- Home
- Cisco Certifications
- 210-255 Implementing Cisco Cybersecurity Operations (SECOPS) Dumps
Pass Cisco CCNA Cyber Ops 210-255 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


210-255 Premium File
- Premium File 179 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Jan 24, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Cisco CCNA Cyber Ops 210-255 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 210-255 Implementing Cisco Cybersecurity Operations (SECOPS) practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
What You Need to Know for the Cisco CCNA Cyber Ops 210-255 Exam
The 210-255 exam is an essential component of the CCNA Cyber Ops certification, focusing on security operations and monitoring within modern network environments. This exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to perform the duties of a security operations analyst, emphasizing practical application, data analysis, and incident response. By preparing for this exam, candidates develop the necessary skills to identify threats, monitor network activity, and respond effectively to security events.
Role of Security Operations Analysts
Security operations analysts are responsible for detecting and responding to cybersecurity incidents, maintaining security monitoring systems, and analyzing data from multiple sources. The 210-255 exam assesses the readiness of candidates to handle these responsibilities in real-world scenarios. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in identifying suspicious patterns, investigating potential incidents, and executing response strategies to mitigate risks.
Exam Structure and Objectives
The exam is designed to test both conceptual knowledge and operational skills. It includes scenario-based questions that require candidates to analyze data, interpret alerts, and make decisions similar to those encountered in security operations centers. Core objectives include understanding incident response procedures, analyzing event data, and employing appropriate operational tools to detect and respond to threats.
Security Monitoring and Event Analysis
A significant focus of the exam is security monitoring, which involves continuously observing network and host activity for signs of anomalies. Candidates are expected to correlate events from various sources, assess the severity of incidents, and prioritize responses. This requires familiarity with security information and event management systems, log analysis techniques, and the interpretation of network traffic patterns.
Incident Detection and Response
The exam emphasizes practical knowledge of incident detection and response workflows. Candidates must understand how to identify indicators of compromise, classify incidents, and initiate response actions. Effective response strategies include containment, eradication, and recovery processes, all of which are evaluated in scenario-based questions to ensure candidates can act decisively in operational environments.
Understanding Threat Landscapes
Candidates preparing for the 210-255 exam must gain a comprehensive understanding of the current threat landscape. This includes awareness of different types of cyber attacks, their techniques, and potential impact on organizational systems. By understanding threat behaviors, candidates can anticipate and detect attacks more effectively, enhancing their operational capabilities.
Data Collection and Correlation
Collecting and correlating data from multiple sources is a critical skill assessed in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to analyze logs, network traffic, and system alerts to identify patterns indicative of malicious activity. This involves filtering large volumes of data, prioritizing incidents, and determining appropriate response measures based on analytical findings.
Security Tools and Technologies
The exam requires knowledge of various security tools and technologies used in monitoring and response. Candidates must understand how to configure and use these tools effectively, including intrusion detection systems, security information and event management platforms, and endpoint monitoring solutions. Familiarity with these technologies ensures that candidates can perform operational tasks efficiently and accurately.
Analytical and Critical Thinking Skills
A core component of the 210-255 exam is assessing analytical and critical thinking abilities. Candidates must interpret complex data, evaluate the severity of incidents, and determine the best course of action. These skills are essential for security operations analysts, who must make informed decisions quickly to mitigate potential threats.
Operational Procedures and Best Practices
The exam also emphasizes adherence to operational procedures and best practices. Candidates must be familiar with standardized incident response frameworks, escalation protocols, and documentation practices. Following these procedures ensures consistency and reliability in managing security events and demonstrates professional competence in operational environments.
Scenario-Based Learning and Simulation
Scenario-based questions in the exam simulate real-world operational challenges. Candidates are presented with events, alerts, and log data and must determine appropriate responses. This approach tests practical application skills, ensuring that candidates can translate theoretical knowledge into effective operational performance.
Integration of Theory and Practice
Preparation for the 210-255 exam requires integrating theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice. Understanding incident response methodologies, event correlation, and monitoring techniques is reinforced through exercises that simulate operational environments. This integration ensures that candidates are equipped to handle practical challenges in security operations roles.
Incident Handling and Response Workflows
Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in handling security incidents through structured workflows. This includes identifying the type of incident, assessing its impact, executing containment measures, and documenting actions taken. Mastery of these workflows ensures that candidates can respond effectively and efficiently to operational threats.
Event Prioritization and Risk Assessment
Prioritizing events and assessing risk is a critical aspect of security operations. The exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to determine the severity and potential impact of incidents, allocate resources appropriately, and ensure timely responses. This skill is essential for maintaining the security and stability of organizational systems.
Developing Operational Efficiency
The exam encourages candidates to develop efficient operational practices. Streamlining workflows, utilizing monitoring tools effectively, and implementing systematic incident handling procedures contribute to operational efficiency. These skills enable analysts to manage multiple events simultaneously without compromising the quality of response.
Threat Detection Techniques
Candidates are tested on various threat detection techniques, including analyzing network traffic, reviewing host activity, and interpreting security alerts. Understanding how to detect anomalies and potential breaches is critical for proactive defense and ensures that incidents are addressed before they escalate.
Understanding Security Metrics
The exam requires familiarity with security metrics and indicators used to evaluate operational performance. Candidates must understand how to measure incident response times, assess the effectiveness of monitoring systems, and analyze trends in security events. These metrics inform decision-making and help improve overall security operations.
Practical Knowledge of SOC Operations
Preparing for the exam provides candidates with insights into Security Operations Center workflows. This includes understanding the roles of SOC personnel, standard operating procedures, and communication protocols. Candidates learn how to coordinate with team members, escalate incidents appropriately, and maintain situational awareness during security events.
Handling Advanced Threats
The 210-255 exam also addresses the handling of advanced threats, such as coordinated attacks, malware outbreaks, and targeted intrusions. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to analyze complex attack patterns, implement containment measures, and ensure recovery of affected systems. Proficiency in managing advanced threats is crucial for operational effectiveness.
Reinforcing Knowledge Through Practice
Repeated practice and scenario-based exercises reinforce operational knowledge. Candidates gain confidence by applying skills in simulated environments, which helps retain key concepts and develop muscle memory for incident response tasks. This hands-on approach is critical for success in both the exam and real-world operations.
Continuous Learning in Cybersecurity Operations
The dynamic nature of cybersecurity requires ongoing learning and adaptation. Preparing for the exam instills a habit of continuous improvement, encouraging candidates to stay updated on emerging threats, new technologies, and evolving operational strategies. This mindset is essential for long-term success in security operations roles.
Professional Competence and Certification Value
Successfully passing the 210-255 exam validates a candidate’s competence in security operations. Certified individuals are recognized for their ability to monitor, analyze, and respond to security incidents effectively. This credential enhances professional credibility and opens opportunities for career advancement within cybersecurity teams.
Building Confidence in Operational Skills
Preparation for the exam builds confidence in operational abilities. Candidates become familiar with security monitoring tools, incident response procedures, and analytical techniques. This confidence ensures that professionals can handle security events competently and make informed decisions under pressure.
Applying Knowledge to Real-World Environments
The exam emphasizes the practical application of skills in real-world operational settings. Candidates learn to apply incident response methodologies, analyze event data, and respond to threats as they would in a professional security operations role. This preparation ensures readiness for the challenges of day-to-day cybersecurity work.
Understanding Cyber Threat Indicators
Candidates gain an understanding of various indicators of compromise, including unusual network patterns, system anomalies, and signs of malicious activity. Recognizing these indicators is fundamental for proactive monitoring and rapid response to potential security incidents.
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills
The exam assesses the ability to make sound operational decisions based on data analysis and threat evaluation. Candidates learn to prioritize incidents, determine appropriate responses, and coordinate with other team members to mitigate risk. Effective decision-making is a core competency for security operations professionals.
Operational Documentation and Reporting
Proper documentation and reporting are critical components of operational roles. Candidates must understand how to record incidents, track responses, and communicate findings to stakeholders. This ensures accountability, supports continuous improvement, and enables informed decision-making.
Preparing for Career Advancement
The 210-255 exam prepares candidates for roles such as security analyst, incident responder, and SOC team member. By mastering operational skills, candidates enhance their employability and position themselves for further advancement in cybersecurity operations.
Integrating Analytical and Practical Skills
The exam emphasizes the integration of analytical thinking and practical operational skills. Candidates must interpret complex data, analyze threats, and implement response measures effectively. This combination of skills ensures comprehensive preparation for operational responsibilities.
Mastering Incident Response Frameworks
Understanding incident response frameworks is a key focus of the exam. Candidates learn structured approaches for managing incidents, including detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery. Mastery of these frameworks ensures that professionals can respond efficiently and consistently.
Preparing for High-Pressure Scenarios
The exam prepares candidates to operate under high-pressure scenarios, simulating the urgency and complexity of real-world incidents. Candidates learn to maintain composure, prioritize effectively, and execute response strategies under stress, which is critical for operational success.
Security Event Correlation
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to correlate multiple security events to identify potential incidents. This involves analyzing data from diverse sources, detecting patterns, and understanding the relationships between events. Effective correlation enhances threat detection and response accuracy.
Developing Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is essential for security operations. Candidates must maintain an understanding of ongoing security events, system statuses, and potential threats. This awareness enables timely and appropriate actions to protect organizational assets.
Efficient Use of Monitoring Tools
The exam tests candidates on their ability to utilize monitoring and analysis tools efficiently. Proficiency in these tools ensures that threats are detected promptly, incidents are managed effectively, and operational workflows are streamlined.
Applying Operational Best Practices
Adherence to best practices in security operations is emphasized throughout the exam. Candidates must understand standardized procedures for monitoring, incident response, and reporting, ensuring consistency and reliability in operational performance.
Developing Threat Mitigation Strategies
Candidates are expected to develop strategies to mitigate threats based on analytical findings. This includes recommending preventive measures, implementing containment procedures, and coordinating with relevant teams to reduce risk.
Reinforcing Knowledge Through Repetition
Consistent practice and review reinforce operational knowledge, enabling candidates to retain critical concepts and apply them confidently during the exam and in professional environments.
Aligning Skills with Professional Expectations
The 210-255 exam aligns skills with the expectations of security operations roles. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to perform key tasks, respond to incidents, and support organizational security objectives effectively.
Enhancing Analytical and Response Capabilities
By preparing for this exam, candidates enhance both analytical and response capabilities, ensuring readiness to manage incidents, detect threats, and maintain operational security.
Preparing for Real-World Security Challenges
The exam provides practical exposure to scenarios that mirror real-world security challenges. Candidates gain experience in evaluating threats, managing incidents, and applying operational knowledge in professional environments.
The 210-255 exam is a comprehensive assessment of security operations skills essential for cybersecurity professionals. Preparation involves mastering incident detection, analysis, response, and operational efficiency. By successfully completing this exam, candidates demonstrate their readiness to function effectively in security operations roles, contributing to organizational safety and establishing a foundation for career growth in cybersecurity.
Deep Dive into Security Event Management
The 210-255 exam evaluates candidates on their ability to effectively manage and interpret security events. This includes collecting data from multiple sources, analyzing event logs, and understanding the relationship between different security alerts. Security event management requires both technical knowledge and critical thinking to ensure that suspicious activities are identified promptly and accurately. Candidates must learn to distinguish between false positives and genuine threats, applying operational judgment to determine the urgency of each event.
Data Analysis for Threat Identification
A core component of the exam is analyzing data to identify potential security threats. Candidates are expected to interpret network traffic, system logs, and application alerts to detect anomalies or malicious activity. This requires an understanding of normal network behavior, common attack vectors, and signs of compromise. By mastering data analysis, candidates enhance their ability to respond proactively and mitigate security risks before they escalate.
Incident Response Planning
Incident response planning is a critical area of focus for the exam. Candidates must understand structured workflows for detecting, analyzing, containing, and eradicating security incidents. The ability to implement effective response strategies ensures that threats are managed systematically, minimizing impact on organizational operations. Candidates also learn the importance of documenting each step of the response process to support post-incident analysis and future preparedness.
Understanding Cyber Threat Intelligence
The exam emphasizes the use of cyber threat intelligence to inform operational decisions. Candidates must learn to leverage information about emerging threats, attack patterns, and known vulnerabilities to anticipate potential security incidents. Integrating threat intelligence into monitoring and response activities enhances the ability to detect sophisticated attacks and improves overall operational readiness.
Utilizing Monitoring and Detection Tools
Proficiency in monitoring and detection tools is essential for success in the 210-255 exam. Candidates are expected to demonstrate familiarity with intrusion detection systems, endpoint monitoring solutions, and security information and event management platforms. Proper configuration and effective use of these tools are crucial for identifying threats, generating alerts, and supporting investigative actions.
Host-Based and Network-Based Analysis
The exam covers both host-based and network-based analysis techniques. Candidates must understand how to monitor endpoints for signs of compromise, including unusual process activity, unauthorized access attempts, and system anomalies. In addition, analyzing network traffic for patterns indicative of attacks, such as scanning activity or unusual data flows, is a critical skill assessed in the exam.
Incident Classification and Prioritization
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to classify incidents based on severity and potential impact. Prioritization ensures that critical threats are addressed promptly while lower-risk events are monitored appropriately. Effective classification and prioritization rely on understanding the organization’s infrastructure, assets, and potential vulnerabilities, enabling efficient allocation of resources during security operations.
Correlation of Security Events
Event correlation is a key aspect of operational efficiency. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to link related alerts, identify patterns, and detect multi-stage attacks. This involves analyzing disparate data points from multiple sources to form a comprehensive view of ongoing security incidents. Strong correlation skills enhance the ability to detect complex threats that may not be apparent when evaluating isolated events.
Threat Detection Methodologies
The exam requires candidates to apply a variety of threat detection methodologies. This includes signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each methodology allows candidates to select the most appropriate approach for different operational scenarios. By combining multiple detection techniques, security analysts can improve the accuracy and reliability of threat identification.
Operational Reporting and Documentation
Accurate documentation and reporting are fundamental to security operations. Candidates are assessed on their ability to record incidents, track response actions, and communicate findings effectively. Proper documentation supports post-incident reviews, informs organizational policy, and provides evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements.
Threat Mitigation and Containment Strategies
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to implement mitigation and containment strategies to limit the impact of security incidents. This includes isolating affected systems, applying patches, removing malicious code, and coordinating with relevant teams to restore secure operations. Effective mitigation reduces downtime and minimizes the potential damage caused by cyber attacks.
Understanding Malware and Attack Vectors
The exam covers various types of malware and attack vectors that candidates may encounter. This includes viruses, worms, ransomware, phishing attacks, and advanced persistent threats. Candidates must understand how these attacks function, their common indicators, and the most effective detection and response measures. Knowledge of malware behavior supports proactive monitoring and enhances operational preparedness.
Security Operations Center Workflows
Candidates are expected to understand the workflows within a Security Operations Center. This includes the roles of different personnel, escalation procedures, and communication protocols during incidents. Familiarity with SOC operations ensures that candidates can function effectively within a team, coordinate responses, and maintain situational awareness during security events.
Event Prioritization Techniques
The ability to prioritize events is critical for operational success. Candidates must learn to evaluate the severity, likelihood, and potential impact of incidents to determine the appropriate level of response. Efficient prioritization allows security teams to focus resources on the most significant threats while maintaining monitoring of less critical events.
Continuous Monitoring and Alert Management
The exam emphasizes continuous monitoring of network and host environments. Candidates must understand how to manage alerts effectively, filter noise, and identify patterns that require further investigation. Effective alert management ensures that analysts can respond to incidents promptly without being overwhelmed by excessive data.
Operational Challenges and Scenario Analysis
Scenario-based questions in the exam present candidates with complex operational challenges. These scenarios require critical thinking, data interpretation, and decision-making skills to determine the appropriate response. By practicing scenario analysis, candidates develop the ability to handle real-world incidents with confidence and accuracy.
Understanding Security Policies and Compliance
The exam assesses candidates’ knowledge of security policies and compliance requirements. Understanding organizational policies, regulatory standards, and best practices is essential for ensuring that operational actions align with established guidelines. This knowledge supports consistent and legally compliant incident handling procedures.
Hands-On Practice for Skill Reinforcement
Practical experience is essential for mastering the skills required in the 210-255 exam. Candidates are encouraged to use virtual labs, simulations, and practice exercises to apply theoretical concepts in controlled environments. Hands-on practice reinforces learning, builds confidence, and develops operational competence.
Integration of Threat Intelligence into Operations
Candidates must understand how to integrate threat intelligence into daily operations. This includes using information about known vulnerabilities, attack trends, and threat actors to enhance detection and response capabilities. Incorporating intelligence into operations improves proactive defense and strengthens overall security posture.
Advanced Incident Response Techniques
The exam evaluates knowledge of advanced incident response techniques, including forensic analysis, malware reverse engineering, and coordinated attack mitigation. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to apply these techniques to complex incidents, ensuring comprehensive resolution and minimal impact on organizational assets.
Network Traffic Analysis and Interpretation
Candidates are tested on their ability to analyze and interpret network traffic for signs of compromise. This includes identifying unusual data flows, detecting unauthorized access attempts, and understanding normal network behavior. Accurate traffic analysis supports early detection and informed decision-making during incidents.
Endpoint Security Monitoring
Monitoring endpoints is a crucial aspect of security operations. Candidates must understand how to track system activity, identify anomalies, and respond to potential threats. Endpoint monitoring provides critical visibility into the state of organizational assets and supports comprehensive incident response efforts.
Incident Investigation Procedures
The exam requires knowledge of systematic incident investigation procedures. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to collect evidence, analyze event data, identify root causes, and recommend corrective actions. Thorough investigations ensure that incidents are resolved effectively and inform improvements in operational processes.
Threat Detection Using Correlation Techniques
Correlation techniques are used to link related events and detect sophisticated attacks. Candidates must understand how to aggregate data, identify patterns, and recognize multi-stage attacks. Effective correlation enhances the ability to detect threats that may not be visible through isolated events.
Security Operations Efficiency
Operational efficiency is a key focus of the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage multiple incidents, optimize monitoring processes, and implement effective response strategies. Efficiency ensures that security teams can maintain continuous protection while minimizing resource expenditure.
Developing Analytical Thinking
The 210-255 exam emphasizes analytical thinking skills. Candidates must evaluate complex data, identify anomalies, and determine appropriate response measures. Strong analytical abilities are essential for effective decision-making in dynamic security operations environments.
Incident Documentation Standards
Proper documentation is crucial for accountability and process improvement. Candidates must understand the standards for recording incident details, response actions, and outcomes. Adhering to documentation standards ensures clarity, supports audits, and enables effective knowledge transfer within security teams.
Understanding Attack Patterns
Candidates are expected to recognize common attack patterns, including phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service attacks. Understanding these patterns helps in early detection, effective response, and mitigation of security incidents. Knowledge of attack patterns also informs threat prevention strategies.
Leveraging Security Tools for Investigation
The exam tests the ability to utilize security tools for investigation purposes. Candidates must be able to configure, operate, and interpret results from monitoring systems, intrusion detection platforms, and forensic tools. Proper use of these tools enhances investigative accuracy and operational effectiveness.
Preparing for Multi-Vector Threats
Candidates must be prepared to handle multi-vector threats that involve simultaneous attacks across different systems or networks. This requires comprehensive monitoring, coordinated response strategies, and the ability to analyze complex incident data to mitigate risks effectively.
Enhancing Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is vital for security operations. Candidates must maintain a clear understanding of ongoing events, system statuses, and emerging threats. Strong situational awareness supports informed decision-making and timely responses to security incidents.
Incident Escalation Procedures
The exam evaluates knowledge of proper incident escalation procedures. Candidates must understand when and how to escalate incidents to higher-level analysts or management. Effective escalation ensures that critical threats receive appropriate attention and resources.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
The dynamic nature of cybersecurity requires ongoing learning. Preparing for the 210-255 exam encourages candidates to continually update their knowledge of emerging threats, new tools, and evolving operational strategies. Continuous learning is essential for maintaining operational competence and professional growth.
The 210-255 exam provides a rigorous assessment of skills required for security operations roles. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to monitor, analyze, and respond to security incidents effectively. Preparing for this exam involves mastering threat detection, incident response, operational workflows, and analytical thinking. Success in the exam demonstrates readiness to perform as a competent security operations analyst and establishes a foundation for career advancement in cybersecurity.
Advanced Threat Analysis
The 210-255 exam evaluates the candidate's ability to perform advanced threat analysis across multiple environments. Candidates must demonstrate the skill to analyze complex data sets from various sources, including network traffic, application logs, and endpoint activity. Mastery of this domain involves understanding the lifecycle of threats, recognizing patterns that indicate advanced persistent threats, and identifying anomalies that may represent emerging attack vectors. Candidates are expected to synthesize information from multiple sources to build a coherent threat assessment and determine the appropriate level of response.
Security Information and Event Management
A key focus of the exam is Security Information and Event Management. Candidates must be able to deploy, configure, and operate SIEM tools to gather, normalize, and correlate data from multiple security devices. Effective use of SIEM systems allows analysts to detect incidents early, reduce false positives, and provide actionable insights to guide response activities. Understanding SIEM capabilities, such as real-time alerting, dashboard monitoring, and historical analysis, is essential for operational success in security operations roles.
Incident Detection Techniques
Candidates are expected to employ multiple incident detection techniques to identify security events. This includes signature-based detection, anomaly detection, heuristic analysis, and behavioral monitoring. Each technique has strengths and limitations, and candidates must know when and how to apply them effectively. Proficiency in detection techniques ensures that security operations teams can uncover hidden threats and reduce the risk of successful attacks.
Host-Based Monitoring
Host-based monitoring is a critical component of the 210-255 exam. Candidates must understand how to monitor individual systems for signs of compromise, including unauthorized access, malware execution, and abnormal process behavior. Skills in host-based monitoring also include the ability to collect forensic evidence and analyze system artifacts to determine the nature and scope of incidents.
Network-Based Monitoring
The exam emphasizes network-based monitoring as an essential aspect of operational security. Candidates must be able to analyze network traffic, identify suspicious flows, and detect malicious activity such as scanning, lateral movement, and data exfiltration. Network monitoring requires knowledge of protocols, traffic patterns, and typical network behavior to effectively distinguish normal activity from security incidents.
Event Correlation and Analysis
Candidates are required to demonstrate proficiency in correlating events from multiple sources to identify complex incidents. Event correlation involves linking disparate alerts, recognizing patterns, and detecting multi-stage attacks that may not be apparent when examining events in isolation. Strong correlation skills enhance the ability to detect sophisticated threats and provide a more complete understanding of the security environment.
Incident Response Methodologies
Understanding structured incident response methodologies is critical for success in the 210-255 exam. Candidates must be familiar with steps including detection, analysis, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident review. Effective incident response ensures that threats are managed efficiently, minimizes business impact, and supports continuous improvement of security operations processes.
Threat Mitigation Strategies
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to implement effective threat mitigation strategies. This includes isolating affected systems, applying patches, removing malicious code, and coordinating with stakeholders to restore secure operations. Proper mitigation reduces exposure, prevents further compromise, and ensures continuity of critical business functions.
Security Operations Center Practices
The exam assesses knowledge of SOC operational practices. Candidates must understand team roles, communication protocols, escalation procedures, and workflow management within a security operations center. Proficiency in SOC practices enables analysts to operate efficiently in high-pressure environments and respond effectively to incidents.
Log Analysis and Interpretation
Log analysis is a core skill for the 210-255 exam. Candidates are expected to collect, examine, and interpret logs from diverse sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and servers. Accurate log analysis allows analysts to reconstruct events, identify the root cause of incidents, and determine the scope and impact of attacks.
Malware Identification and Handling
Candidates must be able to identify various forms of malware and understand appropriate response measures. This includes recognizing indicators of compromise, understanding malware propagation techniques, and applying containment strategies. Effective malware handling is essential for protecting organizational assets and preventing further spread.
Forensic Investigation Techniques
The exam covers forensic investigation techniques used to analyze compromised systems. Candidates must be able to collect evidence, preserve integrity, analyze artifacts, and report findings. Forensic skills support incident response, legal requirements, and post-incident reviews.
Intrusion Detection and Analysis
Candidates are required to demonstrate knowledge of intrusion detection methods and analysis. This includes using IDS/IPS systems, analyzing alerts, and investigating suspicious network activity. Effective intrusion detection allows for early identification of attacks and supports timely response actions.
Event Prioritization and Escalation
The exam evaluates the ability to prioritize security events based on severity, potential impact, and organizational risk. Candidates must also know when to escalate incidents to higher-level analysts or management. Proper prioritization and escalation ensure that critical threats receive immediate attention while less urgent events are monitored.
Security Policy Application
Candidates are expected to understand and apply organizational security policies during incident management. This includes compliance with regulatory requirements, internal procedures, and best practices. Applying policies ensures consistency in response actions and supports legal and operational accountability.
Vulnerability Assessment Integration
The exam emphasizes integrating vulnerability assessment into daily operations. Candidates must understand how to identify, analyze, and remediate vulnerabilities as part of proactive threat management. Regular assessment and remediation reduce the attack surface and improve overall organizational security posture.
Continuous Monitoring Practices
Continuous monitoring is a fundamental component of security operations. Candidates must be able to implement processes that provide real-time visibility into network and host environments. Continuous monitoring allows for rapid detection of anomalies and supports immediate response to potential threats.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in advanced analytics and reporting. This includes creating dashboards, generating alerts, and presenting findings to stakeholders. Analytical reporting supports informed decision-making and strategic planning in security operations.
Threat Intelligence Utilization
The exam tests candidates on integrating threat intelligence into operational practices. This includes leveraging information on threat actors, attack vectors, and emerging threats to enhance monitoring and response activities. Threat intelligence improves proactive detection and strengthens overall defense mechanisms.
Multi-Stage Attack Detection
Candidates must be capable of identifying and responding to multi-stage attacks that span multiple systems or networks. Detecting these complex threats requires comprehensive monitoring, effective correlation of events, and analytical reasoning.
Endpoint and Network Integration
The exam covers integrating endpoint and network monitoring to provide a holistic view of security posture. Candidates must understand how to correlate data from different sources to detect incidents that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Operational Efficiency in Incident Handling
Operational efficiency is assessed through the ability to handle multiple incidents concurrently, optimize monitoring workflows, and maintain situational awareness. Efficient operations ensure timely responses while maximizing the use of available resources.
Scenario-Based Problem Solving
Candidates are evaluated on their problem-solving skills through realistic scenarios. These scenarios test critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and application of operational knowledge. Scenario-based assessment ensures candidates are prepared for real-world cybersecurity challenges.
Building Analytical Skills
The exam emphasizes developing strong analytical skills to evaluate security data, detect anomalies, and make informed decisions. Analytical proficiency is essential for effective incident response and operational decision-making.
Integration of Security Tools
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to integrate and effectively use various security tools, including SIEM systems, intrusion detection platforms, and forensic analysis software. Proper tool integration enhances incident detection, response accuracy, and operational efficiency.
Preparing for the Exam Through Hands-On Practice
Practical exercises and simulations are crucial for reinforcing theoretical knowledge. Candidates are encouraged to engage in hands-on labs that simulate real-world security incidents to develop operational confidence and proficiency.
Maintaining Situational Awareness
Maintaining situational awareness is vital for effective security operations. Candidates must monitor ongoing events, system states, and emerging threats continuously to ensure timely and appropriate responses.
Incident Documentation and Reporting
Proper documentation of incidents is required to support analysis, compliance, and process improvement. Candidates must be able to create detailed reports that capture incident details, response actions, and outcomes.
Handling Multi-Vector Threats
The exam emphasizes the ability to respond to attacks that involve multiple vectors simultaneously. Candidates must coordinate response efforts, analyze complex data, and mitigate risks effectively to prevent escalation.
Incident Containment Techniques
Candidates are expected to demonstrate knowledge of containment strategies to limit damage during incidents. This includes isolating affected systems, controlling network access, and applying immediate corrective measures.
Forensic Evidence Preservation
Preserving forensic evidence during incident handling is critical. Candidates must ensure that data integrity is maintained and that evidence is properly collected for potential legal or investigative use.
Using Advanced Monitoring Features
The exam requires familiarity with advanced monitoring features, such as automated alerting, pattern recognition, and historical analysis. These features enhance threat detection capabilities and improve operational effectiveness.
Evaluating Security Metrics
Candidates must understand how to use security metrics to assess operational performance, detect trends, and identify areas for improvement. Metrics provide insight into incident response efficiency and the effectiveness of monitoring strategies.
Enhancing Security Operations Capabilities
The 210-255 exam evaluates the ability to enhance security operations through continuous improvement. Candidates must apply lessons learned from past incidents, incorporate new tools, and refine operational procedures to strengthen overall security posture.
Cyber Threat Scenario Analysis
Candidates are tested on their ability to analyze complex cyber threat scenarios. This involves identifying attack vectors, evaluating potential impacts, and determining appropriate response strategies. Scenario analysis ensures preparedness for evolving threats.
Incident Recovery and Remediation
Effective incident recovery involves restoring affected systems to a secure state while minimizing operational disruption. Candidates must demonstrate strategies for remediation, patching, and ensuring that systems are resilient against future attacks.
Coordination with Stakeholders
Candidates must be able to coordinate with various stakeholders, including IT teams, management, and external partners, during incident response. Clear communication and collaboration ensure efficient handling of security events.
Leveraging Automated Response
The exam includes evaluating the use of automated response mechanisms to improve operational efficiency. Candidates must understand how to configure automated alerts, responses, and workflows to reduce manual intervention and enhance reaction time.
Continuous Skill Development
The dynamic nature of cybersecurity requires ongoing skill development. Preparing for the 210-255 exam encourages candidates to continuously update their knowledge of emerging threats, new technologies, and evolving operational practices.
Incident Analysis Workflow
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to follow a structured workflow for incident analysis, including detection, investigation, mitigation, and reporting. A systematic workflow ensures consistency and effectiveness in security operations.
Mastering the content and skills assessed in the 210-255 exam equips candidates to operate effectively in security operations environments. From threat detection and incident response to forensic analysis and operational efficiency, success in this exam demonstrates readiness to handle complex cybersecurity challenges and contributes to professional growth in the field.
Advanced Network Security Monitoring
The 210-255 exam focuses on advanced network security monitoring techniques. Candidates are required to demonstrate the ability to monitor large-scale networks, analyze data streams, and detect potential security incidents in real time. Understanding the normal patterns of network traffic is crucial to identify anomalies and potential breaches. Candidates must also know how to implement effective alerting systems that prioritize incidents based on severity and potential impact, enabling timely responses to threats.
Threat Intelligence Application
Effective use of threat intelligence is a major component of the exam. Candidates need to integrate intelligence feeds from multiple sources to enhance the detection of emerging threats. This involves evaluating the reliability of threat information, correlating it with internal security events, and applying actionable intelligence to prevent or mitigate attacks. Threat intelligence also guides the creation of more robust detection rules and informs strategic security planning.
Security Incident Investigation
The exam emphasizes the ability to conduct comprehensive security incident investigations. Candidates must identify indicators of compromise, trace attack vectors, and reconstruct attack timelines. This process involves correlating data from network devices, host systems, and security applications to form a clear picture of the incident. Analytical thinking and attention to detail are critical to determine the scope, impact, and source of security breaches.
Endpoint Threat Detection
Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in endpoint monitoring and threat detection. This includes analyzing system logs, detecting unauthorized processes, and recognizing signs of malware activity. Proper endpoint monitoring allows for early identification of threats before they propagate through the network, minimizing potential damage. Candidates must also know how to isolate and remediate affected endpoints effectively.
Log Analysis and Correlation
Log analysis is a central aspect of the 210-255 exam. Candidates must be skilled in collecting, parsing, and analyzing logs from diverse sources including servers, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Correlating events from multiple logs enables analysts to detect multi-stage attacks that may otherwise go unnoticed. Understanding how to leverage log data for incident detection, response, and reporting is essential for operational success.
Security Information and Event Management
The exam assesses the candidate’s ability to use Security Information and Event Management systems for effective threat monitoring. Candidates must be able to configure SIEM tools, normalize log data, and create correlation rules to detect complex threats. Proficiency in SIEM enhances situational awareness, reduces false positives, and supports rapid response to incidents. Understanding reporting capabilities and dashboard customization is also important for ongoing operational oversight.
Multi-Stage Attack Detection
Candidates must recognize and respond to multi-stage attacks. These attacks often involve multiple vectors such as phishing, lateral movement, and exfiltration. Identifying the stages of such attacks requires correlation of events, anomaly detection, and understanding of attack patterns. Effective detection of multi-stage attacks is critical to preventing full compromise of systems and data.
Incident Response Strategies
The 210-255 exam requires knowledge of structured incident response processes. Candidates must understand procedures for detecting, analyzing, containing, and eradicating threats. This includes applying mitigation strategies, coordinating with relevant stakeholders, and ensuring minimal disruption to business operations. Incident response also involves post-incident analysis to improve future security measures.
Security Event Prioritization
Candidates are expected to prioritize security events based on risk, impact, and urgency. Understanding the relative severity of incidents ensures that critical threats are addressed promptly while less urgent events are monitored effectively. Proper prioritization helps optimize operational resources and improves overall response effectiveness.
Network Intrusion Analysis
Analyzing network intrusions is a core skill assessed in the exam. Candidates must detect suspicious traffic, identify attack signatures, and investigate anomalies. Knowledge of protocols, traffic flows, and normal network behavior is essential to distinguish legitimate activity from malicious activity. Effective intrusion analysis contributes to early threat detection and rapid containment.
Host-Based Intrusion Analysis
The exam evaluates the ability to perform host-based intrusion analysis. This involves monitoring file integrity, examining process behavior, and detecting unauthorized system modifications. Candidates must understand how to gather forensic evidence from endpoints and use it to support incident investigations and remediation efforts.
Malware Handling and Containment
Candidates are required to demonstrate knowledge of malware identification and containment strategies. This includes recognizing different types of malware, understanding their behavior, and implementing measures to prevent further infection. Proper handling of malware ensures the protection of organizational assets and maintains system integrity.
Incident Documentation and Reporting
Effective documentation is critical for the 210-255 exam. Candidates must create detailed incident reports that capture the nature of the threat, actions taken, and outcomes. Documentation supports organizational accountability, compliance, and continuous improvement of security operations. Accurate reporting also facilitates communication with stakeholders and aids in future incident analysis.
Integration of Security Tools
The exam tests candidates on integrating various security tools into operational workflows. This includes SIEM, intrusion detection systems, forensic analysis tools, and monitoring platforms. Proper integration enhances detection capabilities, streamlines response procedures, and improves overall security operations efficiency.
Advanced Threat Hunting
Candidates must be proficient in advanced threat hunting techniques. This involves proactively searching for threats that may bypass automated detection systems. Threat hunting requires analytical skills, deep knowledge of attack patterns, and familiarity with monitoring tools. The ability to detect hidden threats before they escalate is critical for maintaining organizational security.
Continuous Monitoring Practices
Continuous monitoring is emphasized for operational effectiveness. Candidates must understand how to implement monitoring processes that provide real-time visibility into network and system activity. Continuous monitoring supports early detection, rapid response, and the identification of long-term security trends.
Forensic Investigation Techniques
The exam evaluates the ability to conduct forensic investigations on compromised systems. Candidates must collect and preserve evidence, analyze artifacts, and reconstruct incidents. Forensic skills support incident response, legal compliance, and organizational learning from past events.
Security Operations Center Workflow
Candidates must understand the workflow within a security operations center, including team roles, communication protocols, and escalation procedures. Proficiency in SOC workflow ensures efficient handling of incidents and enhances coordination among security teams.
Event Correlation and Analysis
Event correlation is essential for detecting complex attacks. Candidates must link related alerts, recognize patterns, and interpret multiple data sources to identify incidents. Correlation improves the accuracy of detection, reduces false positives, and supports comprehensive incident response.
Scenario-Based Analysis
The 210-255 exam includes scenario-based analysis to test practical application of knowledge. Candidates must analyze realistic security incidents, determine attack vectors, and recommend appropriate responses. Scenario-based assessment ensures readiness for real-world operational challenges.
Operational Efficiency
Candidates are expected to demonstrate operational efficiency in handling multiple incidents, optimizing workflows, and managing resources. Efficient operations allow for rapid response to critical events while maintaining ongoing monitoring and analysis.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Candidates must integrate threat intelligence into operational practices. This includes using information on emerging threats, attack methodologies, and threat actors to inform monitoring and response activities. Effective intelligence integration strengthens detection capabilities and improves incident mitigation.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
The exam assesses skills in applying advanced analytics to security data. Candidates must generate actionable insights, create dashboards, and report findings to stakeholders. Analytics support strategic decision-making and enhance the effectiveness of security operations.
Endpoint and Network Integration
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to integrate endpoint and network monitoring data to achieve a comprehensive security view. Correlating diverse data sources improves detection accuracy and incident response.
Automated Response Techniques
Knowledge of automated response mechanisms is tested in the exam. Candidates must configure and manage automated alerts, responses, and workflows to reduce manual intervention and accelerate reaction times.
Cyber Threat Scenario Planning
Candidates are expected to evaluate complex cyber threat scenarios, anticipate attack outcomes, and formulate response strategies. Scenario planning prepares analysts for evolving threats and supports proactive defense measures.
Incident Containment and Recovery
The exam emphasizes techniques for containing and recovering from security incidents. Candidates must isolate affected systems, restore secure operations, and apply corrective measures to prevent recurrence.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Candidates must demonstrate commitment to continuous learning to stay current with emerging threats, evolving tools, and best practices in security operations. Continuous development is essential for long-term effectiveness in cybersecurity roles.
Mastering the 210-255 exam content equips candidates to perform at an advanced level in security operations. From threat detection and monitoring to forensic analysis and incident response, success in this exam validates readiness to handle complex cybersecurity challenges and contributes to professional growth in operational security.
Security Event Correlation
The 210-255 exam emphasizes the ability to correlate security events across multiple sources to detect complex attack patterns. Candidates must be able to analyze logs from firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoint protection platforms, and network devices, linking seemingly unrelated events to identify coordinated attacks. This skill ensures early detection of multi-stage threats and reduces the likelihood of breaches going unnoticed. Analysts are expected to create correlation rules and filters to prioritize actionable events and reduce false positives while maintaining situational awareness of the entire network infrastructure.
Threat Detection and Analysis
A critical component of the 210-255 exam is proficiency in threat detection. Candidates must understand common attack vectors, malicious behaviors, and emerging threats to identify potential intrusions. This requires knowledge of network protocols, communication patterns, and system behaviors. Analysts are expected to use monitoring tools to detect anomalies and suspicious activity, interpreting the significance of alerts and making informed decisions on incident escalation. Continuous evaluation of threat intelligence is necessary to refine detection strategies and anticipate evolving attacks.
Incident Response Management
The exam assesses the candidate’s ability to manage the incident response lifecycle. This includes detecting, analyzing, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security incidents. Candidates must demonstrate an understanding of how to document and report incidents accurately, ensuring that all steps comply with organizational policies and best practices. Effective incident management requires coordination with multiple teams, clear communication, and timely execution of response procedures to minimize the impact of security events.
Network Intrusion Analysis
Analyzing network intrusions is a key area covered in the 210-255 exam. Candidates must identify suspicious traffic patterns, abnormal protocol usage, and indicators of compromise within network flows. They should be able to distinguish between legitimate anomalies and malicious behavior, providing actionable insights to prevent further exploitation. Familiarity with intrusion detection systems, packet capture tools, and network monitoring platforms is essential to accurately analyze and interpret data.
Endpoint Security Monitoring
Candidates are expected to monitor and analyze endpoint security to detect potential threats. This involves examining system logs, identifying unauthorized processes, and recognizing malware behavior. Knowledge of endpoint protection solutions and their integration with broader monitoring systems is crucial. Analysts should be able to take proactive measures to isolate compromised endpoints and remediate threats efficiently while maintaining operational continuity.
Forensic Investigation Techniques
Forensic analysis is an important skill for the 210-255 exam. Candidates must be able to collect, preserve, and analyze digital evidence from endpoints, servers, and network devices. This involves understanding file systems, memory analysis, and artifact examination. Forensic investigations support incident response, enable root cause analysis, and provide documentation for compliance or legal requirements. Detailed and methodical investigation skills are essential to ensure accuracy and reliability of findings.
Log Analysis and Management
Proficiency in log analysis is crucial for security operations. Candidates must collect, parse, and analyze logs from multiple sources to detect security events. This includes identifying abnormal patterns, correlating events, and maintaining log integrity for auditing purposes. Effective log management supports proactive threat detection, incident investigation, and organizational reporting requirements, enabling analysts to maintain continuous oversight of system and network security.
Security Operations Center Practices
The 210-255 exam evaluates knowledge of Security Operations Center practices. Candidates should understand SOC workflows, including alert triage, escalation procedures, and incident documentation. They must be able to integrate various monitoring and detection tools into the SOC environment, ensuring efficient processing of security events. Understanding team roles, communication protocols, and operational coordination is essential to maintain effective incident response and overall security posture.
Malware Analysis and Containment
Candidates are expected to identify, analyze, and contain malware threats. This includes understanding the behavior of different malware types, such as ransomware, spyware, and Trojans. Analysts must know how to isolate infected systems, prevent lateral movement, and implement remediation measures to protect organizational assets. Malware containment requires a combination of technical skills, situational awareness, and adherence to security protocols.
Security Information and Event Management
The exam covers the application of Security Information and Event Management platforms. Candidates must configure SIEM systems, normalize log data, create correlation rules, and generate actionable alerts. Proficiency in SIEM enables analysts to detect complex threats, prioritize responses, and produce comprehensive security reports. Understanding SIEM dashboards and reporting tools is essential for maintaining visibility and operational effectiveness.
Advanced Threat Hunting
Advanced threat hunting is emphasized as part of proactive security operations. Candidates should be able to analyze network and endpoint data to identify hidden threats that may bypass automated detection. This requires knowledge of attack methodologies, threat actor behavior, and analytical techniques. Threat hunting enables early detection of sophisticated attacks, reducing risk and supporting proactive security measures.
Data and Event Analysis
Candidates must be skilled in analyzing security events and data to detect incidents. This involves interpreting network traffic, system logs, and endpoint activity to determine potential threats. Analysts should be able to identify correlations, understand the context of alerts, and assess the severity of security events. Effective data analysis supports informed decision-making and timely incident response.
Incident Documentation and Reporting
The 210-255 exam requires expertise in documenting and reporting incidents accurately. Candidates must record event details, investigative steps, and response actions clearly. Proper documentation supports compliance, organizational accountability, and continuous improvement in security operations. Reports should be actionable, precise, and structured to facilitate communication with stakeholders and support future investigations.
Integration of Security Tools
Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to integrate various security tools for operational efficiency. This includes SIEM platforms, intrusion detection systems, endpoint monitoring tools, and forensic analysis applications. Tool integration enhances detection capabilities, streamlines response procedures, and ensures comprehensive coverage of security monitoring activities.
Continuous Monitoring and Analysis
Continuous monitoring practices are essential for effective cybersecurity operations. Candidates should implement real-time monitoring of networks and systems to detect anomalies and threats promptly. This involves using monitoring dashboards, alerting mechanisms, and automated processes to maintain visibility across the environment. Continuous analysis allows for timely response and long-term security trend identification.
Scenario-Based Security Evaluation
The exam incorporates scenario-based analysis to test practical application of knowledge. Candidates must evaluate realistic security incidents, determine attack vectors, and recommend appropriate mitigation strategies. Scenario-based evaluation ensures readiness for operational challenges and validates analytical and problem-solving skills in real-world environments.
Automated Response Implementation
Candidates are expected to apply automated response techniques to improve operational efficiency. This includes configuring automated alerts, scripts, and remediation workflows to address common threats quickly. Automated responses help reduce manual intervention, accelerate reaction times, and enhance consistency in security operations.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Effective use of threat intelligence is a key skill for the 210-255 exam. Candidates should incorporate intelligence on emerging threats, attack methods, and threat actor activities into monitoring and response processes. Threat intelligence enhances detection accuracy, informs proactive measures, and supports strategic security planning.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Candidates must be able to assess risks and prioritize incidents based on potential impact and urgency. Evaluating the severity of threats ensures that critical events receive immediate attention while lower-priority alerts are managed appropriately. Risk prioritization optimizes resource allocation and improves overall incident management effectiveness.
Post-Incident Analysis
The exam emphasizes post-incident analysis to learn from past events. Candidates should review incidents to identify root causes, evaluate response effectiveness, and implement improvements. Post-incident analysis supports continuous learning, strengthens defenses, and reduces the likelihood of future breaches.
Cybersecurity Workflow Optimization
Candidates are expected to optimize cybersecurity workflows for efficiency and effectiveness. This involves streamlining monitoring processes, coordinating response activities, and improving communication among teams. Optimized workflows enhance operational performance and ensure timely handling of security incidents.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Applying advanced analytics to security data is a critical skill. Candidates must generate actionable insights, identify trends, and create meaningful reports for stakeholders. Analytics support decision-making, enhance situational awareness, and improve the overall effectiveness of security operations.
Endpoint and Network Visibility
Candidates must ensure comprehensive visibility across both endpoints and networks. Correlating data from multiple sources provides a complete security overview, enabling detection of threats that might otherwise remain hidden. Visibility supports timely response and enhances the ability to prevent or mitigate security incidents.
Compliance and Regulatory Awareness
Understanding compliance requirements and regulatory frameworks is essential for security operations. Candidates must ensure that monitoring, detection, and response practices align with legal and organizational standards. Awareness of regulatory obligations supports accountability and risk management in operational security.
Continuous Professional Development
Candidates are expected to pursue ongoing learning to maintain expertise in emerging threats, technologies, and best practices. Continuous development ensures that analysts remain effective in rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscapes and adapt to new operational challenges.
Collaboration and Communication Skills
The 210-255 exam also evaluates candidates on collaboration and communication within security teams. Effective communication ensures that critical information is shared promptly, incidents are coordinated efficiently, and stakeholders are informed accurately. Strong interpersonal skills support cohesive and effective security operations.
Strategic Threat Mitigation
Candidates must understand strategies to mitigate long-term and sophisticated threats. This involves analyzing attack trends, implementing proactive measures, and adjusting security policies based on observed threat patterns. Strategic mitigation strengthens the security posture and minimizes organizational risk.
Mastery of the 210-255 exam topics equips candidates to perform advanced security operations with confidence. From incident detection and analysis to forensic investigation, threat hunting, and operational optimization, success in this exam demonstrates readiness to handle complex cybersecurity challenges and supports professional growth in the field of security operations
Advanced Threat Modeling
Candidates preparing for the 210-255 exam must develop skills in advanced threat modeling to anticipate potential attack paths. This includes understanding attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures and mapping them against organizational assets and network architecture. The ability to model threats helps in designing detection rules, prioritizing defenses, and implementing preventive measures. Analysts are expected to assess vulnerabilities, predict exploitation scenarios, and refine security controls to mitigate risks effectively.
Security Automation and Orchestration
Proficiency in security automation and orchestration is critical for efficient operations. Candidates should understand how to implement automated workflows for alert triage, incident response, and threat mitigation. Automation reduces response time, ensures consistent handling of events, and frees analysts to focus on complex security issues. Orchestration involves coordinating multiple tools and processes, integrating endpoint monitoring, SIEM platforms, and threat intelligence feeds to streamline operations.
Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics is an essential component of the 210-255 exam. Candidates must analyze user, device, and network behaviors to detect anomalies that may indicate insider threats or compromised accounts. This includes establishing baselines for normal behavior, identifying deviations, and correlating anomalies across multiple data sources. Behavioral analysis enables proactive detection and enhances overall situational awareness within the security environment.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Integration
Integrating cyber threat intelligence into daily security operations is emphasized for candidates. Analysts must incorporate intelligence from external sources, such as threat feeds and advisories, as well as internal sources from past incidents. This allows for timely detection of emerging threats, informed decision-making, and proactive defense measures. Candidates should be able to classify, prioritize, and operationalize threat intelligence effectively.
Vulnerability Assessment and Management
The 210-255 exam covers vulnerability assessment practices. Candidates must be able to identify weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications and assess their potential impact. Effective vulnerability management involves prioritizing remediation efforts, applying patches, and monitoring for exploitation attempts. Analysts should understand the tools and techniques used to scan for vulnerabilities and interpret results to enhance organizational security posture.
Security Event Prioritization
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to prioritize security events based on risk and potential impact. This involves differentiating between low-level alerts and high-severity incidents that require immediate attention. Prioritization ensures optimal allocation of resources and helps prevent critical threats from being overlooked. Effective event triage is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing business disruption.
Incident Escalation and Coordination
Understanding incident escalation procedures is a key aspect of the 210-255 exam. Candidates must know how to escalate incidents according to organizational policies, involving higher-level analysts or management when necessary. Coordination across teams ensures that incidents are addressed efficiently, minimizing impact. Candidates should also be able to document escalation steps clearly to support future review and analysis.
Log Correlation and Analysis
Log correlation is a crucial skill for 210-255 candidates. Analysts must collect and analyze logs from various devices, including firewalls, routers, endpoints, and servers. By correlating log data, analysts can identify patterns indicative of multi-stage attacks and distinguish false positives from genuine threats. Effective log analysis enhances threat visibility and supports informed decision-making during incident response.
Forensic Evidence Handling
Candidates must be adept at handling forensic evidence to ensure its integrity during investigations. This involves proper collection, preservation, and analysis of digital artifacts from endpoints, network devices, and cloud environments. Maintaining a chain of custody and following established procedures is essential to support internal investigations or legal proceedings. Forensic skills enable analysts to uncover attack origins and understand the scope of compromise.
Network Traffic Analysis
Network traffic analysis is a critical area tested in the 210-255 exam. Candidates should be able to monitor and interpret network flows, detect unusual activity, and identify potential intrusions. This includes analyzing packet captures, examining protocol behavior, and recognizing suspicious communication patterns. Proficiency in network traffic analysis helps in early threat detection and supports proactive defense strategies.
Endpoint Threat Detection
Candidates must understand methods for detecting threats on endpoints. This includes monitoring system processes, identifying malware, and analyzing file and memory behaviors. Effective endpoint threat detection relies on integrating endpoint protection platforms with centralized monitoring solutions to maintain comprehensive visibility and rapid response capabilities.
Security Operations Metrics
The exam evaluates knowledge of security operations metrics. Candidates must be able to define key performance indicators for monitoring SOC effectiveness, such as mean time to detect, mean time to respond, and incident resolution rates. Metrics provide insight into operational performance, highlight areas for improvement, and support data-driven decision-making in security operations.
Malware Reverse Engineering
Knowledge of malware reverse engineering is important for advanced incident analysis. Candidates should understand the techniques for deconstructing malware, identifying its behavior, and determining its impact. Reverse engineering assists in creating signatures, developing mitigation strategies, and understanding threat actor methodologies.
Threat Hunting Methodologies
The 210-255 exam emphasizes threat hunting as a proactive security practice. Candidates must be able to search for hidden threats using data analysis, anomaly detection, and hypothesis-driven investigation. Threat hunting enables analysts to detect sophisticated attacks that may evade automated monitoring, improving overall security posture and incident preparedness.
Security Incident Documentation
Accurate documentation of security incidents is crucial for compliance and operational review. Candidates must record the details of incidents, investigative steps, response actions, and lessons learned. Comprehensive documentation supports knowledge transfer, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement in security processes.
SOC Workflow Optimization
Candidates are expected to optimize SOC workflows for efficiency. This includes streamlining alert triage, integrating automation, and enhancing communication between analysts. Optimized workflows reduce response times, improve coordination, and increase overall operational effectiveness in handling security events.
Security Policy Implementation
The exam evaluates understanding of implementing and enforcing security policies. Candidates must be able to translate organizational policies into actionable monitoring, detection, and response procedures. This ensures that operations align with regulatory requirements and organizational standards, maintaining consistent security practices.
Security Awareness Integration
Integrating security awareness into operational procedures is tested for 210-255 candidates. Analysts should collaborate with other departments to ensure that security practices are understood and followed. This includes providing guidance on recognizing threats, following incident reporting procedures, and promoting a culture of security mindfulness.
Risk Mitigation Planning
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to plan risk mitigation strategies. This involves assessing potential threats, evaluating their impact, and implementing measures to reduce exposure. Effective planning ensures that high-risk assets are prioritized and that preventive controls are in place to minimize potential damage from incidents.
Continuous Improvement in Security Operations
Continuous improvement is a key focus for 210-255 preparation. Candidates should be able to analyze past incidents, identify weaknesses in processes, and implement improvements. This iterative approach strengthens security operations, enhances detection capabilities, and ensures preparedness for evolving threats.
Collaboration and Incident Communication
Effective collaboration and communication are critical in security operations. Candidates must coordinate with team members, management, and other stakeholders during incident response. Clear communication ensures that incidents are handled efficiently, critical information is shared promptly, and organizational response is cohesive.
Advanced Threat Mitigation Strategies
Candidates are expected to develop advanced threat mitigation strategies. This includes deploying layered defenses, monitoring for attack patterns, and implementing proactive measures. Strategic mitigation helps protect critical assets, reduce risk exposure, and improve overall resilience against sophisticated threats.
Integration of Emerging Technologies
The 210-255 exam evaluates understanding of integrating emerging technologies into security operations. Candidates must assess how new tools, platforms, and security solutions can enhance monitoring, detection, and response capabilities. Integration of modern technologies supports adaptive defense strategies and strengthens operational efficiency.
Security Event Simulation
Candidates should be able to perform security event simulations to test detection and response procedures. Simulations help identify gaps in monitoring, evaluate response workflows, and train analysts in handling complex scenarios. This practice ensures that SOC teams are prepared for real-world incidents and can respond effectively under pressure.
Post-Event Analysis and Reporting
Post-event analysis is essential to understand the effectiveness of security operations. Candidates must review incidents, evaluate response actions, and document outcomes. Lessons learned from post-event analysis guide process improvements, enhance future detection, and support informed decision-making for ongoing security management.
Professional Development in Security Operations
Ongoing professional development is crucial for maintaining expertise in security operations. Candidates must stay current with emerging threats, new technologies, and evolving operational practices. Continuous learning ensures that analysts can adapt to changing environments and maintain proficiency in advanced security operations.
Conclusion
Mastering the skills and knowledge areas covered in the 210-255 exam equips candidates to excel as security operations analysts. From advanced threat modeling and incident response to threat hunting, automation, and post-event analysis, the certification validates a professional’s ability to operate effectively in high-pressure security environments. Success in this exam demonstrates readiness to manage complex cybersecurity operations and contributes to a comprehensive understanding of modern security practices.
Cisco CCNA Cyber Ops 210-255 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 210-255 Implementing Cisco Cybersecurity Operations (SECOPS) certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- 200-301 - Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- 350-401 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
- 300-410 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
- 350-701 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies
- 300-715 - Implementing and Configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine (300-715 SISE)
- 350-601 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Data Center Core Technologies (DCCOR)
- 350-801 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies (CLCOR)
- 300-420 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)
- 300-415 - Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)
- 200-901 - DevNet Associate (DEVASC)
- 200-201 - Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS)
- 300-425 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-425 ENWLSD)
- 300-710 - Securing Networks with Cisco Firewalls
- 820-605 - Cisco Customer Success Manager (CSM)
- 350-901 - Developing Applications using Cisco Core Platforms and APIs (DEVCOR)
- 350-501 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR)
- 300-620 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (DCACI)
- 400-007 - Cisco Certified Design Expert
- 300-730 - Implementing Secure Solutions with Virtual Private Networks (SVPN 300-730)
- 300-430 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-430 ENWLSI)
- 500-220 - Cisco Meraki Solutions Specialist
- 300-435 - Automating Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)
- 100-150 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking
- 300-810 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Applications (CLICA)
- 350-201 - Performing CyberOps Using Core Security Technologies (CBRCOR)
- 700-805 - Cisco Renewals Manager (CRM)
- 300-820 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Cloud and Edge Solutions
- 300-735 - Automating Cisco Security Solutions (SAUTO)
- 300-815 - Implementing Cisco Advanced Call Control and Mobility Services (CLASSM)
- 300-610 - Designing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure for Traditional and AI Workloads
- 300-745 - Designing Cisco Security Infrastructure
- 300-510 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions (SPRI)
- 300-440 - Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)
- 100-140 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) IT Support
- 300-720 - Securing Email with Cisco Email Security Appliance (300-720 SESA)
- 300-725 - Securing the Web with Cisco Web Security Appliance (300-725 SWSA)
- 300-215 - Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR)
- 300-835 - Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO)
- 300-515 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider VPN Services (SPVI)
- 300-910 - Implementing DevOps Solutions and Practices using Cisco Platforms (DEVOPS)
- 700-250 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Sales
- 300-445 - Designing and Implementing Enterprise Network Assurance
- 300-635 - Automating Cisco Data Center Solutions (DCAUTO)
- 500-442 - Administering Cisco Contact Center Enterprise
- 300-615 - Troubleshooting Cisco Data Center Infrastructure (DCIT)
- 300-630 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure - Advanced
- 500-560 - Cisco Networking: On-Premise and Cloud Solutions (OCSE)
- 500-444 - Cisco Contact Center Enterprise Implementation and Troubleshooting (CCEIT)
- 700-750 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Engineer
- 700-240 - Cisco Environmental Sustainability Overview
- 700-245 - Environmental Sustainability Practice-Building
- 700-150 - Introduction to Cisco Sales (ICS)
- 800-150 - Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians
- 100-490 - Cisco Certified Technician Routing & Switching (RSTECH)
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Cisco certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 210-255 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Cisco certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 210-255 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 210-255 preparation materials for the Cisco certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 210-255 materials for the Cisco certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 210-255 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Cisco certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 210-255. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 210-255 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 210-255 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Cisco certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 210-255 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 210-255 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

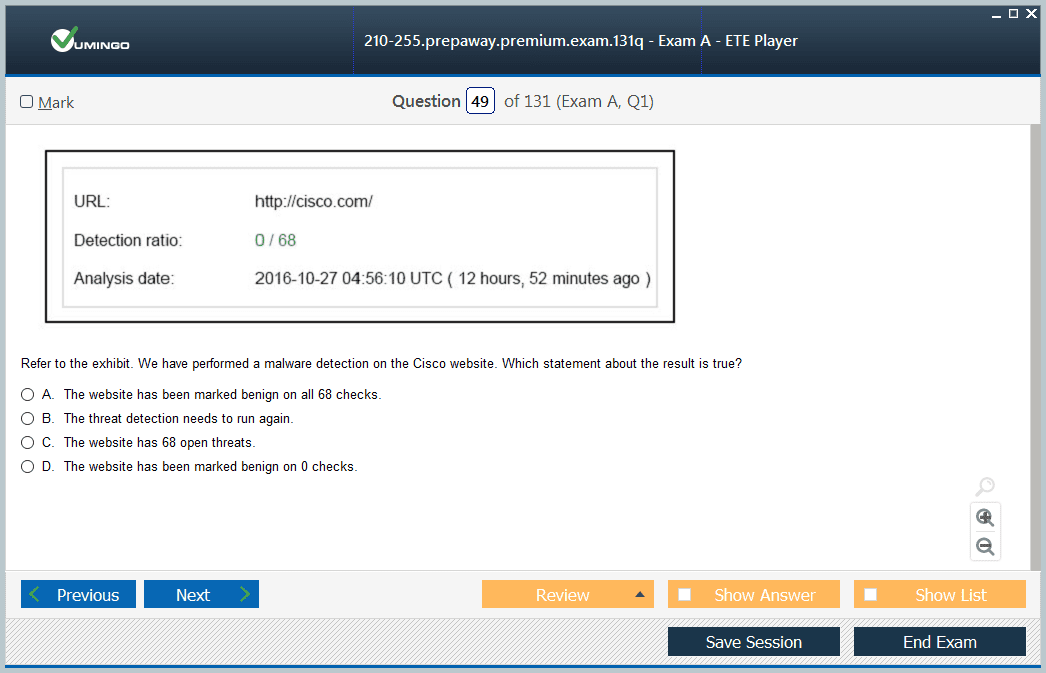
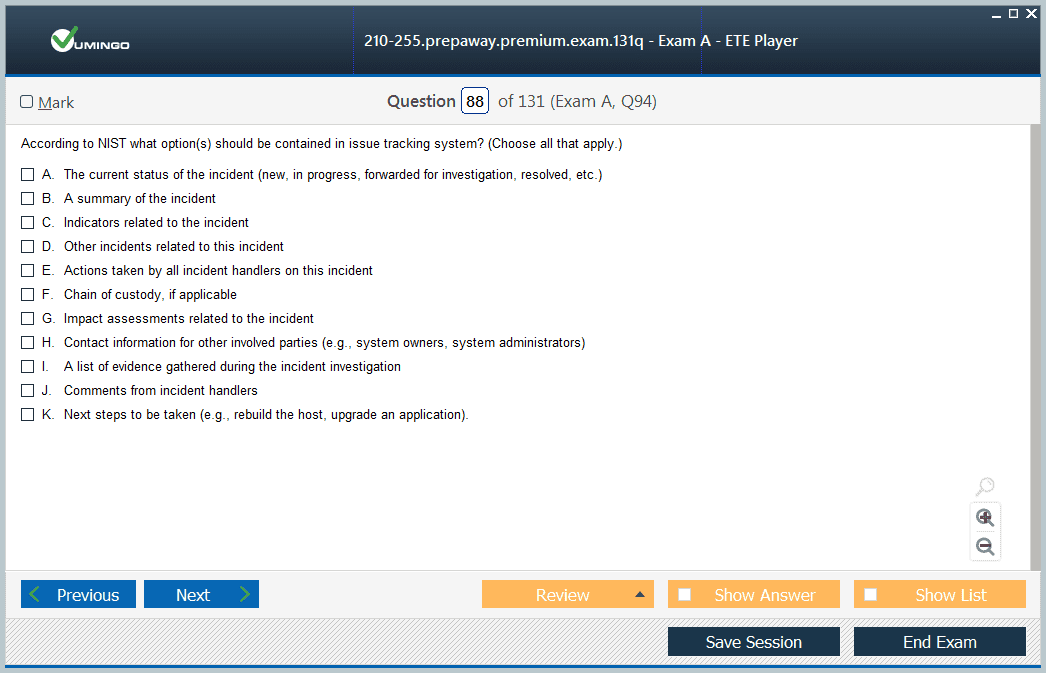
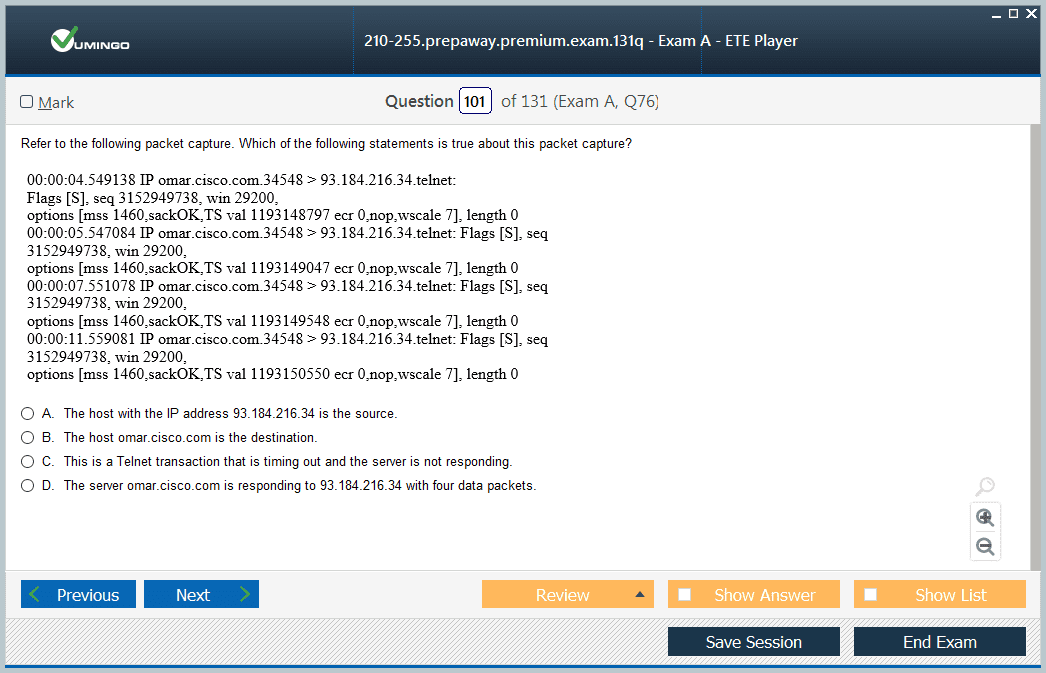
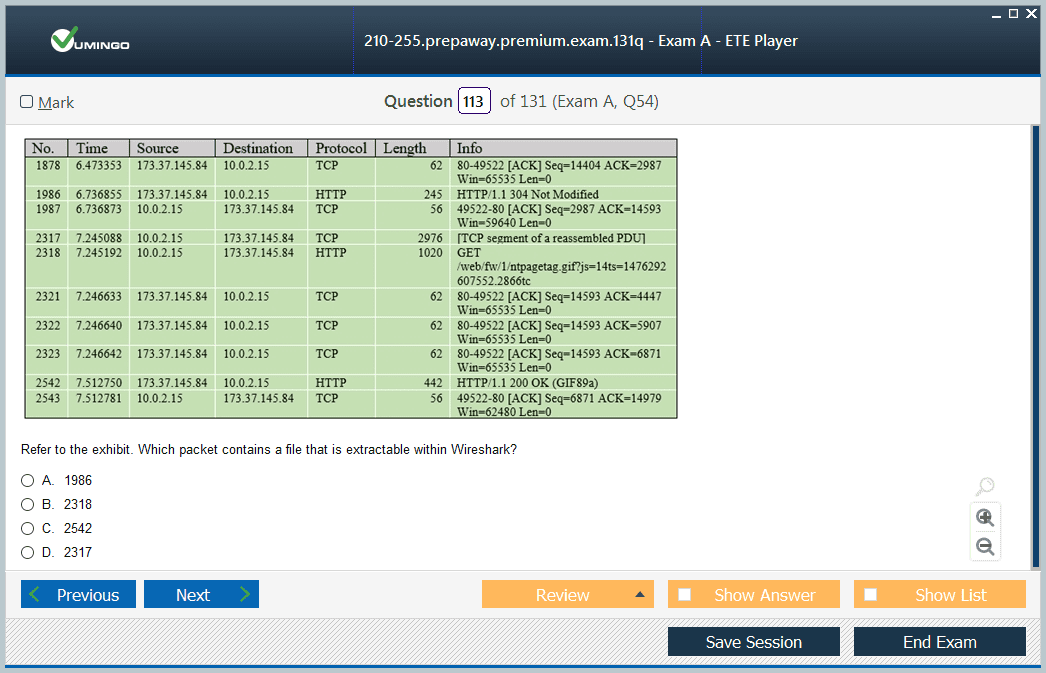




dumps are good .
but also study official material
These dumps are still valid, but be aware that some questions are wrong (about 15%).
20 new questions -> difference between CSIRT and PSIRT, NIST SP800-61 r2, CVSS, the difference between IDS/IPS logs vs NetFlow logs.
I thank God. scored 931
Thanks