AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions Certification Video Training Course
The complete solution to prepare for for your exam with AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions certification video training course. The AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions certification video training course contains a complete set of videos that will provide you with thorough knowledge to understand the key concepts. Top notch prep including Microsoft DevOps AZ-400 exam dumps, study guide & practice test questions and answers.
AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions Certification Video Training Course Exam Curriculum
Setup Azure and Azure DevOps
-
3:00
1. Lecture - About Azure free account
-
5:00
2. Demo - Creating an Azure account
-
2:00
3. Lecture - Azure DevOps Structure
-
4:00
4. Demo - Set up Azure DevOps
-
2:00
5. Lecture - About Service Connections
-
4:00
6. Demo - Create a Service Connection
ARM Templates
-
6:00
1. Lecture - About ARM Templates
-
7:00
2. Demo - Finding ARM Template Sources
-
5:00
3. Lecture - About ARM template Sources
-
6:00
4. Demo - Deployment using ARM Templates
Source Control
-
2:00
1. Lecture - About Azure Repos
-
2:00
2. Demo - Installing git
-
7:00
3. Demo - Push Code to Azure Repos
Azure Pipelines
-
4:00
1. Lecture - About Azure Pipelines
-
6:00
2. Demo - Build Pipeline
-
4:00
3. Demo - Validating JSON errors
-
3:00
4. Lecture - About Pipeline Artifacts
-
9:00
5. Demo - Release Pipeline
Deployment Mode
-
4:00
1. Lecture - About Deployment Mode
-
9:00
2. Demo - Incremental and Complete Mode
-
6:00
3. Demo - Parameter Overriding
Production Deployments
-
2:00
1. Lecture - About CI/CD
-
6:00
2. Demo - CICD
-
2:00
3. Lecture - About Production Deployments
-
13:00
4. Demo-Production Deployments - Part 1
-
10:00
5. Demo-Production Deployments - Part 2
-
10:00
6. Demo-Production Deployments - Part 3
About AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions Certification Video Training Course
AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions certification video training course by prepaway along with practice test questions and answers, study guide and exam dumps provides the ultimate training package to help you pass.
AZ-400: DevOps Solutions Expert – Designing and Implementing DevOps Practices
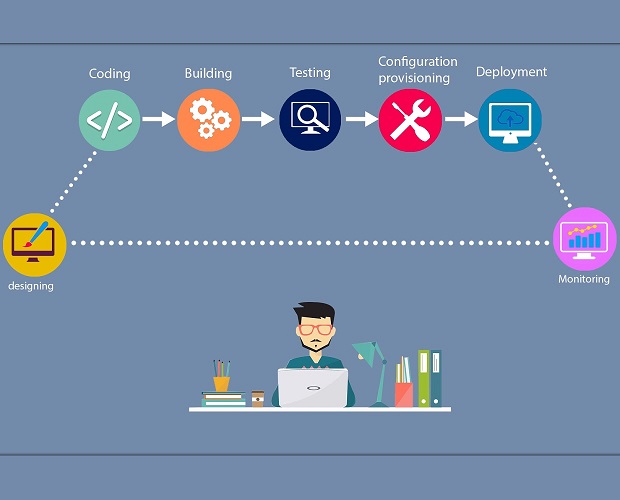
The AZ-400 certification focuses on designing and implementing DevOps practices for modern software development and IT operations. This course prepares you to understand, plan, and integrate DevOps strategies effectively using Microsoft Azure. You will learn how to improve collaboration between development and operations teams, automate processes, and deliver software faster with higher quality.
Importance of DevOps Skills
Modern organizations rely on DevOps to accelerate software delivery while maintaining reliability and security. Professionals with DevOps skills are in high demand. AZ-400 equips you with the expertise to implement continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure as code on the Azure platform.
Learning Objectives
After completing this course, you will be able to design and implement DevOps strategies, manage source control, automate build and release pipelines, implement security controls, and monitor application performance. You will also gain practical knowledge of Azure DevOps tools, GitHub, and other related services.
Course Description
This course offers a structured learning path from the fundamentals of DevOps to advanced practices. You will start by understanding DevOps culture and principles, then move to practical implementation using Azure tools. The course includes real-world scenarios to ensure you can apply your knowledge effectively.
Understanding DevOps Culture
DevOps is more than just tools; it is a cultural shift. The course emphasizes collaboration between development, operations, and business teams. You will explore how to break down silos, foster communication, and create a culture of continuous improvement.
Prerequisites and Requirements
Basic knowledge of software development and IT operations is recommended. Familiarity with Azure services, cloud computing concepts, and version control systems will be helpful. This course is designed for professionals who already have experience in managing projects, coding, or IT infrastructure.
Skills You Will Gain
You will gain skills in designing and implementing DevOps practices on Azure. This includes creating CI/CD pipelines, managing source control with Git, deploying applications using containers and Kubernetes, and implementing monitoring and feedback systems. Security and compliance practices in a DevOps context are also covered.
Who This Course is For
This course is ideal for DevOps engineers, cloud engineers, software developers, IT professionals, and system administrators. It is suited for individuals who want to advance their career in DevOps or prepare for the AZ-400 certification. Professionals aiming to lead DevOps transformations in their organizations will benefit greatly.
Why Choose This Course
The course combines theoretical knowledge with practical exercises. You will work on Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and other real-world tools. By the end, you will have the confidence to design and implement DevOps practices and pass the AZ-400 certification exam.
Azure DevOps Tools Overview
Azure DevOps provides a suite of tools to manage the entire software development lifecycle. It enables teams to plan work, manage code, build and deploy applications, and monitor performance. The platform integrates with GitHub and other version control systems, offering flexibility for different development workflows. Understanding these tools is critical for implementing DevOps practices efficiently.
Understanding Azure DevOps Services
Azure DevOps is composed of multiple services that support DevOps processes. These services include Azure Repos, Azure Pipelines, Azure Boards, Azure Test Plans, and Azure Artifacts. Each service addresses specific aspects of DevOps, from source control to continuous integration and delivery, testing, and package management. Familiarity with each service helps streamline workflows and improve collaboration across teams.
Azure Repos for Source Control
Azure Repos provides Git repositories or Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) for managing source code. Git is widely used for distributed version control, allowing multiple developers to collaborate efficiently. Using Azure Repos, teams can manage branches, track changes, and implement pull requests for code reviews. Proper source control is the foundation of effective DevOps practices.
Git Workflow Best Practices
Adopting a structured Git workflow is essential. Branching strategies like feature branching, release branching, and trunk-based development support parallel work streams. Pull requests enable code review and quality checks before integration. Commit messages should be descriptive and consistent, providing traceability for changes. Automation of merging and testing ensures that code quality is maintained.
Implementing Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) is a practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a shared repository. Azure Pipelines allows automated builds and tests whenever code is committed. This practice reduces integration issues, identifies bugs early, and improves overall code quality. Pipelines can be configured to run unit tests, static code analysis, and security scans automatically.
Building Azure Pipelines
Azure Pipelines provides a cloud-hosted service to automate builds, tests, and deployments. You can define pipelines using YAML files or a visual designer. Pipelines support multiple languages and platforms, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and containerized applications. Configuring triggers ensures that pipelines run automatically when specific events occur, such as code commits or pull requests.
Continuous Delivery and Deployment
Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI by automatically deploying code to staging or production environments. Azure Pipelines supports multi-stage deployments, approval workflows, and rollback mechanisms. Continuous Deployment enables immediate release of new features to users. Implementing CD ensures faster feedback, reduces manual errors, and improves software reliability.
Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows infrastructure to be managed using configuration files. Tools like Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates, Terraform, and Bicep enable automated provisioning of resources. IaC promotes consistency, repeatability, and version control for infrastructure. It also integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines to deploy both code and infrastructure together.
Configuration Management
Configuration management ensures that systems remain consistent and reproducible across environments. Azure Automation, Desired State Configuration (DSC), and Chef or Ansible can manage configurations automatically. These tools reduce manual intervention, enforce policies, and ensure that development, testing, and production environments remain aligned.
Monitoring and Feedback Loops
Monitoring is a key part of DevOps. Azure Monitor, Application Insights, and Log Analytics provide visibility into system performance, application behavior, and user experience. Feedback loops enable teams to detect issues, analyze root causes, and implement improvements quickly. Real-time monitoring supports proactive management and continuous improvement.
Implementing Security in DevOps
DevOps practices must incorporate security at every stage, known as DevSecOps. Azure DevOps integrates security scanning tools, automated testing, and compliance checks within pipelines. This approach ensures that vulnerabilities are detected early, policies are enforced, and applications meet regulatory requirements. Security should never be an afterthought but an integral part of DevOps processes.
Artifact Management
Azure Artifacts allows teams to create, host, and share packages such as NuGet, npm, and Maven. Artifact management supports dependency management, version control, and secure sharing of reusable components. Integrating artifacts with pipelines ensures consistent and reliable deployments across environments.
Branch Policies and Code Quality
Branch policies enforce code quality standards, requiring pull requests, approvals, and successful builds before merging. Policies prevent unstable code from entering main branches and maintain consistency in development practices. Automated tests, linting, and static analysis enhance code reliability and reduce defects in production.
Containerization and DevOps
Containerization isolates applications and dependencies into portable units. Docker and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) simplify deployment, scaling, and management of containerized workloads. Integrating containers into CI/CD pipelines improves deployment speed, consistency, and scalability while reducing conflicts between environments.
Managing Kubernetes Deployments
Kubernetes orchestrates containerized applications for production environments. Azure Kubernetes Service offers managed clusters, simplifying infrastructure management. CI/CD pipelines can automate application deployment, scaling, and updates in AKS. Observability tools monitor cluster health, performance, and resource utilization, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Automated Testing Strategies
Automated testing is essential to maintain quality in DevOps workflows. Unit tests, integration tests, and functional tests should run automatically in pipelines. Testing early and often detects defects quickly, reduces risk, and improves confidence in deployments. Test reporting and dashboards provide transparency for stakeholders.
Scaling DevOps Practices
Scaling DevOps requires standardization, automation, and monitoring across multiple teams and projects. Implementing templates, reusable components, and best practices reduces duplication and ensures consistency. DevOps metrics such as deployment frequency, lead time, and mean time to recovery (MTTR) help measure success and identify areas for improvement.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective DevOps relies on collaboration between developers, operations, security teams, and business stakeholders. Tools like Azure Boards and Teams facilitate task management, tracking, and communication. Transparency in work items, priorities, and progress ensures alignment and reduces bottlenecks in the software delivery process.
Implementing Compliance Controls
Regulatory compliance is critical in many industries. Azure DevOps allows integration with compliance frameworks, policy enforcement, and automated audits. Ensuring compliance throughout the pipeline reduces risk, improves governance, and demonstrates adherence to legal and industry standards.
Managing Pipeline Environments
Pipeline environments define the stages through which applications move, from development to testing to production. Environment-specific configurations, approvals, and deployment gates ensure safe and controlled releases. Monitoring environment health and performance allows proactive interventions and continuous improvement.
Leveraging Cloud-Native Services
Azure provides cloud-native services such as serverless computing, managed databases, and AI integration. Incorporating these services into DevOps workflows enables rapid innovation, scalability, and cost optimization. Cloud-native approaches simplify operations while supporting agile development practices.
Continuous Feedback and Improvement
A culture of continuous feedback ensures that teams learn from every release. Metrics, monitoring, and user feedback provide actionable insights. Iterative improvements enhance software quality, user satisfaction, and operational efficiency. DevOps is not a one-time implementation but a continuous evolution.
Advanced Pipeline Design Principles
Designing advanced pipelines requires understanding the flow of code from development to production. Pipelines should be modular, reusable, and easy to maintain. Implementing multi-stage pipelines allows separate handling of development, testing, staging, and production environments. This separation improves reliability, reduces errors, and ensures controlled deployments.
YAML-Based Pipelines
YAML pipelines provide code-as-configuration for automation. Using YAML enables version control for pipeline definitions and promotes consistency across teams. Templates can be used to standardize repetitive tasks, reduce duplication, and enforce best practices. YAML pipelines support parameters, conditional tasks, and triggers, making automation flexible and efficient.
Multi-Stage Pipelines
Multi-stage pipelines allow defining multiple stages in a single pipeline. Each stage can represent an environment or a specific process, such as build, test, or deployment. Stages can have approvals, gates, and automated tests to ensure quality. Multi-stage pipelines provide visibility and control over every step in the DevOps process.
Pipeline Templates and Reusability
Templates allow reusing pipeline configurations across multiple projects. This approach reduces duplication, enforces best practices, and speeds up onboarding for new projects. Templates can include common build steps, test routines, and deployment configurations. Centralized template management ensures consistency across teams and environments.
Continuous Integration Best Practices
Continuous Integration is a core DevOps principle. CI ensures that code is integrated frequently, tested automatically, and verified for quality. Best practices include committing small changes, running automated tests for every commit, using branching strategies, and integrating code analysis tools. CI reduces integration risks and accelerates development cycles.
Automated Testing in Pipelines
Automated testing ensures quality and reliability. Unit tests validate individual components, integration tests verify interactions between modules, and functional tests simulate real-world use cases. Automated testing should be included in pipelines to detect issues early, reduce manual intervention, and provide immediate feedback to developers.
Test Environments Management
Managing test environments is crucial for reliable validation. Pipelines can provision temporary environments using IaC, run tests, and then clean up resources automatically. This approach reduces infrastructure costs and ensures tests run in consistent, controlled environments. Environment configuration should mimic production to identify potential issues early.
Deployment Strategies
Choosing the right deployment strategy improves reliability and minimizes downtime. Strategies include blue-green deployments, canary releases, rolling updates, and feature toggles. Each strategy provides a different balance of risk, complexity, and user impact. Advanced pipelines should support multiple deployment strategies to meet project needs.
Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-green deployment involves maintaining two identical environments. The new version is deployed to the inactive environment, tested, and then switched to production. This approach reduces downtime and allows easy rollback if issues occur. Monitoring and automated checks ensure the new environment is stable before traffic is redirected.
Canary Releases
Canary releases involve deploying updates to a small subset of users before full rollout. This strategy helps detect issues early with minimal impact. Monitoring key metrics and user feedback is essential to determine whether to continue, rollback, or adjust the release. Canary releases are often automated using pipelines and feature flags.
Rolling Updates
Rolling updates deploy changes gradually across servers or instances. This approach reduces downtime and ensures continuous availability. Pipelines can automate the deployment sequence, monitor health, and trigger rollback if failures occur. Rolling updates are suitable for high-availability applications that cannot tolerate full downtime.
Feature Flags and Toggle Management
Feature flags allow enabling or disabling features without deploying new code. This approach supports experimentation, phased rollouts, and quick rollback. Pipelines can integrate feature flag management to control releases, run A/B tests, and minimize risk in production. Feature flags also improve collaboration between developers and product managers.
Infrastructure as Code in Advanced Pipelines
Advanced pipelines incorporate IaC to provision, configure, and manage infrastructure automatically. Tools like ARM templates, Terraform, and Bicep integrate with pipelines to deploy resources consistently. IaC enables version-controlled, repeatable infrastructure deployments, reducing configuration drift and manual errors.
Environment-Specific Configurations
Pipelines should support environment-specific settings for development, testing, and production. Variables, secrets, and configuration files allow customization without modifying code. Secure storage of secrets and sensitive data is essential, and pipelines should integrate with Azure Key Vault or similar services.
Secrets Management and Security Integration
Managing secrets securely is critical in DevOps. Azure Key Vault allows storing API keys, certificates, and passwords securely. Pipelines can retrieve secrets during build or deployment without exposing them in logs or code. Integrating security checks, vulnerability scanning, and policy enforcement ensures compliance and reduces risks.
Monitoring Pipelines and Feedback
Monitoring pipelines provides insights into performance, failures, and bottlenecks. Azure DevOps provides logs, metrics, and dashboards to track pipeline health. Feedback loops from monitoring help identify improvement areas, optimize build times, and prevent recurring failures. Continuous feedback is key to improving pipeline efficiency.
Automated Rollback and Recovery
Automated rollback ensures stability in case of deployment failures. Pipelines can detect errors using health checks, logs, and performance metrics. If an issue is detected, the system can revert to a previous stable state automatically. Automated recovery reduces downtime and minimizes the impact on users.
DevSecOps Practices in Pipelines
Integrating security into pipelines ensures that vulnerabilities are detected early. Static code analysis, dependency scanning, container image scanning, and policy enforcement should be automated. Security testing should be part of CI/CD to maintain compliance and reduce the risk of breaches.
Compliance as Code
Compliance as Code allows defining rules, policies, and regulations as part of the pipeline. Automated checks verify that deployments meet organizational and regulatory requirements. Azure Policy and custom scripts can enforce compliance in infrastructure and applications. This approach reduces manual audits and ensures consistent adherence.
Advanced Container Deployment
Containers simplify deployment and scaling of applications. Pipelines should support building, testing, and deploying container images. Integrating with Azure Kubernetes Service or other container orchestration platforms enables automated scaling, health monitoring, and resource optimization. Container-based deployments improve portability and reliability.
Kubernetes Integration
Kubernetes orchestrates containerized workloads efficiently. Advanced pipelines can automate deployment, scaling, and updates in AKS clusters. Monitoring cluster health, resource usage, and application performance is critical. Pipelines should include automated rollback, canary deployments, and integration with CI/CD for seamless operations.
Continuous Feedback from Production
Collecting feedback from production ensures continuous improvement. Application Insights, logs, metrics, and user feedback provide insights into performance and user experience. Pipelines can trigger alerts, updates, or rollbacks based on real-time monitoring. Continuous feedback supports proactive maintenance and rapid iteration.
Metrics and Key Performance Indicators
Measuring DevOps success requires tracking metrics like deployment frequency, lead time, mean time to recovery, and defect rates. KPIs provide actionable insights into process efficiency and reliability. Pipelines should integrate monitoring and reporting to visualize performance trends and identify improvement opportunities.
Collaboration in Large Teams
Advanced DevOps pipelines support collaboration across multiple teams. Azure Boards, pull requests, and branch policies facilitate communication and task management. Shared pipelines, templates, and reusable components ensure consistency and reduce duplication across teams. Transparency in workflow improves coordination and delivery speed.
Continuous Improvement Culture
A culture of continuous improvement is central to DevOps success. Teams should analyze metrics, gather feedback, and refine pipelines, tools, and processes regularly. Encouraging experimentation, learning from failures, and implementing best practices ensures sustainable improvement in software delivery.
Monitoring and Observability in DevOps
Monitoring is a critical aspect of DevOps, ensuring applications and infrastructure perform as expected. Observability goes beyond monitoring by providing insights into why systems behave a certain way. Azure Monitor, Application Insights, and Log Analytics are core tools for gathering metrics, logs, and traces. Monitoring allows teams to detect anomalies, diagnose issues, and improve system reliability.
Azure Monitor Capabilities
Azure Monitor collects data from applications, infrastructure, and networks. Metrics and logs are stored and analyzed to provide actionable insights. Dashboards can visualize performance trends, alerts can notify teams of issues, and queries can identify root causes. Integration with other Azure services enables centralized monitoring across all components of the application ecosystem.
Application Insights for Performance Monitoring
Application Insights provides deep application performance monitoring. It tracks response times, request rates, and dependency calls. End-to-end transaction tracing helps identify performance bottlenecks. Application Insights also collects exceptions, logs, and user telemetry, allowing teams to detect issues quickly and proactively resolve problems.
Log Analytics and Data Analysis
Log Analytics enables advanced querying of logs collected from applications, servers, and networks. Custom queries provide insights into trends, anomalies, and operational issues. Logs can be correlated across different systems to identify patterns and understand root causes. Integrating Log Analytics into CI/CD pipelines ensures continuous monitoring of deployments and operations.
Creating Dashboards and Visualizations
Dashboards provide a centralized view of system health and performance. Custom visualizations help stakeholders quickly understand application behavior and infrastructure status. Dashboards can display metrics, logs, alerts, and key performance indicators. Sharing dashboards across teams improves collaboration and ensures transparency in monitoring efforts.
Implementing Alerts and Notifications
Alerts notify teams of critical issues in real-time. Azure Monitor supports metric-based, log-based, and activity-based alerts. Notifications can be sent via email, SMS, Teams, or integrated with ITSM systems. Configuring alert rules ensures prompt response to incidents, reducing downtime and improving service reliability.
Proactive Monitoring Strategies
Proactive monitoring involves identifying potential problems before they impact users. Synthetic transactions, load testing, and anomaly detection help anticipate issues. Continuous monitoring of application performance, infrastructure utilization, and dependencies allows teams to address problems early, preventing disruptions and maintaining reliability.
Logging Best Practices
Effective logging provides insight into application behavior and system events. Logs should be structured, consistent, and include meaningful context. Sensitive information must be secured or masked. Centralized logging with correlation identifiers allows tracking requests across multiple services, simplifying troubleshooting and root cause analysis.
Metrics Collection and Analysis
Collecting metrics enables teams to track system health and performance trends. Metrics can include CPU usage, memory consumption, response times, error rates, and throughput. Analyzing metrics over time helps detect performance degradation, plan capacity, and optimize resource allocation. Automated pipelines can integrate metrics collection for continuous feedback.
Incident Management and Response
Incident management ensures timely resolution of issues. Azure Monitor and ITSM integrations support incident tracking, prioritization, and resolution. Automated workflows can escalate critical incidents and trigger remediation actions. Continuous analysis of incidents helps identify recurring problems and implement preventive measures.
Root Cause Analysis and Postmortems
Root cause analysis (RCA) identifies the underlying causes of incidents. Postmortem reviews capture lessons learned, process gaps, and improvement opportunities. RCAs ensure that recurring issues are prevented and that teams continuously improve operational practices. Documenting findings fosters organizational learning and knowledge sharing.
Security Monitoring in DevOps
Security monitoring integrates into DevOps pipelines to detect vulnerabilities and threats. Tools like Azure Security Center, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, and third-party scanners identify misconfigurations, compliance violations, and potential attacks. Continuous monitoring ensures that security is maintained throughout the software lifecycle.
Compliance and Governance
Compliance ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and organizational policies. Azure Policy and Blueprints enforce rules for resources, configurations, and deployments. Governance practices include auditing, access control, and reporting. Integrating compliance into pipelines reduces manual oversight and ensures continuous enforcement of policies.
Identity and Access Management
Managing identities and access is essential for secure DevOps operations. Azure Active Directory enables centralized identity management, role-based access control, and multi-factor authentication. Pipelines should integrate access policies to prevent unauthorized deployments and maintain system security.
Secrets and Key Management
Secrets such as API keys, certificates, and passwords must be managed securely. Azure Key Vault provides centralized storage, encryption, and access control. Pipelines can retrieve secrets during builds and deployments without exposing them. Secure secrets management reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with security standards.
Threat Detection and Vulnerability Scanning
Automated threat detection and vulnerability scanning identify potential risks in code, containers, and infrastructure. Integrating security scanners into CI/CD pipelines allows early detection of vulnerabilities. Teams can remediate issues before deployment, ensuring secure software delivery and reducing exposure to attacks.
Container Security
Containerized environments require specialized security practices. Image scanning, vulnerability assessment, and runtime protection help secure containers. Azure Security Center and third-party tools provide continuous monitoring and compliance checks. Integrating container security into pipelines ensures that deployed applications meet security standards.
Governance Automation
Automating governance ensures consistent policy enforcement. Scripts, templates, and Azure Policy definitions enforce compliance across resources and deployments. Automated governance reduces manual effort, prevents configuration drift, and provides audit-ready documentation. Teams can focus on delivering value while maintaining control over infrastructure and processes.
Monitoring Cost and Resource Utilization
Monitoring resource usage and cost helps optimize cloud spending. Azure Cost Management tracks consumption, forecasts expenses, and provides recommendations. Pipelines can include resource tagging and automated cleanup of unused resources to manage costs efficiently. Resource monitoring ensures sustainability and operational efficiency.
Service Level Objectives and Agreements
Defining Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) sets expectations for availability, performance, and reliability. Monitoring tools track adherence to these targets. Teams can proactively address deviations and ensure that service commitments to stakeholders are met.
Continuous Feedback from End Users
User feedback is essential for continuous improvement. Telemetry, surveys, and analytics provide insights into user experience and satisfaction. Pipelines can integrate feedback collection and analysis to guide development priorities and enhance application quality. Continuous feedback closes the loop between development, operations, and users.
Automation in Monitoring and Response
Automation enhances monitoring and response efficiency. Automated remediation scripts, scaling actions, and alert handling reduce manual intervention. Pipelines can trigger automated actions based on predefined conditions, ensuring fast resolution and minimal downtime. Automation supports resilience and reliability in complex systems.
Analytics for Decision Making
Data-driven decision making improves operational efficiency. Analytics on performance metrics, incidents, and user behavior guide prioritization and resource allocation. Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Power BI provide visualization, reporting, and insights. Integrating analytics into DevOps pipelines ensures informed and timely decisions.
Integrating Monitoring into Pipelines
Monitoring should be integrated throughout the CI/CD process. Build, test, and deployment stages should include checks for performance, security, and compliance. Automated alerts and dashboards provide immediate feedback to developers and operations teams. Integration ensures continuous visibility and proactive management of applications.
Continuous Improvement through Metrics
Metrics drive continuous improvement in DevOps. Deployment frequency, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery are key indicators of process efficiency. Analyzing trends helps teams identify bottlenecks, optimize pipelines, and enhance overall performance. Continuous measurement and improvement ensure sustainable DevOps success.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Effective monitoring requires collaboration between development, operations, and security teams. Sharing dashboards, logs, alerts, and insights promotes transparency and faster resolution of issues. Knowledge sharing ensures that best practices are adopted across teams and that lessons learned are applied to future projects.
Prepaway's AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions video training course for passing certification exams is the only solution which you need.
Pass Microsoft DevOps AZ-400 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers As Seen in the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


AZ-400 Premium Bundle
- Premium File 355 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 22, 2026
- Training Course 27 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 784 Pages
Student Feedback
Can View Online Video Courses
Please fill out your email address below in order to view Online Courses.
Registration is Free and Easy, You Simply need to provide an email address.
- Trusted By 1.2M IT Certification Candidates Every Month
- Hundreds Hours of Videos
- Instant download After Registration
A confirmation link will be sent to this email address to verify your login.
Please Log In to view Online Course
Registration is free and easy - just provide your E-mail address.
Click Here to Register





