- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 70-345 Designing and Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Dumps
Pass Microsoft MCSE 70-345 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


70-345 Premium File
- Premium File 166 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Mar 05, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Microsoft MCSE 70-345 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 70-345 Designing and Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Mastering Microsoft 70-345: Exchange Server Certification Preparation
The Microsoft 70-345 exam, focused on designing and deploying Exchange Server, evaluates the ability to plan, implement, manage, and troubleshoot complex messaging environments. This exam is intended for IT professionals with significant experience in Exchange Server administration, typically requiring hands-on expertise in deploying and maintaining enterprise messaging solutions. It emphasizes both strategic design and operational management, ensuring that certified professionals can handle a full spectrum of responsibilities in an Exchange Server environment.
Planning and Deploying Mailbox Databases
A key area of the exam is planning and deploying mailbox databases, which are central to Exchange Server functionality. Administrators must understand the architecture of mailbox databases, including database availability groups and high availability strategies. This involves configuring multiple databases for redundancy, balancing server loads, and designing failover solutions that ensure continuous availability. Candidates also need to develop backup and recovery strategies for mailbox data, applying best practices to protect against data loss while maintaining optimal performance.
Monitoring and troubleshooting mailbox databases is an essential skill. Administrators must be able to identify performance bottlenecks, diagnose replication failures, and apply corrective measures to maintain service reliability. This includes understanding database health metrics, error logs, and recovery procedures, which together form the backbone of resilient mailbox infrastructure management.
Managing Client Access Services
Client access services provide the interface through which users connect to Exchange Server. Effective planning involves deploying services such as Outlook Web Access, Exchange ActiveSync, and mobile device connectivity while ensuring that configurations meet organizational requirements. Administrators must design site-resilient solutions and implement load balancing to optimize user experience and system reliability.
Troubleshooting client access issues is another critical competency. Candidates need to analyze connectivity problems, examine authentication workflows, and resolve configuration errors. This requires an in-depth understanding of client protocols, service endpoints, and security considerations. Planning mobility solutions and site-resilient configurations ensures uninterrupted access for end-users while maintaining the integrity and performance of the Exchange environment.
Implementing and Managing Transport Services
Transport services handle the flow of email messages and are fundamental to messaging reliability. Candidates must design and manage transport pipelines, configure connectors, and implement message hygiene to protect against spam and malware. Troubleshooting transport services involves analyzing message queues, identifying delivery delays, and resolving mail flow issues efficiently.
High availability planning for transport services is essential, ensuring that mail continues to flow even during server outages. This requires knowledge of redundancy strategies, failover mechanisms, and load distribution methods. Administrators must also understand the integration of transport services with compliance and security policies, ensuring that all messages are processed according to organizational and regulatory standards.
Exchange Infrastructure, Recipients, and Security
Managing the broader Exchange infrastructure encompasses Active Directory integration, recipient management, and security configuration. Candidates are expected to design and implement organizational structures, configure mail-enabled objects, and assign permissions using role-based access control. Ensuring security across the Exchange environment involves configuring encryption, implementing rights management, and enforcing compliance policies.
Administrators also need to understand identity management, including account provisioning, delegation, and access auditing. These capabilities ensure that users have appropriate access while sensitive data remains protected. Designing security strategies that align with organizational policies and compliance requirements is a critical part of the certification objectives, demonstrating proficiency in maintaining a secure messaging environment.
Compliance, Archiving, and Auditing
Compliance management, archiving, and auditing are central to maintaining organizational and regulatory standards. Candidates must implement data loss prevention strategies, configure archiving solutions, and enforce message retention policies. eDiscovery procedures and administrative auditing are essential skills, ensuring that messaging data can be retrieved and reviewed efficiently while maintaining legal and regulatory compliance.
Administrators must also monitor and maintain compliance systems, addressing policy violations and updating configurations as regulations evolve. Understanding how to integrate archiving, retention, and auditing into the broader messaging infrastructure ensures that organizations can operate securely and meet oversight requirements without compromising service performance.
Coexistence, Hybrid Deployments, and Migration
Advanced scenarios such as hybrid deployments, coexistence with older Exchange versions, and migrations are critical areas of expertise. Candidates must plan and manage integration with cloud messaging environments, troubleshoot hybrid configurations, and ensure seamless coexistence with legacy systems. Migration planning involves transferring mailboxes, public folders, and configuration settings while minimizing disruption to users.
Understanding the lifecycle of Exchange infrastructure, from legacy systems to hybrid or cloud-integrated environments, requires comprehensive knowledge of architecture, deployment strategies, and troubleshooting methodologies. Administrators must ensure continuity of service and data integrity throughout these transitions, demonstrating proficiency in complex infrastructure management.
Preparation Strategies
Success in the 70-345 exam requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Candidates should systematically review all exam domains, focusing on planning, deploying, managing, and troubleshooting core Exchange components. Hands-on practice with mailbox databases, client access, transport services, security configurations, and compliance features is essential to reinforce understanding.
Structured study approaches, including review of exam objectives and reference materials, provide a foundation for knowledge retention. Candidates should explore practical scenarios, simulate troubleshooting situations, and analyze system logs to develop problem-solving skills relevant to real-world Exchange administration.
Skills and Competencies
Key competencies assessed in the exam include the ability to design resilient infrastructure, configure high availability solutions, secure messaging systems, maintain compliance, and troubleshoot operational issues. Candidates must demonstrate both operational expertise and strategic planning skills, ensuring that messaging services remain reliable, secure, and scalable.
Proficiency in Active Directory integration, role-based access control, data loss prevention, archiving, and hybrid deployments reflects a comprehensive understanding of Exchange Server administration. Candidates must be capable of applying these skills in diverse scenarios, balancing organizational requirements with technical constraints.
Exam Structure and Format
The exam typically includes multiple-choice and multi-response questions, assessing both conceptual understanding and practical application. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to analyze scenarios, make informed decisions, and apply best practices to solve problems. Time management and familiarity with question formats are important for completing the exam efficiently and accurately.
The assessment measures knowledge across mailbox management, client connectivity, transport infrastructure, compliance, security, and hybrid environments. Each domain requires detailed understanding and practical application skills to ensure candidates can effectively manage Exchange Server environments under real-world conditions.
Building Proficiency
Developing proficiency for the exam involves continuous learning and hands-on practice. Candidates should engage with Exchange Server environments, exploring configuration options, testing high availability solutions, implementing security policies, and performing compliance tasks. Understanding interdependencies between services and their impact on overall system performance is crucial for mastering complex administration tasks.
Regular review of objectives, scenario-based exercises, and simulated troubleshooting enhances readiness. Candidates should focus on areas requiring additional attention, refining skills to ensure competence in deploying, managing, and troubleshooting all aspects of Exchange Server.
Practical Application
Applying knowledge in practical settings reinforces theoretical understanding. Administrators should configure mailbox databases, manage client access services, monitor transport services, enforce security measures, and implement compliance policies in controlled environments. Simulating real-world issues allows candidates to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills required for both the exam and professional practice.
Experience with migrations, hybrid deployments, and coexistence scenarios provides valuable exposure to complex Exchange infrastructures. Candidates gain insight into operational challenges, risk mitigation strategies, and effective deployment planning, building confidence in managing enterprise messaging systems.
Mastery of Exchange Server
Mastery of Exchange Server administration is achieved through continuous engagement with its features and challenges. Candidates must balance operational efficiency, system reliability, and compliance requirements while ensuring seamless user experiences. This holistic understanding equips professionals to design and deploy Exchange solutions that meet organizational needs while adhering to best practices and technical standards.
Comprehensive knowledge of mailbox databases, client access, transport services, security, compliance, and hybrid environments reflects advanced expertise. Administrators must integrate these domains effectively, applying both strategic and operational skills to maintain robust messaging infrastructure.
The Microsoft 70-345 exam is a rigorous assessment that validates advanced skills in designing, deploying, and managing Exchange Server environments. Success requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical experience, and strategic understanding of enterprise messaging systems. Candidates who thoroughly prepare across all domains, including mailbox management, client connectivity, transport services, infrastructure security, compliance, and hybrid deployments, are well-positioned to demonstrate proficiency.
Achieving certification confirms the ability to manage complex Exchange Server environments, ensuring reliable, secure, and compliant messaging systems. This expertise enhances professional credibility, supports career advancement, and establishes proficiency in designing and maintaining enterprise-grade messaging solutions.
The focus on planning, implementation, troubleshooting, and compliance ensures that certified professionals are equipped to address both operational challenges and strategic organizational needs, reflecting comprehensive mastery of Exchange Server administration.
Advanced Planning for Exchange Server Deployments
In the 70-345 exam, one of the essential areas is the ability to plan Exchange Server deployments that are efficient, scalable, and resilient. Effective planning starts with understanding organizational requirements, including user counts, expected mail flow, storage demands, and compliance needs. Administrators must assess infrastructure capabilities and design a deployment strategy that accommodates both current needs and future growth. This includes choosing appropriate server roles, configuring high availability, and implementing redundancy strategies to minimize downtime.
Deployment planning also involves network design considerations. Candidates need to ensure that client connectivity, mailbox availability, and transport services operate seamlessly across multiple sites. This includes implementing site-resilient architectures, load balancing solutions, and strategic placement of database availability groups to maintain service continuity in the event of server or network failures.
Configuring Mailbox Databases
A deep understanding of mailbox database architecture is required for 70-345 candidates. Administrators must configure databases to optimize performance while providing fault tolerance. This includes deploying database availability groups, configuring replication between servers, and managing mailbox storage limits to prevent performance degradation.
Database configuration also involves setting retention policies, archiving strategies, and backup procedures. Administrators must implement regular backup schedules and test restore procedures to ensure that mailbox data can be recovered reliably. Monitoring database health is crucial, with proactive identification of issues like replication failures or storage bottlenecks to avoid service disruptions.
Client Access Services Management
Client access services are pivotal for user interaction with Exchange. Candidates are expected to deploy and manage protocols such as MAPI, Outlook Web Access, and Exchange ActiveSync. Understanding authentication mechanisms, security requirements, and mobility integration is essential to provide a seamless experience for end-users.
Designing site-resilient client access solutions involves configuring load balancers, redundancy, and failover systems to ensure uninterrupted connectivity. Troubleshooting client access issues requires analyzing connection logs, identifying misconfigurations, and resolving authentication or network-related problems efficiently.
Transport Services and Mail Flow
Transport services control how messages move through the Exchange environment. Candidates must manage transport pipelines, configure send and receive connectors, and implement message hygiene techniques to prevent spam or malware. Understanding routing, mail flow topology, and connector configuration is critical for ensuring reliable message delivery.
Administrators should also plan for high availability of transport services. This includes setting up redundant transport servers, monitoring queues, and implementing failover mechanisms to maintain message flow during outages. Troubleshooting mail delivery issues involves analyzing logs, identifying delays, and resolving configuration or network problems that may impact transport reliability.
Security and Compliance Administration
Exchange Server 2016 environments require robust security and compliance strategies. Candidates must configure role-based access control to manage permissions effectively, implement data encryption, and enforce organizational security policies. Integrating Exchange with directory services ensures that authentication and authorization are consistent and secure across the organization.
Compliance tasks include implementing data loss prevention policies, configuring message retention and archiving, and maintaining eDiscovery capabilities. Administrators must monitor compliance adherence, audit user activities, and generate reports to meet regulatory and organizational standards. Effective security and compliance administration ensures that sensitive data is protected while users maintain access to necessary resources.
Hybrid Deployments and Coexistence
Hybrid deployments, where on-premises Exchange integrates with cloud-based solutions, present additional challenges. Candidates must plan, deploy, and manage hybrid configurations to ensure seamless coexistence. This includes configuring mail flow, directory synchronization, and authentication between on-premises and cloud environments.
Coexistence with earlier versions of Exchange also requires careful planning. Administrators must ensure that mailboxes, public folders, and configuration settings are compatible, and that user access remains uninterrupted during migrations or upgrades. Understanding the complexities of hybrid and coexistence scenarios demonstrates proficiency in advanced Exchange management.
Archiving and eDiscovery
Managing archiving and eDiscovery is critical for regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. Administrators must configure mailbox archiving, retention policies, and message records management to ensure that data is preserved according to organizational rules. eDiscovery procedures allow for the retrieval of specific mailbox content for legal or compliance purposes.
Candidates must implement auditing to track administrative actions and user activity, maintaining visibility into system usage and compliance adherence. Proper configuration of these features ensures that organizations can respond effectively to legal requests, internal audits, or regulatory inquiries.
Troubleshooting Strategies
A significant portion of 70-345 focuses on troubleshooting operational issues across Exchange Server environments. Candidates need to develop problem-solving methodologies to identify root causes and apply corrective actions. This includes analyzing performance metrics, reviewing system logs, and simulating failure scenarios to prepare for unexpected outages.
Proficiency in troubleshooting requires understanding dependencies between services, such as how mailbox database issues may affect client access or mail flow. Effective troubleshooting ensures minimal downtime and maintains organizational productivity. Candidates must also be able to implement proactive monitoring strategies to detect issues before they escalate.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
High availability and disaster recovery planning are central to maintaining reliable Exchange services. Candidates must design solutions that provide redundancy, failover capabilities, and rapid recovery in case of server or site failures. This includes configuring database availability groups, implementing geographically dispersed servers, and testing recovery procedures regularly.
Understanding recovery strategies allows administrators to maintain service continuity while protecting critical data. Proper planning and implementation of high availability and disaster recovery measures are essential for minimizing operational risks and maintaining user confidence in messaging services.
Exchange Server Administration Skills
Overall, the 70-345 exam assesses a wide range of administration skills. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage mailboxes, client access, transport services, security, compliance, hybrid environments, and disaster recovery. Each domain requires both theoretical understanding and practical expertise to ensure that administrators can deploy, configure, and troubleshoot Exchange Server environments effectively.
Hands-on experience reinforces learning, allowing candidates to apply theoretical concepts in real-world scenarios. Skills in scripting, automation, and performance monitoring further enhance the ability to manage complex environments efficiently. Understanding dependencies between different Exchange components ensures cohesive administration and optimized service delivery.
Practical Experience and Scenario-Based Learning
Gaining practical experience is essential for mastery of Exchange Server 2016. Scenario-based learning allows candidates to explore real-world situations, such as implementing high availability, managing mail flow issues, or configuring security policies. This type of learning develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are necessary for both exam success and professional competence.
Through practical exercises, candidates learn to identify potential pitfalls, optimize system configurations, and implement best practices. Hands-on engagement helps reinforce theoretical knowledge, ensuring that administrators are prepared for operational challenges in enterprise environments.
Integration with Organizational Infrastructure
Candidates must understand how Exchange Server integrates with other organizational infrastructure components, including Active Directory, DNS, network services, and security frameworks. This integration ensures that messaging services operate smoothly and securely within the broader IT ecosystem.
Effective integration requires knowledge of directory synchronization, authentication protocols, and network topologies. Administrators must ensure that Exchange Server interacts seamlessly with existing systems, providing reliable messaging services while maintaining compliance and security standards.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing Exchange Server performance is another critical aspect of the exam. Candidates must monitor system metrics, manage storage allocation, and configure server roles to maximize efficiency. Load balancing, caching strategies, and database optimization techniques help maintain high availability and responsiveness for users.
Performance tuning also involves proactive identification of bottlenecks, applying corrective actions, and planning for capacity growth. Understanding the impact of configuration changes on overall system performance ensures that administrators can maintain optimal operation under varying workloads.
The 70-345 exam evaluates a comprehensive set of skills required for designing, deploying, and managing Exchange Server 2016 environments. Mastery of mailbox databases, client access services, transport infrastructure, security, compliance, hybrid deployments, and disaster recovery is essential. Candidates who combine theoretical understanding with practical experience, scenario-based learning, and hands-on administration are well-prepared to manage complex Exchange environments effectively.
Proficiency in planning, deployment, troubleshooting, and performance optimization ensures that certified administrators can maintain secure, reliable, and scalable messaging systems. Success in this exam demonstrates readiness to handle advanced Exchange Server responsibilities and contributes to professional growth in enterprise messaging administration.
Advanced Mailbox Database Management
Managing mailbox databases in Exchange Server requires a strategic approach that ensures both performance and reliability. Administrators must design database structures that support the organizational user load while implementing high availability through database availability groups. Configuring replication between multiple servers prevents data loss and provides continuity in case of hardware or software failures. Regular monitoring of database health is necessary to identify replication issues, storage constraints, or performance bottlenecks. Implementing backup and recovery strategies ensures that mailbox data can be restored promptly, maintaining business continuity.
Retention policies and archiving strategies play a critical role in mailbox management. Administrators must establish rules for data lifecycle management, ensuring that older or inactive emails are appropriately archived while still remaining accessible for compliance or auditing purposes. These policies must be carefully balanced to optimize storage usage without affecting user access or mailbox performance.
Client Access Services Architecture
Client access services provide the interface between users and the Exchange infrastructure. Candidates need to understand how to deploy and manage protocols such as MAPI, POP3, IMAP, and Exchange ActiveSync, ensuring secure and reliable client connectivity. Implementing load balancing and failover mechanisms enhances service availability and provides seamless access during peak demand or server outages.
Security and authentication mechanisms must be properly configured to protect against unauthorized access. Administrators should manage certificates, configure encryption, and enforce secure connection protocols. Troubleshooting client access issues involves analyzing connection logs, network pathways, and authentication processes to resolve issues promptly. Mobility solutions, such as synchronization with mobile devices, require careful planning to maintain secure and efficient access across multiple platforms.
Transport Services Optimization
Transport services form the backbone of message flow in Exchange Server. Candidates must plan, deploy, and manage transport pipelines to ensure efficient message delivery. Configuring send and receive connectors, transport rules, and message hygiene systems helps control spam, malware, and unwanted content. Administrators need to monitor transport queues and implement proactive measures to prevent message delays or failures.
High availability in transport services is critical. Deploying redundant servers, monitoring queue health, and implementing failover strategies ensures uninterrupted mail flow. Troubleshooting requires detailed analysis of routing logs, connector configurations, and message tracing to resolve delivery issues. Understanding the interdependencies between mailbox databases, client access services, and transport services is essential for maintaining a cohesive messaging environment.
Security Implementation and Compliance
Security management in Exchange Server involves protecting data while maintaining accessibility. Candidates must implement role-based access control, manage user permissions, and enforce organizational security policies. Integration with directory services ensures consistent authentication and authorization across the infrastructure.
Compliance tasks include data loss prevention, retention policies, message archiving, and eDiscovery capabilities. Administrators must configure these systems to meet regulatory and internal standards, ensuring that sensitive information is protected and auditable. Auditing administrative and user actions provides visibility into system usage and supports compliance requirements. Secure configuration and regular monitoring prevent data breaches and maintain organizational trust.
Hybrid Deployments and Integration
Hybrid deployments extend Exchange capabilities to cloud environments while maintaining on-premises infrastructure. Candidates need to plan and implement hybrid configurations, including mail flow, directory synchronization, and authentication integration. Coexistence with earlier Exchange versions requires careful planning to maintain compatibility, user access, and uninterrupted service.
Administrators must understand federation, cross-premises connectivity, and the implications of hybrid environments on security, compliance, and messaging performance. Effective hybrid deployment ensures that users experience consistent and reliable access regardless of the infrastructure location.
Archiving and eDiscovery Management
Archiving strategies preserve mailbox content while optimizing storage. Administrators must configure archive mailboxes, apply retention policies, and implement message records management to maintain compliance. eDiscovery tools allow the retrieval of specific content for legal or organizational purposes.
Auditing ensures that administrative actions and user activities are tracked, supporting transparency and accountability. Properly configured archiving and eDiscovery systems enable organizations to respond to investigations, audits, and regulatory requirements efficiently. These features require ongoing monitoring and adjustment to accommodate changing organizational needs.
Troubleshooting and Problem Resolution
Effective troubleshooting is a core skill for Exchange Server administrators. Candidates must be able to identify and resolve issues across mailbox databases, client access services, transport systems, and hybrid deployments. This requires familiarity with system logs, monitoring tools, and diagnostic commands.
Proactive monitoring and scenario-based testing help identify potential issues before they impact users. Administrators should develop structured troubleshooting methodologies to efficiently resolve connectivity issues, database failures, transport delays, or security breaches. Scenario-based practice strengthens the ability to respond to complex real-world problems.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery Planning
Designing for high availability and disaster recovery ensures that Exchange Server continues to operate during failures. Candidates must implement redundant infrastructure, configure database availability groups, and test failover procedures. Recovery strategies should include both local and geographically distributed solutions to mitigate the impact of hardware, software, or site failures.
Regular testing and documentation of recovery procedures ensure that the organization can quickly restore services and minimize downtime. Administrators should continuously refine strategies based on lessons learned from drills and operational experience.
Performance Tuning and Monitoring
Optimizing Exchange Server performance requires ongoing monitoring and fine-tuning. Administrators must track system metrics, manage storage allocation, and configure server roles to handle user demand efficiently. Load balancing, caching strategies, and database maintenance contribute to overall responsiveness and reliability.
Performance tuning also involves identifying bottlenecks, evaluating server configurations, and planning for future capacity. Maintaining optimal performance supports user satisfaction, reduces operational risks, and ensures that messaging services scale with organizational growth.
Integration with Enterprise Infrastructure
Exchange Server does not operate in isolation. Candidates must understand how it integrates with Active Directory, DNS, network services, and security frameworks. Proper integration ensures consistent authentication, authorization, and messaging reliability.
Administrators should plan infrastructure to accommodate Exchange dependencies, including directory synchronization, certificate management, and network routing. This integration provides seamless service delivery while maintaining security and operational efficiency.
Scenario-Based Administration
Hands-on experience through scenario-based exercises is essential for mastering Exchange Server management. Simulating real-world challenges, such as configuring high availability, troubleshooting mail flow, or managing compliance, reinforces theoretical knowledge.
Practical exercises help administrators anticipate operational challenges, implement best practices, and develop problem-solving strategies. Scenario-based learning ensures readiness for both exam success and professional responsibilities in complex enterprise environments.
Advanced Security and Compliance Strategies
Administrators must continuously adapt security and compliance strategies to address evolving threats and regulations. This includes configuring encryption, managing sensitive information, auditing user activity, and ensuring that messaging systems meet organizational and regulatory requirements.
Implementing layered security measures, monitoring system integrity, and enforcing strict access controls are critical for maintaining trust and protecting organizational data. A strong understanding of compliance frameworks and best practices is essential for effective Exchange Server administration.
Cloud Integration and Hybrid Management
Managing hybrid environments involves coordinating on-premises and cloud services. Administrators must ensure seamless mail flow, directory synchronization, and consistent security policies across platforms. Monitoring hybrid systems and resolving integration challenges is critical to maintain service continuity and user satisfaction.
Knowledge of federation, cross-premises mail routing, and hybrid administration tools allows administrators to manage complex environments effectively. Continuous evaluation and optimization ensure that hybrid deployments support organizational objectives efficiently.
Automation and Scripting
Automation enhances efficiency in managing Exchange Server environments. Administrators should develop scripts to automate repetitive tasks, such as mailbox management, compliance reporting, and monitoring. PowerShell proficiency allows for precise control and rapid execution of administrative tasks, improving reliability and reducing operational overhead.
Effective automation enables administrators to maintain consistent configurations, quickly implement changes, and minimize the potential for human error. This skill is crucial for managing large-scale Exchange environments efficiently.
Mastering the 70-345 exam requires comprehensive knowledge of Exchange Server 2016 architecture, deployment strategies, mailbox management, client access services, transport infrastructure, security, compliance, hybrid environments, and high availability. Candidates must combine theoretical understanding with practical experience to ensure operational efficiency, reliability, and security.
Proficiency in troubleshooting, scenario-based administration, performance tuning, and integration with enterprise infrastructure ensures that administrators can manage complex messaging systems confidently. Achieving mastery in these domains demonstrates readiness to handle advanced Exchange Server responsibilities and contributes to professional expertise in enterprise messaging administration.
Mail Flow Architecture and Transport Optimization
Understanding mail flow architecture is essential for administrators working with Exchange Server. The transport service handles all internal and external message routing, ensuring that messages are delivered efficiently and securely. Candidates must design and manage send and receive connectors, implement transport rules, and configure message hygiene to control spam and prevent malware propagation. Monitoring transport queues and performance metrics allows administrators to detect bottlenecks and resolve delivery issues proactively.
High availability for transport services requires redundant pathways and failover mechanisms. Administrators should plan transport redundancy, ensuring that messages continue to flow even during server outages or network disruptions. Integration with mailbox databases and client access services ensures seamless end-to-end message delivery and reliability.
Client Access Services Deployment
Client access services provide the interface between users and Exchange resources. Administrators must configure services such as Outlook on the web, MAPI over HTTP, and mobile device synchronization to provide secure and reliable access. Proper deployment involves configuring authentication methods, load balancing, and failover solutions to maintain service continuity during high-demand periods.
Mobility management is a key aspect, requiring administrators to configure Exchange ActiveSync policies, manage mobile device access, and enforce security protocols. Troubleshooting connectivity issues involves examining client logs, service health, and network paths to ensure consistent user experience.
Mailbox Database Planning and High Availability
Mailbox databases are central to the storage and management of organizational email. Candidates must plan database structures that accommodate organizational growth, balancing performance, storage utilization, and redundancy. Implementing database availability groups allows for high availability and site resilience, ensuring that mailbox data remains accessible even in the event of server or site failures.
Administrators must also plan and execute backup and recovery strategies, testing restoration procedures regularly to ensure that data loss is minimized. Monitoring database health, analyzing replication status, and performing regular maintenance are critical tasks to prevent service interruptions and maintain optimal performance.
Security Implementation and Role-Based Access Control
Securing Exchange Server involves multiple layers of protection. Administrators must implement role-based access control to enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users and administrators have only the permissions necessary to perform their tasks. Integration with directory services allows centralized authentication and authorization, supporting consistent access policies.
Security strategies include encryption, secure transport protocols, and certificate management to protect data in transit and at rest. Auditing user actions and administrative changes provides accountability and supports regulatory compliance. Implementing information rights management and configuring compliance policies further strengthens the security posture of the messaging environment.
Compliance, Archiving, and eDiscovery
Administrators must ensure that Exchange Server meets organizational and regulatory requirements for data retention, discovery, and auditing. Configuring data loss prevention policies, archiving solutions, and message retention strategies helps organizations manage content effectively. eDiscovery tools allow administrators to search, retrieve, and preserve relevant information for legal or regulatory purposes.
Auditing administrative and user actions ensures transparency and accountability, supporting investigations and compliance reporting. Maintaining these systems requires continuous monitoring, periodic reviews, and updates to retention and security policies to reflect organizational and regulatory changes.
Hybrid Deployments and Cloud Integration
Hybrid deployments combine on-premises Exchange infrastructure with cloud-based services to provide flexibility and scalability. Administrators must plan hybrid configurations, including mail routing, directory synchronization, and authentication integration. Ensuring coexistence with earlier versions of Exchange requires careful planning to maintain compatibility and uninterrupted access.
Understanding federation and cross-premises connectivity is essential for managing hybrid environments effectively. Administrators must monitor system performance, troubleshoot integration issues, and maintain consistent security and compliance policies across all platforms. Hybrid management enables organizations to leverage cloud capabilities while preserving control over on-premises infrastructure.
Troubleshooting and Monitoring
Proficiency in troubleshooting is critical for Exchange Server administrators. Candidates must be able to identify and resolve issues across mailbox databases, transport services, client access services, and hybrid deployments. Utilizing system logs, message tracing, and monitoring tools allows administrators to pinpoint the source of problems and apply corrective actions efficiently.
Structured troubleshooting methodologies enable rapid resolution of connectivity issues, database failures, message delivery delays, or security breaches. Scenario-based exercises and simulations strengthen problem-solving skills and prepare administrators for real-world operational challenges.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery Planning
Designing high availability and disaster recovery strategies ensures continuity of messaging services. Administrators must implement redundant infrastructure, configure database availability groups, and test failover procedures. Recovery strategies should include both local and geographically dispersed solutions to mitigate the impact of hardware, software, or site failures.
Regularly testing recovery procedures and documenting them ensures that services can be restored promptly. Continuous refinement based on operational experience and lessons learned enhances organizational resilience and minimizes downtime.
Performance Optimization and Resource Management
Maintaining optimal performance requires monitoring server metrics, managing storage allocation, and configuring server roles effectively. Load balancing, caching, and resource allocation strategies improve responsiveness and reduce operational bottlenecks. Administrators should identify potential performance issues and proactively adjust system configurations to meet organizational demands.
Performance optimization also involves capacity planning for future growth, ensuring that infrastructure can handle increasing workloads while maintaining service levels. Efficient resource management supports user satisfaction and contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Automation and Scripting
Automation streamlines repetitive administrative tasks and enhances consistency. Administrators should develop scripts to manage mailboxes, configure compliance settings, monitor system health, and execute bulk operations. Proficiency with scripting tools such as PowerShell allows precise control over administrative tasks, reduces human error, and saves time.
Effective automation supports scalability, enabling administrators to manage large Exchange environments efficiently. By automating routine tasks, administrators can focus on strategic planning, troubleshooting, and optimization.
Scenario-Based Administrative Practice
Hands-on experience is vital for mastering Exchange Server management. Scenario-based exercises, such as configuring high availability, implementing compliance policies, troubleshooting mail flow, and managing hybrid deployments, reinforce theoretical knowledge.
Practicing with realistic scenarios develops problem-solving skills, enhances operational readiness, and prepares administrators for the responsibilities encountered in enterprise environments. These exercises simulate real-world challenges, ensuring that administrators can apply their knowledge effectively.
Advanced Security Strategies
Administrators must continuously evolve security measures to address emerging threats. Implementing encryption, managing sensitive data, enforcing access controls, and monitoring system integrity are essential for protecting organizational resources. Integrating security policies with compliance and retention requirements ensures that messaging systems remain both secure and auditable.
Proactive security monitoring, vulnerability assessments, and adherence to best practices reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Understanding advanced security strategies enables administrators to maintain a robust and resilient messaging environment.
Integration with Enterprise Services
Exchange Server interacts with various enterprise services such as Active Directory, network infrastructure, and security frameworks. Proper integration ensures consistent authentication, authorization, and messaging reliability. Administrators must plan for directory synchronization, certificate management, and network routing to maintain seamless service delivery.
Coordinating Exchange with enterprise infrastructure allows administrators to leverage existing services while ensuring that messaging operations remain secure, efficient, and reliable. Understanding these dependencies is crucial for successful deployment and ongoing management of Exchange environments.
Mastering the 70-345 exam requires in-depth understanding of Exchange Server 2016 design, deployment, management, and troubleshooting. Administrators must be proficient in mailbox database management, client access services, transport architecture, security implementation, compliance, hybrid deployment, and high availability.
Hands-on experience, scenario-based practice, and a strong grasp of integration with enterprise services ensure operational efficiency, reliability, and security. Achieving expertise in these areas demonstrates readiness to manage complex Exchange environments and supports professional growth in enterprise messaging administration.
Mailbox Database Architecture and Management
Understanding mailbox database architecture is fundamental for administrators preparing for the 70-345 exam. Mailbox databases store user data, including emails, calendars, and contacts, and their design affects performance, scalability, and availability. Administrators must plan databases based on user load, storage capacity, and redundancy requirements. Implementing multiple databases and distributing them across servers enhances fault tolerance and load balancing. Regular monitoring of database health, replication status, and storage utilization ensures consistent performance and prevents service interruptions.
High availability is achieved through Database Availability Groups (DAGs), which provide automatic failover between mailbox servers. Administrators must design DAGs considering site resilience, network connectivity, and replication topology. Backup and recovery strategies are also critical, involving consistent snapshots, recovery testing, and retention planning. Effective mailbox database management ensures that organizational data remains accessible, secure, and efficiently maintained.
Client Access Services and Connectivity
Client access services provide the interface between users and the Exchange infrastructure. Administrators need to configure services such as Outlook on the web, MAPI over HTTP, and mobile device synchronization to deliver reliable and secure access. Authentication methods, certificate management, and load balancing play a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
Planning and implementing mobility solutions involves configuring policies for mobile devices, managing synchronization, and enforcing security protocols. Monitoring client connectivity helps identify performance bottlenecks or configuration issues. Administrators must also ensure site resilience for client access services, enabling users to connect seamlessly even during server outages or network disruptions.
Transport Services and Message Flow
Transport services govern the routing of messages within the Exchange environment and between external systems. Administrators must design and configure send and receive connectors, transport rules, and message hygiene solutions to manage message flow effectively. Monitoring queues, logs, and system performance metrics allows timely identification of delivery issues or bottlenecks.
High availability for transport services requires redundant configurations and failover planning. Administrators should implement site-resilient transport solutions, ensuring messages continue to flow during service interruptions. Understanding message flow, prioritization, and routing optimizations is critical for maintaining reliability and performance across large enterprise deployments.
Security, Compliance, and Access Control
Securing Exchange Server involves enforcing role-based access control, configuring permissions, and integrating with directory services for centralized authentication. Administrators must implement security policies to protect user data and administrative accounts, including encryption, secure protocols, and auditing mechanisms.
Compliance management is a key aspect, including data loss prevention, message retention, archiving, and eDiscovery. Administrators configure retention policies, manage mailbox and administrative auditing, and ensure adherence to regulatory or organizational requirements. Planning security and compliance measures in conjunction with infrastructure design strengthens data integrity and operational reliability.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
High availability and disaster recovery planning are essential for ensuring continuous messaging operations. Administrators design redundant mailbox, transport, and client access services to maintain service continuity during server or site failures. DAG configurations, backup strategies, and failover testing are critical components of disaster recovery plans.
Regular assessment and updates of recovery procedures ensure that organizational data can be restored quickly and efficiently. Integrating high availability and disaster recovery measures into everyday administrative tasks enhances resilience and reduces potential downtime for end users.
Hybrid Deployments and Migration
Hybrid deployments combine on-premises Exchange environments with cloud-based services to offer flexibility and scalability. Administrators plan hybrid configurations, including directory synchronization, authentication integration, and mail routing. Managing coexistence with earlier Exchange versions requires careful planning to maintain compatibility and user experience.
Migration strategies involve moving mailboxes, data, and services from older environments to Exchange 2016, with minimal disruption. Administrators must troubleshoot coexistence issues, maintain security standards, and ensure consistent compliance policies across hybrid infrastructures. Understanding federation and cloud integration helps optimize hybrid deployments while maintaining control over on-premises resources.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Maintaining optimal performance requires monitoring server metrics, resource allocation, and service health. Administrators must identify potential bottlenecks, adjust configurations, and implement caching or load balancing where necessary. Capacity planning ensures that infrastructure can accommodate organizational growth without impacting service quality.
Resource management involves balancing mailbox distribution, transport workloads, and client access demands. Proactive optimization minimizes delays, enhances user experience, and contributes to the efficiency of the overall Exchange environment.
Automation and Administrative Scripting
Automation reduces repetitive administrative tasks and increases efficiency. Administrators use scripting tools to manage mailboxes, configure compliance settings, monitor system health, and execute bulk operations. Mastery of scripting allows for precise control over administrative functions, reduces errors, and saves time.
Automating routine processes supports scalability, enabling administrators to manage large environments effectively. Automation also allows IT teams to focus on strategic planning, performance tuning, and troubleshooting, enhancing overall operational capability.
Scenario-Based Practice
Hands-on practice is crucial for mastering Exchange Server administration. Simulating real-world scenarios such as configuring DAGs, managing transport rules, implementing compliance policies, or performing hybrid migrations helps administrators develop problem-solving skills and operational confidence.
Scenario-based exercises reinforce theoretical knowledge, demonstrating the application of concepts in practical settings. This approach prepares administrators for challenges encountered in enterprise environments, ensuring readiness to address issues efficiently and effectively.
Integration with Enterprise Infrastructure
Exchange Server relies on integration with other enterprise systems, including Active Directory, network infrastructure, and security frameworks. Proper coordination ensures consistent authentication, authorization, and seamless messaging operations. Administrators plan for directory synchronization, certificate management, and network routing to maintain reliable service delivery.
Integration with enterprise services enables administrators to leverage existing infrastructure while maintaining operational efficiency and security. Understanding dependencies across the environment is critical for planning, deploying, and managing Exchange Server effectively.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Proficiency in troubleshooting allows administrators to quickly identify and resolve issues affecting mail flow, database availability, client access, or hybrid connectivity. Utilizing diagnostic tools, message tracing, and system logs enables efficient root cause analysis.
Developing structured troubleshooting methodologies enhances problem-solving skills and ensures minimal impact on users. Continuous practice with complex scenarios strengthens readiness for handling operational challenges in large-scale Exchange deployments.
Messaging Compliance and Auditing
Administrators must maintain messaging compliance through retention policies, auditing, and regulatory adherence. Configuring auditing for both administrative and user actions ensures accountability and transparency. Monitoring compliance systems helps identify gaps, maintain records, and enforce organizational standards.
Effective management of compliance tools, including archiving, eDiscovery, and data loss prevention, ensures that organizations meet legal and operational requirements. Regular review and updates of policies maintain their relevance and effectiveness over time.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Exchange Server administration requires ongoing learning to stay current with evolving technologies, security practices, and operational strategies. Administrators should engage in practical exercises, explore new features, and refine skills in planning, deployment, and troubleshooting.
Continuous skill development enhances operational efficiency, reduces errors, and strengthens the administrator’s capability to manage complex Exchange environments. It ensures that messaging infrastructure remains resilient, secure, and responsive to organizational needs.
Achieving proficiency in the 70-345 exam demands comprehensive understanding of Exchange Server 2016, including mailbox database management, client access, transport services, security, compliance, hybrid integration, and high availability. Practical experience, scenario-based exercises, and familiarity with enterprise integration strengthen operational readiness. Mastery of these concepts ensures administrators can design, deploy, manage, and troubleshoot complex messaging environments efficiently while maintaining security, compliance, and high availability.
Exchange Server Infrastructure Design
Designing an Exchange Server infrastructure is central to ensuring performance, reliability, and scalability. Administrators must assess organizational requirements, including user population, mailbox sizes, messaging patterns, and service level expectations. Based on these factors, they design the server topology, including mailbox servers, client access servers, and transport servers. Proper placement of roles, redundancy planning, and load distribution are critical to maintaining continuous service.
Site resilience is also an important design consideration. Administrators must plan for multiple datacenter deployments, ensuring DAGs and client access services can failover seamlessly. Network considerations, including latency, bandwidth, and security policies, are integrated into the infrastructure design to maintain performance across distributed locations. Effective planning at this stage reduces operational issues and simplifies future expansions.
Mailbox Database Deployment and Management
Mailbox database deployment requires careful planning to optimize performance, storage efficiency, and availability. Administrators create databases based on capacity requirements, redundancy, and expected growth. Implementing DAGs provides high availability and automatic failover capabilities, ensuring mailboxes remain accessible even during server failures.
Ongoing management includes monitoring replication health, storage utilization, and database performance. Administrators also schedule regular backups, test restore procedures, and implement retention policies. Addressing potential performance bottlenecks, maintaining database integrity, and ensuring compliance are essential for sustaining organizational messaging operations.
Client Access Service Configuration
Client access services allow users to interact with Exchange resources using Outlook, web clients, and mobile devices. Administrators configure authentication methods, certificates, and connectivity protocols to ensure secure and reliable access. Implementing MAPI over HTTP, Outlook on the web, and ActiveSync provides seamless client connectivity while enforcing security standards.
Load balancing and redundancy planning are crucial to prevent service interruptions. Monitoring connection health, analyzing user activity patterns, and addressing connectivity issues proactively improves user experience. Additionally, administrators design site-resilient client access services to ensure continuous access during network or server outages.
Transport Services Management
Transport services are responsible for routing messages within Exchange and to external systems. Administrators configure send and receive connectors, transport rules, and anti-spam and anti-malware filters to maintain message integrity and deliverability. Monitoring transport queues, logs, and performance metrics allows early detection of issues.
Site resilience and redundancy for transport services ensure uninterrupted message flow during server or network disruptions. Administrators implement monitoring and troubleshooting processes, optimizing routing paths and applying message hygiene policies to maintain system reliability. Understanding how transport services interact with mailbox and client access services is vital for effective administration.
Security and Compliance Management
Securing Exchange Server involves configuring role-based access control, permissions, and integration with directory services. Administrators implement policies to protect user and administrative accounts, enforce encryption standards, and monitor access through auditing.
Compliance management addresses organizational and regulatory requirements, including data retention, eDiscovery, archiving, and auditing. Administrators configure retention policies, perform mailbox and administrative audits, and implement data loss prevention strategies. Aligning security and compliance with overall infrastructure ensures that messaging data is protected and accessible under defined policies.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
High availability and disaster recovery planning guarantee messaging continuity in case of server or site failures. Administrators design redundant mailbox, client access, and transport services, configure DAGs, and implement backup and restore procedures.
Regular testing and validation of recovery procedures help ensure rapid restoration of services. Administrators also monitor system health and maintain failover configurations to minimize downtime. Effective disaster recovery planning integrates with everyday management tasks to enhance operational resilience.
Hybrid Integration and Migration Strategies
Hybrid Exchange deployments combine on-premises servers with cloud-based services to enhance scalability and flexibility. Administrators plan hybrid configurations, including directory synchronization, authentication integration, and mail flow routing. Coexistence with previous Exchange versions requires careful management to maintain seamless service.
Migration planning involves transferring mailboxes, services, and data with minimal disruption. Administrators address compatibility, security, and compliance considerations during migration. Knowledge of hybrid scenarios, federation, and cloud integration ensures consistent service delivery across both on-premises and cloud environments.
Performance Optimization
Maintaining optimal performance requires ongoing monitoring of server health, resource usage, and message flow. Administrators analyze workloads, identify bottlenecks, and adjust configurations to enhance efficiency. Capacity planning ensures that infrastructure can accommodate future growth while maintaining responsiveness.
Optimization also involves balancing database distribution, transport workloads, and client access requests. Proactive performance management reduces latency, improves reliability, and supports consistent user experience across all services.
Automation and Scripting
Automating administrative tasks streamlines operations and reduces errors. Administrators use scripting tools to manage mailboxes, configure policies, monitor systems, and execute bulk operations. Automation allows repetitive tasks to be handled efficiently while ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Scripting supports scalability, enabling administrators to manage large environments effectively. It also frees up time for strategic planning, troubleshooting, and performance tuning. Mastery of automation techniques is essential for efficient Exchange administration in complex environments.
Advanced Troubleshooting
Effective troubleshooting requires understanding the interdependencies between mailbox databases, client access, transport services, and security systems. Administrators use diagnostic tools, logs, and message tracing to identify and resolve issues quickly.
Structured troubleshooting approaches reduce downtime and prevent recurrence of problems. Scenario-based problem-solving builds experience and confidence, preparing administrators for real-world operational challenges in enterprise Exchange environments.
Auditing and Messaging Compliance
Auditing ensures accountability and adherence to organizational policies. Administrators track administrative and user actions, review mailbox activities, and implement monitoring mechanisms. Compliance management includes data retention, archiving, and eDiscovery processes to maintain legal and organizational standards.
Regular review and updates of compliance policies keep systems aligned with changing regulations and organizational requirements. Administrators must ensure that auditing, retention, and compliance measures are integrated effectively within the Exchange environment.
Continuous Learning and Practical Application
Ongoing learning is critical for administrators to remain proficient in Exchange Server management. Hands-on practice with infrastructure deployment, high availability configurations, hybrid scenarios, and compliance enforcement strengthens expertise.
Scenario-based exercises help administrators apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings, enhancing problem-solving abilities. Continuous development ensures that administrators can manage, optimize, and secure complex messaging environments while adapting to evolving technologies.
Preparing for the 70-345 exam requires deep knowledge of Exchange Server 2016 architecture, mailbox management, client access, transport services, security, compliance, hybrid integration, and high availability. Mastery of these domains, combined with practical experience, scenario-based practice, and familiarity with enterprise infrastructure, ensures administrators are equipped to design, deploy, manage, and troubleshoot complex messaging environments effectively. Successful preparation encompasses both conceptual understanding and hands-on proficiency, fostering confidence and operational competence in real-world Exchange Server administration.
Exchange Server Security Strategy
A comprehensive security strategy for Exchange Server 2016 requires both proactive planning and ongoing management. Administrators must secure communication channels by implementing encryption for data in transit and at rest. This includes configuring TLS for mail flow, enforcing HTTPS for client access, and applying encryption policies for mailbox data. Identity and access management is a key focus, with administrators implementing role-based access control, multi-factor authentication, and monitoring administrative privileges to prevent unauthorized access.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential. Administrators review access logs, evaluate system configurations, and address potential security gaps. Policies for password management, account lockout thresholds, and mailbox access permissions are enforced to reduce the risk of breaches. Integration with directory services ensures consistent authentication and policy enforcement across the organization.
Compliance and Data Governance
Compliance management in Exchange 2016 revolves around meeting organizational and regulatory requirements. Administrators configure data retention policies, enabling automatic archiving and deletion based on legal or business needs. Message Records Management ensures that emails are preserved for required periods and disposed of when no longer necessary.
eDiscovery capabilities allow administrators to locate, review, and export mailbox content for legal or investigative purposes. Auditing mechanisms track user actions and administrative modifications, providing accountability and traceability. Implementing data loss prevention rules protects sensitive information, monitoring messages for policy violations and applying automated actions to prevent leaks.
High Availability Planning
High availability is critical for maintaining uninterrupted messaging services. Administrators design and deploy Database Availability Groups, which replicate mailbox databases across multiple servers to provide automatic failover. Monitoring replication health, latency, and consistency ensures mailbox availability.
Site resilience planning extends high availability across geographic locations. This includes configuring cross-site DAGs, redundant client access services, and transport service failover mechanisms. Testing failover scenarios and validating recovery processes ensures that services continue to operate during planned maintenance or unplanned outages.
Transport and Message Routing
Transport services in Exchange 2016 handle the flow of messages internally and externally. Administrators configure send and receive connectors, define message routing rules, and implement transport rules to enforce compliance and security. Anti-spam and anti-malware filters are applied to protect the environment from threats.
Monitoring transport queues and server performance allows for proactive identification of delivery issues. Administrators optimize message routing paths and maintain redundancy to prevent bottlenecks. Proper transport management ensures timely and secure delivery of messages across the organization.
Client Access Optimization
Client access services provide the interface for users to connect via Outlook, mobile devices, and web clients. Administrators configure authentication protocols, certificates, and load balancing to ensure secure, efficient, and resilient access. Implementing MAPI over HTTP and Autodiscover services enhances connectivity and simplifies client configuration.
Monitoring client connectivity, response times, and error rates helps maintain optimal user experience. Planning for site-resilient client access ensures that service disruptions are minimized and that users can seamlessly connect to the environment from various locations and devices.
Hybrid Deployments and Coexistence
Hybrid Exchange environments integrate on-premises servers with cloud-based services. Administrators configure directory synchronization, hybrid mail flow, and authentication to enable a seamless experience. Managing coexistence with earlier Exchange versions requires attention to compatibility, mail flow, and client access configurations.
Migration strategies include moving mailboxes, services, and settings with minimal disruption. Administrators must plan for user communication, data integrity, and compliance during the transition. Hybrid deployments enhance flexibility and scalability while maintaining centralized control over the messaging environment.
Performance and Capacity Management
Maintaining Exchange performance involves monitoring server resources, mailbox database health, and service responsiveness. Administrators evaluate CPU, memory, and storage utilization, adjusting configurations to prevent performance degradation. Capacity planning ensures that infrastructure can support anticipated growth and workloads.
Database placement, transport workload distribution, and client access traffic management are optimized to reduce latency and improve reliability. Regular performance analysis and tuning allow administrators to proactively address potential bottlenecks and maintain consistent service quality.
Automation and Scripting
Automation reduces repetitive administrative tasks, enhances accuracy, and supports large-scale environments. Administrators use scripting to manage mailboxes, configure policies, generate reports, and implement bulk changes efficiently. Scripts can be scheduled or triggered based on events, improving operational efficiency and consistency.
Automation also supports compliance enforcement, monitoring, and alerting. By integrating scripting into daily management, administrators free up time for strategic planning, troubleshooting, and service optimization, ensuring that routine tasks are performed reliably and efficiently.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics
Effective troubleshooting requires an understanding of the interactions between mailbox databases, client access, transport services, and security mechanisms. Administrators use logs, message traces, and diagnostic tools to isolate issues and implement solutions quickly.
A structured approach to problem-solving includes identifying symptoms, gathering relevant data, analyzing potential causes, and applying corrective actions. Scenario-based troubleshooting prepares administrators for real-world challenges, minimizing downtime and service disruption.
Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring of Exchange Server provides insights into system health, usage patterns, and potential issues. Administrators track server performance, database replication, message queues, client connectivity, and security events. Reporting tools generate actionable data for capacity planning, compliance verification, and operational optimization.
Proactive monitoring allows administrators to address issues before they impact users, maintaining reliability and performance. Regular reporting supports management oversight, audit requirements, and decision-making for infrastructure improvements.
Practical Application and Experience
Hands-on experience is essential for mastering Exchange Server administration. Administrators gain proficiency by deploying servers, configuring services, managing databases, implementing security measures, and performing migrations in test or lab environments.
Practical exercises reinforce theoretical knowledge, improve problem-solving skills, and provide familiarity with real-world scenarios. This experiential learning ensures that administrators can apply concepts effectively in enterprise environments, maintaining operational efficiency and reliability.
Preparing for the 70-345 exam requires a deep understanding of Exchange Server 2016 design, deployment, and management. Mastery of security, compliance, high availability, transport, client access, hybrid integration, performance optimization, automation, troubleshooting, and disaster recovery is essential. Combining conceptual knowledge with hands-on experience ensures administrators are capable of maintaining secure, efficient, and resilient messaging environments while meeting organizational and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Mastering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 through the 70-345 exam framework demands a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical concepts and practical implementation strategies. The certification emphasizes designing, deploying, and managing Exchange environments in complex enterprise settings. It challenges administrators to integrate multiple components, including mailbox databases, client access services, transport services, security configurations, compliance mechanisms, and hybrid deployment scenarios. Achieving proficiency in these areas ensures that IT professionals can provide reliable, scalable, and secure messaging services for organizations of any size.
A critical component of preparation involves understanding the architecture and operational principles of Exchange Server 2016. Administrators must be capable of planning and deploying mailbox databases with high availability and site resilience in mind. Knowledge of client access services is equally important, including strategies for authentication, connectivity optimization, load balancing, and monitoring. Transport services management ensures that messages are routed efficiently, with proper compliance, hygiene, and resilience built into the system.
Security and compliance remain central to effective Exchange administration. Role-based access control, encryption, auditing, and data loss prevention safeguard organizational data and maintain regulatory compliance. Administrators are expected to design and implement strategies for message retention, archiving, eDiscovery, and auditing to meet both business and legal requirements. Familiarity with hybrid deployments and coexistence scenarios enhances organizational flexibility, enabling seamless integration with cloud services while maintaining control over on-premises resources.
Performance optimization, monitoring, and troubleshooting are vital skills for maintaining service reliability. Administrators must continuously evaluate resource utilization, optimize database placement, manage workloads, and proactively resolve issues to prevent service disruption. Automation through scripting improves operational efficiency, allowing for rapid configuration changes, bulk operations, and consistent policy enforcement. Backup and disaster recovery planning ensures that data integrity and service continuity are maintained under all circumstances, reinforcing organizational resilience.
Hands-on experience plays a pivotal role in translating knowledge into actionable skills. Simulating real-world scenarios, conducting lab exercises, and testing deployment, migration, and recovery processes provide practical insights that theoretical study alone cannot offer. These experiences develop problem-solving abilities and prepare administrators for the challenges of managing a live Exchange environment.
In conclusion, preparing for the 70-345 exam equips IT professionals with the expertise required to manage and optimize Exchange Server 2016 environments effectively. It combines deep technical knowledge with practical application, emphasizing security, compliance, high availability, performance, and adaptability. Mastery of these areas ensures that administrators can deliver secure, efficient, and resilient messaging solutions, supporting organizational productivity and maintaining the integrity of communication systems. This certification validates an individual’s capability to oversee complex Exchange infrastructures, positioning them as skilled professionals capable of meeting the demands of modern enterprise IT environments.
Microsoft MCSE 70-345 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 70-345 Designing and Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- AB-100 - Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect
- AB-731 - AI Transformation Leader
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MO-300 - Microsoft PowerPoint (PowerPoint and PowerPoint 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 70-345 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 70-345 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 70-345 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 70-345 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 70-345 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 70-345. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 70-345 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 70-345 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 70-345 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 70-345 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

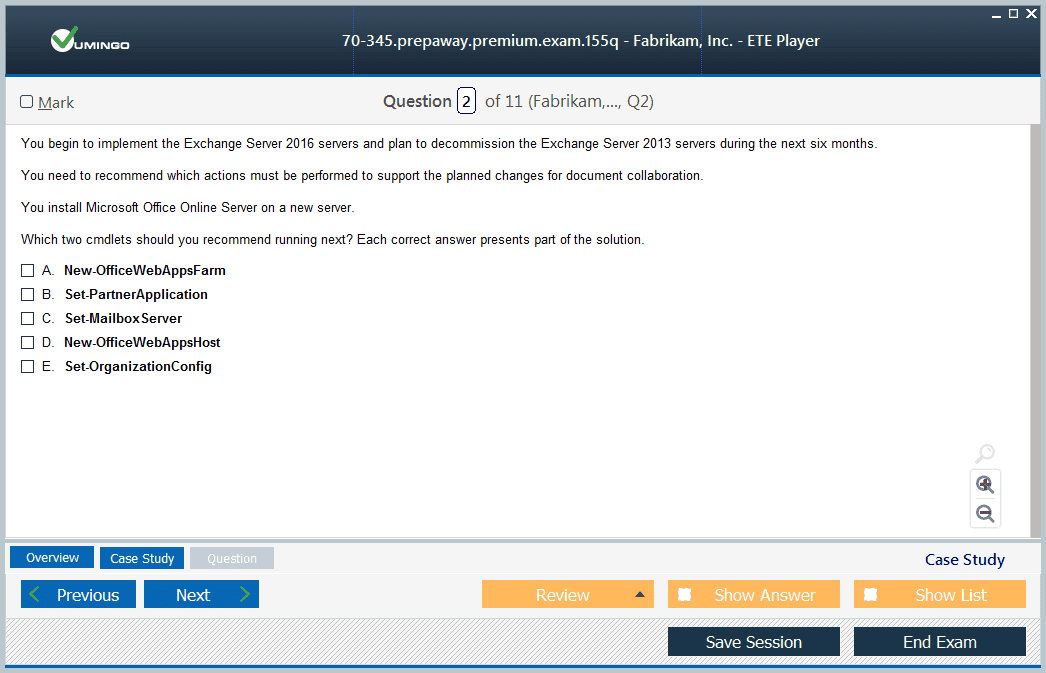
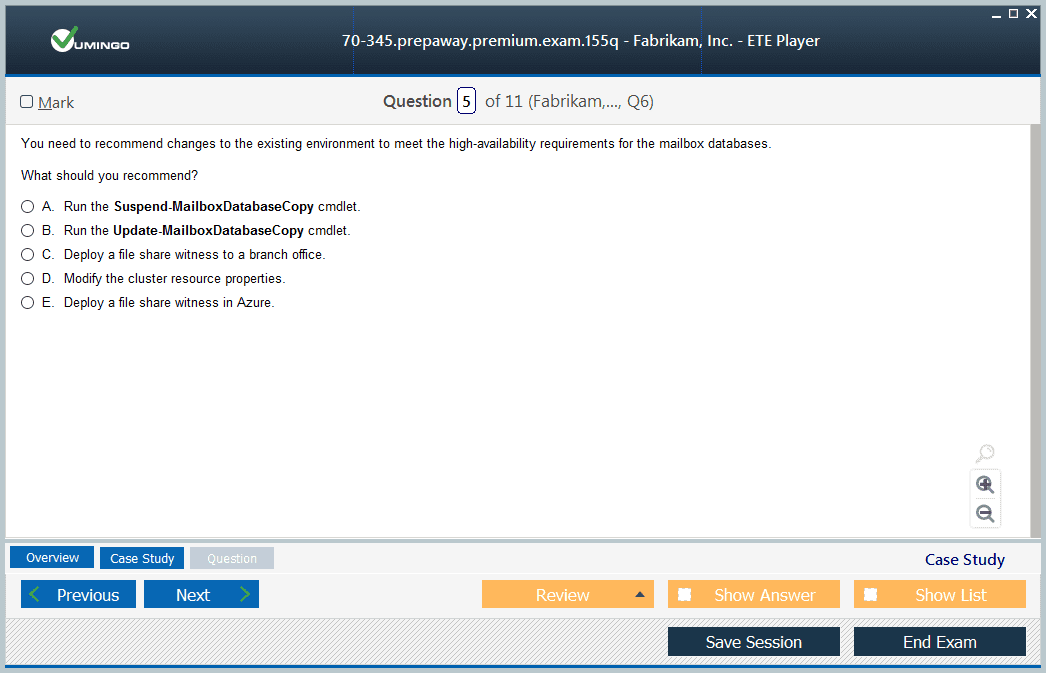
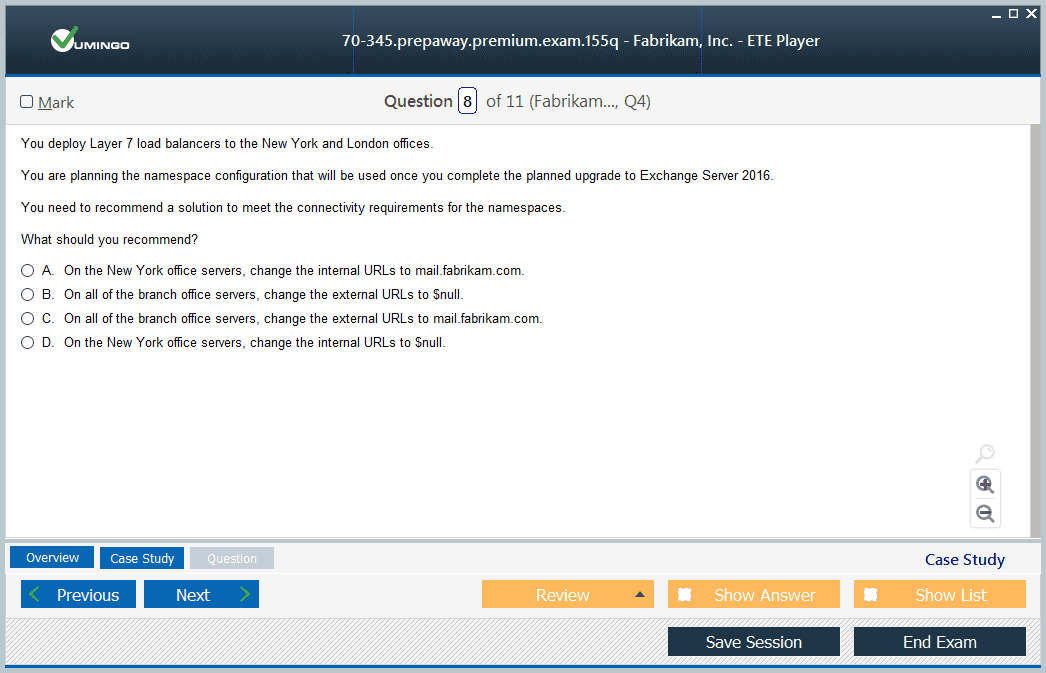
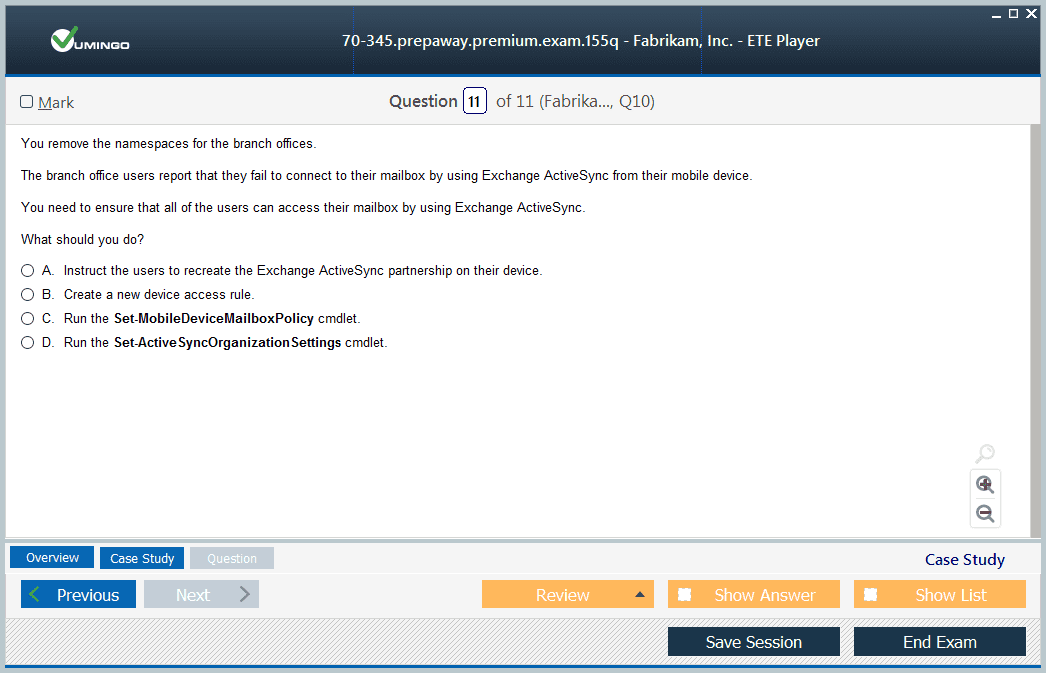




Regards,
Manento
100% Vaild
You need to identify which host in the message path is responsible for the delivery delay.
What should you do?
A. Review the contents of the protocol logs.
B. Search the message tracking logs.
C. Search the delivery reports for the message
D. Review the contents of the application log E. Input the message header to the Exchange Remote Connectivity Analyzer
Answer : C
You have a user named User1 who must send encrypted email messages to a user
Question No : 2 - (Topic 1)
Question No : 3 - (Topic 4)
Microsoft 70-345 : Practice Exam
Leaders in it certification 5
named User2 in another organization.
User1 and User2 have certificates issued from a trusted third-party certification authority (CA).
You need to ensure that User1 can send the encrypted email messages to User2
A. Instruct User2 to send a digitally signed email message to User1.
B. Instruct User2 to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Send the CSR to User1.
C. Instruct User1 to send a digitally signed email message to User2
D. Instruct User1 to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Send the CSR to User2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You plan to deploy a data availability group (DAG) across two locations. You will use a Microsoft Azure virtual machine as a witness server.
You need to configure the network infrastructure to support the planned deployment.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Answer :
In Azure , Deploy a multi - Site VPN
Configure on-premises VPN devices
In Azure , create a logical network object for each data centre, and register the on-premisis DNS servers
User1 and User2 have certificates issued from a trusted third-party certification authority (CA).
You need to ensure that User1 can send the encrypted email messages to User2
A. Instruct User2 to send a digitally signed email message to User1.
B. Instruct User2 to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Send the CSR to User1.
C. Instruct User1 to send a digitally signed email message to User2
D. Instruct User1 to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Send the CSR to User2