- Home
- Cisco Certifications
- 200-155 Introducing Cisco Data Center Technologies Dumps
Pass Cisco CCNA Data Center 200-155 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


200-155 Premium File
- Premium File 201 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Feb 04, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Cisco CCNA Data Center 200-155 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 200-155 Introducing Cisco Data Center Technologies practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
A Complete Guide to Getting Cisco 200-155 Certified
The 200-155 exam evaluates the foundational networking skills required for professionals in data center environments. Candidates must understand the architecture and operation of data center networks, ensuring they can configure, manage, and troubleshoot devices effectively. Core concepts such as TCP/IP, Ethernet switching, VLANs, and routing form the backbone of the exam. Mastery of these areas ensures that learners can manage high-density environments and maintain reliable communication across multiple network segments.
In addition to theoretical knowledge, hands-on experience is critical. Practicing configurations on physical or simulated devices reinforces understanding of concepts and provides the skills necessary to implement solutions in real-world scenarios. By systematically practicing network configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting, candidates can confidently approach both the exam and operational challenges in data centers.
Understanding Switching and Segmentation
Switching technologies are central to data center networking. Candidates must understand how to configure VLANs to logically segment networks, manage broadcast domains, and improve security. Trunking allows multiple VLANs to traverse a single physical link, and candidates must be able to configure trunk ports using protocols such as 802.1Q.
Advanced switching concepts, including EtherChannel, spanning tree protocols, and PortFast, are vital for ensuring redundancy, avoiding loops, and providing efficient convergence. Configuring EtherChannel in modes like LACP or static aggregation enhances bandwidth while maintaining fault tolerance. Understanding root bridge election, path costs, and BPDU Guard settings ensures that the network remains stable even in complex topologies.
Routing in Data Center Environments
Routing ensures efficient data flow between subnets and networks. The 200-155 exam covers both static and dynamic routing principles. Candidates should be proficient in configuring and troubleshooting protocols such as OSPF and EIGRP, understanding their behavior in IPv4 and IPv6 networks, and implementing route summarization to optimize routing tables.
Distance vector and link-state routing protocols have distinct characteristics, and understanding their operation is essential. Candidates must know how to verify routing operations, analyze routing tables, and troubleshoot connectivity issues. Knowledge of route redistribution, passive interfaces, and filtering allows for precise control over traffic paths, ensuring data center networks operate efficiently and maintain high availability.
WAN Connectivity and Redundancy
Data centers often require interconnections between multiple sites, making WAN technologies essential. Candidates must understand point-to-point links, hub-and-spoke topologies, and full-mesh configurations. WAN protocols such as PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE provide authentication, encapsulation, and flexibility in connecting distributed networks.
Tunneling protocols such as GRE allow the creation of virtual point-to-point connections over existing IP infrastructure, offering scalability and operational flexibility. Dual-homed and redundant configurations ensure continuous operation in case of link failures. Hands-on practice in configuring WAN links, testing connectivity, and troubleshooting performance issues equips candidates with skills needed to maintain resilient networks.
Infrastructure Services and High Availability
High availability is critical in data center networks to ensure that applications and users experience minimal downtime. Protocols like HSRP allow for seamless failover between routers, maintaining default gateway availability. Candidates must understand HSRP configuration options including priority settings, preemption, and versions to design networks with resilient failover mechanisms.
Other infrastructure services, such as DHCP, DNS, and NAT, are essential for network operation. Correct configuration ensures devices receive proper addressing, can communicate across network segments, and maintain connectivity during network changes. Quality of Service strategies help prioritize critical traffic such as voice and video, ensuring performance consistency in high-demand environments. Candidates must understand classification, marking, shaping, and policing of traffic to maintain optimal performance.
Security Fundamentals in Data Centers
Security is a critical component of data center networks. Candidates need to understand VLAN segmentation, access control lists, and port security to protect critical resources. Authentication mechanisms such as 802.1x ensure that only authorized devices and users gain access to the network.
Understanding the impact of security measures on performance and redundancy is essential. Configurations must maintain protection without introducing bottlenecks or single points of failure. Monitoring through SNMP and syslog allows administrators to detect unusual activity and respond proactively. Candidates should practice reviewing logs, verifying configurations, and implementing policies that balance security with operational efficiency.
Virtualization and Overlay Networks
Virtualized environments are increasingly common in data centers, requiring candidates to understand how virtual networks interact with physical infrastructure. Virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlays like VXLAN extend Layer 2 connectivity over Layer 3 networks. Candidates must configure virtual interfaces, monitor traffic, and ensure isolation between applications while sharing physical resources.
Coordinating virtual and physical network components helps anticipate performance bottlenecks, plan for redundancy, and implement consistent Quality of Service policies. Practical exercises in virtual network configuration reinforce understanding and prepare candidates for real-world implementation scenarios.
Troubleshooting and Network Monitoring
Effective troubleshooting is a cornerstone of managing data center networks. Candidates must follow a structured approach, starting with physical layer verification, moving through Layer 2 and Layer 3 analysis, and considering application-level connectivity issues. Tools such as ping, traceroute, and interface statistics are essential for isolating problems and implementing solutions efficiently.
Proactive monitoring ensures potential issues are detected before impacting operations. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry provide continuous insights into performance, resource utilization, and system health. Candidates should practice interpreting monitoring data, verifying configuration changes, and testing failover scenarios. This approach ensures networks remain operational and resilient under varying conditions.
Integrating Knowledge for Certification Success
The 200-155 exam evaluates a candidate’s ability to integrate multiple networking aspects, from switching and routing to virtualization and security. Candidates must combine theoretical understanding with hands-on practice to demonstrate competency in designing, configuring, and maintaining data center networks.
Simulated lab exercises reinforce knowledge, allowing candidates to apply concepts in practical scenarios. Repeated practice builds confidence and prepares learners for the complexity of the exam. Mastery of core principles, operational procedures, and troubleshooting strategies equips candidates with the skills required to manage high-density networks and positions them for advancement in data center networking roles.
Preparing Strategically for the Exam
A systematic approach is essential for exam readiness. Candidates should allocate sufficient time to study foundational concepts, practice device configurations, and review network design principles. Understanding the interrelation between different network components ensures that configurations are applied effectively, and troubleshooting is performed methodically.
Time management, consistent practice, and review of critical topics are essential strategies for preparation. Simulating real-world scenarios enhances practical skills and improves confidence. Candidates should combine focused study, hands-on lab work, and scenario-based problem solving to ensure comprehensive readiness for the exam.
Leveraging Resources Effectively
High-quality study resources cover all exam objectives and provide a mix of theoretical explanations and practical exercises. Resources should be structured to facilitate step-by-step learning, covering switching, routing, WAN connectivity, infrastructure services, security, virtualization, and monitoring. Hands-on exercises reinforce theoretical knowledge, and practice scenarios help candidates anticipate potential challenges.
Integrating study material with lab exercises strengthens understanding, builds confidence, and ensures that candidates are prepared for both the exam and professional tasks. A well-rounded approach that combines multiple learning methods is crucial for success in the 200-155 exam and for developing long-term skills in data center networking.
Preparing for the 200-155 exam requires a blend of comprehensive theoretical study, practical exercises, and systematic review. Candidates must master core networking principles, understand advanced switching and routing features, configure virtualized environments, implement high availability, and apply security measures effectively. Hands-on practice reinforces knowledge, builds confidence, and ensures readiness for complex scenarios.
A structured preparation plan, consistent practice, and focused study of all relevant topics equip candidates to succeed in the exam. Mastery of foundational networking skills ensures proficiency in real-world data center operations, allowing professionals to manage high-density environments efficiently and support business-critical applications with confidence.
Advanced Data Center Switching and Routing Concepts
In preparing for the 200-155 exam, candidates must delve into advanced switching and routing topics that are crucial for managing high-density data center networks. Beyond basic VLAN and trunk configurations, candidates should understand complex spanning tree topologies, including Rapid PVST+ and MST. These protocols help maintain loop-free network operations while ensuring fast convergence during topology changes. Root bridge selection, port cost analysis, and the implementation of PortFast and BPDU Guard features are essential to ensure predictable network behavior.
EtherChannel configurations further enhance network performance and reliability. Understanding static aggregation and dynamic negotiation protocols such as LACP and PAGP enables candidates to implement redundant links while maximizing available bandwidth. Combining these features allows for resilient, high-performance switching infrastructures capable of handling the scale and traffic patterns typical of modern data centers.
Layer 3 Routing Strategies
Routing in data center networks extends beyond mere connectivity. Dynamic routing protocols like OSPF and EIGRP play a critical role in ensuring efficient traffic flow across multiple subnets. Candidates must understand area design, route summarization, and the differences between distance vector and link-state protocols. Effective route redistribution and route filtering techniques allow precise control over traffic paths, preventing routing loops and minimizing latency.
The exam also tests a candidate's ability to troubleshoot routing issues and verify protocol operations. Practical exercises in configuring routing tables, analyzing protocol behavior, and resolving convergence issues reinforce understanding. Mastery of these routing strategies ensures that candidates can design scalable networks with high availability, where traffic moves efficiently under normal and failure conditions.
WAN Integration and Tunneling
Data centers often extend connectivity across multiple locations, making WAN technologies and tunneling protocols vital. Candidates should understand point-to-point connections, hub-and-spoke designs, and full-mesh topologies. Protocols such as PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE provide authentication and encapsulation, allowing secure and efficient communication over WAN links.
GRE tunnels enable the creation of virtual point-to-point connections, allowing Layer 2 networks to extend over Layer 3 infrastructure. Understanding single- and dual-homed configurations helps candidates design networks resilient to link failures. Practical experience in configuring WAN links, verifying tunnel connectivity, and troubleshooting issues equips candidates with the skills necessary for real-world operations and ensures readiness for the exam.
High Availability and Infrastructure Services
Ensuring continuous availability is a cornerstone of data center networking. Protocols like HSRP provide gateway redundancy, enabling seamless failover during router outages. Candidates must grasp HSRP priority, preemption, and version configurations to implement resilient networks.
Core infrastructure services, including DHCP, DNS, and NAT, are essential for operational stability. Candidates should understand how to configure these services to ensure devices obtain proper addressing and maintain connectivity across multiple network segments. Additionally, implementing Quality of Service (QoS) strategies ensures that latency-sensitive applications, such as voice and video, receive the necessary bandwidth and priority. Candidates must understand classification, marking, shaping, and policing of traffic to maintain consistent performance.
Security Implementation in Data Centers
Security in data center environments requires multi-layered approaches. VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and port security isolate sensitive resources and restrict unauthorized access. Authentication protocols such as 802.1x prevent unverified devices from joining the network, reducing the risk of intrusion.
Candidates must evaluate the impact of security configurations on network performance, ensuring that measures do not introduce bottlenecks or compromise redundancy. Monitoring tools like SNMP and syslog provide insights into network activity, allowing administrators to detect and respond to threats proactively. Understanding the integration of security into overall network design ensures that protection is consistent and effective without compromising operational efficiency.
Virtualization and Overlay Networking
Virtualization has reshaped data center architecture, requiring candidates to understand how virtual networks interact with physical infrastructure. Virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlays such as VXLAN extend Layer 2 networks over Layer 3 infrastructure, enabling scalable and flexible network designs.
Candidates should know how to configure virtual interfaces, monitor traffic between virtual and physical networks, and ensure isolation between tenants or applications sharing the same infrastructure. Coordinating virtual and physical resources is essential for anticipating performance bottlenecks, planning redundancy, and maintaining consistent QoS policies. Practical labs in virtualized environments reinforce theoretical knowledge and prepare candidates for both exam scenarios and professional responsibilities.
Network Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Effective troubleshooting combines systematic methodology with analytical tools. Candidates must start with physical layer verification, progress through Layer 2 and Layer 3 analysis, and evaluate application-level connectivity issues. Tools such as ping, traceroute, and interface statistics are crucial for isolating faults and verifying network behavior.
Proactive monitoring is equally important, using SNMP, syslog, and telemetry to maintain insight into performance and resource utilization. Candidates should practice interpreting monitoring data, validating configuration changes, and testing failover scenarios to ensure stability under various conditions. A disciplined approach to troubleshooting and performance monitoring prepares candidates for both the exam and operational challenges in real-world data centers.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Readiness
The 200-155 exam requires the integration of multiple networking concepts, from switching and routing to virtualization, security, and high availability. Candidates must develop the ability to analyze, configure, and troubleshoot networks holistically. Hands-on labs and simulated scenarios help reinforce these concepts, allowing candidates to apply knowledge in realistic environments.
Repeated practice ensures that candidates gain confidence in network configuration, problem-solving, and performance optimization. A thorough understanding of design principles, operational procedures, and troubleshooting methodologies equips candidates to manage complex data center networks efficiently, making them capable of handling large-scale infrastructures and critical workloads.
Effective Study and Practice Techniques
Strategic preparation for the 200-155 exam involves a balance of theory, configuration practice, and scenario analysis. Candidates should allocate time to study core principles, practice device configurations, and simulate troubleshooting scenarios. Reviewing and reinforcing knowledge in areas such as VLAN design, routing protocols, WAN connectivity, and virtual overlays is essential for ensuring comprehensive readiness.
Lab exercises allow candidates to experiment with multiple configurations, verify network behavior, and develop problem-solving skills. By combining structured study, hands-on experience, and scenario-based learning, candidates build confidence and gain the practical expertise required for both exam success and professional competence in data center networking.
Advanced Traffic Management and QoS
Data center networks often carry a mix of latency-sensitive and high-volume traffic. Candidates must understand traffic classification, prioritization, and resource allocation to ensure optimal performance. Implementing QoS strategies, including marking, shaping, and policing, allows critical applications like video, voice, and storage traffic to maintain consistent performance even under heavy load.
Analyzing traffic patterns and implementing appropriate policies enables candidates to maintain low latency, high throughput, and balanced network utilization. These skills are essential for the 200-155 exam, as they reflect the ability to design networks that are not only functional but also performant and reliable in demanding environments.
Advanced Routing and Protocol Interactions
Data center networks often utilize multiple routing protocols simultaneously. Candidates must understand interactions between OSPF, EIGRP, and static routes, as well as techniques for route redistribution and filtering. Analyzing routing tables and implementing optimal routing strategies ensures efficient traffic flow and reduces the potential for routing loops.
Candidates should practice configuring multi-protocol environments, understanding route preferences, and troubleshooting convergence issues. Mastery of these concepts ensures that data center networks are scalable, redundant, and capable of adapting to changing topologies without compromising performance or reliability.
Success in the 200-155 exam requires an integrated understanding of switching, routing, virtualization, WAN connectivity, security, and QoS in data center environments. Candidates must combine theoretical knowledge with practical experience, practicing configuration, troubleshooting, and monitoring in realistic scenarios.
A disciplined study approach, consistent lab exercises, and scenario-based problem solving equip candidates with the skills needed to manage complex data center networks. Mastery of these concepts ensures exam readiness while providing the practical expertise necessary to operate, optimize, and secure high-density data center environments effectively.
Virtualization and Overlay Networking
Data center networks increasingly rely on virtualization to maximize resource utilization and flexibility. Understanding how virtual switches, distributed virtual interfaces, and overlays interact with physical network infrastructure is essential for 200-155 exam candidates. Virtualization allows multiple virtual networks to operate on the same physical hardware while maintaining isolation between tenants or applications. Candidates should be familiar with configuring virtual network interfaces, implementing VLAN tagging, and using overlays such as VXLAN to extend Layer 2 connectivity across Layer 3 domains.
Overlay networks provide scalability and mobility by decoupling virtual network traffic from the underlying physical topology. Candidates need to understand how to map virtual networks to physical resources, ensuring performance and redundancy. Managing the interaction between virtual and physical network components helps anticipate bottlenecks, optimize traffic flows, and maintain consistent QoS policies. Hands-on practice in virtualized lab environments reinforces these concepts, allowing candidates to test configurations, monitor performance, and troubleshoot potential issues.
Multi-Site Redundancy and High Availability
Ensuring high availability in multi-site data centers is a critical aspect of network design. Candidates must understand the principles of redundancy at multiple levels, including device, link, and site redundancy. Protocols such as HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP provide gateway failover, enabling continuous access for users even during router outages. Candidates should be able to configure these protocols, adjust priorities, and test failover behavior to ensure seamless network operation.
Beyond gateway redundancy, candidates must grasp the design of resilient WAN connectivity between sites. Point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, and full-mesh topologies have distinct implications for scalability, fault tolerance, and performance. Dual-homed connections and redundant WAN links provide additional protection against failures. Understanding these strategies allows candidates to design networks capable of maintaining service continuity during link or device failures.
Advanced QoS Implementation
Data centers often carry a mix of latency-sensitive and high-volume traffic, making advanced QoS strategies essential. Candidates should understand traffic classification, marking, shaping, and policing to ensure that critical applications, such as storage replication, voice, and video, receive sufficient resources. Implementing end-to-end QoS policies requires awareness of traffic flow across multiple network segments, including physical and virtual devices.
Candidates must also be familiar with hierarchical QoS configurations, which allow administrators to apply policies at various levels, from individual interfaces to aggregate traffic classes. Monitoring and verifying QoS behavior through traffic analysis ensures that policies achieve the intended results, maintaining consistent performance under variable loads. Practical exercises in configuring, testing, and troubleshooting QoS policies reinforce these essential skills.
Security and Access Controls in Complex Environments
Security in data center networks requires both proactive and reactive measures to protect critical assets. Candidates should understand VLAN segmentation, ACLs, port security, and 802.1x authentication to prevent unauthorized access and isolate sensitive traffic. These mechanisms must be deployed without creating performance bottlenecks or single points of failure.
Monitoring and logging are essential for maintaining security and operational awareness. Collecting SNMP and syslog data allows administrators to detect anomalies, investigate potential threats, and respond promptly. Candidates should practice analyzing log files, verifying configuration changes, and implementing policies that balance security with operational efficiency. Integrating security into overall network design ensures comprehensive protection across all layers.
Advanced Routing Scenarios
Candidates preparing for the 200-155 exam should be proficient in complex routing scenarios that go beyond basic connectivity. Configuring and troubleshooting OSPF and EIGRP in multi-area or multi-AS environments is a key requirement. Candidates must understand route summarization, redistribution, and filtering techniques to control traffic flow and prevent routing loops.
Analyzing routing tables, monitoring protocol convergence, and testing failover scenarios are essential for validating network behavior. Candidates should be able to troubleshoot inconsistencies, resolve unreachable networks, and optimize route paths for efficiency and redundancy. This ensures that data center traffic moves reliably across multiple subnets and sites.
Monitoring, Troubleshooting, and Performance Optimization
Effective monitoring and troubleshooting are critical skills for data center network management. Candidates should develop systematic approaches to identify issues, starting with physical connectivity checks and progressing through Layer 2 and Layer 3 analysis. Tools such as ping, traceroute, interface statistics, and log analysis are essential for isolating and resolving problems.
Proactive monitoring allows administrators to detect potential issues before they impact operations. Utilizing SNMP, syslog, and telemetry data helps track performance, resource utilization, and anomalous activity. Candidates should practice interpreting these data sources, verifying configurations, and testing failover procedures to ensure resilience. Combining troubleshooting expertise with monitoring ensures network stability and reliability in high-density environments.
Integrating Knowledge for Practical Scenarios
Success in the 200-155 exam relies on integrating multiple areas of data center networking. Candidates must combine knowledge of advanced switching, routing, security, virtualization, WAN connectivity, and QoS to solve practical network scenarios. Simulated lab exercises reinforce understanding by allowing candidates to apply theoretical concepts in real-world configurations.
Practicing complex scenarios, such as configuring multi-site redundancy, implementing overlay networks, and testing failover mechanisms, builds confidence and prepares candidates for both the exam and professional responsibilities. Repeated practice in lab environments strengthens problem-solving abilities and ensures that candidates can manage large-scale data center networks efficiently.
Design and Operational Best Practices
Candidates should be familiar with best practices for designing and operating data center networks. Proper network segmentation, redundancy planning, and protocol selection are critical for achieving performance, scalability, and reliability. Effective documentation, configuration management, and operational procedures contribute to a network that can adapt to changing demands without compromising service.
Practical exercises in implementing these best practices help candidates internalize the principles of effective design and operational management. By understanding both theoretical concepts and their application, candidates develop the ability to design, maintain, and optimize data center networks for long-term success.
Mastery of the 200-155 exam content requires a comprehensive understanding of data center networking, including advanced switching, routing, virtualization, WAN connectivity, QoS, security, and high availability. Candidates must combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice, focusing on configuration, troubleshooting, monitoring, and optimization.
Structured study, practical labs, and scenario-based exercises ensure readiness for the exam while preparing candidates for real-world challenges. Integrating multiple networking concepts, testing failover and redundancy, and verifying performance builds the expertise necessary to manage complex data center networks effectively. Success in the 200-155 exam demonstrates proficiency in both fundamental and advanced data center networking skills, establishing a foundation for career growth and operational excellence.
Advanced Switching and Routing Concepts
Data center networks require a deep understanding of advanced switching techniques to optimize performance and ensure reliability. Candidates preparing for the 200-155 exam should focus on VLAN configuration, trunking, and spanning tree protocols to maintain loop-free environments while supporting high availability. VLANs allow segmentation of traffic, reducing broadcast domains and improving security and performance. Trunking methods, including 802.1Q encapsulation, are essential for carrying multiple VLANs across a single link, and candidates must understand how to configure and troubleshoot these trunks.
Spanning tree protocols, such as Rapid PVST+ and MST, provide network redundancy while preventing loops. Candidates should study root bridge election, path cost calculation, and understand the purpose of features like PortFast, BPDU Guard, and BPDU Filter in maintaining a stable network. EtherChannel aggregation techniques, including static, LACP, and PAGP, offer both increased bandwidth and redundancy, and proficiency in configuring and troubleshooting these channels is crucial for exam success and practical data center operations.
Layer 3 routing is equally critical, as data centers often contain multiple subnets and complex topologies. Candidates must understand the differences between distance vector and link-state protocols and be able to configure and troubleshoot dynamic routing using OSPF and EIGRP. Knowledge of OSPF areas, route summarization, redistribution, and the application of passive interfaces allows for optimized routing and traffic control. EIGRP configuration for both IPv4 and IPv6 networks is a key skill, ensuring efficient path selection and quick convergence in response to network changes.
WAN Connectivity and Network Extensibility
Data centers often span multiple locations, making WAN technologies a crucial component of the 200-155 exam objectives. Candidates must understand point-to-point connections, WAN topologies, and tunneling protocols. Protocols like PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE are used for establishing connections with authentication and encapsulation. GRE tunnels provide virtual point-to-point links over IP networks, supporting flexible and scalable designs.
Understanding WAN topologies, such as hub-and-spoke, point-to-point, and full-mesh, is essential for designing networks that balance redundancy, performance, and scalability. Single and dual-homed configurations provide insight into fault-tolerant designs that maintain connectivity under failure conditions. Hands-on experience in configuring WAN links, verifying tunnel connectivity, and troubleshooting issues prepares candidates for real-world data center operations and ensures readiness for the exam.
Infrastructure Services and High Availability
High availability is a central concern in data center networking. Candidates must understand protocols like HSRP for default gateway redundancy, including priority, preemption, and version settings. Knowledge of DHCP, DNS, and NAT services ensures proper addressing and communication across networks. Implementing these services requires understanding their impact on network design, redundancy, and performance.
Quality of Service is another important aspect of infrastructure management. Candidates should be familiar with traffic classification, marking, shaping, policing, and prioritization strategies. Ensuring that latency-sensitive applications, such as voice or storage replication, receive appropriate resources is essential for maintaining performance standards. Practical experience in implementing QoS policies and monitoring traffic flows is critical for confirming that network policies are effective.
Security and Access Management
Securing a data center network involves a combination of proactive and reactive measures. VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and port security help control access and protect sensitive traffic. Candidates should understand authentication mechanisms such as 802.1x and their role in limiting network access to authorized devices. Configuring these features without creating performance bottlenecks or single points of failure is a key skill assessed in the exam.
Monitoring and logging support both security and operational awareness. Collecting and analyzing SNMP, syslog, and telemetry data allows administrators to identify unusual activity and respond quickly to potential threats. Candidates should practice interpreting logs, verifying configurations, and integrating security measures into network design to maintain consistent protection while ensuring operational efficiency.
Virtualization and Overlay Networks
Virtualization is a cornerstone of modern data center design, and candidates must understand how virtual networks interact with physical infrastructure. Virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlay protocols such as VXLAN extend Layer 2 connectivity over Layer 3 networks, enabling flexible and scalable network designs. Candidates must be able to configure virtual interfaces, monitor traffic, and ensure isolation between applications or tenants while sharing underlying resources.
Understanding the coordination between virtual and physical components is essential to prevent bottlenecks, plan for redundancy, and enforce consistent QoS policies. Hands-on practice in virtualized labs strengthens these skills, allowing candidates to simulate real-world scenarios and ensure reliable traffic flow between virtualized workloads and physical network devices.
Troubleshooting and Performance Management
Effective troubleshooting is critical for maintaining data center network reliability. Candidates must develop systematic approaches to identify and resolve issues, starting with physical connectivity checks and progressing through Layer 2 and Layer 3 analysis to application-level considerations. Using diagnostic tools such as ping, traceroute, and interface statistics is essential for isolating problems efficiently.
Proactive performance monitoring is equally important. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry provide continuous visibility into network health, resource utilization, and potential failures. Candidates should practice analyzing monitoring data, verifying configuration changes, and testing failover scenarios to ensure operational stability. Combining troubleshooting with proactive monitoring equips candidates to maintain high levels of network availability in complex environments.
Integration of Core Concepts
The 200-155 exam evaluates candidates on their ability to integrate knowledge across multiple domains, including advanced switching, routing, security, WAN connectivity, virtualization, QoS, and high availability. Mastery of these concepts enables professionals to design, configure, and manage data center networks efficiently. Practical labs and scenario-based exercises are invaluable for reinforcing theoretical knowledge and building confidence in applying these skills under real-world conditions.
Repeated practice in designing and configuring network solutions, implementing redundancy, and verifying performance strengthens problem-solving abilities. Candidates who develop a holistic understanding of data center networking principles can anticipate challenges, optimize network performance, and maintain robust operations. Success in the exam demonstrates readiness for professional responsibilities and positions individuals for career advancement in data center networking.
Design and Operational Best Practices
Data center networks demand careful planning and operational discipline. Candidates should focus on best practices, including segmentation, redundancy planning, protocol selection, and configuration management. Proper design ensures scalability, high availability, and optimal performance, while operational procedures such as documentation, change management, and monitoring ensure the network can adapt to evolving requirements.
Hands-on experience with these best practices allows candidates to internalize the principles of effective design and operation. Understanding both theoretical and practical aspects equips professionals to manage complex environments, troubleshoot efficiently, and maintain service continuity while optimizing network resources.
Mastering the 200-155 exam requires a deep understanding of data center networking, encompassing advanced switching and routing, virtualization, security, WAN connectivity, QoS, and high availability. Candidates must integrate theoretical knowledge with practical exercises, focusing on configuration, troubleshooting, monitoring, and optimization.
Structured preparation, lab practice, and scenario-based learning ensure candidates are ready for the exam and real-world network operations. Integrating multiple concepts, testing redundancy, and validating network performance cultivates the skills necessary to manage complex data center networks successfully. Achieving certification confirms proficiency in foundational and advanced data center networking principles and provides a solid foundation for career growth and operational excellence.
Core Switching Techniques
Data center networks rely heavily on advanced switching features to maintain performance and stability. Candidates preparing for the 200-155 exam must understand VLAN segmentation, which allows the creation of separate broadcast domains to improve traffic management and enhance security. Trunking is a critical component that enables multiple VLANs to traverse a single physical link, and knowledge of 802.1Q encapsulation is necessary for proper configuration and troubleshooting.
Spanning tree protocols, including Rapid PVST+ and MST, are crucial for maintaining loop-free topologies while providing redundancy. Exam candidates should understand root bridge selection, path cost calculation, and the function of features like PortFast, BPDU Guard, and BPDU Filter in supporting network stability. EtherChannel configurations provide both increased bandwidth and redundancy, and candidates must be able to configure static, LACP, and PAGP channels while identifying and resolving potential issues.
Layer 3 Routing Essentials
Routing in data center environments ensures efficient traffic flow across complex networks with multiple subnets. Candidates should be able to distinguish between distance vector and link-state protocols and configure dynamic routing using OSPF and EIGRP. Understanding OSPF area design, route summarization, and the behavior of EIGRP for both IPv4 and IPv6 networks is essential for exam preparation.
Analyzing routing tables, troubleshooting route propagation, and implementing route redistribution or passive interfaces are key skills. Effective routing strategies ensure minimal latency, high availability, and optimized use of network resources. Candidates should practice both theoretical configuration and hands-on troubleshooting to solidify these skills.
WAN Connectivity and Tunneling
Data centers often connect across multiple sites, requiring candidates to understand WAN technologies and tunneling protocols. Point-to-point connections, including PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE, provide encapsulation and authentication, while GRE tunnels allow virtual point-to-point connections across IP networks.
Familiarity with WAN topologies, such as point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, and full-mesh, helps in designing scalable and redundant networks. Candidates should understand dual-homed and single-homed configurations, ensuring network continuity under failure conditions. Practical exercises in configuring WAN links, verifying tunnel connectivity, and troubleshooting WAN issues are essential for reinforcing these concepts.
Infrastructure Services and Redundancy
High availability is a central theme in data center design. Candidates must understand protocols like HSRP for gateway redundancy, including priority, preemption, and version settings. Understanding the interaction of DHCP, DNS, and NAT within the network ensures devices communicate effectively and reliably across different segments.
Quality of Service is also critical in prioritizing traffic for latency-sensitive applications such as voice and storage replication. Candidates need to know traffic classification, marking, shaping, policing, and prioritization techniques. Hands-on experience in configuring and monitoring QoS policies ensures that theoretical knowledge is applied correctly and that network performance meets operational requirements.
Security and Network Access Control
Securing a data center network involves implementing VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and port security to isolate sensitive traffic and protect critical resources. Authentication mechanisms such as 802.1x enforce access control by permitting only authorized devices to connect. Candidates should understand the trade-offs between security measures and network performance, ensuring that protection does not create bottlenecks or single points of failure.
Monitoring and logging are crucial for identifying unusual activity and potential security threats. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry data allow administrators to analyze network behavior proactively. Candidates should practice reviewing logs, verifying security settings, and integrating security principles into overall network design to maintain operational efficiency while safeguarding resources.
Virtualization and Overlay Networks
Virtualized environments introduce new challenges in data center networking. Candidates must understand the integration of virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlay networks such as VXLAN to extend Layer 2 connectivity over Layer 3 networks. Configuring virtual interfaces, monitoring traffic, and ensuring tenant or application isolation are critical skills.
Understanding the interaction between virtual and physical network components helps prevent performance bottlenecks and ensures consistent quality of service. Candidates should practice in virtual labs to simulate real-world scenarios, reinforce configuration skills, and prepare for the practical aspects of the exam.
Troubleshooting and Performance Monitoring
Troubleshooting is a key skill assessed by the 200-155 exam. Candidates should develop a systematic approach, starting with physical connectivity, progressing through Layer 2 and Layer 3 configuration checks, and extending to application-level analysis. Tools like ping, traceroute, and interface statistics are essential for diagnosing and resolving network issues.
Proactive monitoring ensures potential problems are identified early. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry provide continuous visibility into network health and utilization. Candidates should practice interpreting monitoring data, validating configuration changes, and testing failover scenarios to ensure network stability under different conditions.
Integration of Knowledge
The 200-155 exam evaluates the ability to integrate knowledge across multiple areas of data center networking. Candidates must be proficient in switching, routing, security, WAN connectivity, virtualization, QoS, and high availability. Understanding how these areas interact allows for efficient network design, configuration, and troubleshooting.
Simulated lab exercises and scenario-based practices help candidates apply theoretical knowledge practically. Repeated hands-on practice reinforces learning, builds confidence, and prepares candidates for both the exam and professional network operations. Mastery of these skills enables effective management of complex data center networks and ensures readiness for real-world responsibilities.
Design Principles and Operational Best Practices
Design and operational principles in data centers focus on scalability, redundancy, and performance optimization. Candidates should understand segmentation strategies, redundancy planning, protocol selection, and configuration management. Following best practices in documentation, monitoring, and change management ensures the network can adapt to evolving requirements while maintaining stability.
Hands-on experience and repeated practice in configuring network components, validating redundancy, and monitoring performance strengthen practical understanding. Candidates who master both theoretical and practical aspects are well-prepared to maintain high-performing, reliable data center networks.
Preparing for the Exam
Success in the 200-155 exam requires combining conceptual knowledge with practical experience. Candidates should allocate time for lab practice, scenario-based exercises, and review of configuration examples. Emphasis on redundancy, security, and troubleshooting ensures readiness for both the exam and operational responsibilities.
Understanding the interactions between switching, routing, virtualization, WAN connectivity, and network services equips candidates to anticipate and solve real-world network challenges. Preparing in this structured manner cultivates the skills necessary for professional growth and effective management of complex data center environments.
The 200-155 exam assesses a candidate’s ability to design, configure, and maintain robust data center networks. Proficiency in advanced switching and routing, WAN technologies, virtualization, QoS, security, and redundancy is essential. Combining theoretical study with practical exercises and monitoring techniques ensures candidates can manage complex networks effectively. Mastering these concepts prepares professionals for the certification and equips them to handle real-world data center operations with confidence, efficiency, and reliability.
Core Switching and Layer 2 Technologies
A strong grasp of core switching technologies is essential for the 200-155 exam. Candidates must understand VLAN creation and management, which allows logical separation of traffic to reduce broadcast domains and improve security. Configuring trunk links is another critical skill, as it enables multiple VLANs to traverse a single physical connection. Mastery of 802.1Q encapsulation and proper identification of native VLANs ensures effective VLAN communication across switches.
Spanning tree protocols like Rapid PVST+ and MST are crucial for maintaining loop-free topologies while providing redundancy. Candidates should understand root bridge election, path cost calculations, and the roles of PortFast, BPDU Guard, and BPDU Filter. Proper configuration of these features ensures network stability and prevents downtime. EtherChannel aggregation, including static, LACP, and PAGP modes, increases bandwidth while providing redundancy. Configuring, verifying, and troubleshooting EtherChannel links is essential for building resilient data center networks.
Layer 3 Routing Concepts
Routing in data centers is not just about connectivity; it is about efficient traffic flow and rapid convergence. Candidates should differentiate between distance vector and link-state protocols, and configure dynamic routing with OSPF and EIGRP. Understanding OSPF area types, route summarization, and EIGRP behavior for both IPv4 and IPv6 is key.
Analyzing routing tables, troubleshooting routing issues, and implementing route redistribution, passive interfaces, and route filtering are vital skills. Efficient routing ensures minimal latency, high availability, and optimized traffic paths. Candidates benefit from hands-on practice in configuring routing protocols, verifying convergence, and resolving conflicts in multi-protocol environments.
WAN Technologies and Tunneling
Data center networks often extend to multiple sites, requiring knowledge of WAN technologies and tunneling protocols. Point-to-point connections, such as PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE, provide encapsulation, authentication, and aggregation options. GRE tunnels allow virtual point-to-point connections over IP networks, enabling flexible network designs.
Candidates should understand WAN topologies, including point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, and full-mesh, and the impact of each on redundancy, scalability, and performance. Familiarity with dual-homed and single-homed configurations is crucial for designing fault-tolerant networks. Practical exercises in WAN link configuration, tunnel verification, and troubleshooting help reinforce these concepts and prepare candidates for real-world deployments.
High Availability and Infrastructure Services
Ensuring high availability in data centers involves multiple mechanisms. Protocols like HSRP provide redundancy for default gateways, with configurations for priority, preemption, and versioning. Understanding HSRP behavior and failover scenarios ensures uninterrupted connectivity. Infrastructure services such as DHCP, DNS, and NAT support communication across network segments, ensuring that devices receive proper addressing and routing.
Quality of Service is essential for prioritizing critical traffic like voice, video, and storage replication. Candidates must understand classification, marking, shaping, policing, and queuing techniques. Hands-on experience in configuring QoS policies and verifying traffic flow ensures that resources are allocated efficiently while maintaining application performance.
Security Principles and Access Control
Securing data center networks requires implementing proactive measures to protect resources and isolate traffic. VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and port security are fundamental components. Authentication methods like 802.1x restrict network access to authorized devices, enhancing overall security. Candidates must balance security measures with network performance, ensuring that protections do not create bottlenecks or single points of failure.
Monitoring and logging are vital for detecting anomalies and potential threats. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry data provide insights into network behavior. Candidates should practice analyzing logs, verifying access control policies, and integrating security into overall network design to maintain both security and operational efficiency.
Virtualization and Overlay Networks
Virtualization adds complexity to data center networks, requiring an understanding of virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlay technologies such as VXLAN. These mechanisms extend Layer 2 connectivity across Layer 3 networks, supporting scalability and multi-tenant isolation. Candidates must understand virtual interface configuration, traffic monitoring, and isolation strategies to maintain network integrity.
The interaction between virtual and physical network components affects performance and reliability. Understanding these interactions helps prevent bottlenecks, plan for redundancy, and enforce consistent QoS policies. Lab practice in virtualized environments allows candidates to experience realistic scenarios, reinforcing theoretical concepts and practical skills.
Troubleshooting and Performance Monitoring
Effective troubleshooting is a core competency tested in the 200-155 exam. Candidates should adopt a structured approach, beginning with physical connectivity, moving to Layer 2 and Layer 3 configurations, and extending to application-level issues. Tools such as ping, traceroute, and interface counters are essential for diagnosing and resolving problems.
Proactive performance monitoring is equally important. SNMP, syslog, and telemetry provide ongoing visibility into network health. Candidates should practice interpreting monitoring data, validating configuration changes, and testing failover scenarios. This approach ensures that networks remain operational, resilient, and efficient under varying conditions.
Integration and Practical Application
The 200-155 exam evaluates the ability to integrate multiple networking domains into a cohesive operational skill set. Mastery of switching, routing, WAN technologies, virtualization, QoS, security, and high availability allows candidates to design, configure, and maintain complex data center networks.
Simulated lab exercises provide opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. Repetition of configuration tasks, troubleshooting exercises, and performance verification strengthens proficiency. This integrated practice builds confidence and prepares candidates for both the exam and real-world network management challenges.
Design Strategies and Operational Best Practices
Designing a data center network requires careful consideration of multiple factors to ensure that it meets the demands of high-density traffic, scalability, and operational efficiency. Candidates preparing for the 200-155 exam should understand how logical segmentation supports both performance and security. By dividing the network into well-defined segments using VLANs and routing domains, traffic can be managed more effectively, and potential congestion points can be minimized. Logical segmentation also enables isolation of sensitive workloads, improving security while allowing easier troubleshooting and management.
Redundancy planning is another critical aspect of data center design. High availability protocols such as HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP allow networks to maintain connectivity even when primary devices fail. Candidates should understand how to configure redundancy at multiple layers, including access, aggregation, and core layers, to prevent single points of failure. EtherChannel configurations, spanning tree enhancements, and dual-homed connections contribute to both resilience and increased bandwidth capacity, ensuring the network can adapt to failure scenarios without disruption to services.
Protocol selection plays a pivotal role in network efficiency and stability. Candidates should be familiar with both Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols, including spanning tree variants, OSPF, and EIGRP. Choosing the right protocol for a specific segment, understanding convergence behavior, and implementing route summarization and redistribution are essential for minimizing downtime and optimizing traffic flow. The integration of these protocols with VLAN configurations, trunking, and overlay technologies ensures a cohesive network that supports diverse workloads and applications.
Configuration management and operational consistency are key to maintaining reliable network performance. Adopting standardized configurations across devices reduces errors, simplifies troubleshooting, and ensures predictable behavior under load. Candidates should also practice verifying interface assignments, trunking parameters, and routing configurations to prevent misconfigurations that could lead to outages or degraded performance. Implementing monitoring systems using SNMP, syslog, and telemetry allows administrators to detect anomalies, measure utilization, and make informed decisions about network expansion or optimization.
Documentation is an essential component of operational best practices. Keeping detailed records of device configurations, VLAN assignments, IP addressing schemes, and redundancy mechanisms allows teams to troubleshoot issues efficiently and supports long-term network planning. Change management procedures further ensure that updates or modifications to the network do not introduce unintended disruptions. Candidates should understand how to implement structured change control processes, including testing, rollback plans, and impact analysis.
Hands-on experience reinforces theoretical knowledge and prepares candidates for practical challenges. Simulating network designs, testing failover scenarios, and monitoring traffic patterns provide insights into the operational dynamics of a data center. This practice helps candidates understand how different design decisions impact performance, redundancy, and security. It also develops critical problem-solving skills, enabling professionals to respond effectively to unexpected network events.
Scalability is another focus area in data center network design. Candidates should understand how to design networks that can grow seamlessly as workloads increase. Using hierarchical network designs, modular device deployment, and overlay technologies such as VXLAN allows data centers to accommodate new applications, tenants, or services without major redesign. Effective scalability planning ensures that performance remains consistent and that operational overhead does not escalate as the network expands.
Performance optimization involves analyzing traffic flows, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing policies that prioritize critical applications. Quality of Service configurations, traffic shaping, and load balancing help ensure that latency-sensitive workloads, such as voice, video, or real-time analytics, receive appropriate resources. Candidates should practice applying QoS policies across multiple layers and verifying their impact on traffic to confirm that performance objectives are met.
Operational excellence combines all these strategies—logical segmentation, redundancy, protocol selection, configuration management, documentation, monitoring, scalability, and performance optimization—into a cohesive framework for managing data center networks. Candidates who master these concepts are capable of designing networks that are resilient, secure, and high-performing, ensuring both exam readiness and practical competency in professional environments.
Integrating theoretical knowledge with practical exercises provides a well-rounded understanding of data center network operations. By focusing on both the design strategies and operational best practices, candidates develop the ability to maintain robust infrastructure, anticipate potential issues, and implement solutions that uphold network reliability and efficiency. Mastery of these areas prepares professionals to meet the rigorous demands of modern data center networks, enabling confident management of complex systems.
Exam Preparation and Skill Consolidation
Success in the 200-155 exam requires a structured preparation strategy. Candidates should dedicate time to lab practice, scenario-based exercises, and configuration reviews. Focus on redundancy, security, and troubleshooting ensures readiness for both exam challenges and real-world operations.
Understanding the interdependence of switching, routing, virtualization, WAN connectivity, and network services enables candidates to anticipate and resolve network issues effectively. Comprehensive preparation fosters the skills needed for certification success and equips professionals to handle complex data center networking environments confidently.
The 200-155 exam tests the ability to design, configure, and maintain high-performing data center networks. Proficiency in advanced switching, routing, WAN connectivity, virtualization, QoS, high availability, and security is essential. Combining theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice ensures candidates can manage complex networks effectively. Mastery of these skills prepares professionals for certification success and equips them to support real-world data center operations with efficiency, reliability, and resilience.
Advanced Layer 2 and Layer 3 Integration
Achieving proficiency in Layer 2 and Layer 3 integration is essential for candidates preparing for the 200-155 exam. Data center networks rely heavily on the interplay between these layers to provide efficient, scalable, and resilient connectivity. Layer 2 technologies, including VLANs, trunking, and spanning tree protocols, form the backbone of traffic segmentation and local network stability. Candidates need to understand how VLANs logically separate traffic to minimize broadcast domains and maintain network security. Proper configuration ensures that devices within the same VLAN can communicate seamlessly while preventing unnecessary traffic from flooding other segments.
Trunking protocols such as 802.1Q allow multiple VLANs to traverse a single physical link, which requires careful planning to ensure correct encapsulation and inter-VLAN communication. Misconfiguration in trunking can lead to traffic loss or misrouted packets, so candidates must verify trunk ports, VLAN assignments, and allowed VLAN ranges.
Layer 3 integration involves routing traffic between VLANs and across subnets. Static routes provide deterministic paths for critical traffic, while dynamic protocols like OSPF and EIGRP adjust automatically to network changes. Candidates should understand OSPF area design, route summarization, and redistribution between protocols to maintain optimal routing efficiency. Verification using routing tables and tools such as traceroute ensures that traffic flows along intended paths, and troubleshooting unreachable networks reinforces practical problem-solving skills. Combining Layer 2 and Layer 3 knowledge allows for a robust network where switches and routers operate cohesively, supporting both performance and security goals.
Redundancy Mechanisms and High Availability
High availability ensures that data center networks remain operational during device failures or link outages. Candidates must understand redundancy mechanisms and the protocols that support seamless failover. HSRP and VRRP allow multiple routers to provide a single virtual gateway IP, so when a primary device fails, traffic automatically reroutes to a backup. Configuring priorities, preemption, and timers is critical to ensure that failover happens predictably without disrupting active sessions.
EtherChannel combines multiple physical links into a single logical interface, offering both redundancy and increased bandwidth. Candidates should learn the differences between static, LACP, and PAGP configurations, as well as verification and troubleshooting methods. Spanning tree protocols, including Rapid PVST+ and MST, prevent loops while allowing redundant paths to remain available. Understanding root bridge selection, path cost calculation, and the impact of PortFast and BPDU Guard ensures that the network remains loop-free and converges quickly during topology changes. Mastery of these redundancy and high availability mechanisms is critical for maintaining uptime in complex environments.
WAN Connectivity and Tunneling Applications
Data centers often extend across multiple sites, requiring secure and efficient WAN connectivity. Candidates must understand WAN technologies, including PPP, MLPPP, and PPPoE, which support point-to-point links with options for authentication and traffic encapsulation. GRE tunnels provide virtual point-to-point connections over existing networks, enabling flexibility in design and connectivity.
Knowledge of WAN topologies—point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, and full-mesh—helps candidates design networks that balance scalability, redundancy, and performance. Single-homed and dual-homed connections provide insights into failover scenarios, allowing for continuous operation even when a primary link fails. Hands-on exercises in configuring WAN links, verifying tunnels, and troubleshooting connectivity issues are essential to solidify theoretical understanding and prepare for both exam scenarios and practical network deployments.
Security Strategies in Data Center Networks
Security is integral to protecting sensitive resources in a data center. Candidates should understand VLAN segmentation, ACL implementation, and port security as core methods to isolate traffic and prevent unauthorized access. Authentication mechanisms, such as 802.1x, ensure that only authorized devices connect to the network, reducing the risk of breaches.
Monitoring and logging using SNMP, syslog, and telemetry enable proactive detection of anomalies. Candidates should practice analyzing logs, implementing access controls, and applying security policies that do not compromise network performance. Integration of security into network design ensures a holistic approach, maintaining operational efficiency while protecting critical resources. Balancing performance with security is essential for ensuring uninterrupted access for legitimate users while mitigating threats effectively.
Virtualization and Overlay Networks
Virtualization has transformed data center architecture, making it essential for candidates to understand how virtual networks interact with physical infrastructure. Virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlay networks such as VXLAN extend Layer 2 connectivity over Layer 3, supporting scalability and multi-tenant isolation. Candidates must configure virtual interfaces, monitor traffic, and ensure isolation between tenants or applications while utilizing shared physical resources efficiently.
Understanding the coordination between virtual and physical network components allows candidates to optimize performance, plan for redundancy, and maintain consistent QoS policies. Hands-on practice in virtual environments strengthens theoretical knowledge and prepares candidates to troubleshoot overlay networks and virtualized workloads effectively. Mastery of virtualization concepts ensures that data center operations remain flexible, scalable, and reliable.
Infrastructure Services and Performance Optimization
Critical infrastructure services such as DHCP, DNS, NAT, and QoS ensure smooth data center operations. Candidates must configure these services to guarantee proper device addressing, seamless inter-segment communication, and traffic prioritization for latency-sensitive applications like voice and video. QoS implementation involves classification, marking, shaping, policing, and prioritization strategies to maintain predictable performance under varying loads.
Practical experience with infrastructure services reinforces theoretical knowledge and allows candidates to verify that policies achieve intended outcomes. Proper implementation ensures network reliability, efficiency, and resilience, while avoiding conflicts with redundancy or security measures. Candidates should practice configuring and monitoring these services to optimize performance and maintain operational integrity.
Troubleshooting and Monitoring
Troubleshooting is a vital skill for managing complex data center networks. Candidates should adopt a structured approach, beginning with physical layer verification, moving through Layer 2 and Layer 3 diagnostics, and examining application-level behavior. Tools such as ping, traceroute, and interface statistics provide essential insights into network health and connectivity.
Proactive monitoring using SNMP, syslog, and telemetry helps identify potential issues before they impact operations. Candidates should interpret monitoring data, verify configurations, and simulate failover scenarios to validate network stability. Combining troubleshooting with monitoring practices ensures that networks remain operational, resilient, and efficient under diverse conditions.
Exam Preparation and Practical Reinforcement
The 200-155 exam evaluates the integration of switching, routing, WAN connectivity, virtualization, infrastructure services, and security. Candidates should focus on understanding how these components interact and applying knowledge in practical scenarios. Simulated labs provide opportunities to configure, verify, and troubleshoot network elements, reinforcing theoretical concepts with hands-on experience.
Repeated practice builds confidence, deepens understanding, and prepares candidates for the complexity of the exam. Mastery of design principles, operational procedures, and troubleshooting strategies ensures readiness to manage real-world data center networks effectively.
Design Principles and Operational Excellence
Data center network design emphasizes scalability, redundancy, performance, and security. Candidates should understand logical segmentation, redundancy planning, protocol selection, and operational best practices. Proper documentation, monitoring, and change management support network evolution while maintaining stability.
Practical exercises in designing, configuring, and testing network components help candidates internalize these principles. Experience with failover scenarios, traffic prioritization, and security configurations ensures that networks remain resilient, efficient, and high-performing. Mastery of design and operational excellence equips candidates to manage data center environments confidently.
Success in the 200-155 exam requires a deep understanding of data center networking technologies, including Layer 2 and Layer 3 integration, redundancy, WAN connectivity, virtualization, security, infrastructure services, and high availability. Integrating theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice equips candidates to handle complex networks effectively. Mastery of these skills ensures exam readiness while preparing professionals to manage real-world data center operations with reliability, efficiency, and confidence.
Conclusion
Achieving proficiency in data center networking requires a thorough understanding of both the theoretical concepts and practical skills that underpin the operation of high-performance, resilient, and scalable networks. The 200-155 exam evaluates candidates on these critical competencies, emphasizing the ability to design, configure, and manage complex data center environments effectively. By mastering core networking principles, candidates demonstrate the ability to handle diverse challenges, from routing and switching integration to WAN connectivity, virtualization, security, and infrastructure services.
A strong foundation in Layer 2 and Layer 3 integration is essential for ensuring seamless communication across segmented networks. Candidates must understand how VLANs, trunking, and routing protocols interact to maintain predictable traffic flows and prevent network loops. The ability to configure inter-VLAN routing, implement static and dynamic routes, and verify protocol operations equips professionals to design networks that are both efficient and resilient. Integrating these skills with redundancy mechanisms such as HSRP, VRRP, EtherChannel, and spanning tree enhancements further strengthens network reliability and minimizes downtime, which is critical in high-density data center environments.
High availability and performance optimization go hand-in-hand in data center operations. Candidates should be adept at configuring redundancy at multiple layers, implementing failover strategies, and monitoring traffic to identify potential bottlenecks. QoS policies, traffic shaping, and prioritization techniques ensure that latency-sensitive applications, such as voice and video, maintain consistent performance. Practical experience in applying these measures allows candidates to anticipate operational challenges and respond proactively, ensuring uninterrupted service and high user satisfaction.
Security is a critical dimension of data center network management. Knowledge of VLAN segmentation, access control lists, port security, and authentication mechanisms ensures that sensitive traffic is isolated and protected. Monitoring and logging tools provide insight into network behavior, enabling timely detection and resolution of security threats. Candidates who can implement robust security strategies while maintaining network performance demonstrate a balanced approach to data center operations that meets both operational and compliance requirements.
Virtualization and overlay networks introduce additional complexity, requiring an understanding of how virtual and physical infrastructures interact. Configuring virtual switches, VLAN tagging, and overlay protocols such as VXLAN enables scalable and multi-tenant network designs. Candidates who can effectively manage virtualized environments, ensuring isolation, performance, and redundancy, are well-prepared to address the demands of modern data centers that rely heavily on virtualized workloads and dynamic resource allocation.
Design strategies and operational best practices form the backbone of efficient data center network management. Candidates should focus on logical segmentation, redundancy planning, protocol selection, configuration standardization, documentation, monitoring, and change management. Hands-on experience reinforces these concepts, providing the ability to test failover mechanisms, monitor performance metrics, and validate network configurations. A well-executed design combined with operational discipline ensures that data center networks remain resilient, scalable, and capable of supporting evolving business needs.
Ultimately, success in the 200-155 exam reflects a candidate’s ability to integrate a wide range of skills and knowledge areas. It confirms readiness to manage real-world data center networks with confidence, efficiency, and reliability. Mastery of the exam objectives not only provides certification but also equips professionals to address operational challenges, optimize network performance, implement secure and redundant designs, and support the dynamic demands of modern data center infrastructures. By combining theoretical understanding with practical expertise, candidates are positioned to excel in both the exam and their professional roles, contributing to the creation and maintenance of robust, high-performing data center environments.
Cisco CCNA Data Center 200-155 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 200-155 Introducing Cisco Data Center Technologies certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- 200-301 - Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- 350-401 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (ENCOR)
- 350-701 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies
- 300-410 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
- 300-715 - Implementing and Configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine (300-715 SISE)
- 350-801 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies (CLCOR)
- 350-601 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Data Center Core Technologies (DCCOR)
- 300-420 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD)
- 300-415 - Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Solutions (ENSDWI)
- 300-425 - Designing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-425 ENWLSD)
- 200-901 - DevNet Associate (DEVASC)
- 300-710 - Securing Networks with Cisco Firewalls
- 200-201 - Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS)
- 820-605 - Cisco Customer Success Manager (CSM)
- 350-901 - Developing Applications using Cisco Core Platforms and APIs (DEVCOR)
- 300-620 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (DCACI)
- 350-501 - Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR)
- 400-007 - Cisco Certified Design Expert
- 300-730 - Implementing Secure Solutions with Virtual Private Networks (SVPN 300-730)
- 300-430 - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Wireless Networks (300-430 ENWLSI)
- 500-220 - Cisco Meraki Solutions Specialist
- 300-435 - Automating Cisco Enterprise Solutions (ENAUTO)
- 300-810 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Applications (CLICA)
- 350-201 - Performing CyberOps Using Core Security Technologies (CBRCOR)
- 100-150 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking
- 300-820 - Implementing Cisco Collaboration Cloud and Edge Solutions
- 300-735 - Automating Cisco Security Solutions (SAUTO)
- 700-805 - Cisco Renewals Manager (CRM)
- 300-815 - Implementing Cisco Advanced Call Control and Mobility Services (CLASSM)
- 300-745 - Designing Cisco Security Infrastructure
- 300-610 - Designing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure for Traditional and AI Workloads
- 300-510 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions (SPRI)
- 300-440 - Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)
- 300-720 - Securing Email with Cisco Email Security Appliance (300-720 SESA)
- 300-835 - Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO)
- 300-910 - Implementing DevOps Solutions and Practices using Cisco Platforms (DEVOPS)
- 700-250 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Sales
- 300-725 - Securing the Web with Cisco Web Security Appliance (300-725 SWSA)
- 300-215 - Conducting Forensic Analysis and Incident Response Using Cisco CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR)
- 300-635 - Automating Cisco Data Center Solutions (DCAUTO)
- 500-442 - Administering Cisco Contact Center Enterprise
- 100-140 - Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) IT Support
- 300-445 - Designing and Implementing Enterprise Network Assurance
- 300-615 - Troubleshooting Cisco Data Center Infrastructure (DCIT)
- 300-630 - Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure - Advanced
- 500-560 - Cisco Networking: On-Premise and Cloud Solutions (OCSE)
- 500-444 - Cisco Contact Center Enterprise Implementation and Troubleshooting (CCEIT)
- 300-515 - Implementing Cisco Service Provider VPN Services (SPVI)
- 700-750 - Cisco Small and Medium Business Engineer
- 700-240 - Cisco Environmental Sustainability Overview
- 700-245 - Environmental Sustainability Practice-Building
- 700-150 - Introduction to Cisco Sales (ICS)
- 800-150 - Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians
- 100-490 - Cisco Certified Technician Routing & Switching (RSTECH)
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Cisco certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 200-155 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Cisco certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 200-155 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 200-155 preparation materials for the Cisco certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 200-155 materials for the Cisco certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 200-155 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Cisco certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 200-155. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 200-155 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 200-155 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Cisco certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 200-155 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 200-155 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

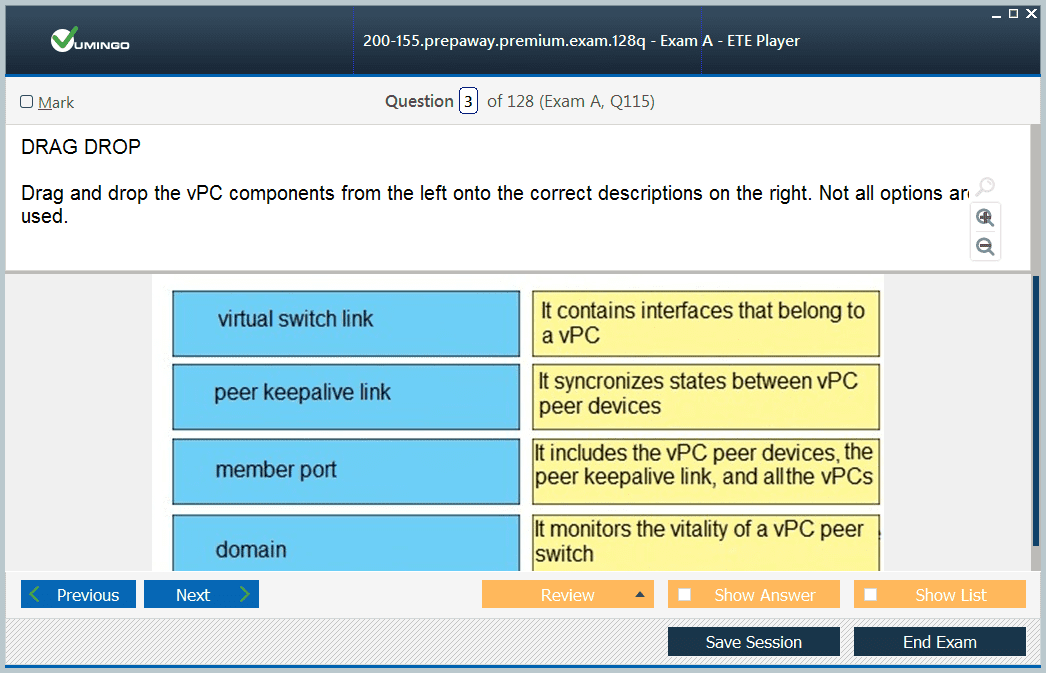
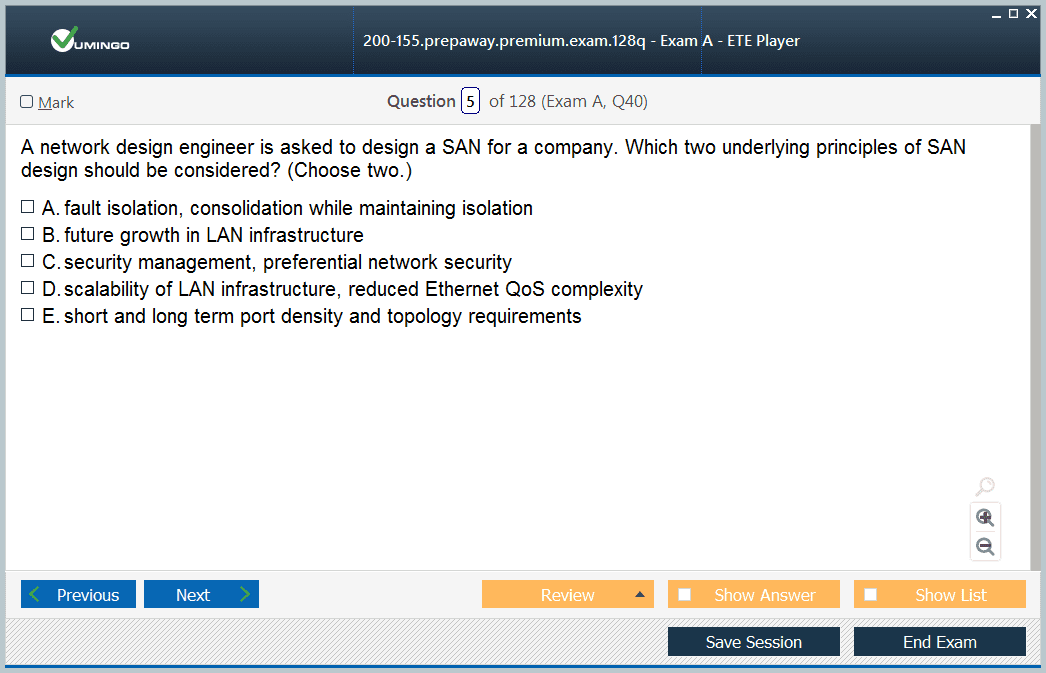
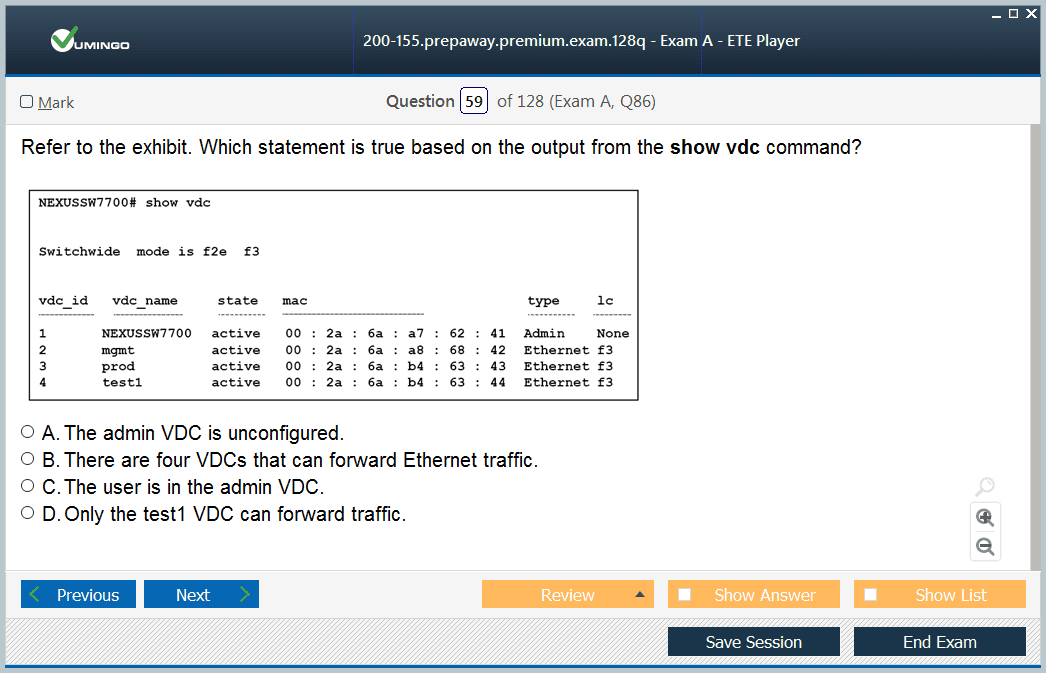





Anyone who can share the latest 200-155 dumps please. Thanks in advance.
Gize
Now looking forward for CCNP DC- 300-175
Question: What two Cisco Nexus Fabric Extenders support 10Gbps server connectivity?
Correct answer: 2232PP and 2248PQ
Wrong answer in ETE: 2148T and 2224TP
Anyone knows if latest dump is valid?
Thanks in advance,
Please I do really need valid dump for 200-155.
Can anyone share me ?
I will really appreciate so much.
BRs
Bon Nivath