- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 98-367 Security Fundamentals Dumps
Pass Microsoft MTA 98-367 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


98-367 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 168 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 31, 2026
- Training Course 66 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 210 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Microsoft MTA 98-367 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 98-367 Security Fundamentals practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Building a Strong Security Foundation with Microsoft 98-367 MTA Security Fundamentals
The Microsoft 98-367 exam serves as a foundational step for individuals pursuing a career in IT security. It introduces core concepts in network security, operating system protection, and software security, offering candidates an understanding of how digital environments can be safeguarded from threats. The exam emphasizes practical application of security principles, ensuring that candidates not only grasp theoretical knowledge but also know how to implement security measures in real-world scenarios. Understanding IT security fundamentals is essential as organizations increasingly rely on technology for daily operations, communication, and data storage.
Security fundamentals involve a layered approach to protecting systems, networks, and data. Candidates are introduced to the concept of defense in depth, which ensures multiple layers of protection are applied to mitigate vulnerabilities. This includes the use of physical security measures, network safeguards, operating system hardening, and secure software practices. The 98-367 exam tests knowledge across these layers to ensure candidates can identify potential weaknesses, evaluate risks, and implement appropriate security controls. A strong grasp of these concepts is essential for IT professionals as it lays the groundwork for advanced security practices and certifications.
Understanding Security Layers
One of the critical areas of the 98-367 exam is the comprehension of security layers. Security layers are designed to prevent unauthorized access, reduce vulnerabilities, and protect sensitive information. Candidates learn to identify the different types of security measures applicable at various levels, including physical security, network security, operating system protection, and application security. Physical security involves protecting hardware from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. Network security focuses on controlling access to networks, monitoring traffic, and using firewalls and intrusion detection systems to safeguard data. Operating system protection ensures that endpoints and servers are configured securely, patched regularly, and monitored for anomalies. Application security involves ensuring that software operates safely, protects user data, and resists common attack techniques such as injection or buffer overflow attacks.
The exam also tests understanding of threat modeling and attack surface analysis. Candidates are expected to evaluate environments for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Social engineering tactics, phishing attempts, and other human-centered threats are considered in this analysis. By recognizing potential threats, candidates can develop strategies to reduce risks and implement proactive defenses. This knowledge is particularly relevant for enterprise environments where multiple users, devices, and applications interact continuously, creating complex attack surfaces.
Network Security Essentials
Network security is a foundational component of the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand how to design, configure, and monitor networks to prevent unauthorized access and maintain data integrity. Network security includes the use of firewalls, virtual private networks, secure protocols, and segmentation to isolate critical systems from potential threats. Understanding TCP/IP, DNS, and other network protocols is essential, as it enables professionals to identify anomalies and implement appropriate safeguards.
Candidates also study intrusion detection and prevention systems, which monitor network activity for suspicious behavior. Effective network security practices involve both reactive measures, such as detecting and responding to attacks, and proactive measures, including network segmentation, access controls, and encryption. Knowledge of these techniques ensures that candidates can maintain secure communication channels within enterprise environments and protect sensitive information from both internal and external threats.
High availability and redundancy in network design are also relevant topics. Candidates must understand how to implement backup systems, failover mechanisms, and disaster recovery plans to ensure continuity of operations. This aspect of network security is particularly important for businesses that rely heavily on IT infrastructure, where downtime or data loss can have significant operational and financial consequences.
Operating System Security
Operating system security is a major domain covered in the 98-367 exam. Candidates learn how to configure operating systems to minimize vulnerabilities, prevent unauthorized access, and protect data integrity. Key areas include user account management, access control policies, patch management, and system hardening. Understanding file system permissions, registry settings, and administrative privileges is essential for securing both client and server machines.
Threats such as malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access attempts are studied to understand how they exploit operating system weaknesses. Candidates are also tested on implementing preventive measures such as antivirus software, system updates, and endpoint security solutions. Proper configuration and continuous monitoring of operating systems are critical to maintaining secure IT environments and preventing breaches. Candidates must also be familiar with event logs, auditing, and monitoring tools to detect suspicious activities.
The exam places emphasis on understanding the balance between security and usability. Configurations must protect data and systems without unnecessarily limiting user productivity. IT professionals must ensure that security measures are effective, efficient, and scalable to accommodate growing organizational needs.
Software Security Practices
Software security is another essential focus of the 98-367 exam. Candidates study methods to protect applications from vulnerabilities and ensure that software functions safely. This includes secure coding practices, patch management, and the use of security tools such as antivirus, anti-malware, and anti-spam applications. Understanding common attack vectors like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows allows candidates to identify and mitigate risks associated with software applications.
Software security also involves managing application permissions, validating input, and implementing encryption for sensitive data. Candidates are taught to recognize potential threats during the software development lifecycle and to apply security measures from design through deployment. These practices ensure that applications operate reliably, protect user data, and reduce the likelihood of exploitation by attackers.
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
The 98-367 exam also covers authentication, authorization, and accounting, commonly referred to as AAA. Authentication verifies the identity of users or devices attempting to access a system or network. Candidates must understand various authentication methods, including passwords, multi-factor authentication, and digital certificates. Authorization determines the level of access granted to authenticated users, ensuring they can only perform actions appropriate to their role. Accounting involves tracking user activity, logging access events, and maintaining records for auditing and compliance purposes.
Effective implementation of AAA principles ensures secure access management in enterprise environments. Candidates are tested on how to integrate authentication methods with network and system policies, enforce role-based access controls, and monitor user activity for security violations. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining secure and accountable IT operations in organizations of all sizes.
Security Policies and Procedures
Developing and enforcing security policies is a critical aspect of the 98-367 exam. Candidates are expected to understand how to create policies that govern acceptable use, access control, data protection, and incident response. Security policies provide a framework for consistent implementation of security measures and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Candidates also learn to evaluate the effectiveness of policies, adjust them as needed, and communicate them to stakeholders.
Incident response procedures are included as part of security policy management. Candidates must understand how to identify, contain, and recover from security incidents while minimizing impact on operations. Documentation, reporting, and analysis of security events are key components of effective policy enforcement. These practices ensure that organizations can respond promptly and effectively to threats while maintaining operational resilience.
Risk Management and Threat Analysis
The exam emphasizes risk management and threat analysis as foundational skills. Candidates learn to assess potential risks, prioritize vulnerabilities, and implement mitigation strategies. Techniques include threat modeling, vulnerability assessments, and security audits. Understanding risk management allows professionals to allocate resources effectively and implement controls that provide the highest level of protection for critical assets.
Social engineering and human-centered threats are also addressed, as they represent a significant portion of security risks. Candidates must recognize common tactics such as phishing, pretexting, and baiting, and develop strategies to educate users and prevent exploitation. This comprehensive approach ensures that both technical and human elements of security are addressed in enterprise environments.
Exam Preparation and Study Strategies
Preparing for the 98-367 exam requires focused study across multiple domains, including security layers, network security, operating system protection, software security, authentication, and policy management. Candidates should use scenario-based learning to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, reinforcing understanding and improving retention. Hands-on practice with security tools, configuration exercises, and threat simulations enhances readiness for both the exam and real-world application.
Time management, review of key concepts, and consistent practice with sample scenarios are recommended strategies. Candidates are also encouraged to explore emerging security trends, as staying current with technologies and threats enhances understanding and prepares them for advanced certifications.
Career Relevance of the 98-367 Certification
The 98-367 certification validates fundamental IT security skills, providing a strong foundation for a career in technology and cybersecurity. Certified professionals are recognized for their ability to implement security measures, manage network and system risks, and respond effectively to threats. These skills are applicable in a variety of roles, including IT support, network administration, systems management, and security analysis. The knowledge gained through the exam also prepares candidates for advanced certifications, expanding career opportunities and enhancing professional growth in the technology sector.
Understanding Threats and Vulnerabilities
A significant portion of the 98-367 exam centers on understanding threats and vulnerabilities within IT systems. Candidates are required to recognize the difference between internal and external threats, including malware, phishing attacks, denial-of-service incidents, and unauthorized access. Internal threats often arise from employees or users who inadvertently or deliberately compromise security. External threats come from hackers, cybercriminals, or other unauthorized entities attempting to exploit vulnerabilities. Understanding the nature and origin of these threats is essential for implementing appropriate security controls.
Vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in systems, networks, or software that can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations. Candidates must learn to identify common vulnerabilities in operating systems, network protocols, and applications. Techniques such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits are crucial in assessing potential risks. Candidates are also expected to evaluate the impact and likelihood of threats exploiting vulnerabilities, prioritizing remediation efforts to protect critical assets effectively.
Social Engineering and Human Factors
Social engineering is an integral concept covered in the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand how attackers manipulate human behavior to gain access to sensitive information or systems. Common techniques include phishing emails, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating. Recognizing these methods enables IT professionals to implement user awareness training and policies that reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
The exam emphasizes the importance of combining technical controls with user education. While firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption are essential, human error remains a leading cause of security incidents. By fostering a security-aware culture and implementing clear reporting procedures, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with social engineering attacks.
Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment is a critical skill for candidates preparing for the 98-367 exam. This process involves identifying potential threats, evaluating the severity of their impact, and determining the likelihood of their occurrence. Risk management encompasses the strategies and actions taken to reduce, transfer, or accept these risks. Candidates are tested on their ability to apply risk management principles to practical scenarios, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to protect critical assets.
Techniques such as threat modeling, asset classification, and vulnerability analysis are emphasized. Candidates must also understand regulatory requirements and compliance standards that influence risk management decisions. Effective risk management ensures that organizations can maintain operational continuity while minimizing exposure to potential security incidents.
Authentication Techniques
Authentication is a fundamental component of IT security and is thoroughly examined in the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand various methods of verifying user and device identities. These include password-based authentication, multi-factor authentication, smart cards, biometrics, and certificate-based methods. Each technique has its strengths and limitations, and candidates are expected to know how to implement them appropriately based on organizational requirements.
The exam also covers authentication protocols such as Kerberos, RADIUS, and TACACS+. Candidates must understand how these protocols function within network environments to provide secure and reliable authentication. Proper implementation of authentication mechanisms ensures that only authorized users can access systems and resources, reducing the likelihood of breaches caused by unauthorized access.
Authorization and Access Control
Authorization is the process of granting users or devices the appropriate level of access based on their verified identity. The 98-367 exam tests candidates on their understanding of access control models, including discretionary access control, mandatory access control, and role-based access control. Candidates must also learn to configure permissions for files, folders, and applications to enforce the principle of least privilege.
Effective access control prevents unauthorized activities and limits the potential damage that can occur if credentials are compromised. Candidates are expected to integrate access control mechanisms with authentication systems and to manage permissions consistently across operating systems, applications, and network resources.
Security Policies and Compliance
Security policies provide a framework for enforcing security measures and ensuring compliance with organizational and regulatory standards. Candidates preparing for the 98-367 exam must understand how to develop, implement, and maintain security policies that cover acceptable use, password management, incident response, and data protection.
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO standards is an essential consideration. Candidates are expected to apply policy enforcement consistently while balancing security needs with operational requirements. Policies also guide the response to security incidents, ensuring that procedures are standardized, documented, and effective in mitigating damage.
Network Security Practices
The 98-367 exam emphasizes practical network security techniques. Candidates must be able to configure firewalls, implement network segmentation, and deploy virtual private networks to protect data in transit. Encryption protocols, secure routing practices, and intrusion detection and prevention systems are also tested. Understanding the design and implementation of secure network architectures is essential for safeguarding organizational assets.
Monitoring network traffic and analyzing logs are key skills. Candidates must learn to detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and respond appropriately. Effective network security practices combine preventive, detective, and corrective controls to create a robust defense against attacks.
Securing Operating Systems
Operating system security is another critical domain for the 98-367 exam. Candidates are tested on system hardening techniques, including patch management, disabling unnecessary services, configuring firewalls, and implementing security templates. Knowledge of user account policies, group policies, and access control lists is essential for protecting both client and server systems.
Endpoint protection is a focus, covering antivirus solutions, anti-malware tools, and monitoring software. Candidates must understand how to detect and respond to security threats, ensuring that systems remain operational and secure. This area also includes understanding audit logs, event monitoring, and system alerts for proactive threat detection.
Software Security Implementation
Software security involves protecting applications and ensuring they function safely. Candidates learn about secure coding practices, patch deployment, and configuration management. Understanding vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows, injection attacks, and cross-site scripting is essential. Candidates must implement protective measures, validate user input, and maintain software updates to reduce risks.
The 98-367 exam also emphasizes the use of security software tools to mitigate threats. Antivirus, anti-spam, and anti-malware solutions are covered, with candidates learning to configure and manage these tools to maintain system integrity. Software security practices ensure that applications do not introduce vulnerabilities into the network environment.
Monitoring and Incident Response
Monitoring systems and responding to incidents are vital skills for candidates. The 98-367 exam tests knowledge of event logging, alert configuration, and threat analysis. Candidates must be able to identify suspicious activities, evaluate the severity of incidents, and apply corrective measures. Incident response planning ensures that organizations can react quickly and effectively to minimize damage.
Candidates also learn to document incidents and analyze trends to prevent future occurrences. Combining proactive monitoring with reactive incident response creates a comprehensive security posture that protects organizational assets and supports operational continuity.
Emerging Technologies and Security Trends
The exam includes concepts related to emerging technologies and their security implications. Candidates study cloud computing, mobile device security, IoT integration, and virtualization. Each of these technologies introduces new attack surfaces and requires updated security strategies. Understanding these trends ensures that candidates can adapt to evolving threats and implement protective measures in modern IT environments.
Cloud security practices such as encryption, identity management, and secure configuration are tested. Mobile device management, endpoint protection, and secure application deployment are also included. Candidates must understand how to balance innovation with risk mitigation to maintain secure and efficient IT operations.
Preparing for the Exam
Effective preparation for the 98-367 exam involves studying all core domains, practicing scenario-based exercises, and applying concepts in real-world environments. Candidates should focus on understanding threats, vulnerabilities, authentication, authorization, network security, operating system protection, and software security. Hands-on practice, lab simulations, and interactive learning enhance comprehension and retention of key concepts.
Time management, review of study materials, and consistent practice are critical for success. Candidates are encouraged to explore case studies, assess practical scenarios, and simulate incident response activities. Staying current with evolving security trends further prepares candidates to apply foundational knowledge in dynamic environments.
Career Applications
Achieving the 98-367 certification validates foundational knowledge in IT security. Certified professionals are equipped to implement security measures, monitor networks, manage vulnerabilities, and respond to incidents. These skills are applicable in entry-level IT roles, including support, network administration, and systems management. The certification also provides a stepping stone for advanced Microsoft certifications, enabling career growth in cybersecurity, network security, and enterprise IT management.
Understanding Security Layers in Depth
The 98-367 exam places strong emphasis on security layers, which serve as the foundation for a comprehensive defense strategy. Security layers consist of multiple levels of protection applied to systems, networks, and applications to reduce the risk of unauthorized access or compromise. Candidates are expected to understand the interplay between physical security, network security, operating system hardening, and application safeguards. Physical security measures include controlling access to server rooms, locking devices, and monitoring entry points. Network security involves implementing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and secure communication protocols. Operating system hardening encompasses patch management, configuring security policies, and monitoring system events. Application security ensures that software is developed, deployed, and maintained in a manner that minimizes vulnerabilities and prevents exploitation.
Candidates are tested on how to integrate these layers to create a robust, multi-tiered defense. This approach ensures that if one layer is compromised, other controls continue to protect critical assets. The exam also requires understanding defense-in-depth principles and how layered security supports compliance with organizational and regulatory standards. Advanced topics include evaluating the effectiveness of each layer, identifying gaps, and implementing additional controls to strengthen the overall security posture.
Advanced Threat Modeling
Threat modeling is a crucial component of the 98-367 exam. Candidates learn to systematically analyze potential threats and assess their impact on IT environments. Threat modeling involves identifying assets, potential attackers, attack vectors, and existing controls. Candidates are expected to create models that evaluate the likelihood and severity of attacks, prioritize vulnerabilities, and recommend mitigation strategies.
The exam covers various threat types, including malware, phishing, denial-of-service attacks, and insider threats. Candidates must also understand how social engineering exploits human behavior to bypass technical controls. By conducting thorough threat modeling, professionals can anticipate attacks, implement proactive measures, and reduce the risk of data breaches or system compromise.
Risk Assessment and Management Strategies
Risk assessment and management are emphasized in the 98-367 exam to ensure candidates can prioritize security efforts effectively. Risk assessment involves evaluating the potential consequences of threats exploiting vulnerabilities. Candidates must calculate risk by considering both the probability of occurrence and the impact on organizational operations.
Risk management strategies include mitigating, transferring, avoiding, or accepting risks. Candidates must understand how to implement safeguards such as encryption, access controls, and redundancy to reduce risk. Additionally, they are tested on integrating risk management into security policies, incident response planning, and overall IT strategy. Proper risk management allows organizations to allocate resources efficiently, protect critical assets, and maintain operational continuity.
Authentication Techniques and Best Practices
Authentication is a core concept tested in the 98-367 exam. Candidates are required to understand methods of verifying the identity of users and devices before granting access to systems. Techniques include passwords, multi-factor authentication, smart cards, biometrics, and digital certificates. Each method has advantages and limitations, and candidates are expected to know when and how to apply them appropriately.
The exam also covers authentication protocols such as Kerberos, RADIUS, and TACACS+. Candidates must understand how these protocols work within enterprise networks to provide secure and reliable authentication. Properly implemented authentication systems reduce the risk of unauthorized access, enhance accountability, and support secure communication across IT environments. Candidates are expected to demonstrate knowledge of configuring, managing, and troubleshooting authentication mechanisms in practical scenarios.
Authorization and Access Control Implementation
Authorization ensures that authenticated users or devices have appropriate permissions for resources and actions. Candidates preparing for the 98-367 exam learn about access control models such as discretionary access control, mandatory access control, and role-based access control. Understanding the principle of least privilege and its application to user accounts, files, and network resources is critical.
Candidates are also tested on configuring permissions, monitoring access, and integrating authorization mechanisms with authentication systems. Effective access control prevents unauthorized activity, reduces the potential impact of compromised accounts, and supports regulatory compliance. The exam emphasizes practical implementation of access controls in real-world scenarios to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity.
Security Policies and Regulatory Compliance
Security policies are fundamental to maintaining consistent and enforceable security practices. The 98-367 exam tests candidates on developing, implementing, and maintaining policies that cover acceptable use, password management, incident response, and data protection. Policies provide a framework for applying technical controls, managing user behavior, and ensuring compliance with organizational and regulatory standards.
Compliance is an integral aspect of security policies. Candidates must understand requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO standards, and how policies enforce adherence to these regulations. Effective policy management involves documenting procedures, educating users, and regularly reviewing and updating policies to reflect changes in technology and threats. Candidates are expected to evaluate the effectiveness of security policies and adjust them to address gaps or emerging risks.
Network Security Configuration
Network security is a major focus area in the 98-367 exam. Candidates learn to configure firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, network segmentation, and virtual private networks. Secure routing, encryption protocols, and access control lists are also covered. Understanding network topologies, TCP/IP, DNS, and other protocols is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing safeguards.
Candidates must also understand monitoring techniques to detect suspicious activity, respond to incidents, and maintain network integrity. This includes analyzing logs, configuring alerts, and applying corrective measures when threats are identified. Effective network security practices combine preventive, detective, and corrective controls to create a resilient network environment capable of supporting enterprise operations.
Operating System Security Techniques
Operating system security is another critical area tested in the 98-367 exam. Candidates learn to harden client and server systems by applying patches, configuring firewalls, restricting unnecessary services, and managing user accounts. Knowledge of file system permissions, registry settings, and security templates is emphasized.
Candidates are expected to implement endpoint protection measures such as antivirus software, anti-malware solutions, and monitoring tools. Event logs and auditing play a critical role in detecting suspicious behavior and maintaining accountability. The exam highlights the importance of balancing security and usability to ensure systems remain secure without unnecessarily restricting legitimate activities.
Software Security and Application Protection
Software security is covered extensively in the 98-367 exam. Candidates are tested on methods to secure applications, protect sensitive data, and prevent exploitation. This includes secure coding practices, vulnerability management, and applying patches. Common attack vectors such as buffer overflows, injection attacks, and cross-site scripting are emphasized, along with techniques to mitigate these risks.
Candidates must understand the deployment and management of security software, including antivirus, anti-spam, and anti-malware tools. These measures protect endpoints, applications, and network resources from unauthorized access or compromise. The exam focuses on the integration of software security practices into broader organizational security strategies.
Monitoring, Logging, and Incident Response
Monitoring and incident response are essential skills for IT professionals and are emphasized in the 98-367 exam. Candidates learn to configure and analyze system logs, detect anomalies, and respond to security incidents. Incident response procedures include identifying threats, containing breaches, recovering systems, and documenting events.
Proactive monitoring allows organizations to detect potential security events before they escalate. Candidates are expected to implement alert systems, review logs regularly, and maintain incident documentation. Effective incident response ensures operational continuity, reduces the impact of security events, and supports compliance with organizational policies and regulatory standards.
Emerging Threats and Security Trends
The 98-367 exam addresses emerging technologies and the associated security challenges. Candidates study cloud computing security, mobile device protection, IoT integration, and virtualization. These technologies introduce new attack surfaces and require updated strategies to mitigate risks. Candidates must understand the security implications of cloud environments, endpoint devices, and connected systems, and how to implement safeguards to maintain a secure IT environment.
Trends such as AI-assisted threat detection, automated security monitoring, and advanced encryption methods are also relevant. Candidates are encouraged to apply these technologies to enhance security practices while understanding their limitations and potential risks. Awareness of evolving threats ensures that certified professionals can adapt to changing environments and maintain robust security measures.
Practical Applications and Scenario-Based Skills
The exam emphasizes scenario-based learning to validate practical application of security knowledge. Candidates are expected to apply concepts in situations such as network breaches, malware outbreaks, or unauthorized access attempts. Scenario-based questions test the ability to analyze threats, evaluate risks, and implement appropriate security measures.
Hands-on skills include configuring firewalls, implementing authentication and access controls, hardening operating systems, and deploying security software. Candidates also learn to respond to incidents, document actions, and evaluate outcomes. These practical exercises ensure that candidates are prepared to apply their knowledge effectively in real-world IT environments.
Exam Preparation Techniques
Preparation for the 98-367 exam involves comprehensive study of all security domains. Candidates should combine theoretical study with hands-on exercises to reinforce learning. Practice labs, simulations, and scenario-based exercises help develop practical problem-solving skills. Reviewing exam objectives, studying common threats, understanding protocols, and practicing configuration tasks enhances readiness.
Candidates are also encouraged to stay current with security trends, emerging technologies, and best practices. Regular review, self-assessment, and application of knowledge to practical exercises improve comprehension and retention, ensuring candidates are well-prepared to succeed in the exam.
Career Relevance and Professional Development
Achieving the 98-367 certification validates foundational IT security knowledge and demonstrates competence in implementing, monitoring, and managing security measures. Certified professionals are equipped to pursue roles in IT support, network administration, systems management, and security analysis. The skills gained provide a strong foundation for advanced certifications, enhancing career prospects and opportunities for professional growth in cybersecurity and IT infrastructure management.
Deep Dive into Authentication Protocols
The 98-367 exam tests candidates on the understanding of authentication protocols that form the foundation of secure communication in enterprise networks. Authentication protocols are responsible for verifying the identity of users and devices before granting them access to network resources. Candidates need to recognize how these protocols function, where they are applied, and their strengths and limitations. Kerberos is one of the most significant authentication protocols covered. It is designed for secure authentication in client-server environments, relying on a trusted third party known as the Key Distribution Center. Candidates must understand how ticket granting and session keys work in Kerberos to reduce the risks of transmitting passwords over a network.
Another protocol tested is NTLM, which provides backward compatibility for legacy systems but has known vulnerabilities that modern enterprises should minimize. The exam also addresses RADIUS and TACACS+, both of which are widely used in enterprise environments to centralize authentication, authorization, and accounting. These protocols are crucial for managing large numbers of users and devices securely. A clear understanding of the differences between RADIUS and TACACS+ is expected, as one is often favored for device authentication and the other for broader AAA services.
Candidates are required to analyze real-world scenarios where these protocols are implemented, identify potential weaknesses, and apply the most suitable authentication method to maintain security. By mastering these protocols, exam takers demonstrate their ability to secure enterprise infrastructures against unauthorized access.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Enterprise Use
The concept of multi-factor authentication is another key area in the 98-367 exam. Multi-factor authentication enhances security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification before granting access. The factors typically include something the user knows, such as a password; something the user has, such as a smart card or token; and something the user is, such as biometric identification.
Candidates must understand the benefits of implementing multi-factor authentication in different contexts, such as protecting remote access connections, securing administrative accounts, or managing sensitive enterprise applications. The exam requires knowledge of how multi-factor authentication reduces the likelihood of successful credential-based attacks like phishing or brute force. In addition, candidates should be able to evaluate the challenges of deploying multi-factor authentication, including user adoption issues, cost considerations, and integration with existing systems.
Understanding multi-factor authentication in enterprise environments highlights a candidate’s readiness to deal with the increasing sophistication of modern cyberattacks. This knowledge ensures that certified individuals can provide effective solutions to balance security and usability.
Role-Based Access Control in Practical Scenarios
Access control mechanisms are another fundamental domain covered by the 98-367 exam. Among these, role-based access control plays a vital role in assigning permissions efficiently in enterprise environments. Candidates are expected to understand how access rights are granted based on user roles within an organization rather than on individual assignments.
In practice, role-based access control simplifies management by grouping permissions according to job responsibilities. For instance, administrators may have broad access to configure systems, while regular employees only receive access to applications or resources essential for their work. Candidates should also recognize how role-based access control supports the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users only have the minimum rights necessary to perform their duties.
The exam may present case scenarios where permissions are improperly assigned, leading to security risks such as excessive access or privilege escalation. Candidates must evaluate such cases, identify misconfigurations, and apply corrective actions. This practical knowledge ensures organizations remain compliant with internal policies and regulatory standards while minimizing the risks associated with unauthorized access.
Security Policies and Their Enforcement
Security policies are an integral part of the 98-367 exam because they guide the consistent implementation of security measures across organizations. A security policy defines acceptable use of systems, data protection requirements, incident response procedures, and guidelines for handling sensitive information. Candidates are tested on how to design, implement, and enforce these policies effectively.
One important area is password management policies, which dictate password complexity, expiration intervals, and account lockout rules. These policies are essential to mitigate risks associated with weak or reused passwords. Candidates also need to understand acceptable use policies that regulate how employees use company resources, such as internet browsing and email services, to reduce exposure to social engineering and malware.
The exam also highlights the role of incident response policies. Candidates must demonstrate their ability to establish guidelines for detecting, reporting, and managing security incidents. A well-structured incident response policy ensures that threats are contained quickly and damage is minimized. By understanding how to enforce security policies, candidates demonstrate their ability to create frameworks that strengthen an organization’s security posture and maintain compliance with regulations.
Advanced Operating System Security Measures
The 98-367 exam requires candidates to go beyond basic operating system configuration and understand advanced security measures that protect both client and server systems. Hardening an operating system involves minimizing its attack surface by disabling unnecessary services, closing unused ports, and applying the latest security patches. Candidates must be familiar with patch management processes and their importance in preventing exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
File system permissions are another area tested in the exam. Candidates must understand how to configure file and folder permissions to prevent unauthorized access. Knowledge of auditing and monitoring settings is also necessary, as these provide accountability and allow organizations to detect suspicious activity.
The exam addresses account management practices such as disabling default accounts, enforcing least privilege, and monitoring privileged accounts. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of tools and configurations available within operating systems that enforce these practices. Proficiency in operating system security ensures candidates are capable of protecting endpoints, which are often the first targets of cyberattacks.
Application Security and Vulnerability Mitigation
Application security is a key focus area of the 98-367 exam because vulnerabilities in software are frequently exploited by attackers. Candidates must understand secure coding principles, patch management for applications, and strategies to protect applications from exploitation.
Common threats such as buffer overflows, cross-site scripting, and SQL injection are highlighted in the exam. Candidates must know how these vulnerabilities work, their impact, and how to mitigate them. For example, input validation and sanitization are critical methods for preventing injection attacks, while secure memory management helps reduce the risk of buffer overflows.
The exam also tests knowledge of security software designed to protect applications, such as web application firewalls and intrusion prevention systems. Candidates are expected to recognize how these tools fit into broader security strategies and how they help in safeguarding applications against evolving threats. Understanding application security ensures candidates are equipped to protect the software environments critical to enterprise operations.
Network Isolation and Segmentation
Network isolation and segmentation are vital techniques covered in the 98-367 exam to enhance network security. Candidates must understand how dividing networks into smaller segments limits the spread of attacks and improves monitoring. For instance, isolating sensitive systems like financial databases from general user traffic reduces the chances of compromise.
Candidates should also understand virtual LANs, subnetting, and the use of firewalls for enforcing segmentation policies. Proper segmentation enhances performance by reducing broadcast traffic while improving security by restricting communication between segments.
The exam emphasizes real-world scenarios where improper segmentation leads to vulnerabilities, such as unrestricted access to sensitive servers. Candidates are expected to evaluate such cases, recommend segmentation strategies, and apply the appropriate tools to enforce them. This skill demonstrates a candidate’s ability to design secure network infrastructures for enterprise environments.
Firewalls and Advanced Filtering Techniques
Firewalls are a major topic in the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand how firewalls monitor and control traffic based on predefined security rules. Knowledge of packet filtering, stateful inspection, and application layer firewalls is required.
The exam also covers the configuration of access control lists to restrict traffic based on source and destination addresses, ports, or protocols. Candidates should be familiar with advanced filtering techniques such as deep packet inspection, which allows detailed analysis of traffic content to identify malicious activity.
In practical scenarios, candidates must demonstrate how to configure firewall rules to prevent unauthorized access while allowing legitimate traffic. They should also understand the balance between security and performance, ensuring that firewalls are configured to minimize disruption to business operations. Mastery of firewall concepts ensures candidates can implement one of the most critical security controls in enterprise networks.
Security Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Security monitoring and intrusion detection systems play a central role in identifying and responding to threats, and the 98-367 exam tests candidates on these areas. Candidates must understand how monitoring tools analyze traffic, generate alerts, and provide visibility into network activity. Intrusion detection systems identify suspicious patterns that may indicate attacks, while intrusion prevention systems take proactive measures to block threats.
The exam requires candidates to analyze logs, identify anomalies, and respond to incidents effectively. For example, candidates may be asked to interpret event logs that reveal unauthorized access attempts or malware activity. By understanding monitoring and intrusion detection systems, candidates demonstrate their ability to maintain visibility into network environments and protect against both external and internal threats.
Security in Cloud and Virtualized Environments
The growing use of cloud computing and virtualization introduces new security challenges, which are covered in the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand the security implications of cloud service models, including infrastructure as a service, platform as a service, and software as a service.
Virtualization introduces risks such as hypervisor vulnerabilities and virtual machine sprawl. Candidates are tested on techniques to secure virtual environments, such as isolating virtual machines, applying patches to hypervisors, and controlling administrative access. They must also recognize the importance of encryption, secure APIs, and identity management in cloud environments.
The exam highlights real-world challenges where organizations fail to secure cloud and virtualized infrastructures, leading to data breaches. Candidates must evaluate these scenarios and apply appropriate safeguards to ensure cloud adoption aligns with enterprise security goals.
Incident Response and Forensics
Incident response is a significant component of the 98-367 exam, requiring candidates to understand how to detect, contain, and recover from security incidents. Candidates must learn the phases of incident response, including preparation, detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned.
Forensics is also tested as part of incident response. Candidates should understand how to preserve evidence, analyze logs, and reconstruct events to determine the root cause of incidents. Proper documentation and reporting are essential for accountability and future prevention.
The exam requires candidates to apply incident response concepts in scenario-based questions, ensuring they can act effectively in real-world situations. This knowledge prepares professionals to minimize the impact of security incidents and support ongoing improvements to organizational defenses.
Preparing for the 98-367 Exam Effectively
Success in the 98-367 exam requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Candidates should study each domain in depth, focusing on the exam objectives while practicing configuration and troubleshooting tasks. Hands-on practice in labs or simulated environments helps reinforce theoretical concepts and builds the problem-solving skills needed for the exam.
Reviewing study guides, practicing with mock scenarios, and testing knowledge with practice questions are effective strategies. Candidates should also stay informed about the latest security threats and technologies, as the exam emphasizes applying concepts to real-world enterprise challenges. Time management during the exam is critical, so candidates should practice answering questions efficiently and accurately.
By preparing thoroughly, candidates not only enhance their chances of passing the exam but also gain valuable skills that are directly applicable to professional roles in IT security.
Encryption and Its Application in Enterprise Environments
Encryption is a central topic in the 98-367 exam. Candidates are tested on how encryption protects data confidentiality, both at rest and in transit. They must understand symmetric encryption, which uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption, which uses a pair of public and private keys.
Real-world enterprise usage requires candidates to understand how encryption applies to secure email, file transfer, and virtual private networks. For example, secure email often relies on public key infrastructure to authenticate senders and protect messages from interception. Virtual private networks use encryption protocols like IPsec or SSL/TLS to provide secure remote access for employees working outside the corporate network.
The exam also emphasizes key management, as poor handling of keys undermines encryption. Candidates should understand concepts such as key rotation, secure key storage, and certificate authorities. By mastering encryption, candidates can demonstrate their ability to safeguard sensitive enterprise data, whether it is stored locally, transmitted across networks, or hosted in cloud environments.
Malware Defense Strategies
Malware is one of the most persistent threats enterprises face, and the 98-367 exam tests candidates on their ability to defend against it. Malware includes viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and rootkits. Each type behaves differently, requiring specific strategies for prevention and removal.
Candidates must understand signature-based detection, which compares files against known malware signatures, and heuristic-based detection, which identifies suspicious behavior even if the malware is unknown. They should also understand the importance of deploying anti-malware solutions at multiple layers, such as endpoints, email gateways, and web proxies.
The exam also addresses malware delivery methods. For example, phishing emails and drive-by downloads are common attack vectors. Candidates must be able to recommend solutions such as user awareness training, secure web gateways, and email filtering systems. Additionally, sandboxing techniques are tested, as they allow enterprises to analyze suspicious files in isolated environments before they are allowed to interact with production systems.
By understanding malware defense strategies, candidates demonstrate their ability to identify, block, and remediate one of the most common enterprise threats.
Identity and Access Management in Enterprises
Identity and access management is a significant focus of the 98-367 exam because controlling who can access resources directly impacts security. Candidates must understand how user accounts are created, managed, and decommissioned, as well as how access permissions are assigned and enforced.
Key elements include authentication, authorization, and accounting. Authentication verifies the identity of users, authorization determines what resources they can access, and accounting tracks their activities for auditing purposes. Candidates must understand directory services like Active Directory, which play a central role in enterprise identity management.
Group policies and security templates are also important. These tools enable administrators to enforce consistent security settings across large numbers of users and devices. The exam requires candidates to evaluate real-world scenarios where improper identity management leads to unauthorized access, and to recommend corrective measures like role-based access control, account lockout policies, and monitoring of privileged accounts.
By mastering identity and access management, candidates demonstrate their readiness to manage user identities effectively in enterprise-scale environments.
Securing Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are an essential part of modern enterprises, and the 98-367 exam tests knowledge of securing them. Candidates must understand the vulnerabilities associated with wireless communication, including eavesdropping, unauthorized access, and rogue access points.
The exam focuses on encryption protocols such as WPA2 and WPA3, which secure wireless communication by encrypting traffic between clients and access points. Candidates should also understand enterprise authentication methods such as 802.1X, which uses RADIUS servers to authenticate users and devices before granting access.
Wireless intrusion prevention systems are another area of focus. These systems detect unauthorized access points, rogue clients, and unusual traffic patterns. Candidates must also understand best practices for wireless security, such as disabling SSID broadcasting in sensitive environments, implementing network segmentation for wireless users, and applying strong password policies.
Mastering wireless security ensures candidates can design and manage wireless infrastructures that provide mobility while maintaining enterprise security standards.
Social Engineering and User Awareness
The 98-367 exam highlights that technical defenses alone cannot protect an enterprise from all threats. Social engineering remains one of the most effective ways attackers compromise systems by exploiting human trust. Candidates must understand the various types of social engineering attacks, including phishing, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating.
The exam requires knowledge of how to recognize these attacks and implement user awareness programs to reduce their effectiveness. User training is critical for teaching employees how to spot suspicious emails, avoid clicking on malicious links, and report potential security incidents promptly.
Candidates should also understand how policies such as mandatory verification for financial transactions or restrictions on sharing sensitive information help mitigate risks. Exam questions may present scenarios where employees unknowingly assist attackers, and candidates must apply preventive measures to reduce these risks. By mastering this area, candidates show they can integrate human-focused defenses into enterprise security strategies.
Patch and Update Management
The 98-367 exam places significant importance on patch management as a core component of enterprise security. Candidates must understand that unpatched systems represent major vulnerabilities that attackers frequently exploit. Patch management involves identifying, testing, deploying, and verifying updates to operating systems, applications, and firmware.
The exam may include scenarios where outdated software leads to a security breach. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to design patch management processes that minimize downtime while ensuring systems remain secure. They should also recognize the importance of testing patches in staging environments before deploying them enterprise-wide to prevent compatibility issues.
Automation tools are also highlighted in the exam. Solutions like Windows Server Update Services help administrators streamline patch deployment and ensure compliance across large environments. Candidates who understand patch and update management demonstrate their ability to maintain secure systems that remain resilient against known vulnerabilities.
Security Implications of Virtual Private Networks
Virtual private networks are another focus of the 98-367 exam because they provide secure remote access to enterprise networks. Candidates must understand the types of VPNs, including remote access VPNs, which connect individual users to a network, and site-to-site VPNs, which connect entire networks securely over the internet.
The exam requires knowledge of tunneling protocols such as PPTP, L2TP, and IPsec. Candidates must evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, recognizing that some legacy protocols like PPTP are no longer secure. IPsec and SSL/TLS remain the most widely used secure VPN technologies in enterprises.
Candidates should also understand how VPNs integrate with authentication systems to ensure only authorized users gain access. Multi-factor authentication is often combined with VPNs to strengthen security. By mastering VPN concepts, candidates demonstrate their ability to implement remote connectivity solutions that maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability of enterprise resources.
Security Auditing and Compliance
Auditing and compliance are critical for enterprise environments, and the 98-367 exam tests candidates on these concepts. Security auditing involves tracking and recording activities within systems to provide accountability and detect suspicious behavior. Candidates must understand how to configure audit policies, collect logs, and analyze events to identify security incidents.
Compliance is another important area. Enterprises must adhere to legal and regulatory requirements, such as data protection laws and industry standards. The exam may test knowledge of how compliance frameworks guide security practices and how failing to comply exposes organizations to legal and financial penalties.
Candidates should also understand how to integrate auditing with centralized log management and security information and event management systems. These tools improve visibility and enable faster responses to threats. By mastering auditing and compliance, candidates show they can align enterprise security practices with organizational and regulatory requirements.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity and disaster recovery are critical components of enterprise security and are covered in the 98-367 exam. Candidates must understand how to design and implement plans that ensure business operations continue during disruptions caused by cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures.
Key elements include backup strategies, redundancy, and failover systems. Candidates should know the differences between full, incremental, and differential backups, as well as the importance of secure storage for backup data. They must also understand recovery time objectives and recovery point objectives, which define acceptable downtime and data loss.
The exam may include scenarios where organizations fail to recover from incidents due to inadequate planning. Candidates must apply knowledge of disaster recovery strategies to recommend solutions such as offsite backups, high availability clusters, and cloud-based recovery systems. By mastering these concepts, candidates demonstrate their ability to maintain resilience in enterprise environments.
Preparing for the Exam with Practical Experience
Finally, the 98-367 exam places emphasis on practical understanding rather than memorization alone. Candidates should prepare by working with real or simulated environments where they can practice configuring firewalls, setting up VPNs, applying encryption, and analyzing logs.
Study resources such as official guides, practice exams, and online labs are essential. Candidates should focus on areas where they feel less confident, ensuring they have well-rounded knowledge across all domains. The exam requires not only technical expertise but also the ability to apply concepts in real-world enterprise scenarios.
Practical experience helps candidates build confidence and efficiency in answering scenario-based questions. By preparing with hands-on practice, candidates demonstrate that they are not only exam-ready but also prepared to contribute effectively to enterprise security operations.
Conclusion
The Microsoft MTA Security Fundamentals exam 98-367 is designed as a foundational step for individuals entering the field of IT security. It introduces candidates to the essential principles of safeguarding systems, networks, applications, and data. Through its focus on layered security, authentication methods, operating system protections, and network defenses, the exam ensures that learners gain a balanced understanding of both technical and human-centered security measures.
A significant value of the exam lies in its emphasis on real-world application. Concepts such as encryption, malware protection, wireless security, patch management, and VPNs are not presented in isolation but as interconnected practices that collectively strengthen enterprise environments. This ensures that candidates are not just preparing for an assessment but also building the mindset required to recognize threats and apply preventive strategies effectively.
Another important aspect is its focus on awareness and responsibility. By including topics like social engineering, security policies, auditing, and compliance, the exam highlights that technology alone cannot secure organizations. People, processes, and planning are equally vital. The integration of business continuity and disaster recovery concepts demonstrates that security is not only about prevention but also about resilience and adaptability.
For individuals beginning their careers in IT, the exam offers clarity and direction. It establishes the vocabulary, scenarios, and frameworks that will be built upon in more advanced certifications and real-world roles. By mastering the fundamentals tested in this exam, learners position themselves to confidently progress into more specialized areas of cybersecurity, such as penetration testing, threat analysis, and enterprise-level risk management.
Ultimately, 98-367 provides more than an introduction—it lays the groundwork for a security-focused career, encouraging learners to combine technical knowledge with practical skills and responsible practices in safeguarding digital environments.
Microsoft MTA 98-367 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 98-367 Security Fundamentals certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- MB-900 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-388 - Introduction to Programming Using Java
Purchase 98-367 Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 98-367 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 98-367 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 98-367 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 98-367 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 98-367 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 98-367. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 98-367 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 98-367 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 98-367 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 98-367 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

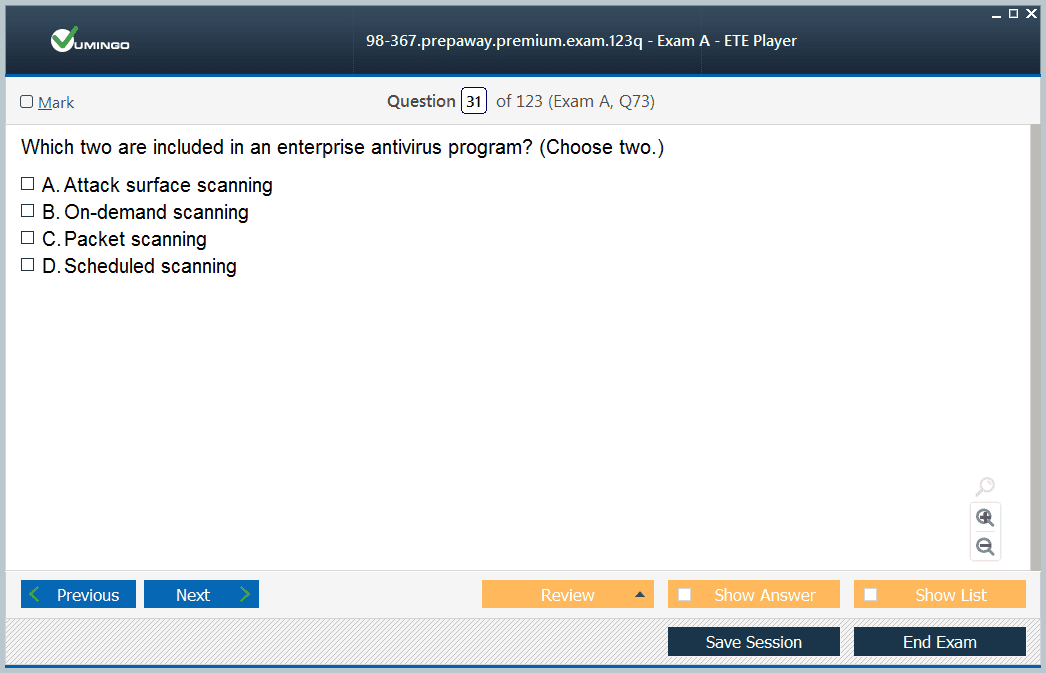
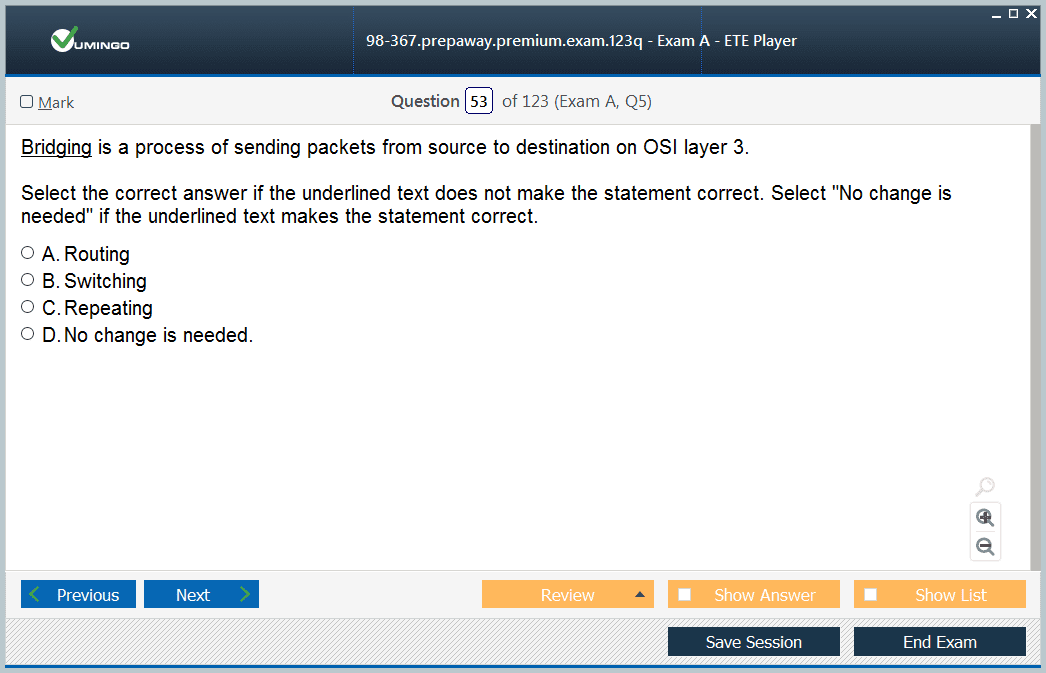
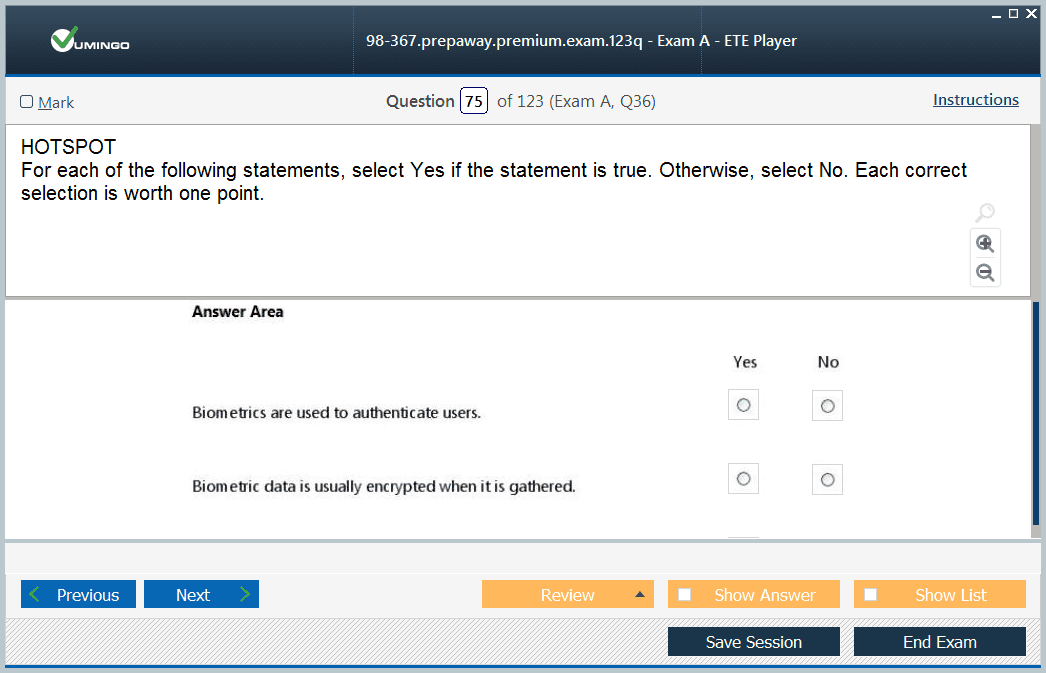
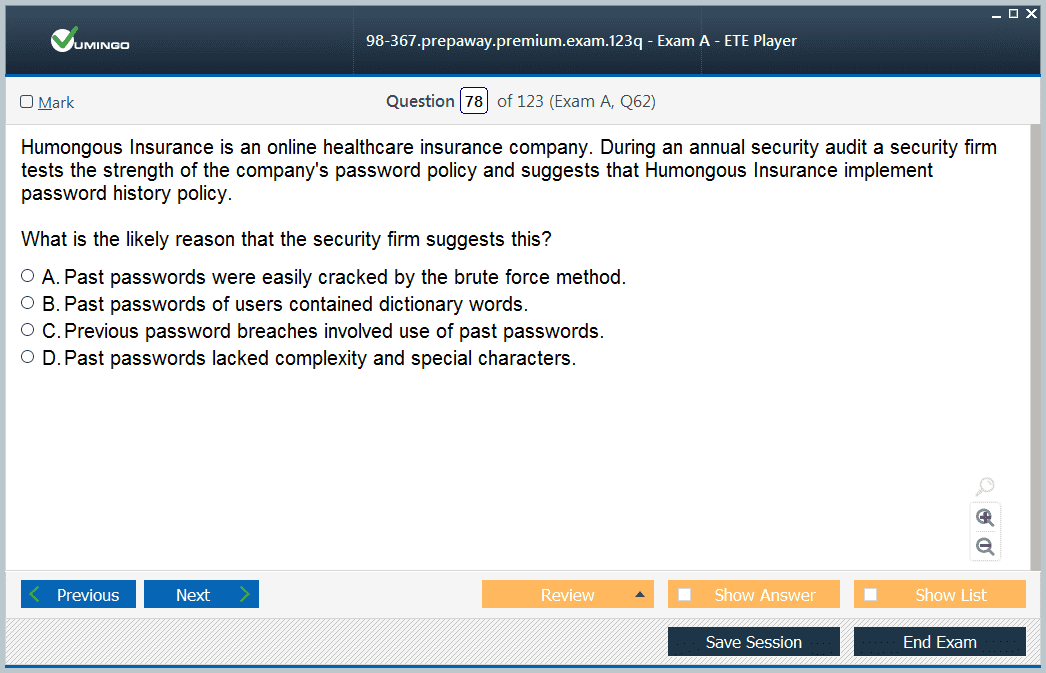








I want to register for the 98-367 exam. Maybe anyone knows the structure of the exam and which resources to use? I checked Microsoft’s website and couldn’t find any helpful information.
Thanks for the replies!