DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Certification Video Training Course
The complete solution to prepare for for your exam with DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals certification video training course. The DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals certification video training course contains a complete set of videos that will provide you with thorough knowledge to understand the key concepts. Top notch prep including Microsoft Azure Data DP-900 exam dumps, study guide & practice test questions and answers.
DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Certification Video Training Course Exam Curriculum
Welcome to the DP-900 Azure Data Fundamentals course
-
3:00
1. Welcome to the course
-
3:00
2. DP-900 Exam Requirements
Core Concepts
-
6:00
1. Database Core Concepts
-
6:00
2. Chart Core Concepts
-
6:00
3. Analytics Techniques
-
3:00
4. ELT and ETL
-
4:00
5. Data Processing Core Concepts
Relational Database Concepts
-
7:00
1. Introduction to Relational DBs
-
7:00
2. Relational Data Structures
-
7:00
3. Azure Relational DB Options
Manage Relational Databases
-
7:00
1. Create an Azure SQL Database
-
4:00
2. Use ARM Templates to Manage SQL Databases
-
3:00
3. SQL Database Security
-
4:00
4. Relational Query Tools
-
3:00
5. Structured Query Language (SQL)
Non-Relational Database Concepts
-
5:00
1. Introduction to Non-Relational DBs
-
6:00
2. Non-Relational Data Types
-
6:00
3. Choose a NoSQL Database
-
5:00
4. Azure Non-Relational DB Options
Manage Non-Relational Databases
-
5:00
1. Create Cosmos DB
-
6:00
2. Query Cosmos DB
-
2:00
3. Use ARM Templates to Manage Cosmos DB
-
3:00
4. Cosmos DB Security
-
3:00
5. Cosmos DB Geo-Replication
Data Analytics Workloads
-
2:00
1. Data Analytics Workloads
-
3:00
2. OLTP
-
5:00
3. OLAP
-
6:00
4. Synapse Analytics SQL Data Warehouse
Data Ingestion and Processing
-
5:00
1. Modern Data Warehouse
-
5:00
2. Azure Data Factory
Data Visualization
-
5:00
1. Data Visualization
-
2:00
2. Power BI Content Workflow
About DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Certification Video Training Course
DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals certification video training course by prepaway along with practice test questions and answers, study guide and exam dumps provides the ultimate training package to help you pass.
DP-900 Azure Data Fundamentals: One-Day Exam Prep Guide
The DP-900 Azure Data Fundamentals certification is designed to provide learners with a foundational understanding of core data concepts within the Microsoft Azure ecosystem. This course is structured as a comprehensive training program that helps learners grasp the essential elements of modern data solutions while preparing them to succeed in the official Microsoft exam.
Why This Course Matters
Data is the foundation of digital transformation. Organizations depend on data to make decisions, improve customer experiences, and optimize operations. Azure has become one of the most trusted cloud platforms for managing, storing, analyzing, and securing data. This course will give you the skills to understand how data is managed in Azure, how databases are structured, and how analytics tools provide insights.
Purpose of the Training
The main purpose of this course is to simplify data fundamentals for learners who may or may not have a background in technology. It is meant to build confidence and provide clarity on the types of data, how they are stored, and how Azure services interact with them. The training follows the outline of the DP-900 exam but delivers the content in a way that is easy to digest and practical.
Course Goals
This training aims to ensure that by the end of the course, learners will have mastered the basics of relational and non-relational data, understood how Azure supports various storage solutions, and gained an introduction to analytics concepts. The goal is not just to pass the exam but also to help learners apply knowledge in real-world scenarios.
What You Will Learn
Learners will explore a wide range of topics that are central to the DP-900 exam. This includes the difference between structured and unstructured data, the fundamentals of relational databases, the role of big data, and how analytics enables business intelligence. Learners will also become familiar with Azure SQL, Cosmos DB, Synapse Analytics, and Azure Data Lake.
Course Modules
This training course is divided into five modules. Each module builds upon the previous one and allows learners to develop a strong foundation in Azure Data Fundamentals. The modules cover core data concepts, relational data, non-relational data, modern data analytics, and exam preparation strategies.
Training Approach
The approach used in this course is designed to simplify complex concepts. Each section begins with clear explanations followed by practical examples. Short scenarios are included to help learners understand how businesses use Azure data services in real life. Instead of long technical explanations, the content is broken into shorter sections with straightforward language.
Requirements for the Course
This course does not require deep technical expertise. Learners do not need prior experience in programming or cloud platforms. However, a general understanding of what data is, along with basic familiarity with technology, will be helpful. A willingness to learn and the ability to dedicate focused study time are the main requirements.
Who This Course is For
This course is designed for individuals who want to begin their journey into cloud-based data solutions. It is ideal for business users who want to understand how Azure manages data. It is also valuable for students considering a career in data, IT professionals who want to validate their fundamental skills, and decision-makers who need to understand the role of data in their organizations.
Course Description in Detail
The DP-900 Azure Data Fundamentals course provides a clear pathway into the world of data management on Microsoft Azure. It focuses on data principles that apply to both traditional and modern cloud environments. Learners will start by exploring what data is and how it is categorized. They will then examine relational databases, which are the backbone of many enterprise systems. Next, the course dives into non-relational data models such as key-value stores, graph databases, and document stores. Finally, the training examines analytics concepts and the power of visualization tools like Power BI.
Structure of the Training
Each module within this course has been carefully designed to balance theory with application. Learners will find real-world scenarios that connect data concepts to business outcomes. By progressing through the modules, learners will gradually move from simple foundational ideas to more advanced insights, preparing them for both the exam and professional applications.
Skills Gained from the Training
Completing this course will allow learners to explain fundamental data concepts confidently. They will understand the difference between transactional and analytical workloads. They will also know how Azure provides managed services for databases, data warehouses, and analytics. By gaining these skills, learners will be equipped to contribute to data projects within organizations.
Course Duration
This course is structured to be completed in a single day for learners who dedicate focused study time. However, the material is detailed enough to allow flexible pacing. Learners can choose to spend more time on specific modules if they require additional practice.
Value of Certification
Earning the DP-900 certification demonstrates a foundational understanding of Azure data services. This credential is recognized by employers and serves as a stepping stone to more advanced certifications such as Azure Data Engineer or Azure AI Engineer. It validates your ability to understand data principles and provides an advantage in pursuing careers in cloud and data technologies.
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this training, learners will be able to describe the types of core data workloads, identify key Azure data services, and explain the differences between relational and non-relational data. They will also have an understanding of the basics of analytics, visualization, and data security within Azure.
Preparing for Success
The DP-900 exam requires clear understanding rather than memorization. Learners should aim to understand why certain Azure services are used for specific workloads. This course prepares learners by providing conceptual clarity and practical examples that can be recalled during the exam.
Next Steps After the Course
Completing this training and earning the DP-900 certification opens doors to advanced learning. Learners may choose to progress to certifications such as DP-203 Data Engineering or DP-300 Database Administration. The DP-900 course creates the foundation upon which more specialized Azure certifications can be built.
Core Data Concepts Introduction
Understanding core data concepts is the first step in mastering the Azure Data Fundamentals certification. This section introduces the essential building blocks of data. It explains what data is, how it is categorized, and why it matters in the modern digital economy.
What is Data
Data is information in its rawest form. It can be numbers, text, images, or even sensor readings. In technology, data is the fuel that powers applications, analytics, and artificial intelligence. Without data, organizations cannot measure performance, understand customers, or make informed decisions.
Structured Data
Structured data refers to information organized in tables, rows, and columns. It is the type of data found in relational databases where each record follows a predefined schema. Examples include customer details, financial transactions, and product inventories. Structured data is easy to search and analyze because it is consistent.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is information that does not follow a fixed schema. It includes videos, emails, social media posts, and sensor logs. Unlike structured data, unstructured data is harder to process because it lacks consistency. However, unstructured data holds immense value for organizations seeking deeper insights.
Semi Structured Data
Semi structured data is information that sits between structured and unstructured formats. Examples include JSON files and XML documents. This type of data has some organizational elements but is flexible in structure. Semi structured data is often used in modern applications because it balances flexibility with organization.
Relational Data Fundamentals
Relational data is built on the concept of tables that are linked together by relationships. In relational databases, entities such as customers and orders are connected through keys. This model has been the foundation of business systems for decades. Relational data is best for transactional systems where accuracy and consistency are essential.
Non Relational Data Fundamentals
Non relational data is stored in systems that do not rely on tables. These databases include document stores, key value pairs, graph databases, and column family stores. They are more flexible than relational databases and can handle large volumes of unstructured data. Non relational data is widely used in applications requiring scalability and fast performance.
Transactional Workloads
Transactional workloads refer to systems that record and process day to day business transactions. These include banking systems, e commerce applications, and reservation platforms. The focus is on accuracy and reliability, ensuring that every transaction is captured correctly.
Analytical Workloads
Analytical workloads are designed for exploring data, identifying trends, and supporting decision making. They involve processing large volumes of historical data to produce insights. Analytical workloads are often used for business intelligence dashboards, forecasting, and advanced reporting.
Batch Processing
Batch processing involves handling large sets of data at once. It is commonly used for tasks like generating monthly reports or processing payroll. Batch processing is efficient for workloads that do not require immediate results but instead process data in scheduled intervals.
Stream Processing
Stream processing involves analyzing data as it arrives in real time. This is essential for applications like fraud detection, IoT monitoring, and live analytics. Azure services such as Stream Analytics allow organizations to react instantly to changes by analyzing continuous streams of incoming data.
The Role of Cloud in Data Management
The cloud has revolutionized the way data is stored, managed, and analyzed. Instead of relying solely on on premise systems, organizations can use cloud platforms like Azure to access scalable and secure services. Cloud data services reduce infrastructure costs and provide advanced capabilities without requiring specialized hardware.
Benefits of Cloud Data Solutions
Cloud based data solutions offer several advantages. They provide scalability, meaning storage and computing power can grow as needed. They ensure reliability with built in redundancy. They also provide security through compliance with global standards. For learners preparing for the DP 900 exam, it is important to recognize how these benefits make Azure an attractive platform for organizations.
Azure Data Services Overview
Microsoft Azure offers a wide range of services that handle data storage, processing, and analytics. These services are designed to meet the needs of different workloads. Some services focus on relational data while others handle non relational or analytical tasks. Understanding which service to use in a given scenario is a key part of exam preparation.
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service. It provides high availability, security, and performance without requiring administrators to manage physical servers. Azure SQL is widely used in enterprise applications and is often the first relational database introduced to learners in this course.
Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed non relational database service. It supports multiple models such as key value, document, graph, and column family. Cosmos DB is highly scalable and ensures low latency across different regions. It is a powerful service for applications that require high performance at a global scale.
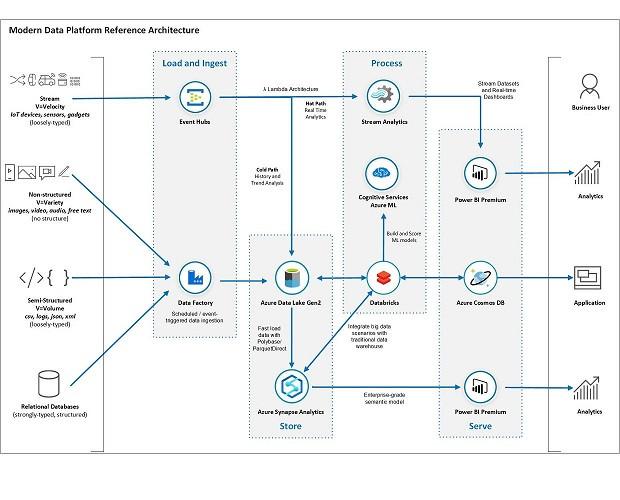
Azure Data Lake
Azure Data Lake is a storage solution designed for big data analytics. It allows organizations to store massive amounts of structured, semi structured, and unstructured data. Data Lake is optimized for parallel processing, making it ideal for scenarios where large data sets must be analyzed.
Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics is an enterprise level service that combines big data and data warehousing. It allows users to analyze structured and unstructured data together. Synapse supports powerful queries and integrates with visualization tools like Power BI. It is an essential tool for building modern analytical solutions.
Power BI
Power BI is a business intelligence platform that allows users to create interactive reports and dashboards. It connects to a wide variety of data sources including Azure services. Power BI enables organizations to transform raw data into meaningful insights that support decision making.
Data Security in Azure
Data security is a major concern for organizations, and Azure addresses this with multiple layers of protection. Security features include encryption, access control, and compliance certifications. Learners must understand how Azure services ensure that sensitive information remains protected.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Compliance with industry standards is another important part of data management. Azure supports compliance with global regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Organizations can trust Azure to meet strict requirements while still benefiting from cloud scale solutions.
High Availability in Azure Data Solutions
High availability ensures that data systems remain operational even during failures. Azure provides features such as automatic backups, geo redundancy, and failover mechanisms. These features ensure business continuity and reliability.
Scalability in Azure Data Solutions
Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle increasing workloads. Azure data services scale automatically based on demand. This flexibility allows organizations to avoid overprovisioning and only pay for the resources they use.
Choosing Between Relational and Non Relational Solutions
One of the key skills in the DP 900 exam is deciding when to use relational versus non relational databases. Relational solutions are best for transactional systems where accuracy is critical. Non relational solutions are better for scenarios requiring flexibility and high performance at scale.
Real World Data Scenarios
Organizations often use a mix of relational and non relational data solutions. For example, an e commerce company may use relational databases for order transactions and a non relational database for storing customer reviews. Understanding these scenarios helps learners apply concepts in practical ways.
Introduction to Data Warehousing
A data warehouse is a system used for storing and analyzing historical data. Unlike transactional databases, data warehouses are optimized for queries and reporting. In Azure, Synapse Analytics serves as the main data warehousing solution.
Introduction to Big Data
Big data refers to extremely large and complex data sets that cannot be processed using traditional systems. Characteristics of big data include volume, velocity, and variety. Azure services such as Data Lake and Synapse are designed to handle big data scenarios.
Role of Analytics in Modern Business
Analytics transforms raw data into meaningful insights. Organizations use analytics to improve efficiency, forecast demand, and personalize customer experiences. Azure supports analytics through services that process both real time and historical data.
Artificial Intelligence and Data
Artificial intelligence relies heavily on data to make predictions and automate tasks. While the DP 900 exam does not dive deeply into AI, it introduces the idea that AI models require clean, structured, and large volumes of data. Azure Machine Learning and AI services are built on top of strong data foundations.
Preparing for Exam Questions on Core Data Concepts
The DP 900 exam often tests knowledge of core concepts by presenting scenarios. For example, learners may be asked to identify which workload requires transactional versus analytical solutions. They may also need to determine which Azure service best fits a given requirement. Understanding these basics will ensure success on the exam.
Understanding Relational Data in Azure
Relational data has been the foundation of enterprise systems for decades. It uses structured formats where data is stored in tables with rows and columns. In Azure, relational data is supported by a variety of services that simplify management, scalability, and security. Understanding relational data is a key objective of the DP 900 exam and a crucial skill for professionals entering the data field.
Why Relational Data Matters
Relational data is important because it enforces structure and consistency. Business systems such as payroll, inventory, customer management, and reservations rely on accuracy. Relationships between entities such as customers and orders or students and courses are modeled through relational principles. This makes relational systems ideal for transactional workloads where precision is required.
Core Concepts of Relational Databases
At the heart of relational databases are tables. Each table represents an entity, such as products or employees. Rows represent individual records, while columns define attributes. A schema is the blueprint that dictates how tables are organized and related. Keys, such as primary keys and foreign keys, define relationships between tables. These principles are fundamental for understanding how Azure implements relational solutions.
Primary Keys and Foreign Keys
A primary key is a unique identifier for each row in a table. For example, a CustomerID can uniquely identify each customer record. A foreign key links one table to another, creating relationships between entities. For instance, an Order table might contain a CustomerID that links back to the Customer table. These keys ensure integrity and consistency across the database.
Normalization and Data Integrity
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve consistency. It ensures that data is stored in the most efficient way. For example, customer addresses are stored in one table instead of being repeated in every order record. Normalization maintains data integrity, which means the data is accurate, consistent, and reliable.
Structured Query Language
Structured Query Language, or SQL, is the standard language used to manage relational databases. SQL allows users to create tables, insert records, update data, and retrieve information. Azure SQL Database fully supports SQL, making it a familiar tool for database administrators and developers alike.
Relational Workloads in Azure
Relational workloads are used when organizations need to process transactions with high accuracy. Examples include recording financial transactions, tracking orders, or managing hospital patient records. Azure provides multiple services that support relational workloads at scale, ensuring that these critical operations run smoothly.
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service that eliminates the need for physical server management. It provides automatic backups, high availability, and built in security. Users focus on designing databases and applications, while Azure handles the underlying infrastructure. This makes it a popular choice for organizations modernizing their systems.
Benefits of Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database offers scalability, which allows databases to handle growing workloads without performance degradation. It also provides built in intelligence to optimize queries and indexes. Security features include encryption, threat detection, and compliance certifications. These benefits make Azure SQL Database a reliable solution for both small businesses and large enterprises.
Deployment Models for Azure SQL
There are different deployment models for Azure SQL Database. The single database model provides isolation and dedicated resources for one database. The elastic pool model allows multiple databases to share resources, which is cost effective for variable workloads. The managed instance model provides near complete compatibility with on premise SQL Server environments, making migrations easier.
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Managed Instance is designed for organizations that want to migrate existing SQL Server workloads to Azure with minimal changes. It supports features such as SQL Agent, cross database queries, and linked servers. This makes it the preferred option for businesses that require compatibility with legacy systems.
Azure Virtual Machines with SQL Server
For organizations that need complete control, SQL Server can be deployed on Azure Virtual Machines. This model provides full administrative access to the operating system and database engine. It is useful for scenarios that require custom configurations or third party software integration. However, it also requires more management responsibility compared to fully managed services.
High Availability in Relational Databases
High availability is critical for relational databases because downtime can impact business operations. Azure ensures high availability through features such as geo replication, failover groups, and automated backups. These features guarantee that relational workloads remain operational even during failures.
Security in Relational Databases
Security is essential for relational data, especially when it involves sensitive information like financial records or healthcare data. Azure SQL Database provides transparent data encryption, advanced threat protection, and role based access control. These features ensure that only authorized users can access or modify data.
Performance Optimization
Performance is a common challenge in relational systems. Azure SQL Database offers tools such as query performance insights, automatic tuning, and index recommendations. These capabilities optimize workloads without requiring constant manual intervention.
Relational Data in Real World Scenarios
Many industries rely heavily on relational data. In retail, relational databases track sales, customers, and inventory. In healthcare, they store patient records and treatment histories. In finance, they manage transactions and regulatory compliance. These examples highlight why relational systems remain the backbone of critical applications.
Integrating Relational Data with Other Services
Azure relational databases do not operate in isolation. They integrate with analytics tools like Power BI, machine learning platforms, and application services. This integration enables organizations to move beyond basic transactions and leverage data for insights and innovation.
Backup and Recovery
Backup and recovery strategies are crucial in relational systems. Azure SQL Database automatically performs backups and allows point in time recovery. This ensures that organizations can recover data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or system failure.
Monitoring and Management
Monitoring tools in Azure allow administrators to track database performance, usage, and security. Features such as Azure Monitor and SQL Insights provide dashboards and alerts. These tools help organizations maintain efficient operations and address issues quickly.
Cost Management for Relational Workloads
Cost is always a factor in cloud services. Azure SQL Database provides flexible pricing models, including pay as you go and reserved capacity. Elastic pools allow organizations to optimize costs when managing multiple databases with varying usage patterns. Understanding these models helps organizations balance performance with budget constraints.
Relational vs Non Relational in Azure
One of the exam objectives is recognizing when to use relational versus non relational solutions. Relational databases are best when consistency and accuracy are required. Non relational databases are more suitable for handling large volumes of unstructured data with flexibility. Learners must be able to match scenarios to the appropriate solution.
Exam Preparation for Relational Data
The DP 900 exam includes questions on relational concepts, SQL, and Azure SQL services. Learners may be asked to identify when to use a managed instance versus a single database, or how normalization improves data integrity. Practicing with case studies and real world scenarios helps reinforce these concepts.
Relational Data and Future Learning
Mastering relational data fundamentals prepares learners for advanced certifications. Those interested in database administration can pursue DP 300. Those focused on data engineering can move toward DP 203. The foundational knowledge of relational systems provides a base for building deeper expertise in the Azure data ecosystem.
Relational Data Concepts
Relational data remains one of the most important aspects of modern computing. Its structured approach ensures reliability and accuracy. Azure SQL services bring these principles to the cloud with added scalability, security, and integration. By mastering relational data in Azure, learners prepare themselves for both the DP 900 exam and professional roles in data management.
Prepaway's DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals video training course for passing certification exams is the only solution which you need.
Pass Microsoft Azure Data DP-900 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers As Seen in the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


DP-900 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 323 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 26, 2026
- Training Course 32 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 672 Pages
| Free DP-900 Exam Questions & Microsoft DP-900 Dumps | ||
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft.test4prep.dp-900.v2026-01-10.by.john.93q.ete |
Views: 119
Downloads: 806
|
Size: 458.77 KB
|
| Microsoft.pass4sure.dp-900.v2021-11-23.by.rachid.89q.ete |
Views: 162
Downloads: 1853
|
Size: 452.83 KB
|
| Microsoft.selftestengine.dp-900.v2021-10-20.by.emily.84q.ete |
Views: 186
Downloads: 1852
|
Size: 367.7 KB
|
| Microsoft.braindumps.dp-900.v2021-09-24.by.bence.76q.ete |
Views: 198
Downloads: 1877
|
Size: 363.43 KB
|
| Microsoft.testking.dp-900.v2021-04-16.by.daris.67q.ete |
Views: 486
Downloads: 2266
|
Size: 224.18 KB
|
| Microsoft.selftestengine.dp-900.v2021-03-16.by.harriet.67q.ete |
Views: 316
Downloads: 2093
|
Size: 224.27 KB
|
| Microsoft.passit4sure.dp-900.v2021-02-03.by.kai.55q.ete |
Views: 379
Downloads: 2139
|
Size: 207.15 KB
|
| Microsoft.testking.dp-900.v2020-09-21.by.joshua.40q.ete |
Views: 803
Downloads: 2610
|
Size: 185.61 KB
|
Student Feedback
Can View Online Video Courses
Please fill out your email address below in order to view Online Courses.
Registration is Free and Easy, You Simply need to provide an email address.
- Trusted By 1.2M IT Certification Candidates Every Month
- Hundreds Hours of Videos
- Instant download After Registration
A confirmation link will be sent to this email address to verify your login.
Please Log In to view Online Course
Registration is free and easy - just provide your E-mail address.
Click Here to Register





