- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- AZ-500 Microsoft Azure Security Technologies Dumps
Pass Microsoft Azure Security AZ-500 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


AZ-500 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 515 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 31, 2026
- Training Course 73 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 635 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Microsoft Azure Security AZ-500 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the AZ-500 Microsoft Azure Security Technologies practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Mastering Azure Security: Preparation Guide for the AZ-500 Exam
Before diving into the specific domains covered by the AZ-500 exam, candidates must establish a solid understanding of fundamental cloud security concepts that underpin all Azure security implementations. These foundational principles include the shared responsibility model, where Microsoft secures the underlying infrastructure while customers protect their data and applications. Understanding defense-in-depth strategies, zero-trust architecture, and the principle of least privilege forms the bedrock of effective Azure security practices. Mastering these concepts early in your preparation ensures you can apply them across various scenarios throughout the exam and in real-world implementations.
The AZ-500 exam assumes candidates possess intermediate-level knowledge of Azure services and security concepts, making preliminary preparation essential for success. Much like professionals who must master Excel interface navigation before tackling advanced spreadsheet functions, Azure security specialists need solid grounding in basic security principles before advancing to complex implementations. Dedicate your initial study weeks to reviewing core security terminology, understanding CIA triad principles (confidentiality, integrity, availability), and familiarizing yourself with common threat vectors that target cloud environments. This foundational knowledge creates the framework upon which all subsequent learning builds, making advanced topics more accessible and comprehensible.
Determining Your Azure Certification Journey Starting Point
Many aspiring Azure security professionals wonder where to begin their certification journey, particularly whether they should pursue foundational certifications before attempting the AZ-500. While the exam doesn't strictly require prior Azure certifications, having completed the Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900) or Azure Administrator Associate (AZ-104) significantly enhances your readiness for the security-focused content. These preliminary certifications establish baseline knowledge of Azure services, resource management, and operational concepts that the AZ-500 builds upon extensively. Without this foundation, you may struggle with exam scenarios that assume familiarity with Azure networking, identity services, and resource deployment.
Professional certification pathways often feature optimal sequencing that maximizes learning efficiency and minimizes knowledge gaps. Similar considerations apply when choosing between AZ-900 and AZ-104 as your Azure starting point before advancing to security specialization. If you're completely new to Azure, the AZ-900 provides gentle introduction to cloud concepts, core services, and Azure fundamentals without overwhelming technical depth. For those with some cloud experience, the AZ-104 offers more substantive administrator-level knowledge directly applicable to security implementations. Assess your current Azure familiarity honestly and select the preparatory path that addresses your specific knowledge gaps rather than rushing directly into AZ-500 preparation without adequate foundation.
Establishing the Prerequisites for Security Specialization Success
The AZ-500 exam targets candidates with hands-on experience implementing security controls, maintaining security posture, and managing identity and access in Azure environments. Microsoft recommends at least one year of practical experience securing Azure workloads before attempting the exam, though this timeline varies based on individual background and study intensity. Beyond general Azure knowledge, familiarity with PowerShell scripting, Azure CLI commands, and JSON-based ARM templates significantly enhances your ability to understand and implement security configurations. Network security concepts including firewalls, VPNs, network segmentation, and traffic filtering also feature prominently throughout the exam domains.
Preparation effectiveness increases dramatically when candidates arrive with appropriate prerequisite knowledge already established. The importance of background preparation mirrors requirements for developer certifications like AZ-204 where specific technical skills form necessary foundations. Before beginning dedicated AZ-500 study, ensure you're comfortable with Azure Active Directory basics, virtual network configuration, storage account security, and virtual machine management. If these topics feel unfamiliar or rusty, dedicate time to hands-on labs strengthening these fundamentals before tackling advanced security topics. This preliminary work prevents frustration during later study when complex security scenarios assume baseline Azure competency.
Crafting Your Personalized Study Strategy and Timeline
Successful AZ-500 preparation requires structured study plans that systematically cover all exam domains while allowing adequate time for hands-on practice and concept reinforcement. Most candidates dedicate 6-8 weeks of focused study, though timelines vary based on existing knowledge and available study hours. Begin by reviewing the official exam skills outline, which details the weighted percentage each domain contributes to your final score. Allocate your study time proportionally, dedicating more hours to heavily-weighted domains like "Manage Identity and Access" (30-35%) and "Implement Platform Protection" (15-20%) while ensuring adequate coverage of all topics.
Strategic planning forms the cornerstone of efficient exam preparation across all certification domains. The disciplined approach required for Azure security mastery parallels methodologies used in data fundamentals preparation where systematic coverage ensures comprehensive readiness. Create a week-by-week study calendar identifying specific topics for each session, incorporating regular practice tests to gauge progress and identify weak areas requiring additional attention. Build buffer time into your schedule accommodating unexpected challenges or topics requiring deeper exploration than initially anticipated. Balance passive learning activities like video courses and reading with active engagement through hands-on labs and practice questions, as practical application cements conceptual understanding far more effectively than passive consumption alone.
Navigating Official Microsoft Learning Resources and Documentation
Microsoft provides extensive official learning resources specifically designed to prepare candidates for the AZ-500 exam, including learning paths on Microsoft Learn, official practice assessments, and comprehensive documentation covering all exam topics. The Microsoft Learn platform offers free, self-paced modules organized by exam objective, complete with hands-on exercises in temporary Azure environments requiring no personal subscription. These modules provide authoritative content directly aligned with exam requirements, making them invaluable primary study resources. Supplement these with official Microsoft documentation for deeper dives into specific services and features, as the exam frequently tests nuanced understanding that only detailed documentation provides.
Effective resource utilization involves knowing when to use different material types for optimal learning outcomes. Much like candidates preparing for advanced analytics exams like DP-500 must balance various learning modalities, AZ-500 aspirants benefit from diverse resource combinations. Use Microsoft Learn modules for structured topic introduction, then deepen understanding through official documentation and white papers. Supplement with community-created content like blogs and video courses for alternative explanations that sometimes clarify challenging concepts more effectively than official sources. However, always verify community content against official documentation, as unofficial sources occasionally contain outdated information or best practices that have evolved since publication.
Understanding Identity and Access Management Core Concepts
Identity and access management represents the largest weighted domain on the AZ-500 exam, requiring deep understanding of Azure Active Directory, conditional access policies, Privileged Identity Management, and identity protection features. Mastering this domain means understanding not just how to configure these services but when to apply specific controls based on organizational requirements and security best practices. Key topics include multi-factor authentication implementation, role-based access control (RBAC) design, service principals and managed identities, Azure AD application integration, and hybrid identity scenarios connecting on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD.
The complexity of identity management in cloud environments demands thorough conceptual understanding paired with extensive hands-on practice. Security principles underlying identity protection share conceptual foundations with broader cybersecurity certification frameworks that emphasize defense-in-depth approaches. Practice creating conditional access policies with varying conditions and controls, implementing Privileged Identity Management for just-in-time administrative access, and configuring identity protection features that detect and remediate identity-based risks. Understand the difference between Azure AD roles and Azure RBAC roles, as confusion between these distinct authorization models frequently appears in exam scenarios. Pay particular attention to troubleshooting scenarios where you must identify why users cannot access resources or why policies don't apply as expected.
Mastering Platform Protection Through Network Security Controls
Platform protection encompasses network security, host security, and container security implementations that protect Azure resources from unauthorized access and attacks. This domain requires solid understanding of network security groups, Azure Firewall, application security groups, service endpoints, private endpoints, and DDoS protection. Candidates must know how to design network segmentation strategies that isolate workloads appropriately while maintaining necessary connectivity. Understanding the differences between various network security mechanisms and when to apply each solution proves essential for both exam success and real-world implementations.
Emerging security paradigms increasingly emphasize network micro-segmentation and zero-trust approaches to platform protection. The evolution of these concepts parallels developments in AI-enhanced cyber defense where intelligent systems augment traditional security controls. Practice implementing hub-and-spoke network topologies with proper security controls at each tier, configuring Azure Firewall rules that balance security with operational requirements, and deploying private endpoints that eliminate public internet exposure for Azure PaaS services. Understand how to secure virtual machine access through Azure Bastion, implement just-in-time VM access through Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and configure network watcher tools for traffic analysis and troubleshooting. The exam frequently presents complex network scenarios requiring you to identify proper security control combinations that satisfy stated requirements.
Implementing Data and Application Security Measures
Protecting data at rest and in transit forms another critical exam domain, encompassing encryption strategies, key management through Azure Key Vault, storage account security, database security, and application security best practices. Candidates must understand various encryption methods available in Azure, including Azure Disk Encryption, Azure Storage Service Encryption, and Transparent Data Encryption for databases. Key Vault mastery extends beyond basic secret storage to include certificate management, key rotation strategies, and access control policies that govern who can perform cryptographic operations versus simply retrieving secrets.
Industrial control systems security principles apply conceptually to Azure application protection strategies, emphasizing defense-in-depth approaches. The systematic risk assessment methodologies taught in GICSP certification programs translate effectively to cloud application security. Practice implementing Azure SQL Database security features including dynamic data masking, always encrypted columns, and row-level security that restricts data access based on user identity. Understand how to secure Azure Storage through shared access signatures with appropriate time limits and permissions, storage account firewalls that restrict access to specific networks, and immutable blob storage protecting against deletion or modification. Application security extends to implementing Azure App Service authentication/authorization, configuring managed identities that eliminate credential management, and deploying Azure API Management with subscription keys and OAuth validation.
Leveraging Security Operations and Monitoring Capabilities
Security operations encompasses continuous monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and compliance management through tools like Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Azure Sentinel. Candidates must understand how to configure these services to collect security-relevant data, create alert rules that notify administrators of suspicious activities, and respond to security incidents following established playbooks. This domain emphasizes practical skills in investigating security alerts, analyzing log data to identify attack patterns, and implementing automated responses that contain threats before they cause significant damage.
The comprehensive monitoring and analytics capabilities required for cloud security mirror enterprise security operations practiced by CISSP-certified professionals managing complex security environments. Practice configuring Microsoft Defender for Cloud security policies, interpreting secure score recommendations, and implementing auto-provisioning for log analytics agents across your Azure resources. Understand how to create Azure Monitor alert rules with appropriate severity levels and action groups, query Log Analytics using KQL (Kusto Query Language) for security investigations, and deploy Azure Sentinel workbooks that visualize security data for easier pattern recognition. The exam tests your ability to select appropriate tools for specific monitoring requirements and troubleshoot situations where expected alerts aren't generating or logs aren't collecting properly.
Recognizing the Evolving Role of AI in Cloud Security
Artificial intelligence and machine learning increasingly influence cloud security implementations, from anomaly detection that identifies unusual access patterns to automated threat intelligence that prioritizes the most critical risks. Microsoft integrates AI capabilities throughout its security services, including behavioral analytics in Azure AD Identity Protection, threat detection in Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and intelligent investigations in Azure Sentinel. Understanding these AI-enhanced features helps candidates appreciate why certain security recommendations appear and how to leverage automated insights for more effective threat response.
The transformation of security operations through artificial intelligence parallels broader industry shifts toward data-driven personalization in technology platforms. While the AZ-500 exam doesn't require deep machine learning knowledge, understanding how AI features enhance security posture proves valuable. Familiarize yourself with risk detection policies in Azure AD Identity Protection that automatically block or require additional verification when AI algorithms detect suspicious sign-in patterns. Explore Microsoft Defender for Cloud's threat detection capabilities that analyze resource logs and network traffic for attack indicators. These AI-augmented security controls represent the future of cloud security, making basic familiarity beneficial for both exam success and career development.
Preparing for Audit-Focused Security Scenarios
Security professionals frequently work with auditors validating compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, making audit-readiness an important aspect of Azure security implementations. The AZ-500 exam includes scenarios involving compliance management through Azure Policy, regulatory compliance monitoring in Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and evidence collection demonstrating adherence to security requirements. Understanding frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS helps contextualize why specific security controls matter and how Azure services facilitate compliance.
Audit and compliance expertise forms a specialized security domain that overlaps significantly with information systems auditing practices. The systematic approach to security validation taught in CISA certification programs applies directly to Azure compliance management. Practice implementing Azure Policy definitions that enforce specific configuration requirements across subscriptions, creating management groups that organize resources for policy inheritance, and reviewing compliance dashboards that identify non-compliant resources requiring remediation. Understand how to use Azure Blueprints for deploying compliant environments with pre-configured policies and RBAC assignments. The exam may present scenarios requiring you to select appropriate compliance controls for specific regulatory requirements or troubleshoot policy assignments that aren't achieving desired compliance outcomes.
Applying Project Management Mindsets to Security Implementations
While the AZ-500 exam focuses on technical security skills, successful Azure security professionals also need project management capabilities for coordinating complex security initiatives across organizations. Understanding how to scope security projects, identify stakeholders with different concerns, and sequence implementation steps appropriately improves both exam performance and career effectiveness. Many exam scenarios present complex environments requiring systematic analysis to determine proper implementation order where certain security controls depend on prerequisites being in place first.
The distinction between product ownership and product management roles offers useful parallels for understanding security project dynamics. Just as product owners and managers fulfill different organizational functions, security architects and security engineers approach challenges from complementary perspectives. When studying security scenarios, practice identifying dependencies between security controls where implementing network segmentation might need to precede application-specific security configuration. Develop systematic approaches to complex scenarios by breaking them into smaller components, identifying what must happen first, and sequencing implementation steps logically. This analytical skill proves valuable for scenario-based exam questions and real-world security projects alike.
Adopting Agile Methodologies in Security Operations
Modern security operations increasingly adopt agile methodologies that emphasize iterative improvement, continuous feedback, and adaptive response to evolving threats. While traditional security planning often followed waterfall approaches with extensive upfront design, cloud security's rapid evolution favors agile approaches that deliver incremental security improvements while remaining flexible to change. Understanding agile principles helps contextualize why certain security implementations might use minimum viable security postures that evolve rather than attempting comprehensive security architecture completed before deployment.
The growing popularity of agile methodologies extends across IT disciplines, with security operations benefiting from iterative approaches. Professionals pursuing Scrum Master certifications learn frameworks equally applicable to security project management. When preparing for the AZ-500, consider security implementations not as one-time configurations but as evolving postures requiring continuous assessment and adjustment. Microsoft Defender for Cloud's secure score exemplifies this iterative approach, providing continuous recommendations for security improvements rather than defining security as a binary achieved/not-achieved state. Practice thinking about security scenarios in terms of phased implementations that deliver immediate value while creating foundations for subsequent enhancements.
Staying Current with Rapidly Evolving Security Landscape
Cloud security evolves rapidly as new threats emerge, security services add features, and best practices mature based on collective experience. Successful AZ-500 candidates complement focused exam preparation with broader awareness of security trends, emerging threats, and Azure service updates that may influence exam content or real-world implementations. Following Microsoft security blogs, participating in Azure security communities, and reviewing service update announcements helps maintain currency in this dynamic field. Understanding that certification preparation represents a snapshot of current best practices while security itself continuously evolves sets appropriate expectations.
The acceleration of change in cloud security parallels broader trends in agile project management and certification programs. Professionals seeking in-demand Scrum certifications recognize that credentials require ongoing learning beyond initial certification. Build habits of continuous learning that extend beyond exam preparation, including subscribing to Microsoft security blogs, following Azure security advocates on social media, and regularly reviewing the Azure updates page for security-related announcements. Practice with hands-on labs even after passing the exam to maintain practical skills and explore new features as they release. This commitment to ongoing learning ensures your Azure security knowledge remains current and valuable throughout your career.
Understanding the Strategic Value of Security Certifications
Pursuing the AZ-500 certification represents more than exam preparation—it signals professional commitment to cloud security excellence and validates skills that organizations increasingly prioritize. Security-focused certifications typically command higher salaries than general IT certifications, with Azure security specialists particularly valued as organizations accelerate cloud adoption while facing increasingly sophisticated threats. Understanding the career benefits of certification helps maintain motivation through challenging study periods and justifies the time investment required for thorough preparation.
Security certification value extends beyond initial credential acquisition to include career advancement opportunities and professional networking. The strategic career benefits of specialized certifications parallel advantages found in Scrum Master certification programs that open new professional pathways. Azure security skills remain in high demand as organizations struggle to find qualified professionals who understand both cloud technologies and security principles. The AZ-500 certification differentiates you in competitive job markets, provides entry to specialized roles with significant responsibility, and creates foundations for advanced certifications like the Azure Solutions Architect Expert. Beyond immediate career benefits, the deep knowledge gained through preparation makes you more effective in current roles where security considerations increasingly influence design decisions.
Embracing Continuous Improvement Through Retrospective Analysis
As you progress through AZ-500 preparation, regularly assess what's working well and what requires adjustment in your study approach. Periodic retrospectives where you reflect on recent learning, identify obstacles that impeded progress, and experiment with different study methods optimize preparation effectiveness. This self-awareness prevents persisting with ineffective approaches and helps you discover learning strategies that match your individual preferences and schedule constraints. Tracking your progress through practice test scores and topic mastery provides objective evidence of improvement while identifying persistent weak areas requiring focused attention.
The retrospective process fundamental to agile methodologies applies productively to individual learning and skill development. Organizations that conduct agile retrospectives for continuous improvement achieve better outcomes through systematic reflection and adaptation. After completing each study section or practice test, spend time analyzing what contributed to successes and what challenged you. Did hands-on labs cement understanding better than reading? Do you retain information better from video courses or written materials? Does studying in shorter frequent sessions work better than longer weekly blocks? These insights allow you to optimize subsequent study based on empirical evidence of what works for you personally rather than following generic study advice that may not match your learning style.
Considering Career Progression Beyond Initial Certification
While achieving AZ-500 certification represents a significant milestone, planning your longer-term career development creates context for immediate preparation while motivating you toward future growth. Azure security certifications exist within broader career pathways potentially including the Azure Solutions Architect Expert, Azure DevOps Engineer Expert, or even Microsoft Certified: Cybersecurity Architect Expert. Understanding these progression options helps you see AZ-500 as one step in a longer journey rather than an isolated credential, providing motivation that extends beyond single exam success.
The career coaching and mentoring aspects of professional development complement technical skill building through certification. Professionals exploring agile coaching careers recognize that credentials open doors to leadership opportunities beyond individual contributor roles. Consider how Azure security expertise positions you for architectural roles, consulting opportunities, or security leadership positions that leverage both technical knowledge and strategic thinking. The AZ-500 certification particularly suits professionals seeking cloud security architect, Azure security consultant, or compliance specialist roles where deep security knowledge combines with Azure platform expertise. Planning this trajectory helps you make study choices that support long-term goals rather than merely achieving passing scores.
Exploring Alternative Education Pathways and Credentials
While the AZ-500 certification focuses specifically on Azure security, broader cybersecurity education and credentials complement and enhance your Azure-specific knowledge. Understanding networking fundamentals, operating system security, application security principles, and threat intelligence enriches your Azure security implementations by providing deeper context for why specific controls matter. Consider supplementing AZ-500 preparation with general cybersecurity education through degree programs, bootcamps, or complementary certifications that broaden your security foundation.
The diverse landscape of educational credentials and pathways creates opportunities for tailored learning that matches individual circumstances. Professionals researching diploma course options encounter similar decisions about optimal education investments. For some candidates, pairing AZ-500 with general certifications like CompTIA Security+ provides valuable security fundamentals that make Azure-specific concepts more comprehensible. Others might benefit from networking certifications that deepen understanding of the network security concepts tested extensively on the AZ-500. Assess your background honestly to identify knowledge gaps that alternative education might address, balancing the value of additional credentials against time and financial investments they require.
Accommodating Individual Learning Needs and Preferences
Successful exam preparation acknowledges that candidates learn differently and may require varied approaches or accommodations to demonstrate their knowledge effectively. Some learners excel with visual content like diagrams and videos, while others prefer text-based reading or hands-on practice. Understanding your learning preferences allows you to select study resources and methods that align with your strengths rather than struggling with approaches that don't match how you process information. For candidates with learning differences or disabilities, understanding available testing accommodations ensures you can demonstrate your knowledge without unnecessary barriers.
Educational accessibility and appropriate accommodations ensure all qualified candidates can pursue certifications regardless of learning differences. The systematic approach to standardized test accommodations applies equally to professional certification testing. Microsoft offers various testing accommodations including extended time, separate testing rooms, screen readers, and other modifications that ensure fair assessment of knowledge rather than testing stamina or processing speed. If you believe accommodations would help you demonstrate your Azure security knowledge more accurately, research the accommodation request process early in your preparation. These adaptations level the playing field, ensuring your certification reflects genuine expertise rather than being limited by factors unrelated to actual security competency.
Setting Realistic Score Expectations and Goals
Understanding the AZ-500 scoring system helps set appropriate expectations and study goals throughout your preparation. Microsoft certification exams use scaled scoring from 100-1000, with 700 representing the passing threshold. This scaled scoring means your raw percentage of correct answers gets adjusted based on question difficulty and exam form, preventing unfair advantage or disadvantage based on which specific questions you receive. The exam includes scored questions that contribute to your final result and unscored pretest items that Microsoft evaluates for future exam versions. You won't know which questions are unscored, making it essential to approach all questions with equal seriousness.
Score interpretation and achievement benchmarks provide helpful frameworks for assessing performance across various assessments. Just as maximum ASVAB scores indicate exceptional performance beyond minimum requirements, Azure certification scores above the passing threshold demonstrate varying mastery levels. While 700 represents passing, scores in the 800-900 range indicate strong command of the material, and scores above 900 suggest exceptional expertise. During preparation, aim for consistent practice test scores well above 700—perhaps targeting 800+—to provide buffer against test day anxiety or difficult question selections. This goal prevents the common mistake of studying only to minimum passing standards, which creates risk if exam day proves more challenging than expected.
Securing Identity Infrastructure with Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory forms the cornerstone of identity security in Azure environments, serving as both authentication provider and access control gateway for cloud resources. The AZ-500 exam heavily emphasizes Azure AD configuration and management, requiring candidates to demonstrate expertise in user and group management, authentication methods, conditional access policies, and identity protection features. Understanding the differences between Azure AD free, Premium P1, and Premium P2 tiers proves essential, as many advanced security features like Privileged Identity Management and Identity Protection require premium licensing. Candidates must know not just how to configure these features but also when specific controls appropriately address stated security requirements.
Preparing for Azure AD security scenarios requires both conceptual understanding and extensive hands-on practice with the service. Similar to how professionals preparing for cloud service certifications must balance theory with practical implementation, AZ-500 candidates need substantial lab time configuring directory features. Practice creating conditional access policies with multiple conditions including user location, device compliance state, application sensitivity, and sign-in risk levels. Implement Privileged Identity Management for just-in-time administrative access, configuring activation requirements, approval workflows, and maximum activation durations. Explore identity protection risk policies that automatically respond to detected risks by requiring password changes or multi-factor authentication. These hands-on experiences transform abstract concepts into practical understanding that survives exam stress.
Implementing Network Security and Connectivity Protection
Network security represents a substantial portion of the platform protection domain, requiring deep understanding of how to secure both network perimeter and internal traffic flows between Azure resources. Virtual network security begins with proper subnet design that isolates workloads appropriately, continues through network security group rules that filter traffic based on source, destination, port, and protocol, and extends to advanced filtering through Azure Firewall or network virtual appliances. Understanding the difference between user-defined routes, service endpoints, and private endpoints proves critical, as these distinct mechanisms each solve specific connectivity and security challenges.
Networking expertise from various certification backgrounds provides transferable knowledge applicable to Azure network security. Professionals with wireless networking credentials often find certain concepts familiar while recognizing cloud-specific nuances. Practice implementing hub-and-spoke network topologies where shared services reside in central hub virtual networks while workload-specific resources deploy to spoke networks with controlled connectivity to the hub. Configure Azure Firewall with application rules allowing specific FQDNs, network rules permitting required IP and port combinations, and threat intelligence filtering that blocks known malicious indicators. Implement service endpoints that keep traffic to Azure PaaS services on the Azure backbone network, and contrast this with private endpoints that inject PaaS resources into your virtual network address space for complete private connectivity.
Deploying and Managing Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center) provides unified security management and advanced threat protection across Azure, on-premises, and multi-cloud environments. This powerful service continuously assesses resource configurations against security best practices, provides secure score recommendations for improvement, and includes optional enhanced security features through Microsoft Defender plans for specific workload types. Understanding the distinction between foundational capabilities available free to all Azure subscriptions and enhanced protections requiring separate enablement and licensing proves essential for exam success. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of security policies, regulatory compliance assessments, and workflow automation that responds to security alerts.
Advanced security monitoring and protection capabilities parallel sophisticated assessment methodologies used in other specialized testing domains. The comprehensive preparation approach suitable for standardized academic assessments translates well to mastering Defender for Cloud's extensive capabilities. Practice enabling Microsoft Defender plans for various resource types including virtual machines, storage accounts, SQL databases, containers, and App Services, understanding the specific protections each plan provides. Configure auto-provisioning to deploy log analytics agents automatically to new resources, ensuring comprehensive visibility. Create custom security policies that reflect organizational requirements beyond Microsoft's default recommendations, and use policy exemptions where legitimate business reasons justify deviations from standard recommendations. Explore just-in-time VM access that opens management ports only when needed and only from authorized locations.
Mastering Key Vault for Secrets and Key Management
Azure Key Vault provides centralized secure storage for secrets, encryption keys, and certificates, eliminating hardcoded credentials in application code while maintaining comprehensive audit logs of cryptographic operations. Understanding Key Vault architecture including access policies versus role-based access control, soft-delete and purge protection features, and firewall rules that restrict access to specific networks forms essential exam knowledge. Candidates must distinguish between storing secrets (connection strings, passwords, API keys), keys (cryptographic keys for encryption/decryption), and certificates (SSL/TLS certificates for application security), as each object type serves distinct purposes with different management requirements.
Specialized knowledge management in secure environments requires understanding proper secrets handling that parallels best practices in various professional domains. Professionals familiar with specialized certification examinations recognize the importance of domain-specific expertise. Practice creating Key Vaults with appropriate access policies granting secrets, keys, and certificates permissions separately to different service principals. Implement managed identities for Azure resources that eliminate credential management entirely by allowing resources to authenticate directly to Key Vault using Azure AD authentication. Configure Key Vault firewall rules that restrict access to specific virtual networks and IP addresses, preventing public internet exposure while maintaining necessary application connectivity. Enable diagnostic logging that captures all Key Vault operations for security monitoring and compliance auditing.
Securing Data at Rest and in Transit
Data protection encompasses encryption strategies for data at rest in storage accounts and databases, as well as data in transit across networks. Azure provides multiple encryption options including platform-managed keys that Microsoft handles automatically, customer-managed keys stored in Key Vault that organizations control, and customer-provided keys supplied per-operation for maximum control. Understanding when each approach appropriately balances security requirements against operational complexity proves essential for both exam scenarios and real-world implementations. Transport layer security for data in transit requires understanding how to enforce HTTPS for web applications, secure database connections, and encrypt traffic between virtual networks.
Comprehensive security implementations require layered approaches to data protection across various states and locations. The systematic preparation methodologies valuable for independent school entrance examinations apply equally to mastering complex security topics. Practice implementing Azure Storage Service Encryption with customer-managed keys stored in Key Vault, including key rotation procedures that maintain security while avoiding service disruption. Configure Azure SQL Database Transparent Data Encryption with customer-managed keys, and contrast this with Always Encrypted feature that protects sensitive columns from database administrators. Implement Azure Disk Encryption for virtual machines using BitLocker (Windows) or DM-Crypt (Linux), understanding the prerequisites including Key Vault configuration and virtual machine access to the vault during boot.
Implementing Application Security Best Practices
Application security extends beyond infrastructure protection to include secure coding practices, application authentication and authorization, and API protection. Azure App Service provides built-in authentication/authorization features that integrate with Azure AD, Microsoft accounts, and social identity providers, eliminating the need for custom authentication code. API Management acts as facade for backend APIs, providing security features including subscription keys, OAuth token validation, IP filtering, and rate limiting that protects services from abuse while maintaining authorized access. Understanding managed identities that allow applications to authenticate to Azure services without storing credentials represents another crucial application security concept.
Application-level security requires holistic thinking about multiple protection layers working together. Professionals preparing for foundational aptitude assessments develop similar systematic approaches to complex problem-solving. Practice enabling App Service authentication with Azure AD integration, configuring allowed audiences and token validation requirements. Implement managed identities for App Service applications, granting these identities appropriate permissions to access Key Vault, Storage accounts, or databases without managing connection strings. Configure API Management policies including subscription key requirements, JWT token validation, IP filtering that restricts access to known sources, and rate limiting that prevents individual consumers from overwhelming backend services. These layered protections create defense-in-depth that maintains security even if individual controls fail.
Designing Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Security Architectures
Modern organizations increasingly operate hybrid environments with resources spanning Azure, on-premises datacenters, and potentially other cloud providers. Securing these distributed architectures requires understanding VPN gateways and ExpressRoute for private connectivity, Azure Arc for extending Azure management to external resources, and Microsoft Defender for Cloud's multi-cloud capabilities. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of how to maintain consistent security posture across distributed infrastructure, centralize security monitoring despite resource dispersion, and implement network security that protects traffic flowing between environments.
Complex distributed architectures that span multiple platforms and locations parallel the comprehensive scenarios tested in various certification domains. The breadth of knowledge required mirrors preparations for Azure architecture design certifications where candidates must understand multiple services working together. Practice configuring site-to-site VPN connections between on-premises networks and Azure virtual networks, implementing appropriate encryption and authentication. Deploy Azure Arc agents to servers running outside Azure, then use Azure Policy to enforce configuration standards and monitor compliance across hybrid infrastructure. Enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud's multi-cloud connectors for AWS or GCP, centralizing security posture assessment and threat detection across multiple platforms through a single interface.
Implementing Security for Azure PaaS Services
Platform-as-a-Service offerings including Azure SQL Database, Azure Storage, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure App Service each include specific security features requiring detailed understanding. Database security encompasses authentication methods, firewall rules, private endpoints, auditing, threat detection, and data classification with protection policies. Storage security includes shared access signatures with appropriate time limits and permissions, storage account firewalls and virtual network service endpoints, and immutable storage that prevents deletion or modification. Understanding which security features apply to which PaaS services and how to implement them correctly forms essential exam knowledge.
Specialized knowledge of individual Azure services builds upon foundational understanding of overall platform capabilities. The service-specific expertise parallels detailed learning required for troubleshooting certification paths where deep understanding of particular technologies proves essential. Practice implementing Azure SQL Database firewall rules that allow specific IP addresses or Azure services, then contrast with private endpoints that provide entirely private connectivity. Configure Azure Storage firewalls restricting access to specific virtual networks, and implement shared access signatures with minimum necessary permissions and shortest acceptable time windows. Enable diagnostic logging for Azure App Service capturing application logs, web server logs, and detailed error messages for security monitoring and troubleshooting.
Monitoring and Responding to Security Events
Security operations centers depend on comprehensive logging, intelligent alerting, and efficient investigation workflows to detect and respond to threats effectively. Azure Monitor provides the foundational telemetry collection and alerting platform, while Log Analytics workspaces store and query collected logs, and Azure Sentinel builds upon these foundations with security-specific correlation rules, investigation tools, and automated response capabilities. Understanding Kusto Query Language (KQL) for querying Log Analytics data proves essential, as many exam scenarios require selecting correct queries to identify specific security events or troubleshoot issues.
Effective security monitoring requires both tool configuration expertise and analytical thinking about threat detection. The investigative mindset developed through various assessment methodologies parallels requirements for support troubleshooting certifications where systematic analysis identifies root causes. Practice writing KQL queries that filter security events by severity, source IP address, affected resources, or timeframe, then aggregate results to identify patterns. Configure Azure Monitor alert rules with appropriate thresholds and action groups that notify security teams through email, SMS, or integration with ticketing systems. Deploy Azure Sentinel analytics rules that correlate events across multiple data sources, identifying attack patterns that individual events wouldn't reveal. Investigate security incidents using Sentinel's investigation graph that visualizes related entities and timelines.
Implementing Governance Through Azure Policy
Azure Policy enables enforcement of organizational standards and compliance assessment at scale, defining allowed resource types, required configurations, and permitted locations for resource deployment. Understanding policy definitions that contain the logic for evaluation, policy assignments that scope definitions to management groups or subscriptions, and policy remediation that corrects non-compliant existing resources forms essential exam knowledge. Candidates must distinguish between audit effects that simply report compliance, deny effects that prevent non-compliant resource creation, and various modification effects that automatically configure compliant settings.
Governance and compliance frameworks require systematic approaches to policy design and implementation across organizational hierarchies. The structured thinking valuable for data analytics certification preparation applies equally to mastering policy-based governance. Practice creating custom policy definitions using JSON syntax, defining appropriate conditions and effects. Implement policy initiatives (formerly called policy sets) that group related policies addressing specific compliance frameworks like PCI-DSS or ISO 27001. Configure remediation tasks that apply policies retroactively to existing resources, understanding that certain effect types like deployIfNotExists require managed identities with appropriate permissions to perform remediation actions. Use exclusion scopes when legitimate exceptions require specific resources to bypass certain policies.
Managing Azure Active Directory Domain Services
Azure AD Domain Services provides managed domain services including domain join, group policy, LDAP, and Kerberos/NTLM authentication without deploying and managing domain controllers. This service bridges cloud-native Azure AD with legacy applications requiring traditional AD DS functionality, creating hybrid scenarios where cloud and on-premises identities synchronize. Understanding when Azure AD DS appropriately addresses application requirements versus when Azure AD native integration proves sufficient forms important exam knowledge. Candidates must demonstrate familiarity with forest trusts, network security considerations, and monitoring requirements specific to managed domain services.
Specialized identity services that bridge cloud and traditional infrastructure require nuanced understanding of multiple authentication systems. The complex integration scenarios parallel knowledge domains in advanced data implementation paths where multiple technologies interconnect. Practice deploying Azure AD DS instances into managed resource groups and virtual networks, understanding the network requirements including dedicated subnets and DNS configuration. Configure synchronization from Azure AD to the managed domain, understanding that this operates as one-way synchronization from cloud to managed domain. Implement secure LDAP access for cloud-based applications that require LDAP authentication, configuring appropriate certificates and network security rules. Enable Azure AD DS domain services monitoring through Azure Monitor, tracking authentication metrics and security events.
Implementing Secure DevOps Practices
DevSecOps integrates security throughout the development lifecycle rather than treating it as pre-deployment gate, requiring understanding of tools and practices that enable developers to build secure applications. Azure DevOps and GitHub Advanced Security provide scanning capabilities including secret scanning that detects accidentally committed credentials, dependency scanning that identifies vulnerable libraries, and code scanning that finds potential security issues. Understanding how to implement security gates in CI/CD pipelines, perform automated security testing, and maintain separation of duties in code deployment represents exam-relevant knowledge.
Security integration throughout development pipelines parallels comprehensive quality assurance approaches used in various industries. The systematic integration mindset reflects principles valuable for data engineering certification paths where automation and quality form central themes. Practice implementing pipeline security gates that require security scans to pass before allowing deployment, configuring appropriate failure thresholds that balance security rigor against development velocity. Enable secret scanning in GitHub repositories, then configure patterns for custom secret types specific to your organization. Implement managed identities for Azure DevOps service connections, eliminating stored credentials in pipeline configurations. Configure deployment permissions that require manual approval for production deployments, implementing separation of duties where code authors cannot directly deploy to sensitive environments.
Leveraging Advanced Analytics for Security Insights
Security analytics transforms raw telemetry into actionable intelligence through pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and threat modeling. Microsoft Sentinel's built-in machine learning capabilities detect anomalies in user behavior, network traffic, and resource access patterns that static rules might miss. Understanding how user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) creates behavioral baselines then alerts on deviations represents exam-relevant knowledge. Candidates should recognize when analytics-driven detection provides value beyond signature-based rules, and understand how to tune analytics to reduce false positives while maintaining sensitivity to genuine threats.
Advanced analytical capabilities in security platforms reflect broader trends toward intelligent systems across technology domains. The data-driven decision making parallels methodologies central to analytics certification programs emphasizing insight extraction from large datasets. Practice enabling UEBA in Microsoft Sentinel, understanding the learning period required before behavioral anomalies can be detected reliably. Review anomaly detection rules that identify unusual patterns in resource access, authentication activities, or data transfers, configuring thresholds that balance sensitivity against alert fatigue. Implement threat intelligence integration that enriches security alerts with indicators of compromise from Microsoft and third-party feeds, providing context about whether suspicious activities match known attack patterns.
Implementing Container and Kubernetes Security
Containerized applications and Kubernetes orchestration introduce specific security considerations including image security, registry access control, pod security policies, and network policies that control traffic between containers. Microsoft Defender for Containers provides vulnerability scanning for container images, runtime threat detection for containerized workloads, and Kubernetes configuration assessments against security best practices. Understanding how to secure Azure Container Registry, implement Azure Kubernetes Service security features, and integrate container security into CI/CD pipelines forms increasingly important exam knowledge as containerization grows in prevalence.
Container security expertise represents specialized knowledge building upon foundational infrastructure security principles. The platform-specific security considerations parallel specialized knowledge domains in business application certifications where platform nuances matter significantly. Practice enabling Microsoft Defender for Containers and reviewing vulnerability assessments for images stored in Azure Container Registry, understanding severity classifications and remediation recommendations. Implement AKS security features including Azure AD integration for cluster access control, pod security policies that restrict container capabilities, and network policies that limit east-west traffic between pods. Configure image scanning in Azure Pipelines that prevents deploying images with high-severity vulnerabilities, implementing security gates that maintain quality without blocking development velocity.
Managing Security for Enterprise Applications
Enterprise applications in Azure AD represent external SaaS applications or custom applications integrated with Azure AD for authentication and authorization. Understanding enterprise application security includes configuring single sign-on with various protocols (SAML, OpenID Connect, OAuth), implementing conditional access policies specific to applications, managing application consent and permissions, and configuring application proxy for publishing on-premises applications to remote users. Candidates must distinguish between enterprise applications registered in Azure AD versus app registrations for applications you're developing, as these related but distinct concepts serve different purposes.
Application integration security requires understanding both identity protocols and Azure AD capabilities for managing external applications. The systematic integration approach reflects principles valuable across ERP implementation domains where multiple systems interconnect securely. Practice configuring enterprise applications with SAML-based single sign-on, understanding attribute mappings between Azure AD and target applications. Implement conditional access policies targeting specific enterprise applications, requiring multi-factor authentication or compliant devices only when accessing high-sensitivity applications. Configure application consent policies that control whether users can consent to applications accessing organizational data, implementing admin consent workflows for applications requiring review before access grants.
Optimizing Manufacturing Security Through Proper Access Controls
While the AZ-500 exam doesn't specifically focus on manufacturing scenarios, understanding how to secure specialized industry workloads demonstrates comprehensive security knowledge applicable across sectors. Manufacturing environments increasingly integrate cloud connectivity for equipment monitoring, production data analytics, and supply chain integration, each requiring careful security implementation. Access control strategies must balance operational requirements with security needs, ensuring production systems maintain high availability while preventing unauthorized access that could disrupt operations or compromise intellectual property.
Industry-specific security implementations require adapting core security principles to particular operational contexts and risk profiles. The specialized application of fundamental concepts parallels approaches in manufacturing certification domains where sector knowledge combines with platform expertise. Practice implementing network segmentation that isolates manufacturing systems from general corporate networks while allowing necessary data flows for analytics and monitoring. Configure conditional access policies permitting production floor equipment access only from facility networks while requiring enhanced authentication for remote access. Implement just-in-time access for maintenance activities, ensuring technicians receive temporary elevated permissions rather than standing administrative rights that increase attack surface.
Implementing Security for Supply Chain Visibility Platforms
Supply chain management platforms increasingly rely on cloud services for real-time visibility, partner collaboration, and predictive analytics, creating security challenges around data sharing with external partners while maintaining appropriate access controls. Understanding how to implement secure B2B collaboration through Azure AD, configure data classification and protection for supply chain information, and monitor access to sensitive logistics data represents practical security knowledge applicable beyond the exam. These scenarios require balancing transparency requirements for partner collaboration against data protection requirements limiting access to authorized parties.
Complex multi-party collaboration scenarios require sophisticated security architectures supporting data sharing while maintaining control. The intricate access patterns parallel considerations in supply chain platform certifications emphasizing secure information exchange. Practice configuring Azure AD B2B collaboration that allows external partner users to access specific applications and resources without requiring separate account credentials. Implement Azure Information Protection labels that classify supply chain documents, applying encryption and usage restrictions that follow documents even when shared externally. Configure Data Loss Prevention policies preventing accidental sharing of sensitive supply chain information through unsanctioned channels, balancing protection against operational requirements for information sharing.
Securing Power Platform and Low-Code Solutions
Microsoft Power Platform components including Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI create citizen development scenarios where non-developers build applications and automation. Securing these low-code solutions requires understanding data loss prevention policies that restrict connector combinations, environment isolation strategies, and application sharing controls. Candidates should understand how Power Platform integrates with Azure security services, including Azure AD for authentication, Key Vault for secret storage in flows, and compliance features ensuring citizen-developed solutions meet organizational security standards.
Low-code platform security requires governance frameworks balancing democratized development against data protection and compliance requirements. The governance emphasis parallels concerns in business application implementation paths where appropriate controls maintain security without stifling innovation. Practice creating data loss prevention policies that prevent connectors handling sensitive data from being combined with consumer-grade connectors that might leak information. Implement environment strategies isolating development, test, and production environments with appropriate access controls. Configure application sharing settings that require maker approval before apps accessing sensitive data can be shared broadly, implementing review workflows that validate security before wide distribution.
Understanding Legacy Integration Security Patterns
While Azure emphasizes modern cloud-native applications, many organizations maintain legacy systems requiring secure integration with cloud services. Understanding how to implement Azure AD Application Proxy for publishing on-premises applications to remote users, configure hybrid identity scenarios synchronizing on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD, and secure ExpressRoute connections linking on-premises networks to Azure demonstrates comprehensive security knowledge. These hybrid scenarios require understanding both cloud-native security controls and how they integrate with traditional security perimeters.
Hybrid environment security requires bridging modern cloud security with traditional datacenter approaches that organizations maintain during cloud migration journeys. The integration complexity parallels considerations in legacy platform certification paths where new and old technologies coexist. Practice deploying Azure AD Connect for hybrid identity, understanding synchronization options including password hash sync, pass-through authentication, and federation with on-premises AD FS. Implement Application Proxy connectors in on-premises environments, configuring backend application access and pre-authentication requirements. Configure ExpressRoute with appropriate encryption and access controls, understanding how private peering enables secure connectivity to Azure virtual networks while Microsoft peering provides optimized routes to Microsoft services.
Implementing Advanced Threat Protection Features
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps (formerly Cloud App Security) provides cloud access security broker (CASB) functionality, discovering shadow IT through proxy integration or log collection, enforcing access policies, detecting threats in cloud application usage, and protecting sensitive information across sanctioned and unsanctioned applications. Understanding how to configure Cloud App Security policies, investigate anomalous user behavior, and integrate with conditional access for real-time access control based on session risk represents advanced security knowledge. Candidates should understand cloud application discovery, risk scoring, and appropriate responses to identified risks.
Advanced threat detection capabilities leverage machine learning and behavioral analytics to identify sophisticated attacks that signature-based detection misses. The intelligent threat identification parallels analytical methodologies in specialized business application security certifications requiring pattern recognition. Practice configuring Cloud App Security policies that trigger on anomalous download volumes, unusual administrative activities, or access from suspicious locations, understanding how to tune sensitivity balancing detection against false positives. Implement session policies integrated with conditional access, enforcing real-time controls like preventing downloads from unmanaged devices or blocking uploads of sensitive documents to personal accounts. Review cloud discovery dashboards identifying unsanctioned applications with high risk scores, then implement policies blocking or limiting access to problematic applications.
Managing Customer Engagement Security
Customer relationship management systems contain sensitive customer information requiring comprehensive protection through access controls, data loss prevention, and audit logging. Understanding how to implement security for Dynamics 365 customer engagement applications, configure record-level security that limits access based on user roles and relationships, and enable field-level security protecting sensitive attributes demonstrates security knowledge applicable to business applications beyond pure infrastructure. These scenarios require understanding both platform security capabilities and how to configure them appropriately for business requirements.
Business application security requires understanding data models and business processes to implement meaningful security aligned with organizational access requirements. The domain-specific security knowledge parallels expertise developed through customer engagement certifications emphasizing platform capabilities. Practice implementing security roles in Dynamics 365 defining create, read, write, delete, append, and assign privileges across business entities. Configure record-level security through business units and hierarchical security models limiting access based on organizational structures. Implement field-level security protecting sensitive attributes like social security numbers or credit card information, ensuring only users with legitimate needs can view protected fields.
Securing Marketing Automation Platforms
Marketing platforms process customer data for segmentation, campaign execution, and analytics, requiring security controls that protect personally identifiable information while enabling marketing operations. Understanding how to implement consent management, configure data retention policies meeting regulatory requirements like GDPR, and secure integration between marketing platforms and customer data sources represents practical security knowledge. These scenarios demonstrate applying security principles to specialized business applications where compliance requirements intersect with operational needs.
Marketing technology security requires balancing data accessibility for marketing effectiveness against privacy protection and regulatory compliance. The nuanced approach reflects considerations in marketing platform certifications where business capability and compliance intersect. Practice implementing consent management in Dynamics 365 Marketing, capturing and respecting customer preferences for communication channels and data usage. Configure data retention policies automatically removing personal information after specified periods, meeting GDPR's data minimization principles. Implement lead scoring and segmentation that leverages customer data while applying appropriate access controls preventing unauthorized personal information exposure.
Managing Finance and Operations Security
Finance and operations applications handle sensitive financial data and operational information requiring comprehensive security including segregation of duties, audit logging, and access controls aligned with financial regulations. Understanding how to implement security roles with appropriate privilege separation, configure audit workbench for compliance monitoring, and secure integration between finance applications and external systems demonstrates security knowledge applicable to ERP implementations. These scenarios require understanding both security controls and business processes they protect.
Enterprise resource planning security requires deep understanding of business processes and regulatory requirements beyond pure technical controls. The comprehensive approach parallels preparation for finance and operations certifications emphasizing business and technical integration. Practice implementing segregation of duties rules preventing individual users from combining incompatible privileges like creating and approving purchase orders. Configure audit policy capturing changes to master data, financial transactions, and security configuration, ensuring compliance evidence for internal and external auditors. Implement security roles aligned with job functions, granting minimum necessary privileges rather than excessive permissions that increase fraud and error risks.
Implementing Distribution and Trade Security
Distribution and trade operations involve supply chain partners, international transactions, and logistics requiring security controls around data sharing, authentication for partner access, and protection of trade secrets. Understanding how to implement partner access through Azure AD B2B collaboration, configure data loss prevention for trade-sensitive information, and secure APIs enabling partner integration demonstrates practical security knowledge applicable beyond the exam. These scenarios require balancing collaboration requirements against intellectual property protection and competitive information security.
Trade and distribution security involves complex multi-party scenarios with varying trust levels and access requirements. The sophisticated security architecture reflects considerations in distribution management certifications emphasizing partner ecosystems. Practice implementing Azure AD B2B collaboration with conditional access policies requiring partners to authenticate from compliant devices or specific geographic locations. Configure Azure Information Protection labels identifying trade-sensitive documents with automatic encryption and usage restrictions preventing unauthorized forwarding or copying. Implement API Management policies for partner-facing APIs, enforcing subscription keys, rate limiting, and IP filtering that prevents abuse while maintaining necessary integration.
Securing Email and Messaging Platforms
Email represents primary attack vector for most organizations, requiring comprehensive security including anti-phishing protection, malware scanning, data loss prevention, and encryption for sensitive communications. Understanding how to configure Exchange Online Protection, implement Microsoft Defender for Office 365, and deploy Azure Information Protection for email classification demonstrates security knowledge relevant to defending against common threat vectors. These scenarios require understanding both technical controls and security awareness training requirements ensuring users recognize and report suspicious emails.
Messaging security requires layered defenses addressing diverse threat types from credential phishing to malware delivery. The comprehensive protection approach parallels emphasis in messaging platform certifications on security and compliance. Practice configuring anti-phishing policies in Defender for Office 365, implementing impersonation protection, mailbox intelligence, and advanced phishing thresholds. Enable Safe Attachments and Safe Links protecting against malicious email attachments and embedded URLs by detonating in sandbox environments before delivery. Implement data loss prevention policies scanning outbound email for sensitive information patterns like credit card numbers or social security numbers, blocking or encrypting messages containing protected data.
Managing Unified Communications Security
Unified communications platforms including Teams and Skype for Business require security controls around meeting access, data sharing, and external collaboration. Understanding how to configure Teams security policies limiting external user capabilities, implement information barriers preventing communication between competing business units, and deploy retention policies meeting compliance requirements demonstrates security knowledge applicable to modern collaboration platforms. These scenarios require balancing security controls against collaboration needs ensuring productivity while maintaining protection.
Collaboration platform security must enable productive communication while preventing unauthorized access and data leakage. The balanced approach reflects considerations in unified communications certifications emphasizing user experience and security. Practice configuring Teams external access policies controlling whether users can communicate with external domains, implementing allow lists for trusted partners while blocking anonymous participants in meetings. Implement information barriers preventing users in competing business units from communicating, finding each other in directory searches, or being added to common Teams channels. Configure retention policies capturing and preserving Teams messages and files for compliance requirements, understanding implications for storage and eDiscovery.
Implementing SharePoint and OneDrive Security
Document collaboration platforms require security controls protecting information at rest and in transit while enabling sharing for collaboration. Understanding how to configure SharePoint site permissions, implement Azure Information Protection integration for document classification, and deploy data loss prevention for OneDrive demonstrates security knowledge applicable to content management platforms. These scenarios require balancing information protection against collaboration requirements ensuring users can share appropriately while preventing accidental or malicious data exposure.
Content collaboration security requires granular access controls and automated protection for documents based on sensitivity classifications. The comprehensive protection approach reflects emphasis in collaboration platform certifications on information governance. Practice implementing SharePoint permission inheritance patterns limiting access to sites, libraries, folders, and individual documents based on business requirements. Configure Azure Information Protection integration enabling users to classify documents directly from Office applications, automatically applying encryption and usage restrictions based on labels. Implement data loss prevention policies scanning SharePoint and OneDrive content for sensitive information, blocking external sharing of protected documents while allowing internal collaboration.
Managing Server Infrastructure Security
While Azure emphasizes platform and software services, organizations maintain virtual machines requiring traditional server security including patch management, antimalware protection, and security baseline enforcement. Understanding how to implement Azure Policy guest configuration that audits and remediates VM operating system settings, deploy Azure Automation update management, and configure Microsoft Defender for servers demonstrates security knowledge bridging infrastructure-as-a-service and managed services. These scenarios require understanding both server security fundamentals and Azure management plane capabilities.
Virtual machine security requires maintaining operating system and application security postures through continuous compliance monitoring and remediation. The comprehensive approach parallels emphasis in server infrastructure certifications on security and management. Practice implementing Azure Policy guest configuration policies auditing Windows server security baselines, automatically remediating deviations from approved configurations. Configure Azure Automation update management deploying operating system patches on defined schedules while allowing testing windows before production deployment. Enable Microsoft Defender for servers providing adaptive application controls that whitelist known-good applications, file integrity monitoring detecting unauthorized changes to critical files, and just-in-time VM access eliminating standing administrative port exposure.
Implementing Active Directory Integration Security
Organizations maintaining on-premises Active Directory require secure integration with Azure AD through synchronization mechanisms, hybrid authentication methods, and careful privilege management. Understanding how to secure Azure AD Connect servers, implement cloud-only administrative accounts for emergency access, and configure password writeback security demonstrates security knowledge applicable to hybrid identity scenarios. These scenarios require understanding both on-premises Active Directory security and cloud identity protection, ensuring neither environment creates vulnerabilities exploitable to compromise the other.
Hybrid identity security requires protecting synchronization infrastructure and carefully managing accounts with administrative privileges spanning both environments. The comprehensive security approach reflects considerations in Active Directory certifications emphasizing identity protection. Practice securing Azure AD Connect servers through restricted access, disabling unnecessary protocols, and implementing security monitoring for synchronization account activities. Create cloud-only break-glass administrative accounts stored in secure locations, enabling emergency Azure access if on-premises Active Directory becomes unavailable or compromised. Configure password writeback with appropriate network security and encryption, understanding security implications of allowing password changes in Azure AD to flow back to on-premises Active Directory.
Managing Group Policy and Configuration Management Security
Group policy and modern device management provide mechanisms for enforcing security configurations across managed endpoints. Understanding how to design Group Policy Objects implementing security baselines, configure Windows Update for Business through Intune, and implement configuration profiles for iOS and Android demonstrates security knowledge applicable to endpoint management. These scenarios require understanding both security requirements and appropriate mechanisms for enforcement across diverse device types and management approaches.
Endpoint configuration management security requires consistent policy enforcement while accommodating diverse device types and operating systems. The comprehensive approach parallels emphasis in infrastructure management certifications on policy and compliance. Practice implementing Windows Security Baselines through Group Policy or Intune, enforcing settings like required antivirus, firewall configuration, and security update installation. Configure Windows Update for Business policies defining update deferrals, quality update deadlines, and feature update behavior balancing security currency against stability requirements. Implement mobile device management configuration profiles restricting device features, requiring encryption, and enforcing passcode complexity across BYOD and corporate-owned mobile devices.
Conclusion
The comprehensive journey through AZ-500 exam preparation reveals that Azure security mastery extends far beyond memorizing service names and configuration options to encompass deep understanding of security principles, threat landscapes, and practical implementation skills applicable across diverse scenarios. The exam's emphasis on scenario-based questions testing your ability to select appropriate security controls for specific situations reflects real-world security work where context determines optimal approaches rather than one-size-fits-all solutions. Successful candidates demonstrate not just knowledge of what Azure security services exist but judgment about when to apply specific controls, how to combine multiple protections for defense-in-depth, and skill troubleshooting security implementations that don't behave as expected.
Career planning beyond initial AZ-500 certification acknowledges that single credentials rarely constitute complete professional development, instead representing milestones in longer learning journeys. Azure security expertise opens doors to specialized roles including cloud security architect, Azure security consultant, and compliance specialist where security knowledge combines with business acumen and communication skills. The certification also serves as a foundation for advanced credentials like Azure Solutions Architect Expert or Cybersecurity Architect Expert, creating progressive pathways toward senior leadership positions. Understanding these progression options helps maintain motivation through challenging preparation periods while providing a framework for long-term skill development extending throughout your security career.
The complementary relationship between Azure-specific security knowledge and general cybersecurity principles suggests value in balancing platform-specific certifications with foundational security credentials providing broader understanding. While the AZ-500 validates Azure implementation skills, general certifications like CISSP or CEH develop security thinking applicable across technologies and platforms, making you more adaptable as cloud platforms evolve and new technologies emerge. This balanced approach creates T-shaped professionals with both deep Azure expertise and broad security knowledge, maximizing career flexibility and problem-solving capability.
The dynamic nature of cloud security where services continuously add features, threat actors develop new attack techniques, and best practices evolve based on collective experience demands commitment to continuous learning extending beyond exam preparation. The study habits and learning strategies developed during AZ-500 preparation serve you throughout your career as frameworks for approaching new topics, evaluating new services, and maintaining current knowledge despite rapid change. Following Microsoft security blogs, participating in Azure community forums, and maintaining hands-on practice with emerging features ensures your security knowledge remains current and valuable rather than becoming obsolete as platforms evolve.
The examination itself represents a significant but temporary challenge in your longer security career journey. While passing the AZ-500 validates important baseline competency, true security expertise develops through years of practical experience implementing security controls, responding to incidents, and adapting to evolving threats. The certification opens opportunities for gaining this experience in roles that might otherwise prove inaccessible, making exam success valuable not for the credential itself but for opportunities it enables. Approach the test as a milestone rather than destination, maintaining the perspective that the deep learning occurring during preparation proves more valuable than the score report acknowledging your passing.
The comprehensive coverage across these three detailed preparation guides provides a roadmap for systematic study addressing all exam domains while building practical skills translating to real-world effectiveness. The emphasis on understanding underlying principles rather than merely memorizing configuration steps creates a foundation supporting not just exam success but career-long adaptability as Azure services evolve and security challenges transform. The specific techniques, study strategies, and knowledge frameworks presented throughout this guide represent distilled wisdom from security professionals and certification experts who have navigated similar journeys, offering you shortcuts and insights that accelerate your preparation while deepening your understanding.
Your commitment to Azure security specialization through AZ-500 certification represents significant professional investment reflecting both current career goals and long-term vision for contributing meaningfully to organizational security in an increasingly cloud-dependent world. The knowledge and skills you develop through preparation serve organizations protecting critical systems and data from sophisticated threats, making your work genuinely important beyond personal career advancement. This sense of purpose can sustain you through challenging study periods, reminding you that temporary discomfort developing expertise yields lasting capability protecting organizations and individuals from very real threats.
As you begin or continue your AZ-500 preparation journey, remember that successful candidates universally report that systematic preparation following structured study plans proves essential for success given the exam's breadth and depth. The investment of time and focused effort required for thorough preparation—typically 6-8 weeks of daily study for most candidates—represents an entirely reasonable price for credentials, opening doors to rewarding career opportunities in high-demand fields. Trust the systematic process outlined throughout these guides, maintain consistency through inevitable challenging periods, and celebrate incremental progress as you systematically build toward comprehensive Azure security mastery culminating in both certification success and genuine capability protecting cloud environments effectively.
Microsoft Azure Security AZ-500 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass AZ-500 Microsoft Azure Security Technologies certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-388 - Introduction to Programming Using Java
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- MB-900 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
Purchase AZ-500 Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the AZ-500 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the AZ-500 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the AZ-500 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The AZ-500 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the AZ-500 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for AZ-500. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the AZ-500 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my AZ-500 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the AZ-500 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed AZ-500 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

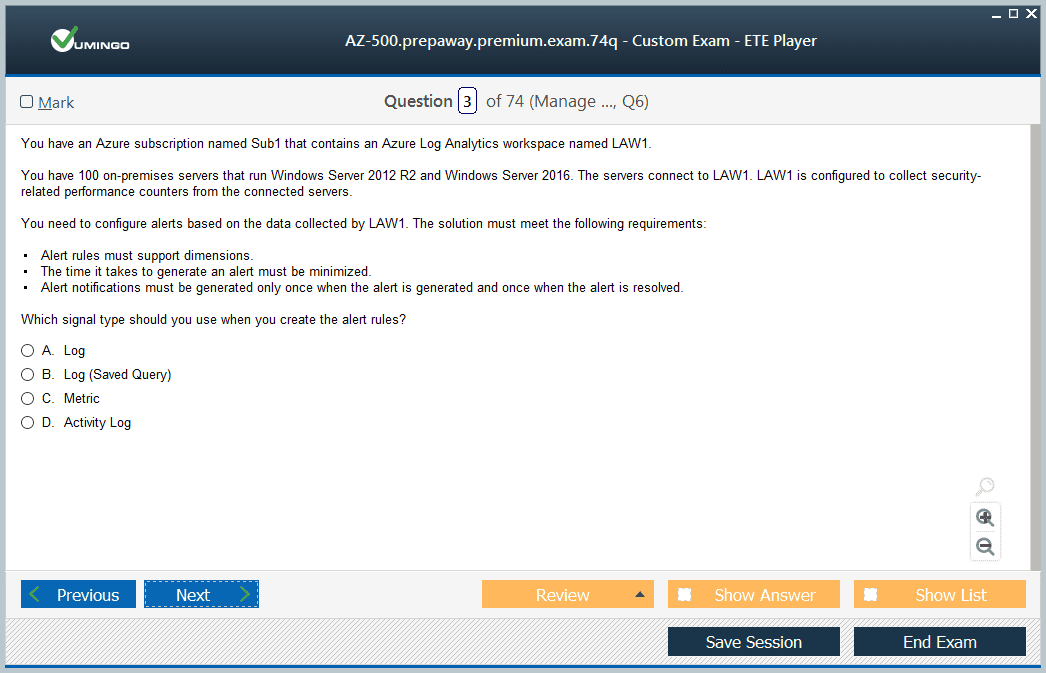
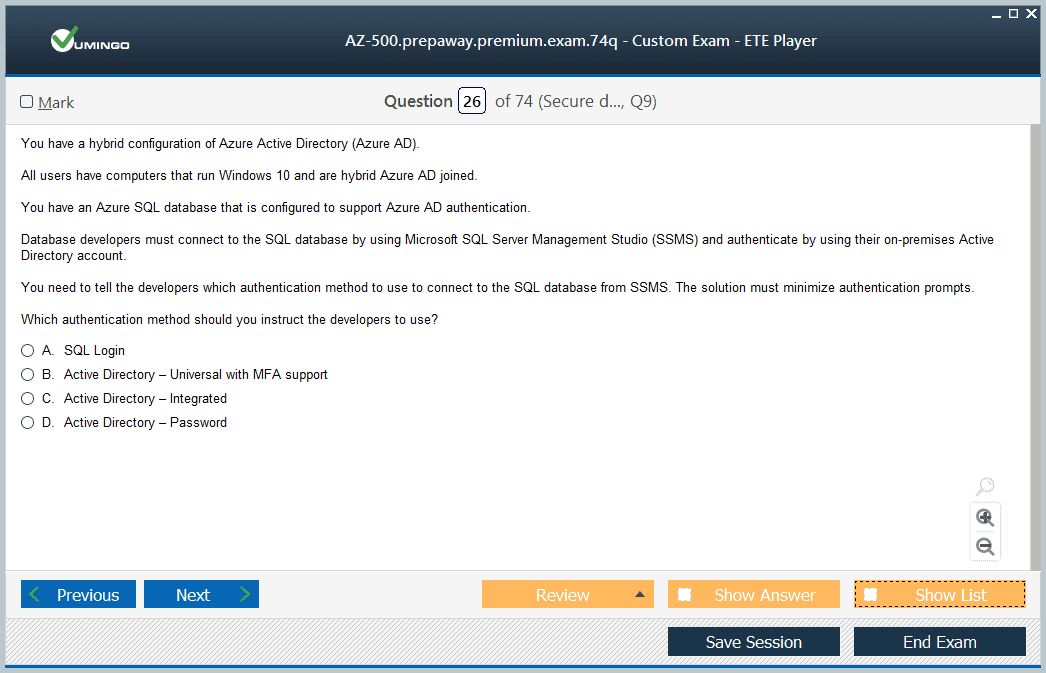
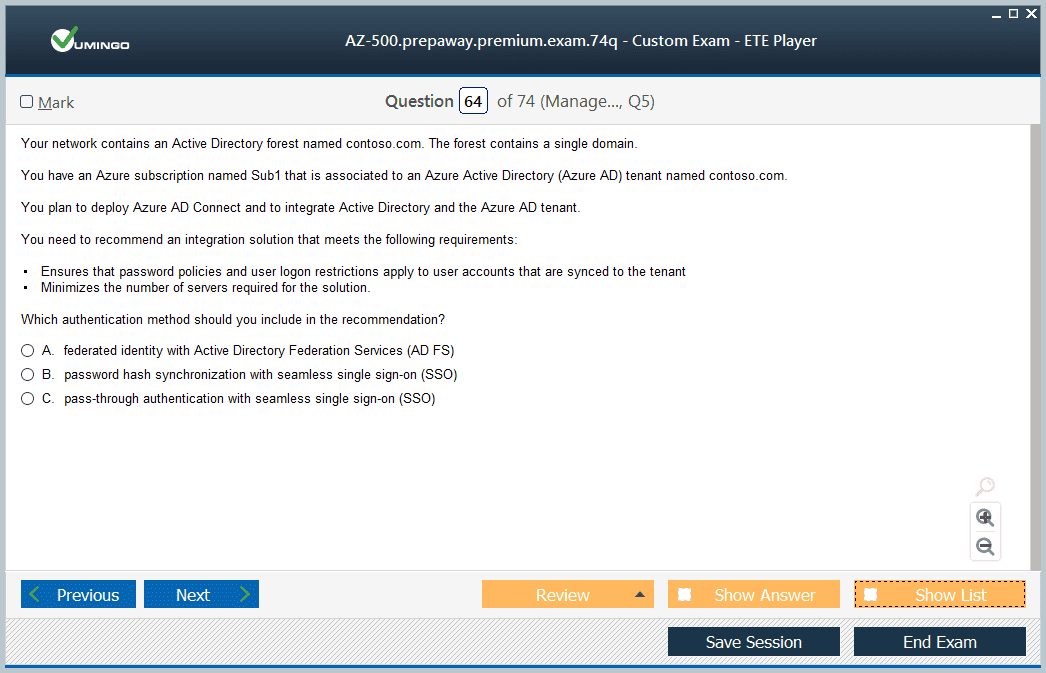
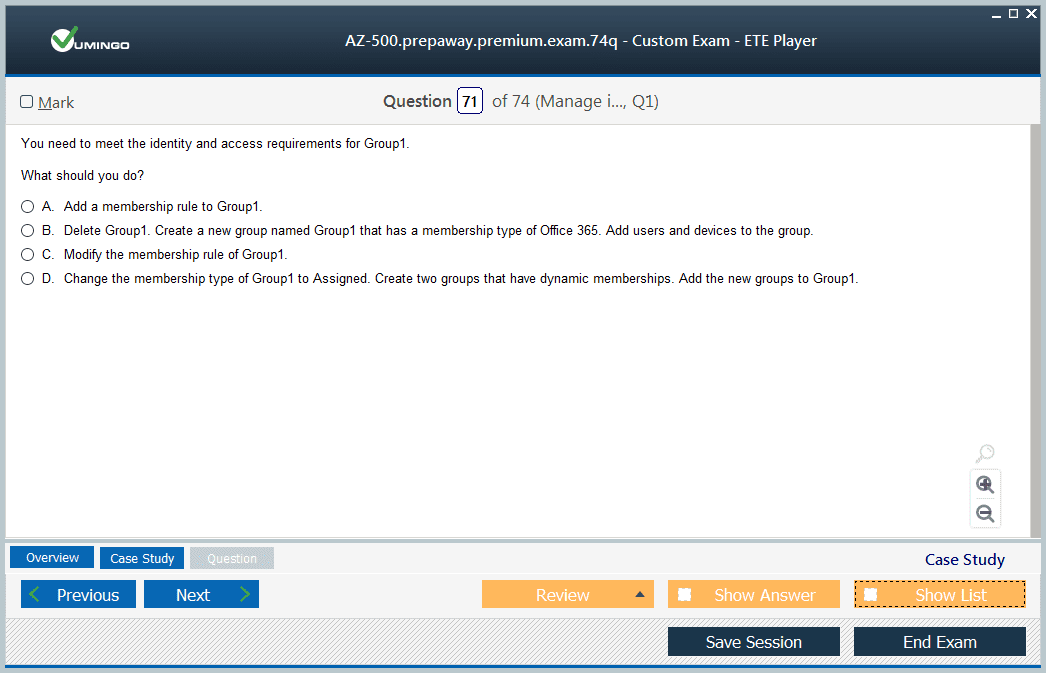








Can you please confirm if these questions and simulator are updated as per new Microsoft new updates of June 2, 2021? Please let me know as I need to write the exam soon.
Thank you