
- 100-150 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking
- 300-820 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Cloud and Edge Solutions
- 300-735 - Automating Cisco Security Solutions (SAUTO)
- 700-805 - Cisco Renewals Manager (CRM)
- 300-815 - Implementing Cisco Advanced Call Control and Mobility Services (CLASSM)
- 300-745 - Designing Cisco Security Infrastructure
- 300-610 - Designing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure for Traditional and AI Workloads
- 300-440 - Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)
- 300-510 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions (SPRI)
- 300-720 - Securing Email with Cisco Email Security Appliance (300-720 SESA)
- 300-835 - Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO)
- 300-910 - Implementing DevOps Solutions and Practices using Cisco Platforms (DEVOPS)
- 500-442 - Administering Cisco Contact Center Enterprise
- 700-250 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Sales
- 300-725 - Securing the Web with Cisco Web Security Appliance (300-725 SWSA)
- 300-635 - Automating Cisco Data Center Solutions (DCAUTO)
- 100-140 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) IT Support
- 300-215 - Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR)
- 300-445 - Designing and Implementing Enterprise Network Assurance
- 500-560 - Cisco Networking: On-Premise and Cloud Solutions (OCSE)
- 500-444 - Cisco Contact Center Enterprise Implementation and Troubleshooting (CCEIT)
- 300-515 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider VPN Services (SPVI)
- 700-750 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Engineer
- 700-240 - Cisco Environmental Sustainability Overview
- 700-245 - Environmental Sustainability Practice-Building
- 700-150 - Introduction to Cisco Sales (ICS)
- 800-150 - Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians
- 100-490 - Cisco Certified Technician Routing & Switching (RSTECH)
- 300-615 - Troubleshooting Cisco Data Center Infrastructure (DCIT)
- 300-630 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure - Advanced
Purchase 300-410 Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Cisco certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 300-410 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Cisco certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 300-410 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 300-410 preparation materials for the Cisco certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 300-410 materials for the Cisco certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 300-410 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Cisco certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 300-410. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 300-410 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 300-410 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Cisco certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 300-410 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 300-410 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

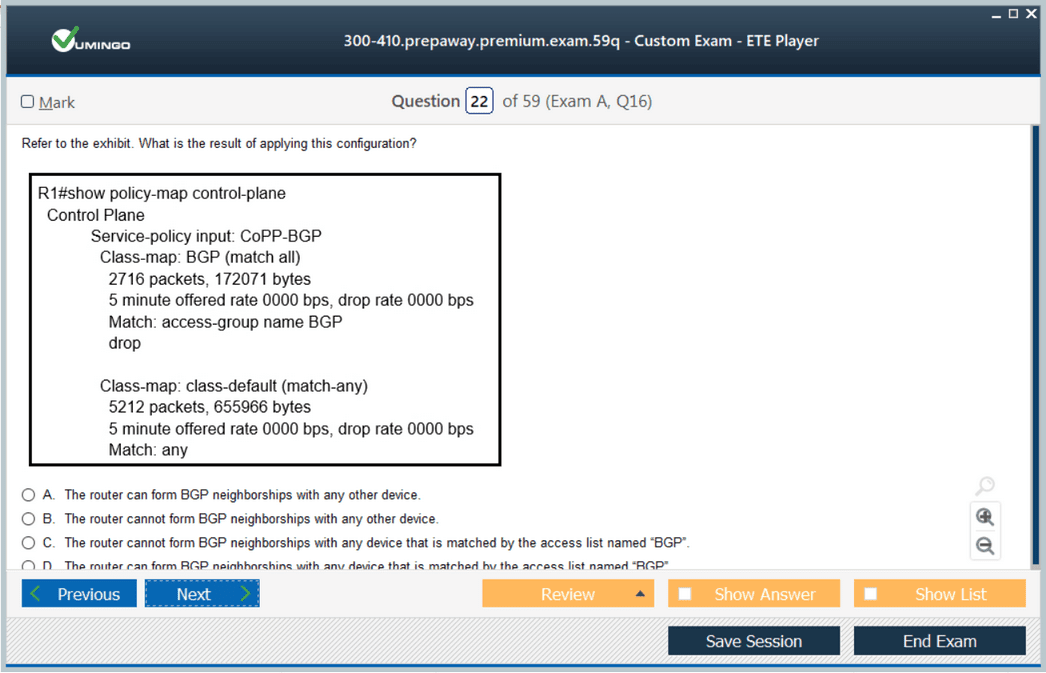
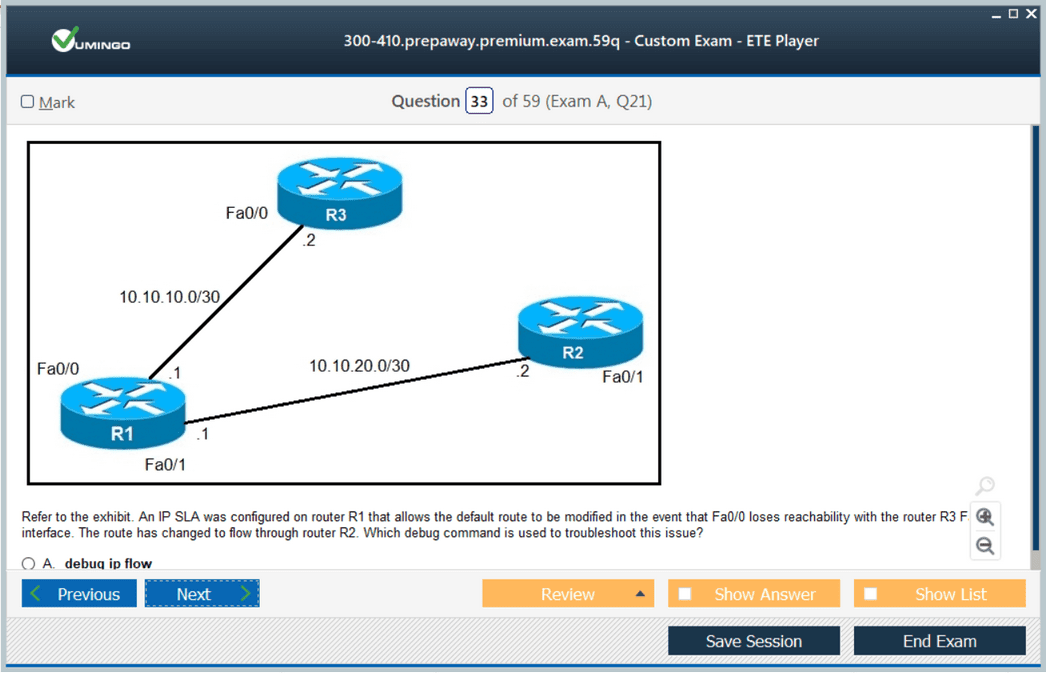
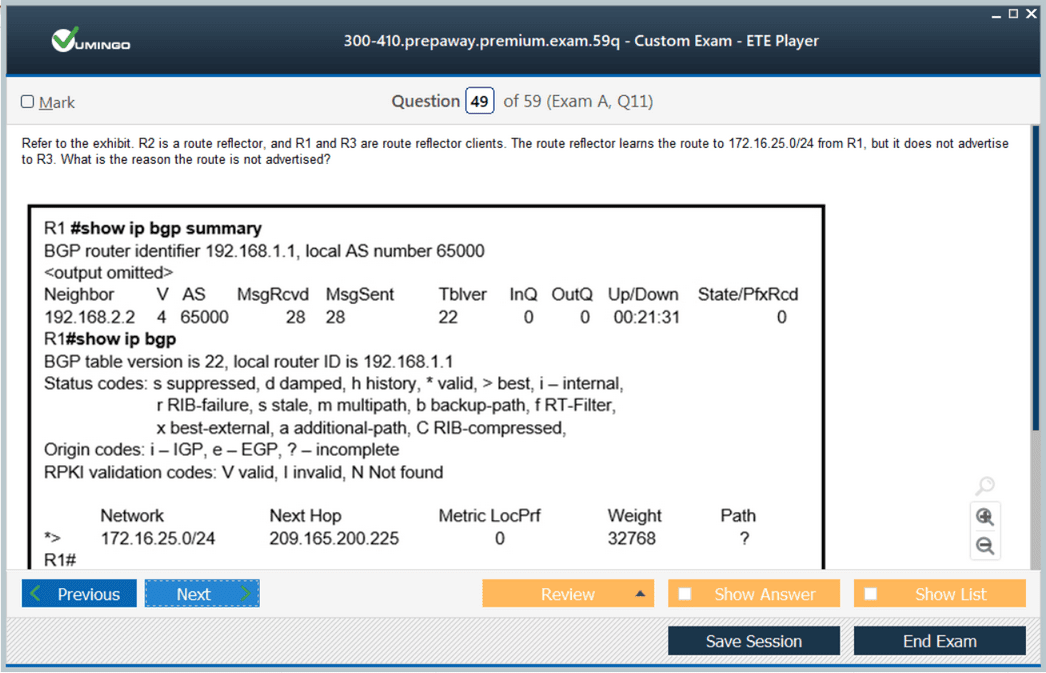








if I buy the Premium does it also come with the ETE premuim software?
is this Dump 300-410 still valid ? many thanks fpr your Help.