- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 70-761 Querying Data with Transact-SQL Dumps
Pass Microsoft MCSA 70-761 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


70-761 Premium File
- Premium File 213 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Feb 22, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Microsoft MCSA 70-761 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 70-761 Querying Data with Transact-SQL practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for Exam 70-761
In the current landscape of database management and development, proficiency in querying data is one of the most crucial skills an IT professional can possess. The ability to efficiently write and optimize queries using Transact-SQL forms the backbone of data handling, reporting, and application support across organizations. Professionals who master these skills are better positioned to manage large-scale databases, ensure data integrity, and enable decision-makers to access accurate and timely information.
The Querying Data with Transact-SQL exam evaluates a candidate’s capability to not only write basic queries but also handle complex scenarios involving multiple tables, advanced filtering, and data aggregation. It measures both practical understanding and the ability to implement solutions that can scale with enterprise demands. Candidates who focus on mastering this skill set gain a competitive edge as they demonstrate their ability to address real-world data challenges efficiently.
Core Skills and Knowledge Areas
The exam emphasizes several key areas essential for proficient data management. These areas include creating SELECT statements to retrieve and manipulate data, applying joins to combine information from multiple tables, and using aggregate functions to summarize information. Candidates must also demonstrate competency in subqueries, table expressions, and more advanced query constructs that allow for dynamic and flexible data retrieval.
Understanding how to handle temporal and non-relational data, transform data using pivot and unpivot operations, and create robust views and stored procedures are additional components that highlight a candidate’s depth of knowledge. Equally important is the ability to implement error handling, manage transactions, and work effectively with various data types and null values. Mastery of these areas ensures that professionals can write reliable, high-performance queries that support organizational objectives.
Exam Structure and Format
The exam is structured to assess both practical and theoretical knowledge through a variety of question types. Candidates typically encounter multiple-choice questions, scenario-based questions, and tasks that require writing or analyzing Transact-SQL code. The duration of the exam and the number of questions provide sufficient scope to evaluate a candidate’s ability to think critically and solve problems efficiently under time constraints.
Passing this exam requires a score that demonstrates proficiency in the core domains. Preparation should focus on both understanding the syntax and semantics of Transact-SQL and developing the ability to apply knowledge in practical scenarios. Candidates benefit from a balanced approach that combines theoretical study with hands-on practice in querying databases.
Practical Applications in the Workplace
Proficiency in Transact-SQL enables professionals to support a wide range of business functions. This includes data reporting, application development, business intelligence, and analytics. Candidates who have mastered the required skills can create optimized queries that retrieve data accurately and efficiently, contributing to better decision-making within the organization.
Advanced capabilities such as implementing joins, working with subqueries, and using set operators allow professionals to solve complex data challenges. Creating views and stored procedures streamlines database operations and ensures consistency in data handling. Understanding error handling and transaction management further enhances the reliability and stability of database systems.
Target Audience and Required Experience
The exam is aimed at professionals who have practical experience with SQL Server and relational database concepts. Ideal candidates include database developers, database administrators, and IT professionals involved in application development or data management. Prior experience with database design, query writing, and transactional data processing is highly recommended to ensure readiness for the exam.
Candidates should have hands-on familiarity with creating, modifying, and executing queries, as well as managing database programmability objects. Experience with real-world database environments allows candidates to approach exam scenarios with confidence and apply solutions effectively.
Exam Domains in Detail
The exam covers several interconnected domains, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of Transact-SQL.
Managing Data with Transact-SQL: This domain emphasizes the ability to retrieve and modify data using SELECT statements, joins, and aggregate functions. Candidates also need to demonstrate skills in applying functions, filtering data, and managing modifications efficiently.
Querying Data with Advanced Components: Focuses on subqueries, table expressions, and grouping or pivoting data. Candidates learn to handle temporal and non-relational datasets and implement complex query constructs that provide flexible and optimized solutions.
Programming Databases with Transact-SQL: Covers creating and managing programmability objects, implementing error handling, managing transactions, and working with various data types and null values. This ensures that candidates can maintain database integrity and handle exceptions effectively.
Preparation Strategies for Success
Effective preparation combines structured study, practical exercises, and familiarity with exam objectives. Candidates should allocate dedicated time to mastering query writing, data transformation, and database programming. Understanding the objectives thoroughly and mapping them to hands-on exercises ensures comprehensive readiness.
Working with sample databases or sandbox environments allows candidates to practice creating queries, implementing stored procedures, and performing data transformations. This experiential learning reinforces theoretical concepts and builds confidence in applying skills under exam conditions.
Training Resources and Learning Approaches
Structured training programs provide guided learning paths that cover the full scope of the exam. These programs include lessons on SQL Server capabilities, basic and advanced SELECT statements, joins, subqueries, table expressions, error handling, and transaction management.
Instructor-led sessions and self-paced modules help candidates develop a strong foundation in Transact-SQL. Practice exercises embedded in these programs simulate real-world scenarios, allowing candidates to apply their knowledge and refine their problem-solving techniques.
Study Materials and References
A variety of resources are available to support preparation. Books and reference materials focus on query writing, data transformation, and database programmability. These resources provide explanations, examples, and exercises aligned with exam objectives, enabling candidates to build both conceptual understanding and practical skills.
Consistent practice with these resources ensures that candidates gain proficiency in executing queries, creating views, implementing stored procedures, and handling complex data transformations. The goal is to develop the ability to respond confidently to exam tasks while reinforcing skills applicable in professional environments.
Practicing Queries and Real-World Application
Hands-on practice is crucial for mastering the skills required for the exam. Writing queries, performing joins, and aggregating data repeatedly helps candidates internalize key concepts. Simulating real-world scenarios, such as transforming datasets, managing transactions, and handling errors, provides practical experience that mirrors professional challenges.
Through consistent practice, candidates can identify areas for improvement and build strategies for efficient query writing. This process not only prepares them for the exam but also equips them with skills directly applicable to day-to-day database operations.
Creating a Study Plan
Developing a structured study plan ensures that candidates cover all exam domains systematically. Allocating time for each objective, balancing theoretical study with practical exercises, and tracking progress helps maintain focus and momentum. A well-organized plan allows candidates to approach preparation methodically, reducing the risk of gaps in knowledge and building confidence for the exam.
Candidates should schedule regular practice sessions, review complex concepts, and apply problem-solving techniques to a variety of scenarios. This approach enables comprehensive coverage of all necessary skills while fostering a deeper understanding of Transact-SQL capabilities.
Strengthening Problem-Solving Skills
Beyond memorizing syntax, the exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to apply logic and problem-solving techniques. Developing proficiency in designing efficient queries, optimizing performance, and troubleshooting errors is essential. Candidates benefit from exercises that challenge them to analyze data requirements, select appropriate query methods, and implement solutions that maintain data accuracy and integrity.
By focusing on problem-solving skills, candidates enhance their readiness for both the exam and real-world database management tasks. This holistic preparation ensures that they can handle unexpected challenges and deliver effective solutions in professional settings.
Understanding Advanced Query Techniques
Advanced techniques such as using subqueries, table expressions, and set operators allow candidates to handle more complex data requirements. Implementing pivot and unpivot operations, aggregating data using grouping sets, and outputting results in structured formats like XML or JSON are critical for modern database management.
Mastery of these techniques ensures that candidates can design queries that are both efficient and adaptable, supporting dynamic reporting and analytical needs. It also demonstrates the ability to think critically and approach database problems with structured solutions.
Emphasizing Transaction Management and Error Handling
Managing transactions and implementing robust error handling are crucial skills for database professionals. Candidates must understand how to ensure data consistency, handle exceptions, and maintain system reliability. These capabilities are not only tested in the exam but also reflect essential workplace competencies.
Practicing scenarios involving transactions, rollbacks, and error detection reinforces understanding and prepares candidates for both the exam and real-world database operations. It builds confidence in managing complex interactions within the database while maintaining integrity and performance.
Achieving mastery in querying data with Transact-SQL requires a combination of theoretical understanding, practical experience, and disciplined preparation. Candidates who thoroughly practice query writing, data manipulation, and database programming develop the skills necessary to handle complex data environments effectively.
Passing the exam validates proficiency in these areas and enhances career prospects, positioning candidates as capable professionals in database management and development. Focused preparation, consistent practice, and a strategic approach ensure readiness for the exam while building a foundation for long-term success in SQL Server roles.
Mastery of Transact-SQL equips professionals to deliver reliable, efficient, and scalable database solutions, making them valuable assets in any organization that relies on data-driven decision-making.
Building Competency in Data Retrieval
Developing expertise in data retrieval is fundamental to becoming proficient in Transact-SQL. Candidates preparing for the exam should focus on understanding how to structure queries that efficiently extract meaningful information from relational databases. This includes mastering the use of SELECT statements to fetch specific columns, applying filtering criteria with WHERE clauses, and ordering results using ORDER BY. Each of these components contributes to the ability to manipulate and present data in a way that meets the needs of applications and reporting systems.
In addition to basic queries, candidates must be able to perform operations across multiple tables using joins. Inner joins, outer joins, and cross joins allow for flexible data retrieval and are essential for working with normalized database structures. Proper use of joins ensures that data integrity is maintained while extracting relevant information from interconnected tables.
Utilizing Functions and Aggregation
Functions play a critical role in transforming and analyzing data. Candidates should focus on mastering built-in functions for string manipulation, date and time calculations, and numeric operations. These functions allow queries to generate precise outputs and support complex calculations without additional processing in applications.
Aggregation functions such as SUM, COUNT, AVG, MIN, and MAX provide the ability to summarize data efficiently. Learning to combine these functions with GROUP BY clauses enables candidates to produce reports that provide insights into business trends and operational performance. Understanding the nuances of aggregation and its impact on query results is crucial for both the exam and practical database work.
Advanced Query Techniques
Beyond basic queries, the exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to work with advanced components. Subqueries, including correlated and non-correlated subqueries, allow for nested data retrieval and dynamic data comparisons. Table expressions, such as common table expressions and derived tables, provide temporary result sets that simplify complex queries and enhance readability.
Candidates should also understand grouping sets, rollup, and cube operations, which allow for multi-dimensional analysis within queries. Pivot and unpivot operations enable data transformation to present results in a more analytical format, supporting decision-making processes. These techniques demonstrate an advanced understanding of Transact-SQL capabilities and are critical for the exam.
Working with Temporal and Non-Relational Data
Handling temporal data requires understanding how to query historical and versioned records. Candidates should be able to apply time-based filtering and retrieve data that reflects changes over specified intervals. This skill is essential for auditing, reporting, and maintaining accurate historical records within databases.
Non-relational data handling, including JSON and XML formats, allows candidates to work with semi-structured information commonly used in modern applications. Being able to parse, query, and transform such data ensures that professionals can integrate diverse data sources into SQL-based systems effectively.
Creating Views and Stored Procedures
Views provide a method for encapsulating queries, creating reusable and consistent data access patterns. Candidates must understand how to create, modify, and manage views, ensuring that they reflect the underlying data accurately and efficiently. Views simplify application development and reporting by providing a consistent interface to complex queries.
Stored procedures enable the encapsulation of business logic within the database. Candidates should be able to create procedures that accept parameters, perform conditional logic, and execute transactional operations. Stored procedures improve maintainability, enforce security, and optimize performance by reducing repetitive query execution.
Implementing Error Handling and Transactions
Robust error handling ensures that queries and procedures can respond to unexpected conditions without compromising data integrity. Candidates must understand the use of TRY...CATCH blocks, error messages, and appropriate rollback mechanisms. This knowledge is essential for maintaining reliable database operations and for demonstrating practical competence in real-world environments.
Transaction management is equally critical. Candidates should be able to begin, commit, and rollback transactions to ensure that changes are applied consistently. Understanding isolation levels and concurrency control helps prevent data conflicts and supports reliable multi-user environments.
Data Types and Null Management
A solid understanding of data types is fundamental for effective database design and query optimization. Candidates should be able to choose appropriate data types for columns, understand type conversions, and anticipate the implications of storing different kinds of data.
Handling NULL values correctly is essential, as they represent unknown or missing information. Candidates must understand how NULL affects comparisons, aggregation, and query results. Proper management of NULL values ensures that queries produce accurate and expected outputs.
Exam Strategy and Time Management
Effective exam preparation requires a structured approach that balances theory and practice. Candidates should allocate time to review each domain thoroughly, practice queries, and solve sample problems. Time management during the exam is equally important, as the ability to complete tasks accurately within the allotted duration reflects practical proficiency.
Working through scenario-based questions helps candidates develop critical thinking skills. These questions often simulate real-world challenges, requiring the application of multiple concepts simultaneously. Practicing with these scenarios ensures that candidates can approach complex problems systematically and efficiently.
Practical Applications and Hands-On Experience
Hands-on practice with SQL Server environments reinforces theoretical knowledge. Candidates benefit from creating sample databases, inserting and updating data, and performing queries across multiple tables. Experimenting with complex query constructs, error handling, and transactions develops confidence in handling diverse scenarios.
Using practical exercises to simulate real-world conditions, such as performance optimization, data transformation, and procedural implementation, bridges the gap between exam preparation and workplace readiness. This experience is invaluable for both passing the exam and succeeding as a SQL professional.
Leveraging Study Materials and References
A wide range of study materials supports preparation. Comprehensive books and guides provide detailed explanations, examples, and practice exercises that align with exam objectives. Candidates should prioritize materials that emphasize query writing, data manipulation, and database programming.
Structured study ensures that candidates address all critical areas, including data retrieval, aggregation, advanced queries, and transaction management. Consistent practice with these materials builds proficiency and reinforces the understanding of complex concepts, preparing candidates for both the exam and practical database work.
Applying Critical Thinking in Query Design
Success in the exam depends not only on memorizing syntax but also on applying logical reasoning. Candidates must analyze data requirements, determine the most efficient query methods, and implement solutions that maintain integrity and performance. This approach demonstrates the ability to think critically and adapt strategies based on data challenges.
Critical thinking skills are cultivated through repeated exposure to complex scenarios. Candidates learn to evaluate different approaches, anticipate potential issues, and optimize query performance. These skills are transferable to professional roles, ensuring that candidates can manage data effectively in diverse environments.
Optimizing Queries for Performance
Performance optimization is a key aspect of advanced Transact-SQL proficiency. Candidates should understand indexing, execution plans, and query optimization techniques. Writing queries that minimize resource usage while maximizing accuracy is essential for handling large-scale databases and ensuring responsive applications.
Optimization techniques include proper indexing strategies, reducing unnecessary joins, and using set-based operations instead of row-by-row processing. Mastery of these strategies demonstrates an understanding of both theoretical and practical aspects of database management.
Integrating Learning with Real-World Scenarios
Preparing for the exam involves connecting theoretical knowledge with real-world applications. Candidates benefit from working on sample databases that simulate enterprise environments. This integration ensures that skills learned during preparation can be applied directly to professional tasks, enhancing both exam readiness and workplace competence.
Scenario-based exercises, such as managing transactions, implementing error handling, and transforming data, reinforce the application of concepts. These exercises enable candidates to approach problems systematically, develop efficient solutions, and validate results through practical execution.
Reinforcing Knowledge Through Repetition
Repetition is essential for internalizing complex concepts. Candidates should practice writing queries, implementing stored procedures, and managing transactions multiple times to reinforce their understanding. Repeated exposure to various scenarios ensures that knowledge becomes intuitive, reducing errors and increasing confidence during the exam.
Regular practice also allows candidates to identify areas where additional focus is needed. By systematically addressing weaknesses, candidates can ensure comprehensive mastery of all exam domains.
Building Confidence Through Practice Tests
Practice tests simulate the conditions of the actual exam, providing candidates with an opportunity to assess their readiness. These tests highlight areas that require further study and help candidates develop effective time management strategies.
Engaging in multiple practice tests ensures that candidates are familiar with question formats, can navigate complex scenarios efficiently, and are prepared to apply critical thinking under time constraints.
Developing a Structured Study Plan
A structured study plan organizes preparation activities, ensuring coverage of all critical domains. Allocating dedicated time for reading, hands-on practice, and review of complex concepts ensures balanced and comprehensive preparation.
Candidates should set realistic goals, track progress, and adjust their study plan based on performance in practice exercises. This structured approach fosters consistent progress and builds confidence for the exam.
Understanding Exam Objectives Fully
Thorough comprehension of exam objectives guides focused preparation. Candidates should review each domain, understand its subtopics, and ensure that practical exercises align with these objectives. Mastery of objectives such as data management, advanced query techniques, and database programmability ensures readiness for all aspects of the exam.
Focusing on objectives allows candidates to prioritize their study, allocate time efficiently, and develop a clear roadmap for exam preparation. This systematic approach maximizes both learning and exam performance.
Applying Knowledge in Professional Contexts
Mastery of Transact-SQL extends beyond the exam. Professionals who develop these skills can contribute to efficient data management, reporting, and application development. Writing optimized queries, managing transactions, and implementing error handling are critical skills that enhance productivity and support organizational goals.
Practical application of knowledge ensures that candidates are not only prepared for the exam but also capable of delivering value in their professional roles. These skills are transferable across multiple projects and database environments, enhancing career prospects.
Strengthening Problem-Solving Capabilities
Problem-solving is a core skill assessed in the exam. Candidates should focus on applying logical reasoning, evaluating alternative solutions, and selecting the most efficient approach. Working on real-world scenarios, such as transforming datasets or handling transactional operations, reinforces these capabilities.
Developing strong problem-solving skills ensures that candidates can approach unexpected challenges confidently. This ability is critical for both exam success and professional competence in managing complex database systems.
Enhancing Query Flexibility and Adaptability
The ability to write flexible queries that adapt to changing requirements is an advanced skill. Candidates should practice dynamic query construction, use parameterized queries, and apply modular design principles. This adaptability ensures that queries remain efficient and maintainable even as business requirements evolve.
Flexibility in query design also allows candidates to handle diverse data sources, integrate semi-structured data, and produce results suitable for various analytical needs. Mastery of this skill demonstrates comprehensive understanding and practical competence.
Reinforcing Learning Through Continuous Practice
Continuous practice solidifies knowledge and builds confidence. Candidates should regularly work with sample datasets, execute complex queries, and refine their approaches based on results. This repetition ensures that concepts become second nature and prepares candidates for both exam scenarios and professional challenges.
Practical exercises also foster critical thinking, efficiency, and the ability to handle large-scale data operations. Continuous engagement with hands-on tasks reinforces theoretical knowledge and ensures comprehensive readiness.
Thorough preparation for the Querying Data with Transact-SQL exam requires dedication, practical experience, and strategic planning. Candidates who combine study of theoretical concepts with hands-on practice develop the skills necessary to excel in writing efficient queries, handling complex data operations, and implementing database programmability.
Mastering the exam objectives positions candidates as proficient SQL professionals, capable of delivering high-quality solutions in real-world environments. Consistent practice, structured study, and application of knowledge ensure readiness for the exam while building a foundation for long-term success in data management and development roles.
Mastering Complex Queries
Advanced querying is a critical skill for candidates preparing for the exam. Understanding how to build complex queries that address multifaceted requirements is essential. This includes using subqueries effectively to retrieve and manipulate nested data, employing correlated subqueries to reference outer query results, and implementing APPLY operators to combine table-valued functions with table data. Mastery of these concepts ensures that candidates can handle intricate data retrieval scenarios and demonstrate advanced proficiency in Transact-SQL.
Using Table Expressions for Efficient Data Management
Table expressions, including common table expressions and derived tables, provide temporary datasets that simplify complex operations. Candidates should practice creating and referencing these expressions within queries to improve readability and maintainability. Common table expressions are particularly useful for recursive queries, allowing candidates to address hierarchical data structures efficiently. Derived tables help in modularizing queries and optimizing execution plans, which is crucial for managing large datasets effectively.
Aggregation, Grouping, and Transforming Data
Understanding how to summarize and transform data is vital for data analysis and reporting. Candidates need to practice using aggregation functions like SUM, COUNT, AVG, MIN, and MAX in combination with GROUP BY clauses. Grouping sets, rollup, and cube operations extend this capability by allowing multi-dimensional aggregation, which is important for complex business reporting. Pivot and unpivot operations are also essential, enabling transformation of data from rows to columns and vice versa, providing versatile ways to present results.
Querying Temporal and Semi-Structured Data
Temporal data management involves retrieving historical data or tracking changes over time. Candidates should focus on writing queries that utilize system-versioned tables and temporal filtering to extract relevant data for auditing and trend analysis. Additionally, handling semi-structured data such as JSON and XML within SQL Server requires proficiency in parsing, querying, and transforming data to integrate it with relational datasets. These skills are increasingly important as modern applications frequently combine structured and semi-structured data sources.
Creating and Managing Views
Views offer a layer of abstraction over complex queries, providing reusable and consistent data access. Candidates must understand how to create views that encapsulate frequently used queries, apply filters, and aggregate data appropriately. Updating views, managing indexed views, and ensuring that they remain in sync with underlying tables are key skills. Views not only simplify query logic but also improve security by restricting access to specific columns and rows, which is an essential consideration for professional database environments.
Developing Stored Procedures and Functions
Stored procedures encapsulate business logic and provide reusable, maintainable query routines. Candidates should practice creating procedures with input and output parameters, implementing conditional logic, and managing transactions within procedures. User-defined functions, including scalar and table-valued functions, allow encapsulation of logic for repeated use within queries. Developing proficiency in these programmability features demonstrates the ability to build efficient, modular, and maintainable database solutions.
Implementing Error Handling and Transactions
Robust error handling ensures database operations can respond appropriately to unexpected conditions. Candidates should master the use of TRY...CATCH blocks, error message logging, and proper rollback procedures to maintain data integrity. Transaction management is equally critical; candidates must understand how to implement BEGIN, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK statements to manage atomic operations. Knowledge of isolation levels and concurrency control ensures that transactions maintain consistency and prevent data conflicts in multi-user environments.
Managing Data Types and Null Values
Understanding data types is fundamental to creating efficient and accurate databases. Candidates should focus on selecting appropriate types for storage and computation, understanding type conversion rules, and optimizing queries based on data type considerations. Proper management of NULL values is crucial, as they represent unknown or missing information. Candidates must understand how NULL affects comparisons, aggregations, and conditional logic to prevent unexpected query results.
Optimizing Query Performance
Query optimization is essential for handling large-scale databases. Candidates should practice analyzing execution plans, indexing strategies, and query structures to improve performance. Set-based operations are generally preferred over iterative row-by-row processing for efficiency. Understanding how to leverage indexes, avoid unnecessary joins, and optimize query design ensures that database operations remain fast and scalable under heavy workloads.
Applying Real-World Scenarios
Connecting theoretical knowledge with practical application is key to exam readiness. Candidates should work with sample databases that simulate enterprise environments to practice implementing queries, managing transactions, and executing error handling. Scenario-based exercises provide an opportunity to apply multiple concepts simultaneously, helping candidates develop the problem-solving skills needed in professional roles. These exercises also reinforce the ability to design efficient and maintainable solutions under realistic constraints.
Structured Study and Time Management
Preparing for the exam requires a structured approach that balances theory, practice, and review. Candidates should develop a study plan that allocates sufficient time to each exam domain, ensuring that all objectives are covered thoroughly. Incorporating regular hands-on practice with queries, transactions, and programmability tasks is critical for reinforcing knowledge. Effective time management during preparation and during the exam itself is essential to ensure that candidates can complete tasks accurately and efficiently.
Leveraging Practice Exercises
Repeated practice with sample queries and exercises is vital for reinforcing skills. Candidates should simulate real-world database operations, including data retrieval, transformation, and programmability tasks. Repeated exposure to complex scenarios helps internalize concepts, enhances problem-solving abilities, and builds confidence. Practice exercises also help identify areas where further study is required, ensuring comprehensive readiness for the exam.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
The ability to approach complex problems logically is a core competency for the exam. Candidates should focus on evaluating different solutions, determining the most efficient approach, and applying appropriate Transact-SQL constructs. This includes transforming data, handling exceptions, and managing transactions effectively. Developing these problem-solving skills ensures that candidates can tackle both exam questions and real-world database challenges with confidence.
Building Proficiency Through Repetition
Consistent practice is key to mastering advanced Transact-SQL concepts. Candidates should repeatedly write queries, implement stored procedures, and execute transactions to reinforce learning. This repetition helps solidify understanding, reduces errors, and enhances the ability to recall and apply concepts under exam conditions. Frequent practice also strengthens the candidate’s ability to handle unexpected challenges and complex queries effectively.
Integrating Knowledge Across Domains
Success in the exam requires integrating skills across multiple domains. Candidates should practice combining data retrieval, aggregation, programmability, and error handling into cohesive solutions. This integrated approach reflects real-world scenarios, where multiple skills must be applied simultaneously to achieve efficient and accurate results. Understanding how to coordinate these skills ensures readiness for both the exam and professional responsibilities.
Evaluating and Improving Performance
Regular self-assessment through practice tests and hands-on exercises helps candidates measure progress and identify areas for improvement. Evaluating query efficiency, correctness, and maintainability ensures that candidates are prepared for complex scenarios. Continuous improvement through feedback and iterative practice builds confidence and reinforces the ability to produce reliable solutions in professional environments.
Adapting to Changing Requirements
Candidates should develop flexibility in query design to accommodate evolving requirements. This includes writing dynamic queries, implementing parameterized procedures, and designing modular solutions that can be adapted to new data structures or business needs. Adaptability is essential for professional success and demonstrates the ability to maintain efficient and maintainable database operations.
Hands-On Experience With Sample Databases
Practical exposure to sample databases is invaluable for mastering the exam objectives. Candidates should practice creating, modifying, and querying tables, executing transactions, and implementing programmability constructs. Working with realistic datasets reinforces theoretical knowledge and builds confidence in applying Transact-SQL skills in real-world contexts.
Applying Critical Thinking to Complex Problems
Critical thinking is required to address challenging scenarios effectively. Candidates should practice analyzing requirements, designing efficient queries, and troubleshooting issues. Applying critical thinking ensures that candidates can navigate complex problems systematically, make informed decisions, and optimize database operations for both performance and accuracy.
Reinforcing Learning Through Continuous Practice
Continuous engagement with practical exercises, complex queries, and scenario-based problems is essential. Repeated practice reinforces knowledge, builds confidence, and ensures that skills are internalized. Candidates who consistently practice and review their work are better prepared for the exam and for professional responsibilities that demand high-level Transact-SQL proficiency.
Developing a Comprehensive Study Plan
A well-structured study plan ensures balanced coverage of all exam objectives. Candidates should schedule dedicated time for reading, hands-on practice, and review of advanced concepts. Prioritizing objectives based on weight and complexity allows for efficient preparation and ensures that candidates are well-prepared for all aspects of the exam.
Integrating Theory and Practice
The most effective preparation combines theoretical understanding with practical execution. Candidates should ensure that they can apply concepts such as joins, aggregations, pivot operations, and stored procedures in realistic scenarios. This integration ensures not only exam readiness but also practical competence for professional database management tasks.
Reinforcing Knowledge With Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-based learning helps candidates apply multiple concepts simultaneously. By working through complex examples, candidates develop the ability to analyze requirements, design efficient solutions, and implement queries that address all aspects of a problem. Scenario practice strengthens problem-solving skills and reinforces understanding of advanced Transact-SQL concepts.
Ensuring Comprehensive Exam Readiness
Preparing for the exam requires attention to all domains, consistent practice, and application of knowledge in realistic contexts. Candidates who integrate hands-on exercises, scenario-based learning, and structured study develop the skills necessary to excel. This preparation ensures not only the ability to pass the exam but also readiness to apply Transact-SQL expertise effectively in professional environments.
Mastering the Querying Data with Transact-SQL exam requires a combination of theoretical understanding, hands-on practice, and strategic preparation. Candidates who dedicate time to practicing complex queries, managing transactions, implementing programmability, and optimizing performance develop the skills required for both the exam and professional database roles. Consistent effort, structured study, and integration of knowledge across domains ensure comprehensive readiness and long-term success as a proficient SQL professional.
Advanced Query Optimization Techniques
Efficient query design is essential for managing large-scale databases and ensuring high performance. Candidates should focus on analyzing query execution plans to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance. Understanding indexing strategies, including clustered, non-clustered, and covering indexes, allows candidates to enhance retrieval speed and reduce resource consumption. Awareness of table partitioning and the use of indexed views can also significantly improve query efficiency in complex scenarios.
Managing Complex Joins
Joins are fundamental in combining data from multiple tables, and candidates must demonstrate expertise in their use. Inner joins, outer joins, cross joins, and self-joins each serve distinct purposes. Mastering these allows candidates to retrieve accurate and complete datasets. Additionally, understanding join precedence and the impact of join order on performance ensures that queries execute efficiently while maintaining correctness.
Utilizing Window Functions
Window functions provide a method to perform calculations across sets of rows related to the current row without collapsing the dataset. Candidates should practice using ranking functions, aggregate functions, and analytic functions to perform running totals, moving averages, and percentiles. Mastery of window functions allows for more sophisticated analysis and is critical for advanced data reporting and business intelligence tasks.
Handling Error Conditions Effectively
Robust error handling ensures that database operations are reliable and maintain integrity. Candidates should focus on TRY...CATCH blocks to capture and manage runtime errors, implement appropriate logging mechanisms, and ensure proper transaction rollback when needed. Effective error handling reduces the risk of data corruption and ensures that database operations can recover gracefully from unexpected conditions.
Implementing Transactions and Concurrency
Transactions provide a mechanism for ensuring atomic operations in databases. Candidates should practice writing BEGIN, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK statements to manage changes consistently. Understanding isolation levels, including read uncommitted, read committed, repeatable read, and serializable, is essential for preventing data anomalies in multi-user environments. Mastery of transaction handling ensures data consistency and reliability under concurrent workloads.
Advanced Data Transformation Techniques
Transforming data for reporting or analysis requires proficiency in pivoting, unpivoting, rollup, and cube operations. Candidates should practice converting rows to columns, performing hierarchical aggregations, and summarizing data across multiple dimensions. These transformations are essential for generating comprehensive reports and for preparing data for business intelligence applications.
Working with Views and Derived Data
Views simplify access to complex queries and enforce data abstraction. Candidates should focus on creating views that encapsulate reusable query logic, applying filters and aggregations where necessary. Indexed views can improve performance for frequently queried datasets. Understanding how to update and maintain views ensures that they remain consistent with underlying tables and can support efficient reporting and data access.
Stored Procedures and Programmable Objects
Stored procedures encapsulate business logic for reuse and maintainability. Candidates should practice creating procedures with input and output parameters, conditional logic, and embedded transactions. User-defined functions, both scalar and table-valued, provide modular computation capabilities that can be incorporated into larger queries. Mastery of these objects demonstrates the ability to build efficient, maintainable, and reusable database solutions.
Managing Data Types and Null Handling
Selecting appropriate data types is crucial for storage efficiency, query performance, and application compatibility. Candidates should understand type conversion rules, implicit and explicit casting, and how different data types affect indexing and computation. Handling NULL values correctly is equally important, as they can impact filtering, aggregation, and logical conditions. Ensuring proper handling of data types and NULLs prevents unexpected results and maintains data integrity.
Querying Semi-Structured and Temporal Data
Modern databases often include semi-structured formats like JSON and XML. Candidates should practice parsing and querying these data types to integrate them with relational data. Temporal data, stored in system-versioned tables, requires specialized queries to retrieve historical values and track changes over time. Proficiency in these areas is essential for auditing, trend analysis, and integrating diverse datasets.
Performance Tuning Strategies
Optimizing queries involves more than writing correct SQL. Candidates must learn to identify slow-running queries using execution plans, apply appropriate indexes, and restructure queries for better performance. Reducing the number of joins, avoiding unnecessary calculations, and using set-based operations over row-by-row processing improves efficiency. Understanding query hints and plan guides also contributes to effective performance tuning in complex environments.
Practicing Real-World Scenarios
Working with realistic datasets helps candidates apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. Scenario-based exercises, including data retrieval, transformation, and transaction management, simulate challenges encountered in professional environments. Practicing with complex queries, joins, aggregations, and error handling in real-world scenarios ensures readiness for both the exam and practical database management tasks.
Developing a Structured Study Approach
Effective preparation requires a structured plan that covers all exam objectives. Candidates should allocate time for reading, hands-on practice, and review of advanced concepts. Prioritizing topics based on exam weight ensures balanced preparation. Consistent practice and iterative review solidify understanding and improve confidence in executing complex queries and handling advanced database scenarios.
Integrating Theory with Practical Application
Candidates should focus on applying theoretical concepts in practical exercises. Writing complex SELECT statements, implementing transactions, creating stored procedures, and performing data transformations bridges the gap between knowledge and execution. Integrating theory with practice reinforces learning, ensures competence, and prepares candidates for real-world database challenges.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Capabilities
The exam requires candidates to demonstrate analytical and critical thinking skills. Practicing problem-solving with complex queries, handling unexpected errors, and optimizing performance enhances these capabilities. Developing strategies for analyzing requirements, designing efficient solutions, and troubleshooting issues builds proficiency and confidence.
Hands-On Experience with Sample Databases
Practical engagement with sample databases is critical. Candidates should create, modify, and query tables, execute transactions, implement programmability objects, and practice transformations. This hands-on experience strengthens understanding, improves query skills, and prepares candidates for exam scenarios that test both knowledge and application.
Continuous Practice and Reinforcement
Consistent practice reinforces learning and builds expertise. Candidates should repeatedly execute queries, implement stored procedures, manage transactions, and transform data to internalize skills. Continuous engagement ensures that knowledge is retained, confidence is enhanced, and readiness for complex exam tasks is achieved.
Evaluating Progress and Adjusting Strategy
Regular assessment through practice exercises and mock tests helps identify strengths and weaknesses. Evaluating query performance, accuracy, and efficiency ensures comprehensive readiness. Candidates should adjust their study strategy based on progress, focusing on areas requiring improvement, and reinforcing skills to achieve mastery.
Combining Skills Across Domains
Success requires integrating multiple skills into cohesive solutions. Candidates must combine data retrieval, aggregation, transformation, programmability, and error handling into unified approaches. Practicing integrated scenarios prepares candidates for real-world tasks and ensures that all exam objectives are addressed effectively.
Adapting to Dynamic Requirements
Database environments often involve changing requirements. Candidates should practice creating flexible, modular queries and procedures that can adapt to evolving data structures and business needs. Adaptability demonstrates professional competence and ensures that solutions remain efficient, maintainable, and scalable.
Preparing for Exam Conditions
Simulating exam conditions through timed practice tests helps candidates manage time effectively and develop test-taking strategies. Practicing under realistic constraints ensures familiarity with exam format, improves accuracy, and builds confidence in executing complex queries within the allotted time.
Comprehensive Knowledge Integration
Candidates should ensure that all exam domains are thoroughly covered, integrating theory, practice, and scenario-based learning. Understanding how to manage data, perform advanced querying, program databases, and handle errors prepares candidates for both the exam and practical professional roles.
Final Preparation Strategies
In the final phase of preparation, candidates should focus on reviewing key concepts, reinforcing hands-on skills, and practicing complex scenarios. Consolidating knowledge ensures that all exam objectives are met and that candidates are confident in their ability to apply Transact-SQL skills effectively.
Achieving mastery in querying data with Transact-SQL requires dedication, structured study, hands-on practice, and application of advanced concepts. Candidates who consistently practice complex queries, optimize performance, manage transactions, and implement programmability develop the skills necessary to succeed in the exam and in professional SQL Server environments. This comprehensive preparation ensures competence, confidence, and readiness to tackle advanced data management and development tasks.
Working with Advanced Joins and Set Operations
Mastery of joins and set operations is a critical skill for handling complex data relationships in SQL Server. Candidates should focus on inner joins, outer joins, cross joins, and self-joins, understanding how each type affects the resulting dataset. In addition, set operations such as UNION, INTERSECT, and EXCEPT enable combining results from multiple queries efficiently. Understanding the execution order and performance implications of these operations is essential to writing optimized queries.
Utilizing Common Table Expressions
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) provide a method to structure complex queries in a readable and maintainable way. Candidates should practice writing both recursive and non-recursive CTEs for hierarchical data, aggregation, and iterative calculations. Mastery of CTEs improves query clarity and enables more efficient execution plans, which is particularly important when working with large datasets.
Handling Aggregations and Grouping Sets
Aggregating data using functions like SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, and COUNT is fundamental. Candidates should also explore advanced grouping mechanisms, including GROUPING SETS, ROLLUP, and CUBE, to perform multi-level summaries. These techniques allow for flexible reporting and analysis, making it easier to generate insights from complex data structures.
Working with Pivot and Unpivot Operations
Pivoting and unpivoting data transform rows into columns or vice versa, which is essential for reporting and analysis. Candidates must practice these operations to summarize data dynamically, generate cross-tab reports, and prepare data for visualization or business intelligence tools. Understanding the syntax and performance considerations is key to applying these transformations effectively.
Querying JSON and XML Data
Modern databases often include semi-structured data in JSON or XML formats. Candidates should focus on parsing, querying, and transforming these data types. Utilizing functions such as OPENJSON, JSON_VALUE, and XML nodes enables integration of semi-structured data with relational tables. Mastery of these techniques enhances the ability to work with diverse datasets in real-world scenarios.
Implementing Error Handling Strategies
Effective error handling ensures robust and reliable database operations. Candidates should become proficient in TRY...CATCH constructs, implementing transaction rollbacks, and logging errors for analysis. Proper error management prevents data corruption and ensures consistent application behavior, which is critical in production environments.
Managing Transactions and Concurrency
Transactions guarantee the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability of database operations. Candidates should understand isolation levels such as READ COMMITTED, REPEATABLE READ, and SERIALIZABLE to prevent anomalies during concurrent access. Implementing transaction handling correctly ensures data integrity and supports multi-user environments.
Creating and Using Stored Procedures
Stored procedures encapsulate reusable logic for complex operations. Candidates should practice creating procedures with parameters, conditional statements, loops, and embedded transactions. Using stored procedures enhances maintainability, reduces redundancy, and improves security by restricting direct table access.
Implementing User-Defined Functions
User-defined functions (UDFs) provide reusable computation or data transformation capabilities. Candidates should explore scalar, inline table-valued, and multi-statement table-valued functions. Proper implementation of UDFs improves modularity and allows complex logic to be incorporated into queries efficiently.
Working with Views
Views simplify access to complex queries and enforce abstraction of underlying tables. Candidates should focus on creating indexed and non-indexed views, applying filters, aggregations, and joins as needed. Views improve maintainability and can enhance query performance when designed appropriately.
Handling NULL Values and Data Types
Proper management of NULL values and data types is essential to ensure accuracy and prevent unexpected results. Candidates should understand implicit and explicit conversions, type precedence, and handling of NULLs in comparisons and aggregate functions. Correct handling avoids logic errors and maintains data integrity.
Implementing Advanced Filtering Techniques
Advanced filtering techniques involve the use of window functions, ranking, and partitioning to analyze subsets of data. Candidates should practice ROW_NUMBER, RANK, DENSE_RANK, and NTILE functions, applying them to real-world scenarios such as reporting, trend analysis, and data segmentation.
Optimizing Query Performance
Query optimization is essential for efficient database operations. Candidates should learn to analyze execution plans, identify slow-running queries, and implement appropriate indexing strategies. Reducing nested loops, avoiding cursors, and using set-based operations improve overall performance. Knowledge of statistics, parameter sniffing, and query hints contributes to more efficient query execution.
Preparing Real-World Scenario Exercises
Engaging with realistic datasets and scenarios helps candidates apply theoretical knowledge. Exercises should include joins, aggregations, transactions, and error handling to simulate practical challenges. This approach builds problem-solving skills and prepares candidates for exam scenarios that test both theoretical understanding and practical application.
Integrating Theoretical Knowledge with Hands-On Practice
Combining theory with practical exercises ensures comprehensive learning. Candidates should focus on writing queries, creating procedures, managing transactions, and performing data transformations. Hands-on practice reinforces learning and prepares candidates for real-world SQL Server tasks and exam questions.
Evaluating Progress Through Practice
Regular practice and self-assessment help candidates identify areas of strength and weakness. Working with sample datasets, solving complex queries, and reviewing performance results strengthens skills. Adjusting study strategies based on evaluation ensures complete preparation and boosts confidence.
Mastering Data Transformation Techniques
Data transformation is key to preparing data for reporting and analysis. Candidates should practice using pivot, unpivot, rollup, and cube functions to summarize, reorganize, and aggregate data effectively. Mastery of these techniques allows efficient data presentation and supports advanced reporting requirements.
Learning Set-Based Programming
Set-based programming emphasizes operations on entire sets of data rather than row-by-row processing. Candidates should focus on creating efficient queries that leverage set-based logic, improving performance and maintainability. Understanding how to translate business requirements into set-based operations is essential for professional database development.
Developing Error Recovery Strategies
Error recovery ensures that databases maintain consistency in case of failures. Candidates should practice transaction rollback, retry mechanisms, and logging errors for analysis. Designing robust error recovery strategies reduces downtime, prevents data loss, and maintains system reliability.
Consolidating Knowledge Across Exam Domains
Integrating multiple skills across all exam domains ensures readiness for both the exam and real-world tasks. Candidates should practice combining joins, subqueries, transactions, transformations, and programmability into cohesive solutions. This holistic approach ensures proficiency in all areas tested by the exam.
Simulating Exam Conditions
Practicing under exam-like conditions helps candidates manage time and handle complex queries efficiently. Timed exercises, structured practice sessions, and scenario-based tasks prepare candidates for the pressure and format of the actual exam. This approach improves confidence and performance during the test.
Reviewing Key Concepts
In the final stage of preparation, candidates should review key concepts, consolidate hands-on skills, and reinforce complex techniques. This review ensures retention of critical knowledge, mastery of essential skills, and readiness to tackle any question on the exam.
Preparing for Advanced Data Management Tasks
Success in the exam reflects readiness for advanced database management tasks. Candidates who master querying, transformation, programmability, transactions, and error handling are well-prepared for professional responsibilities. Comprehensive preparation ensures competence and confidence in managing SQL Server environments effectively.
Integrating Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring and tuning are essential skills for managing production databases. Candidates should practice identifying performance bottlenecks, using execution plans, and applying optimization strategies. Integrating performance monitoring into routine practice ensures readiness for real-world database administration tasks.
Utilizing Sample Databases for Practice
Working with sample databases provides practical experience in implementing queries, transformations, and transactions. Candidates should create, modify, and query tables, implement procedures, and practice error handling. Hands-on interaction with sample datasets builds confidence and reinforces theoretical understanding.
Reinforcing Programming Logic
Candidates should focus on embedding logical operations, conditional statements, loops, and control flow in T-SQL code. Mastery of programming logic enhances the ability to create sophisticated queries, manage complex datasets, and implement business logic efficiently.
Practicing Advanced Query Patterns
Advanced query patterns include nested subqueries, correlated subqueries, common table expressions, and complex joins. Candidates should practice these patterns to solve intricate problems efficiently. Mastery of advanced queries ensures readiness for both exam scenarios and professional database development.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
Solving real-world database problems develops analytical thinking and problem-solving capabilities. Candidates should practice designing solutions, debugging queries, optimizing performance, and handling unexpected data scenarios. Strengthening these skills ensures exam success and professional competence.
Continuous Reinforcement Through Practice
Regular practice solidifies knowledge, reinforces techniques, and ensures proficiency. Candidates should maintain a consistent schedule of exercises, focusing on all exam objectives. Continuous engagement enhances retention, improves efficiency, and builds confidence.
Understanding Query Execution Plans
Execution plans provide insight into how SQL Server processes queries. Candidates should analyze plans to identify costly operations, optimize index usage, and restructure queries for performance gains. Understanding execution plans is essential for advanced query tuning and efficiency.
Combining Skills for Comprehensive Solutions
Candidates should integrate data retrieval, transformation, programmability, and error handling into comprehensive solutions. Practicing integrated tasks ensures that all skills are applied cohesively and prepares candidates for complex exam scenarios.
Preparing for Exam Day
Final preparation includes reviewing objectives, practicing under timed conditions, and consolidating hands-on experience. Ensuring familiarity with all exam topics, reviewing challenging scenarios, and practicing complex queries builds confidence for exam day.
Achieving success in querying data with Transact-SQL requires dedication, structured preparation, hands-on practice, and mastery of advanced concepts. Candidates who consistently practice joins, subqueries, transactions, transformations, and programmability develop the skills necessary to excel in the exam and in professional database environments. Comprehensive preparation ensures competence, confidence, and readiness for advanced data management challenges.
Advanced Techniques for Managing Data
Understanding and manipulating data efficiently is central to SQL Server expertise. Candidates preparing for the exam should focus on writing complex queries that retrieve, filter, and modify data accurately. Practicing with scenarios that involve multiple tables, various join types, and advanced filtering ensures readiness to handle real-world datasets. Performance considerations, such as indexing and query structure, should be considered while practicing to develop efficient solutions.
Leveraging Functions and Expressions
Functions and expressions in Transact-SQL allow candidates to manipulate and transform data in powerful ways. Using scalar functions, aggregate functions, and built-in expressions, candidates can summarize, calculate, and format data for analysis or reporting. Mastery of functions enhances flexibility in querying and reduces the need for complex procedural logic, which is critical in both exam and professional environments.
Working with Subqueries and Table Expressions
Subqueries and table expressions provide modularity and clarity in query design. Candidates should practice writing correlated and non-correlated subqueries, common table expressions, and derived tables. These constructs allow breaking complex queries into manageable components while improving readability and maintainability. Understanding execution context and performance impact is essential for efficient query design.
Querying Temporal and Semi-Structured Data
Modern databases often include temporal data or semi-structured formats such as JSON and XML. Candidates should focus on writing queries that accurately retrieve historical data, track changes over time, and parse semi-structured formats. Techniques like temporal tables, JSON_VALUE, and XML nodes are integral to managing diverse datasets and ensuring data consistency.
Creating Views and Managing Data Access
Views simplify query management and enforce data abstraction. Candidates should practice creating both standard and indexed views, understanding their impact on query performance and security. Views enable simplified access to complex joins or aggregations while protecting underlying table structures, a critical skill for database development and administration tasks.
Implementing Stored Procedures and Functions
Stored procedures and user-defined functions encapsulate reusable logic and provide modularity. Candidates should focus on creating parameterized procedures, handling transactions within procedures, and implementing scalar or table-valued functions. Mastery of these tools ensures maintainable, secure, and efficient database operations.
Managing Transactions and Error Handling
Reliable data management depends on proper transaction control and error handling. Candidates should understand transaction isolation levels, rollback scenarios, and implementing TRY...CATCH blocks. Practicing these skills ensures data integrity, prevents anomalies during concurrent access, and equips candidates to handle runtime errors effectively.
Using Advanced Aggregation Techniques
Advanced aggregation techniques, including GROUPING SETS, ROLLUP, and CUBE, enable multi-level summarization and analysis. Candidates should practice combining these techniques with filtering, joins, and subqueries to generate comprehensive reports. Mastery of aggregation ensures efficiency and precision in analyzing large datasets.
Pivoting and Transforming Data
Pivot and unpivot operations allow candidates to reformat datasets for reporting and analysis. Practicing dynamic pivoting, transforming columns into rows, and vice versa is crucial for handling various data presentation requirements. This skill also facilitates integration with reporting tools and dashboards.
Applying Window Functions
Window functions enable ranking, running totals, and moving averages without collapsing rows. Candidates should practice functions like ROW_NUMBER, RANK, DENSE_RANK, NTILE, and aggregate window functions to perform advanced analysis. Understanding partitioning and ordering within window functions is essential for precise query results.
Optimizing Query Performance
Efficient query design is a critical skill. Candidates should focus on analyzing execution plans, optimizing joins, using indexes effectively, and avoiding cursor-based operations when possible. Understanding query cost, parallelism, and statistics ensures better performance and prepares candidates for real-world database optimization scenarios.
Integrating Error Prevention in Query Design
Preventing errors during query execution enhances reliability. Candidates should use validation checks, constraints, and error handling constructs to ensure data integrity. Developing strategies for error prevention helps maintain consistency and reduces the likelihood of runtime failures.
Preparing with Sample Databases
Hands-on experience with sample datasets allows candidates to practice diverse query patterns, transformations, and data manipulations. Practicing with realistic scenarios builds familiarity with SQL Server behavior and improves problem-solving skills applicable to both the exam and professional tasks.
Simulating Real-World Challenges
Candidates should create exercises that mirror real-world database problems. This includes managing multi-table queries, implementing business logic through stored procedures, handling transactions, and performing data transformations. Simulating challenges improves readiness and builds confidence in applying knowledge under exam conditions.
Understanding Set-Based Programming
Set-based operations focus on processing multiple rows simultaneously rather than using iterative row-by-row methods. Candidates should practice using set operations for updates, deletions, and data aggregation. Mastery of set-based logic improves query efficiency and aligns with best practices in SQL Server development.
Consolidating Knowledge Across Domains
Success in the exam requires integrating skills across all domains. Candidates should combine data retrieval, transformation, transaction management, programmability, and error handling into cohesive solutions. Consolidation ensures holistic understanding and readiness for complex queries.
Reviewing Exam Objectives
Thorough review of exam objectives ensures that candidates cover all necessary skills and knowledge areas. Revisiting filtering, joins, subqueries, transactions, error handling, aggregation, and transformation techniques reinforces understanding and prepares candidates for potential exam questions.
Practicing Under Timed Conditions
Simulating exam timing helps candidates manage pace and focus during the test. Timed practice sessions build endurance, reduce stress, and improve performance when tackling complex scenarios within the exam duration.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
Continuous practice with increasingly complex queries develops analytical and problem-solving skills. Candidates should approach exercises by identifying patterns, optimizing logic, and verifying results to strengthen their capacity to handle unexpected challenges.
Maintaining Consistent Practice
Consistent engagement with all exam topics ensures retention of knowledge and refinement of skills. Structured practice schedules, iterative review, and progressive difficulty of exercises contribute to comprehensive preparation.
Implementing Comprehensive Solutions
Candidates should focus on integrating querying, transformation, programmability, transactions, and error handling into full solutions. This approach mirrors real-world database tasks and ensures proficiency across multiple areas, improving exam readiness.
Preparing for Advanced Database Tasks
The skills gained while preparing for the exam are directly applicable to professional roles. Mastery of querying, transformation, programming, and data management enables candidates to tackle advanced SQL Server tasks, enhancing career opportunities and practical competence.
Understanding Execution Plans
Execution plans provide insight into query processing and performance optimization. Candidates should analyze plans to identify bottlenecks, improve index usage, and restructure queries for efficiency. Familiarity with execution plans is crucial for high-level query optimization and real-world database management.
Reviewing and Refining Queries
Regular review of written queries helps identify inefficiencies, errors, and areas for improvement. Candidates should refine queries to optimize performance, enhance readability, and ensure correctness. Iterative review strengthens mastery and builds confidence for exam conditions.
Developing Programming Logic in T-SQL
Embedding programming constructs such as conditional statements, loops, and variables within T-SQL code allows for sophisticated logic implementation. Candidates should practice designing modular, reusable, and maintainable code to handle complex database operations efficiently.
Combining Multiple Skills
Integrating querying, transformation, programming, and error handling ensures comprehensive understanding. Candidates should practice combining these skills in cohesive exercises to prepare for complex exam scenarios and professional responsibilities.
Conclusion
Success in the exam requires disciplined preparation, extensive hands-on practice, and mastery of advanced T-SQL concepts. Candidates who dedicate time to understanding joins, subqueries, transactions, data transformation, and programmability develop the expertise necessary for the exam and professional database environments. Comprehensive preparation ensures competence, efficiency, and confidence in managing SQL Server data effectivel
Microsoft MCSA 70-761 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 70-761 Querying Data with Transact-SQL certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- AB-100 - Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- AB-731 - AI Transformation Leader
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MO-300 - Microsoft PowerPoint (PowerPoint and PowerPoint 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 70-761 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 70-761 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 70-761 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 70-761 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 70-761 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 70-761. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 70-761 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 70-761 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 70-761 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 70-761 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

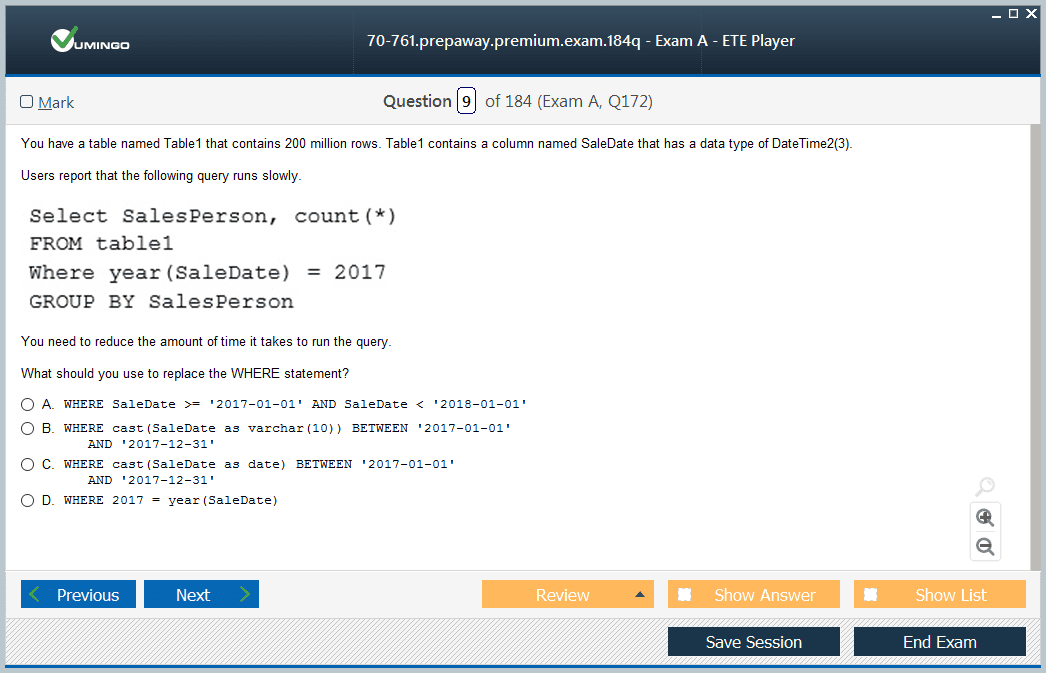
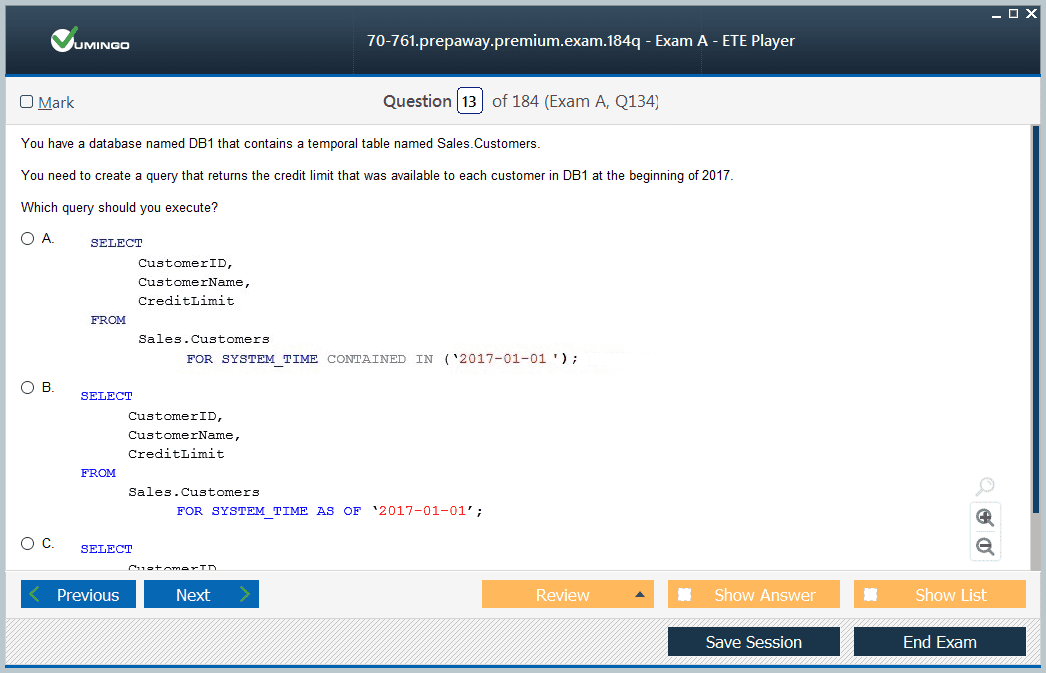
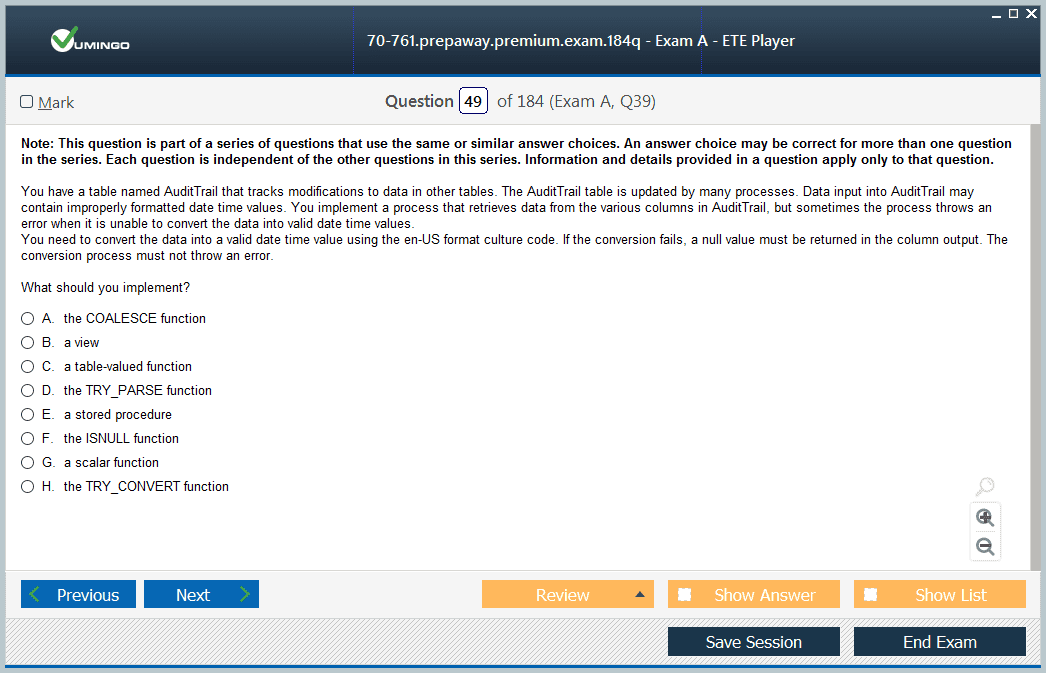
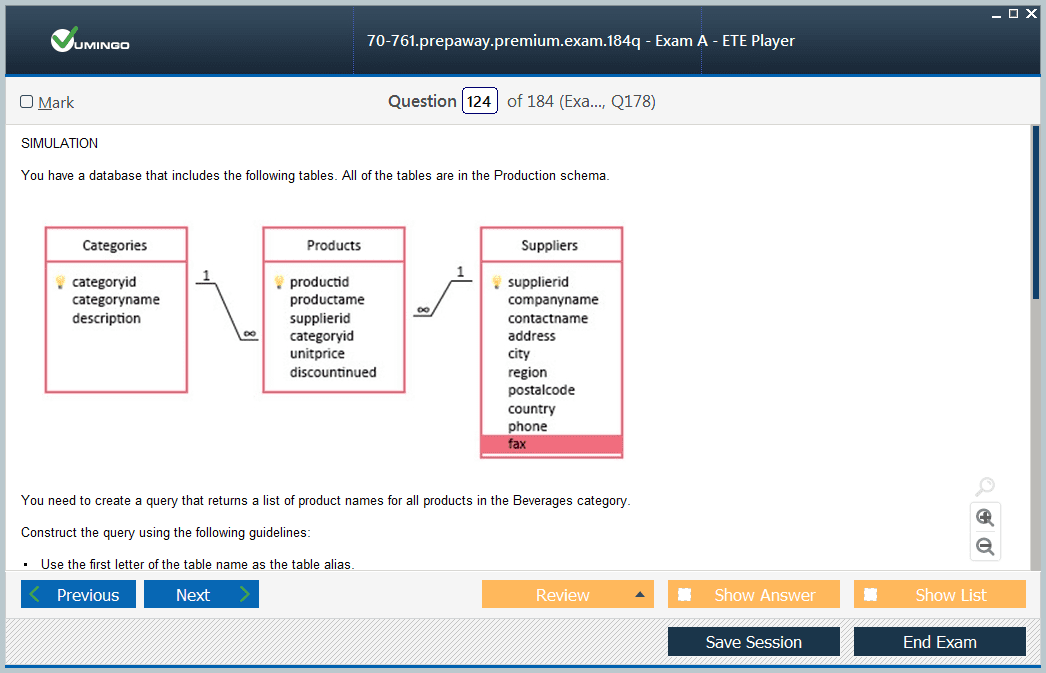




My passing score was 870.
Thanks you, Prepaway
Here is the proof
https://www.youracclaim.com/badges/ef503dc2-adf5-4acd-8862-d4586d3485bf/facebook?fbclid=IwAR2SU4xsMD7Y7rujIkCQf1nzsi6xpI8J6anK3xT3IUAtXC2AbcT_LW0152U
im satisfied with the result.
Dumps valid on 80%.
set with 82 and 91 q can be used, but there is lot of bad answers.