- Home
- ITIL Certifications
- ITILFND ITIL Foundation Dumps
Pass ITIL ITILFND Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


ITILFND Premium File
- Premium File 549 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Jan 31, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All ITIL ITILFND certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the ITILFND ITIL Foundation practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Study Smart for ITILFND: Detailed Overview of What the Exam Covers
The ITILFND exam is designed to provide candidates with a comprehensive understanding of the principles, practices, and terminology of the IT service management framework. The exam evaluates knowledge of the service lifecycle, key processes, roles, and responsibilities within service management, as well as the relationship between IT services and business objectives. Candidates are expected to demonstrate an understanding of core concepts, including service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. Preparation for the exam involves mastering these concepts, understanding how processes interrelate, and applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios in service management.
Understanding Service Management Concepts
Service management is central to the ITILFND syllabus. Candidates must grasp the concept of services as a means to deliver value to customers while facilitating outcomes they want to achieve. Services consist of combinations of people, processes, and technology working together to deliver measurable value. Understanding the distinction between service provision and service consumption is key. Service providers create and deliver services, while customers use them to achieve desired outcomes. Candidates also study the importance of aligning IT services with organizational objectives, ensuring that IT contributes strategically to business success. Grasping these concepts helps candidates evaluate how IT services are managed, measured, and improved to provide optimal value.
The ITIL Service Lifecycle
The ITIL service lifecycle forms the foundation of the ITILFND exam. Candidates explore five stages: service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. Service strategy focuses on understanding business needs, market analysis, and financial management of services. Service design addresses how to develop services effectively, including service level management, capacity planning, availability, and continuity. Service transition involves deploying new or modified services efficiently, covering change management, configuration management, and knowledge management. Service operation ensures that services are delivered effectively and consistently, encompassing incident management, problem management, and request fulfillment. Continual service improvement focuses on evaluating performance and identifying opportunities to enhance services, aligning IT with evolving business objectives.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Candidates must understand the roles and responsibilities involved in service management. Roles are defined to ensure accountability, efficient service delivery, and alignment with organizational objectives. Key roles include service owner, process owner, process manager, and service desk staff. Service owners are responsible for specific services and ensuring they meet agreed objectives. Process owners design, implement, and maintain processes, while process managers ensure operational efficiency and continuous improvement. Service desk staff provide a single point of contact for users, managing incidents and service requests. Understanding these roles enables candidates to evaluate organizational structures and responsibilities in supporting service management objectives.
ITIL Processes and Functions
The ITILFND exam requires knowledge of processes and functions that enable effective service management. Processes are structured activities designed to achieve specific objectives, while functions are units or teams performing operational tasks. Candidates study processes such as incident management, problem management, change management, service level management, capacity management, availability management, and configuration management. Each process has defined objectives, inputs, outputs, and metrics. Functions such as the service desk, technical management, IT operations management, and application management support the processes operationally. Candidates must understand how processes and functions interact to deliver efficient, reliable services and how performance is measured to ensure continual improvement.
Service Strategy Principles
Service strategy principles provide guidance on planning and managing IT services to support business outcomes. Candidates explore the development of service portfolios, financial management, demand management, and business relationship management. Service portfolio management ensures that services are aligned with organizational priorities and resources are allocated effectively. Financial management evaluates the cost and value of services to support investment decisions. Demand management identifies patterns of business activity and resource requirements to optimize service delivery. Business relationship management focuses on maintaining productive interactions between service providers and customers. Mastering service strategy enables candidates to analyze the rationale behind service offerings and the impact on business objectives.
Service Design Considerations
Service design emphasizes translating strategic objectives into operational services. Candidates learn about designing services that are reliable, scalable, and aligned with business requirements. Key considerations include availability management, capacity management, continuity management, information security management, supplier management, and service level management. Availability management ensures services are accessible when needed, capacity management optimizes resources to meet demand, and continuity management prepares organizations for disruptions. Information security management safeguards data and processes, while supplier management ensures third-party services support business objectives. Service level management defines, negotiates, and monitors service agreements to maintain quality and satisfaction. Understanding these elements equips candidates to evaluate design decisions and their impact on operational effectiveness.
Service Transition Planning and Management
Service transition focuses on implementing new or modified services efficiently and effectively. Candidates study change management, release and deployment management, knowledge management, configuration management, and transition planning. Change management evaluates, authorizes, and implements modifications to minimize risk and disruption. Release and deployment management coordinates deployment activities, ensuring successful implementation. Knowledge management ensures accurate information is available for decision-making, while configuration management maintains records of assets and relationships. Transition planning coordinates all activities to deliver services on time and within scope. Mastery of service transition principles enables candidates to assess how organizations manage changes while maintaining service quality and stability.
Service Operation Activities
Service operation ensures that IT services are delivered consistently and meet agreed objectives. Candidates learn about incident management, problem management, event management, request fulfillment, and access management. Incident management restores normal service quickly to minimize impact, while problem management identifies root causes to prevent recurrence. Event management monitors and responds to system changes, request fulfillment handles user requests, and access management controls permissions to maintain security. Candidates also study monitoring tools, performance metrics, and reporting practices. Understanding service operation processes helps candidates evaluate operational effectiveness, user satisfaction, and service reliability.
Continual Service Improvement
Continual service improvement focuses on evaluating and enhancing IT services to achieve ongoing business value. Candidates study metrics, key performance indicators, benchmarking, and process maturity assessments. Identifying opportunities for improvement, analyzing trends, and implementing corrective actions ensures services evolve with organizational needs. CSI also emphasizes aligning IT services with changing business objectives and ensuring that lessons learned from previous activities inform future improvements. Candidates learn structured methods to assess performance, recommend improvements, and monitor outcomes, enabling a culture of continuous enhancement.
Key Metrics and Measurement
Understanding metrics is vital for evaluating service performance and effectiveness. Candidates learn to use key performance indicators, service level agreements, and operational metrics to assess process efficiency and service quality. Metrics enable identification of gaps, benchmarking against best practices, and tracking improvements over time. Candidates study how to select relevant metrics, interpret data, and apply insights to enhance service delivery. Measurement and analysis ensure that decisions are evidence-based and aligned with business objectives, supporting continual improvement initiatives.
Roles of Technology and Tools
Candidates are introduced to the role of technology and tools in supporting IT service management. Automated systems assist in tracking incidents, managing changes, monitoring performance, and maintaining configuration databases. Tools facilitate process standardization, reporting, and communication, enabling teams to operate efficiently. Candidates learn how technology enhances service visibility, supports decision-making, and enables proactive management. Understanding the integration of tools with processes and functions equips candidates to evaluate IT service management practices effectively.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential in IT service management. Candidates learn how processes and roles rely on clear information flow, coordinated activities, and shared understanding of objectives. Stakeholder communication ensures transparency, while collaboration between teams enables efficient problem resolution and service delivery. Candidates study methods for reporting, feedback, and escalation, which are critical for maintaining service quality and customer satisfaction. Mastering communication and collaboration practices supports professional competence in service management contexts.
Practical Application of ITIL Concepts
Practical application is a core aspect of preparing for the ITILFND exam. Candidates engage with scenario-based exercises to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world service management situations. This includes evaluating process effectiveness, designing service solutions, managing changes, resolving incidents, and implementing improvements. Practical exercises reinforce understanding, develop problem-solving skills, and enable candidates to demonstrate competence in applying ITIL principles within organizational contexts. Scenario-based practice ensures readiness for the challenges encountered in professional service management roles.
Exam Strategy and Preparation Techniques
Successful preparation for the ITILFND exam involves structured study, consistent practice, and focused revision. Candidates are encouraged to review the syllabus thoroughly, identify strengths and weaknesses, and allocate time for intensive study of complex topics. Practice questions, sample scenarios, and mock exams reinforce knowledge and improve time management. Reviewing key terms, processes, roles, and lifecycle stages ensures comprehensive coverage. Strategic preparation, combined with practical application exercises, enhances confidence, retention, and exam performance.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
The ITILFND syllabus encourages continuous learning beyond exam preparation. Candidates are trained to adopt a mindset of ongoing improvement, reflecting on processes, identifying gaps, and implementing enhancements. Learning from practical experiences, performance evaluations, and benchmarking promotes professional growth. Continuous improvement ensures that IT services evolve to meet changing business needs, and that individuals develop the knowledge and skills necessary for long-term success in service management roles.
Integration of Knowledge and Skills
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to integrate knowledge of service management principles, processes, roles, technology, and measurement. Understanding how different aspects of the ITIL framework interact is critical for effective planning, implementation, operation, and improvement of services. Integrating theoretical knowledge with practical scenarios demonstrates readiness to contribute meaningfully to service management practices and ensures that candidates are prepared for real-world responsibilities.
The ITILFND exam provides a detailed foundation in IT service management, covering principles, lifecycle stages, processes, roles, technology, metrics, and continual improvement. Candidates develop a deep understanding of how IT services support business objectives, manage risks, and deliver value to customers. Practical application, scenario-based exercises, and reflective learning reinforce knowledge, enhance problem-solving skills, and prepare candidates for professional service management roles. Mastery of ITIL concepts equips candidates to plan, execute, and evaluate services effectively, contributing to organizational success and professional development
Advanced Understanding of Service Strategy
Service strategy forms the foundation for IT service management and is a major focus in preparing for the ITILFND exam. Candidates learn that service strategy is about defining the perspective, position, plans, and patterns that a service provider needs to execute to meet business outcomes. It involves understanding customer needs, the market space, and internal capabilities to deliver value through IT services. Key concepts include service portfolio management, financial management, demand management, and business relationship management. Service portfolio management ensures alignment between services offered and organizational objectives, enabling prioritization of investments. Financial management evaluates the cost, value, and budgeting of services. Demand management analyzes patterns of business activity to optimize resources, while business relationship management fosters a productive relationship between the service provider and customers. Mastery of service strategy allows candidates to understand how strategic decisions shape service delivery and organizational value.
Service Design in Depth
Service design translates strategic objectives into effective service solutions. Candidates study the design of new or modified services that meet current and future business requirements. Key components include service level management, availability management, capacity management, IT service continuity management, information security management, and supplier management. Service level management defines and negotiates agreements with customers and monitors adherence. Availability management ensures services are reliable and accessible according to agreed metrics. Capacity management plans and optimizes resources to meet expected demand. IT service continuity management ensures services can recover from disruptions. Information security management protects data, infrastructure, and processes, while supplier management ensures that third-party services support business objectives efficiently. Candidates learn how these design elements interrelate to deliver cohesive and high-quality services.
Service Transition and Change Management
Service transition focuses on ensuring that new or changed services are implemented successfully with minimal disruption. Candidates are trained to understand processes such as change management, release and deployment management, configuration management, and knowledge management. Change management assesses the impact, risk, and approval of proposed changes to ensure smooth transitions. Release and deployment management coordinates the implementation of service releases to minimize disruption. Configuration management maintains an accurate record of service components and their relationships, enabling effective tracking and control. Knowledge management ensures accurate information is available to support decision-making and improve service quality. Service transition planning involves coordinating activities across all processes to ensure that services meet expectations and are delivered efficiently.
Service Operation Processes
Service operation ensures that services are delivered effectively, meeting agreed service levels and supporting business outcomes. Candidates study key operational processes including incident management, problem management, event management, request fulfillment, and access management. Incident management restores normal service quickly to minimize disruption. Problem management identifies root causes and implements solutions to prevent recurrence. Event management monitors and responds to significant events that may affect services. Request fulfillment ensures that user requests are handled efficiently, and access management controls permissions to protect sensitive information. Understanding these processes enables candidates to evaluate operational effectiveness, maintain service quality, and ensure that IT services consistently meet business needs.
Continual Service Improvement
Continual service improvement focuses on identifying and implementing enhancements to IT services to align with changing business requirements. Candidates learn methods for measuring performance, analyzing trends, and implementing corrective actions. Metrics, key performance indicators, benchmarking, and maturity assessments are central to CSI. Reviewing past performance, identifying gaps, and making improvements ensure that services remain relevant, efficient, and valuable to the organization. Candidates also learn how to integrate feedback from users and stakeholders into the improvement cycle, promoting a culture of ongoing enhancement. Mastery of CSI concepts prepares candidates to recommend improvements and demonstrate value from service management activities.
Metrics, Reporting, and Measurement
Metrics and measurement are essential for managing and improving IT services. Candidates study how to define, track, and interpret metrics to assess performance and efficiency. Service level agreements provide benchmarks for evaluating whether services meet expectations. Operational metrics track process efficiency, defect resolution, and incident trends. Analysis of metrics supports informed decision-making, continuous improvement, and alignment with business objectives. Candidates also learn how to communicate results effectively to stakeholders, demonstrating transparency, accountability, and the value of IT service management initiatives.
Technology and Tool Integration
The ITILFND syllabus emphasizes the role of technology and tools in supporting service management practices. Automated tools assist in tracking incidents, managing changes, monitoring performance, maintaining configuration databases, and reporting metrics. Tools standardize processes, enhance communication, and enable real-time monitoring and analysis. Candidates learn to evaluate how tools support process efficiency, improve service visibility, and provide actionable insights. Understanding tool integration allows candidates to assess how technology can optimize service delivery, facilitate decision-making, and support continual improvement initiatives.
Roles, Responsibilities, and Organizational Structures
Candidates are trained to understand the various roles and responsibilities within service management to ensure accountability and effective service delivery. Key roles include service owner, process owner, process manager, and service desk staff. Service owners are accountable for specific services, ensuring alignment with business objectives. Process owners design, implement, and maintain processes, while process managers ensure operational effectiveness. Service desk staff provide a single point of contact for users, managing incidents, service requests, and communication. Understanding these roles allows candidates to assess organizational structures, responsibilities, and how they contribute to overall service quality and business alignment.
Risk Management in IT Service Management
Risk management is an integral part of IT service management and a focus of ITILFND preparation. Candidates learn to identify potential risks to services, evaluate their impact and likelihood, and implement strategies to mitigate or control them. Effective risk management ensures service reliability, reduces potential disruptions, and protects organizational assets. Candidates study proactive approaches to risk identification, monitoring, and response planning. Integrating risk management into service strategy, design, transition, operation, and improvement ensures that IT services consistently meet objectives and provide value to the organization.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication is essential for successful service management. Candidates learn techniques for engaging with stakeholders, reporting performance, communicating changes, and providing updates on service delivery. Transparent communication builds trust, ensures alignment with business objectives, and facilitates collaboration between teams. Stakeholder engagement includes understanding expectations, gathering feedback, and providing clarity on service outcomes. Mastery of communication practices enables candidates to coordinate effectively across organizational units and enhance service quality.
Practical Application and Scenario Exercises
Applying theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios is a critical component of ITILFND exam preparation. Candidates engage with exercises that simulate real-world service management challenges, such as designing service solutions, handling incidents, managing changes, and implementing process improvements. Scenario-based learning reinforces understanding, develops critical thinking, and builds confidence in applying ITIL concepts in organizational settings. Practical exercises enable candidates to demonstrate competence in planning, executing, and evaluating service management activities effectively.
Exam Strategy and Preparation Techniques
Strategic preparation for the ITILFND exam involves structured study plans, consistent practice, and review of key concepts. Candidates are advised to analyze the syllabus, allocate study time according to topic complexity, and focus on areas requiring deeper understanding. Practice questions and mock scenarios reinforce learning and improve time management. Reviewing processes, roles, lifecycle stages, and service principles ensures comprehensive coverage. Combining theoretical study with practical exercises enables candidates to approach the exam with confidence, demonstrating both knowledge and applied skills.
Continual Learning and Professional Growth
The ITILFND framework emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and development. Candidates are encouraged to reflect on past experiences, identify improvement opportunities, and integrate lessons into future service management practices. Continuous learning fosters adaptability, enhances problem-solving skills, and ensures that IT services evolve to meet business requirements. Developing a mindset of ongoing improvement prepares candidates for long-term success in service management roles, enabling them to contribute strategically to organizational objectives.
Integration of ITIL Concepts
Successful ITILFND candidates understand how to integrate knowledge of service lifecycle stages, processes, roles, technology, metrics, and continual improvement. Integration allows for coherent service management practices, where processes and functions work in harmony to deliver value. Candidates learn to assess how changes in one area affect others, ensuring alignment with objectives and consistent service delivery. Holistic understanding of ITIL concepts prepares candidates to manage complex service environments and implement best practices effectively.
Advanced Metrics and Performance Analysis
Candidates study advanced approaches to metrics and performance evaluation to assess service quality and process efficiency. Key performance indicators, operational metrics, and benchmarking provide insight into strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. Data analysis supports decision-making, resource allocation, and prioritization of improvement initiatives. Candidates learn how to interpret trends, identify root causes of performance issues, and implement corrective actions. Understanding performance metrics enables candidates to evaluate effectiveness, optimize services, and communicate results to stakeholders professionally.
Leveraging Technology for Service Optimization
ITILFND emphasizes the strategic role of technology in optimizing service management. Candidates learn how to select, implement, and utilize tools that support incident tracking, problem management, change management, configuration management, and reporting. Technology enhances process efficiency, provides real-time insights, and enables proactive monitoring. Candidates also study the integration of technology with human resources, ensuring that processes are executed effectively and consistently. Knowledge of technological support enables candidates to evaluate organizational capabilities and recommend improvements to enhance service quality.
Professional Collaboration and Teamwork
Collaboration across teams is critical for successful service delivery. Candidates study how to coordinate between service owners, process managers, operational staff, and stakeholders to achieve objectives efficiently. Teamwork ensures that processes are followed, incidents are resolved quickly, changes are implemented smoothly, and improvement initiatives are executed effectively. Candidates also learn techniques for conflict resolution, information sharing, and maintaining alignment across multiple teams. Developing collaboration skills enables candidates to contribute to high-performing service management environments.
Scenario-Based Problem Solving
Scenario-based problem solving is a vital part of ITILFND exam readiness. Candidates practice resolving issues that simulate real-world service management challenges. Exercises include analyzing incident trends, managing changes under constraints, prioritizing service requests, and implementing process improvements. These activities develop analytical skills, decision-making abilities, and practical understanding of ITIL principles. Scenario practice ensures candidates can apply theoretical knowledge confidently and demonstrate professional competence during the exam.
Continuous Service Improvement Application
Candidates learn how to implement continual service improvement initiatives within organizations. This involves analyzing performance, identifying inefficiencies, recommending enhancements, and monitoring results. CSI ensures that services remain relevant, efficient, and aligned with business objectives. Candidates also study how to use feedback from customers and stakeholders to drive improvements. Understanding CSI principles ensures that candidates can maintain high-quality service delivery and contribute to long-term organizational success.
The ITILFND exam provides a detailed foundation in IT service management, encompassing service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Candidates develop the skills to plan, implement, manage, and evaluate services effectively. Mastery of roles, processes, technology, metrics, and collaboration practices ensures candidates can align IT services with business objectives, optimize performance, and deliver value. Practical application through scenario-based exercises reinforces knowledge and professional competence, preparing candidates to excel in service management roles and contribute strategically to organizational success
Introduction to ITILFND Advanced Concepts
The ITILFND exam requires candidates to not only understand the foundational concepts of IT service management but also to grasp how these concepts integrate to support business objectives effectively. Candidates are expected to analyze how processes, roles, and functions interconnect across the service lifecycle. Preparation involves detailed study of service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement. Each stage of the lifecycle builds on previous knowledge and demonstrates how IT services create value for organizations. A comprehensive understanding equips candidates to evaluate scenarios, propose solutions, and ensure IT services align with organizational priorities.
Strategic Management of Services
Service strategy underpins the design and delivery of IT services. Candidates learn that service strategy involves defining the approach for delivering value, analyzing market space, managing resources, and establishing service offerings. Service portfolio management is central to strategy, ensuring that the organization prioritizes and invests in services that meet business needs. Financial management evaluates the cost, budgeting, and value of services to guide decision-making. Demand management examines business activity patterns to anticipate resource requirements. Business relationship management fosters strong communication between service providers and customers, ensuring expectations are understood and addressed. Candidates must apply strategic thinking to evaluate how IT initiatives support broader organizational goals and optimize resource utilization.
Detailed Exploration of Service Design
Service design translates strategic objectives into actionable plans for service delivery. Candidates study comprehensive areas including service level management, availability management, capacity management, IT service continuity, information security, and supplier management. Service level management ensures that services meet agreed-upon performance targets. Availability management guarantees accessibility and reliability. Capacity management aligns resources with anticipated demand. IT service continuity ensures services can recover from disruptions without impacting critical operations. Information security management safeguards data and infrastructure. Supplier management ensures external providers meet organizational requirements. Understanding how these elements integrate allows candidates to evaluate designs for effectiveness, efficiency, and resilience.
Service Transition and Change Implementation
Service transition focuses on delivering new or modified services into live environments with minimal risk. Candidates are required to understand change management, release and deployment management, configuration management, and knowledge management. Change management ensures proposed modifications are evaluated, approved, and implemented with controlled risk. Release and deployment management coordinates deployment schedules and resources to avoid disruption. Configuration management maintains detailed records of service components and their interrelationships. Knowledge management ensures accurate information is available to staff for decision-making and problem resolution. Transition planning orchestrates activities to ensure that service changes meet objectives and maintain operational stability.
Operational Excellence in Service Management
Service operation is concerned with delivering IT services efficiently and reliably on a daily basis. Candidates explore key operational processes including incident management, problem management, event management, request fulfillment, and access management. Incident management addresses service interruptions promptly to restore normal operation. Problem management identifies root causes and implements preventive actions. Event management monitors activities and triggers appropriate responses. Request fulfillment handles routine service requests efficiently. Access management controls permissions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can perform specific actions. Candidates learn how operational processes support service continuity, quality, and customer satisfaction while maintaining compliance and security standards.
Continual Service Improvement Methodologies
Continual service improvement focuses on the systematic evaluation and enhancement of IT services. Candidates study the use of metrics, key performance indicators, benchmarking, and maturity models to monitor and improve service delivery. CSI involves analyzing trends, identifying gaps, and implementing corrective measures to optimize performance. Feedback from users and stakeholders is incorporated to ensure services evolve according to organizational needs. Candidates learn structured approaches to process improvement, aligning IT service capabilities with business objectives. Mastery of CSI ensures that services remain relevant, efficient, and capable of delivering sustainable value over time.
Performance Metrics and Reporting
Candidates must understand how to measure service performance effectively. Key performance indicators, operational metrics, and service level agreements provide measurable data to evaluate process efficiency and service quality. Metrics enable identification of trends, areas for improvement, and resource optimization. Reporting communicates performance outcomes to stakeholders, ensuring transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making. Candidates learn to interpret metrics, derive insights, and implement strategies to enhance service performance. Proficiency in measurement and reporting ensures that IT services can be continually optimized to meet organizational requirements.
Technology Integration and Support Tools
The integration of technology and tools is essential for efficient service management. Candidates explore how automated systems support incident tracking, problem resolution, change control, configuration management, and reporting. Tools provide process standardization, improve communication, and enable real-time monitoring. Candidates study how to evaluate the effectiveness of tools and their alignment with organizational goals. Understanding technology integration allows candidates to optimize service delivery, streamline workflows, and facilitate evidence-based decision-making. Effective use of tools enhances visibility, control, and efficiency across the service lifecycle.
Organizational Roles and Responsibilities
Understanding roles and responsibilities is critical for maintaining accountability in IT service management. Candidates study service owners, process owners, process managers, and service desk staff. Service owners are accountable for ensuring specific services meet business objectives. Process owners design and maintain processes, while process managers oversee operational performance. Service desk staff act as the primary point of contact for users, managing incidents and requests. Clear role definition ensures efficient service delivery, coordination between teams, and alignment with organizational objectives. Candidates learn to evaluate how structures support process execution and service quality.
Risk Management Principles
Risk management is a vital aspect of IT service management. Candidates study methods for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks associated with IT services. Effective risk management ensures continuity, reduces service disruption, and protects organizational assets. Candidates are trained to anticipate potential problems, implement preventative measures, and respond to emerging threats. Integrating risk management across strategy, design, transition, operation, and improvement ensures services maintain reliability and contribute to business value. Understanding risk principles enables candidates to prioritize activities and make informed decisions under uncertain conditions.
Effective Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Communication is fundamental for successful IT service management. Candidates learn how to engage stakeholders, provide clear reporting, and coordinate activities across teams. Effective communication supports alignment with business objectives, enhances transparency, and facilitates collaboration. Candidates study methods for conveying performance data, escalating issues, and providing guidance to ensure service quality. Engaging stakeholders ensures expectations are managed, feedback is integrated, and continuous improvement is informed by practical insights. Mastery of communication techniques is essential for maintaining trust, accountability, and effective service delivery.
Scenario-Based Application
Scenario-based learning is central to preparing for the ITILFND exam. Candidates apply knowledge to real-world situations, analyzing incidents, managing changes, resolving problems, and recommending improvements. Scenario exercises develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. They reinforce understanding of the interconnection between processes, roles, and technology. Practical application ensures that candidates can demonstrate competence, evaluate options effectively, and implement ITIL practices in professional contexts. Scenario-based preparation also enhances confidence and readiness for exam questions that require applied knowledge.
Exam Preparation Techniques
Strategic preparation for the ITILFND exam involves structured study, practice, and review. Candidates are advised to analyze the syllabus, allocate time according to topic complexity, and focus on weaker areas. Practice questions, sample scenarios, and mock exams help reinforce knowledge, improve time management, and develop confidence. Reviewing core processes, service lifecycle stages, roles, and concepts ensures comprehensive understanding. Integrating theoretical study with scenario-based exercises allows candidates to approach the exam with clarity, demonstrating both knowledge and practical competence.
Continuous Learning and Development
The ITILFND framework encourages ongoing learning beyond exam preparation. Candidates are trained to analyze performance, reflect on experiences, and implement improvements continuously. Continuous learning enhances professional skills, fosters adaptability, and ensures that IT services evolve in line with organizational needs. Candidates develop the ability to identify gaps, optimize processes, and support innovation. A mindset of continual development prepares candidates for sustained professional success and enables meaningful contributions to organizational IT service management.
Integration of ITIL Concepts
Candidates must understand how different ITIL elements integrate to form a cohesive service management framework. Knowledge of strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement allows candidates to evaluate processes holistically. Integration ensures alignment between services, business objectives, roles, and technology. Candidates study how changes in one process affect others and how to maintain balance across the lifecycle. Holistic understanding equips candidates to manage services effectively, implement best practices, and drive organizational value.
Advanced Process Evaluation
Candidates examine processes in detail to assess efficiency, effectiveness, and alignment with objectives. Process evaluation includes analyzing incident resolution times, change implementation success, problem recurrence rates, and service request fulfillment. Evaluation also involves measuring process maturity, compliance with standards, and opportunities for improvement. Candidates learn how to interpret results, prioritize enhancements, and ensure processes support both operational needs and strategic goals. Advanced evaluation skills prepare candidates to optimize IT service delivery and maintain high levels of quality and reliability.
Optimization of Services through Technology
Technology plays a crucial role in supporting service optimization. Candidates learn to leverage automated tools for monitoring, reporting, and managing IT services. Integration of technology with processes enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and provides actionable insights. Candidates study how to select appropriate tools, assess their effectiveness, and ensure they support service objectives. Optimized use of technology enables proactive management, continuous monitoring, and informed decision-making, leading to improved service quality and user satisfaction.
Team Collaboration and Leadership
Effective service management relies on teamwork and leadership. Candidates study techniques for coordinating activities across roles, resolving conflicts, sharing knowledge, and maintaining alignment. Collaboration ensures smooth operation, efficient problem resolution, and successful implementation of improvements. Leadership skills, including guiding teams, decision-making, and motivating staff, are also emphasized. Developing collaborative and leadership abilities prepares candidates to manage complex service environments and contribute strategically to organizational goals.
Practical Application of Improvement Initiatives
Candidates are trained to apply continual service improvement principles in practical contexts. This includes analyzing operational data, identifying gaps, recommending enhancements, and implementing changes. Practical application ensures services remain aligned with business needs and provides measurable improvements in quality and efficiency. Candidates learn to use performance metrics, stakeholder feedback, and process evaluation to guide decisions. Applying CSI concepts strengthens professional competence and prepares candidates to implement real-world service improvements effectively.
Exam Readiness and Confidence Building
Comprehensive preparation for the ITILFND exam involves integrating study, practice, and application. Candidates review core concepts, engage with scenarios, and assess their understanding through mock exercises. Building familiarity with processes, roles, lifecycle stages, and key principles enhances confidence and exam readiness. Strategic planning, focused study, and practical application ensure that candidates are prepared to answer questions accurately and demonstrate their ability to apply ITIL principles in professional settings.
Professional Competence in Service Management
The ITILFND exam emphasizes both knowledge and the ability to apply service management principles. Candidates develop professional competence by understanding the integration of processes, roles, technology, and improvement initiatives. They learn to assess service quality, optimize operations, and contribute to organizational objectives. Practical application, scenario analysis, and performance evaluation equip candidates to function effectively in professional service management roles and support continuous organizational improvement.
The ITILFND exam provides an in-depth understanding of IT service management, covering service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Candidates develop skills in process management, operational excellence, risk management, technology integration, collaboration, and performance evaluation. Scenario-based practice reinforces theoretical knowledge and ensures practical readiness. Mastery of ITIL concepts enables candidates to plan, execute, and optimize IT services effectively, ensuring alignment with business objectives and the delivery of consistent value. Professional competence gained through preparation equips candidates to manage services efficiently and contribute strategically to organizational success
Foundations of IT Service Management
The ITILFND exam emphasizes a strong grasp of IT service management fundamentals. Candidates are expected to understand the role of IT in supporting business objectives and delivering value. IT services are viewed as assets that must be managed efficiently and effectively to meet customer needs. Core principles include understanding the service lifecycle, service value creation, and alignment with business priorities. Candidates study how IT services interact with processes, people, and technology to ensure quality, reliability, and continuous improvement. A solid foundation prepares candidates to integrate lifecycle stages and processes into coherent service management practices.
Service Strategy and Portfolio Management
Service strategy is a key component of the ITILFND syllabus. Candidates learn to analyze business requirements, define service offerings, and manage service portfolios effectively. Service portfolio management ensures that services are strategically aligned and investment decisions reflect business priorities. Candidates study financial management principles, including budgeting, accounting, and charging models, to understand how financial planning supports service decisions. Demand management is explored to anticipate patterns of business activity and optimize capacity planning. Business relationship management techniques enable maintaining strong relationships with stakeholders, ensuring that IT services meet expectations and contribute to organizational objectives.
Service Design Principles
Service design focuses on translating strategy into practical solutions that deliver value. Candidates study the comprehensive design of services, including service level management, availability, capacity, continuity, security, and supplier management. Service level management defines, negotiates, and monitors agreements to ensure services meet agreed expectations. Availability management ensures consistent service access, while capacity management aligns resources with anticipated business demand. IT service continuity management ensures services can recover from disruptions with minimal impact. Information security management safeguards data, processes, and infrastructure. Supplier management ensures that external providers support service objectives efficiently. Candidates are trained to integrate these elements to create robust, effective, and sustainable services.
Service Transition and Change Control
Service transition is concerned with the safe and effective deployment of services into live environments. Candidates explore change management, release and deployment management, configuration management, and knowledge management. Change management evaluates proposed modifications, ensures approval processes, and mitigates risks. Release and deployment management coordinates the implementation of changes and new services while minimizing operational disruption. Configuration management maintains accurate records of service components and their interrelationships. Knowledge management ensures staff have access to accurate information to support decisions, problem resolution, and service quality. Effective transition planning allows services to be delivered successfully and ensures alignment with business and operational needs.
Service Operation and Process Execution
Service operation ensures services are delivered reliably, efficiently, and in accordance with agreements. Key processes include incident management, problem management, event management, request fulfillment, and access management. Incident management restores normal operations quickly to minimize business impact. Problem management identifies root causes and prevents recurring issues. Event management monitors operations to detect and respond to conditions that may affect service delivery. Request fulfillment addresses routine service needs efficiently. Access management protects sensitive information by controlling permissions. Candidates learn how these processes interact to maintain service quality, enhance user satisfaction, and support organizational objectives.
Continual Service Improvement
Continual service improvement focuses on identifying opportunities to enhance services and processes. Candidates study the use of performance metrics, key performance indicators, benchmarking, and maturity models to monitor, analyze, and improve service delivery. CSI involves assessing past performance, identifying gaps, and implementing corrective actions. Feedback from stakeholders and users is used to drive improvement initiatives. Candidates learn structured methods for embedding improvement into everyday operations, ensuring services remain efficient, effective, and aligned with business priorities. CSI reinforces the importance of learning from experience to enhance service quality and organizational value.
Metrics, Reporting, and Performance Analysis
Understanding metrics is essential for monitoring service performance and process effectiveness. Candidates study how to define, collect, and analyze data related to service levels, operational efficiency, and user satisfaction. Key performance indicators measure critical aspects of service performance. Operational metrics track process efficiency, incident resolution times, and problem recurrence. Reporting translates data into actionable insights for stakeholders, enabling informed decision-making. Candidates learn to interpret trends, identify improvement opportunities, and implement strategies to enhance service quality. Proficiency in metrics and reporting ensures services are evaluated systematically and continuously improved.
Technology Support and Tools
Candidates are expected to understand how technology supports IT service management practices. Automated tools facilitate incident tracking, change management, configuration management, performance monitoring, and reporting. These tools standardize processes, enhance communication, and provide real-time insights into service performance. Candidates study how to select and integrate tools effectively to optimize efficiency, accuracy, and consistency. Understanding the role of technology enables candidates to recommend improvements, streamline workflows, and support the delivery of high-quality services.
Roles, Responsibilities, and Organizational Structure
The ITILFND exam requires candidates to understand the roles and responsibilities within service management. Roles include service owners, process owners, process managers, and service desk personnel. Service owners are accountable for the performance and delivery of specific services. Process owners design and maintain processes, while process managers ensure operational effectiveness. Service desk staff provide frontline support, managing incidents and service requests. Clear role definition promotes accountability, efficient service delivery, and seamless coordination between teams. Candidates learn to evaluate organizational structures to ensure alignment with service objectives and process requirements.
Risk and Change Management
Risk management is integrated throughout the ITILFND framework. Candidates study techniques to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks that could impact service delivery. Risk assessment ensures services are reliable, secure, and aligned with business needs. Change management processes control the implementation of modifications to reduce disruptions and maintain service integrity. Candidates learn to prioritize actions based on risk severity, anticipate potential issues, and develop contingency plans. Effective risk and change management enhances service reliability and supports organizational stability.
Stakeholder Communication and Engagement
Communication with stakeholders is critical to IT service management success. Candidates study strategies for providing clear reporting, managing expectations, and ensuring alignment with business objectives. Engaging stakeholders involves gathering feedback, addressing concerns, and keeping users informed about service performance and changes. Candidates learn techniques for effective communication that build trust, facilitate collaboration, and support continuous service improvement. Proficiency in stakeholder engagement enables candidates to maintain alignment between IT services and organizational priorities.
Scenario-Based Learning and Application
Practical application through scenarios reinforces understanding of ITILFND concepts. Candidates simulate real-world challenges such as incident response, change implementation, problem resolution, and service improvement initiatives. Scenario-based exercises develop analytical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. Candidates apply lifecycle principles, processes, and roles to realistic situations, ensuring they can demonstrate competence in practical contexts. This approach enhances readiness for the exam and professional application of ITIL principles.
Integrated Lifecycle Understanding
Candidates are trained to understand how service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement integrate into a unified lifecycle. Integration ensures processes and functions operate cohesively to deliver value. Candidates evaluate the impact of changes across lifecycle stages and align activities to maintain consistency, efficiency, and service quality. Holistic understanding enables candidates to manage complex service environments effectively and ensures that services consistently meet business objectives.
Advanced Process Evaluation
The ITILFND exam emphasizes assessing the efficiency, effectiveness, and maturity of service management processes. Candidates study metrics to evaluate incident resolution times, change success rates, service request handling, and problem recurrence. Analysis identifies opportunities for improvement, ensures compliance with standards, and informs resource allocation decisions. Candidates learn to apply evaluation techniques to optimize processes and maintain service excellence, supporting long-term organizational goals.
Optimization of Services with Technology
Technology enhances service management by automating processes, providing monitoring capabilities, and delivering actionable insights. Candidates explore how tools support incident management, problem resolution, change control, configuration tracking, and reporting. Integrating technology with human processes ensures consistency, reduces errors, and improves response times. Candidates learn to select appropriate tools, evaluate their effectiveness, and implement solutions that optimize service delivery and efficiency.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Effective teamwork is essential for delivering high-quality services. Candidates study techniques for coordinating between service owners, process managers, operational staff, and stakeholders. Collaboration ensures smooth incident management, effective change implementation, and successful service improvement. Candidates learn conflict resolution, knowledge sharing, and alignment strategies to enhance team performance. Mastery of collaboration prepares candidates to operate effectively in complex service environments.
Continual Service Improvement in Practice
Candidates apply CSI principles to identify service gaps, implement improvements, and monitor outcomes. Techniques include analyzing performance data, evaluating process maturity, and integrating stakeholder feedback. Practical application ensures services evolve to meet changing business needs and achieve operational excellence. Candidates develop skills to maintain service quality, optimize processes, and contribute strategically to organizational objectives.
Exam Preparation and Readiness
Preparation for the ITILFND exam involves structured study plans, scenario-based practice, and review of core concepts. Candidates analyze the syllabus, allocate time based on topic complexity, and focus on areas requiring deeper understanding. Practice exercises reinforce knowledge, enhance time management skills, and build confidence. Reviewing processes, roles, lifecycle stages, and improvement methodologies ensures comprehensive coverage. Combining theoretical study with practical application prepares candidates to answer questions accurately and demonstrate applied competence.
Professional Competence and Practical Application
The ITILFND exam assesses both theoretical knowledge and the ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios. Candidates learn to integrate processes, roles, technology, and improvement initiatives to deliver effective IT services. Professional competence involves assessing service quality, optimizing operations, managing risks, and implementing enhancements. Practical application of ITIL principles ensures candidates can contribute strategically to service management initiatives and achieve organizational objectives effectively.
Long-Term Learning and Development
The ITILFND framework encourages continuous development and professional growth. Candidates are trained to reflect on experiences, analyze performance, and implement improvements. Ongoing learning enhances adaptability, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. Candidates develop the ability to maintain high service quality, optimize processes, and support continuous innovation. A commitment to continuous development ensures long-term success in service management roles.
The ITILFND exam equips candidates with comprehensive knowledge of IT service management, covering strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Candidates develop skills in process management, operational excellence, risk assessment, technology integration, collaboration, and performance evaluation. Scenario-based practice reinforces applied knowledge and professional readiness. Mastery of ITIL concepts enables candidates to plan, deliver, and optimize IT services effectively, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and delivering consistent value to stakeholders
The ITILFND exam requires candidates to have a comprehensive understanding of IT service management, extending beyond basic principles to a deeper analysis of processes, roles, and functions. Candidates must understand how each component of the service lifecycle contributes to value creation and aligns with organizational objectives. This involves examining the interactions between service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement, and understanding how these stages influence decision-making, resource allocation, and performance measurement. A detailed understanding of these concepts allows candidates to evaluate scenarios, identify areas for optimization, and apply ITIL best practices in complex service environments.
Service Strategy and Business Alignment
Service strategy forms the foundation for effective IT service management. Candidates study how to develop service strategies that align with organizational goals, prioritize investment, and optimize resources. Service portfolio management is a critical focus area, ensuring that the right services are developed and maintained to meet business needs. Financial management concepts, including budgeting, cost analysis, and charging models, provide insight into the economic value of services and inform strategic decisions. Demand management and business relationship management are explored to anticipate usage patterns, manage expectations, and maintain strong stakeholder engagement. Candidates are trained to assess business requirements, evaluate options, and make informed decisions that enhance service value.
Service Design and Capability Planning
Service design translates strategy into actionable plans for service delivery. Candidates study service level management, capacity management, availability management, IT service continuity management, information security management, and supplier management. Service level management ensures that services meet agreed performance targets. Capacity management ensures that IT resources meet demand efficiently. Availability management guarantees consistent service accessibility, while IT service continuity planning prepares services to recover quickly from disruptions. Information security management protects data and infrastructure, and supplier management ensures third-party providers deliver services that meet organizational standards. Understanding these areas enables candidates to design resilient, efficient, and customer-focused services that support long-term business objectives.
Service Transition and Implementation Management
Service transition focuses on introducing new or modified services into operational environments with minimal disruption. Candidates study change management, release and deployment management, configuration management, and knowledge management. Change management ensures that all modifications are assessed, authorized, and implemented with controlled risk. Release and deployment management coordinates the timing and resources for delivering services effectively. Configuration management maintains detailed records of service components and their relationships to ensure accuracy and traceability. Knowledge management facilitates informed decision-making and supports staff in service delivery. Candidates learn how to plan transitions strategically to maintain stability while implementing improvements that enhance service performance.
Operational Processes and Service Delivery
Service operation emphasizes the efficient and reliable delivery of IT services. Key processes include incident management, problem management, event management, request fulfillment, and access management. Incident management focuses on restoring normal service quickly to minimize business impact. Problem management identifies root causes of issues and implements preventive measures. Event management monitors service activity to detect and respond to conditions affecting service quality. Request fulfillment handles user requests efficiently, and access management ensures proper authorization for system access. Candidates explore how these processes interconnect to maintain service continuity, improve user satisfaction, and ensure compliance with operational standards.
Continual Service Improvement Practices
Continual service improvement ensures that IT services evolve to meet changing business needs and deliver optimal value. Candidates study techniques for analyzing performance metrics, identifying improvement opportunities, and implementing corrective actions. Benchmarking, key performance indicators, and maturity models are applied to assess service quality and process effectiveness. Feedback from users and stakeholders is integrated to guide enhancements. Candidates learn structured approaches for embedding improvement initiatives into daily operations, ensuring that services remain efficient, effective, and aligned with business objectives. CSI reinforces the importance of learning from experience and creating a culture of ongoing enhancement.
Metrics, Reporting, and Performance Analysis
Measuring and analyzing service performance is critical for maintaining quality. Candidates study the development and application of metrics to monitor operational efficiency, process performance, and service delivery. Key performance indicators and operational metrics are used to track incident resolution times, change implementation success, service request handling, and problem recurrence. Reporting translates data into actionable insights for management and stakeholders, informing decisions and guiding improvement efforts. Candidates learn to interpret metrics, identify trends, and implement strategies to optimize service delivery. Effective measurement and reporting ensure transparency, accountability, and continuous enhancement of services.
Technology Integration and Support Tools
Technology plays a significant role in supporting service management processes. Candidates study how automated tools facilitate incident tracking, change management, configuration management, monitoring, and reporting. Tools standardize processes, enhance communication, and provide real-time data for informed decision-making. Candidates evaluate tool selection and integration strategies to ensure alignment with organizational objectives and process requirements. Understanding technology support enables candidates to recommend enhancements, optimize workflows, and maintain consistent service quality while improving efficiency and reducing operational risks.
Roles, Responsibilities, and Governance
Candidates must understand organizational roles and responsibilities essential for effective IT service management. Service owners are accountable for the performance of specific services, process owners design and maintain processes, process managers ensure effective operation, and service desk personnel provide frontline support. Governance structures ensure accountability, process adherence, and alignment with strategic objectives. Candidates study how well-defined roles contribute to coordinated service delivery, efficient problem resolution, and optimized resource utilization. Understanding governance ensures that IT services operate within defined standards, policies, and regulatory requirements.
Risk Management and Compliance
Risk management is integrated throughout the ITILFND framework. Candidates examine approaches for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks associated with IT services. Effective risk management ensures service continuity, protects assets, and supports compliance with organizational and regulatory standards. Candidates study the application of risk assessment across the lifecycle, including proactive identification of potential issues and implementation of contingency plans. Integrating risk management with change control and operational processes reduces the likelihood of service disruptions and supports strategic decision-making.
Stakeholder Communication and Engagement
Effective communication with stakeholders is vital to IT service management success. Candidates study methods for reporting service performance, managing expectations, and coordinating with business units. Engaging stakeholders ensures alignment between service delivery and business needs, facilitates feedback, and supports continuous improvement. Candidates learn techniques for clear, concise communication that promotes transparency, builds trust, and enables collaborative problem-solving. Mastery of stakeholder engagement is essential for maintaining service quality and achieving organizational objectives.
Scenario-Based Learning and Application
Scenario-based exercises are central to preparing for the ITILFND exam. Candidates apply their knowledge to realistic situations, addressing incidents, managing changes, resolving problems, and implementing service improvements. These exercises develop critical thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. Scenario practice reinforces understanding of the interconnection between processes, roles, and technology, preparing candidates to demonstrate competence in practical, professional contexts. This approach also improves confidence in answering exam questions that require applied knowledge rather than theoretical recall.
Integration Across the Service Lifecycle
Candidates must understand how service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement interact to form a cohesive service lifecycle. Integration ensures processes, roles, and functions operate effectively to deliver consistent value. Candidates study how changes in one stage impact others and learn methods for maintaining alignment, efficiency, and quality across the lifecycle. Holistic understanding allows candidates to manage services strategically, anticipate risks, and optimize operations while maintaining alignment with business objectives.
Advanced Process Evaluation
The ITILFND exam emphasizes evaluating processes to ensure they are efficient, effective, and aligned with organizational goals. Candidates study performance metrics to assess incident resolution efficiency, change implementation success, service request handling, and problem recurrence. Evaluating process maturity and compliance helps identify improvement opportunities and optimize resource allocation. Candidates learn to interpret evaluation results, prioritize enhancements, and implement improvements that strengthen service delivery and support long-term objectives.
Optimization Through Technology and Automation
Technology and automation play key roles in optimizing IT services. Candidates study how tools support monitoring, reporting, process execution, and problem resolution. Effective use of technology standardizes workflows, reduces errors, and provides actionable insights. Candidates learn strategies for selecting, implementing, and evaluating tools to ensure they enhance service delivery and operational efficiency. Leveraging technology allows organizations to deliver higher quality services, respond proactively to issues, and maintain consistent performance.
Collaboration, Teamwork, and Leadership
Teamwork and leadership are critical for effective service management. Candidates examine methods for coordinating roles, resolving conflicts, sharing knowledge, and aligning efforts toward organizational objectives. Leadership skills include guiding teams, making informed decisions, and motivating staff to achieve performance goals. Collaboration ensures efficient incident management, effective change deployment, and successful implementation of service improvements. Mastery of teamwork and leadership principles enables candidates to operate effectively in complex environments and drive organizational success.
Practical Application of Continual Improvement
Candidates apply continual service improvement principles to identify gaps, recommend changes, and implement enhancements. Practical application involves analyzing operational data, assessing process maturity, and integrating stakeholder feedback. This approach ensures that services evolve in line with business needs and achieve measurable improvements in quality and efficiency. Developing the ability to apply improvement principles in practice prepares candidates to implement effective changes and optimize IT service delivery.
Exam Readiness Strategies
Preparation for the ITILFND exam involves structured study, scenario practice, and review of core concepts. Candidates analyze the syllabus, allocate study time based on topic complexity, and focus on areas requiring deeper understanding. Practice exercises reinforce knowledge, improve time management, and build confidence. Reviewing processes, lifecycle stages, roles, and improvement methodologies ensures thorough coverage. Combining theoretical study with practical application equips candidates to approach the exam with clarity, demonstrating both knowledge and applied competence.
Professional Competence and Knowledge Application
The ITILFND exam evaluates both knowledge and practical competence. Candidates learn to integrate processes, roles, technology, and improvement initiatives to deliver effective IT services. Professional competence includes assessing service quality, optimizing operations, managing risks, and implementing enhancements. Applying ITIL principles in realistic contexts ensures candidates can contribute strategically to service management initiatives and support organizational objectives effectively.
Continuous Professional Development
The ITILFND framework encourages ongoing learning and professional growth. Candidates are trained to reflect on experiences, analyze performance, and implement improvements continuously. Continuous development enhances adaptability, problem-solving skills, and decision-making abilities. Candidates develop the capability to maintain high service quality, optimize processes, and support innovation. Commitment to continuous learning ensures long-term effectiveness in service management roles and contributes to sustained organizational value.
Integration of Service Lifecycle Stages
Candidates must understand the interrelationship between service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Integration ensures consistency, efficiency, and alignment with business goals. Candidates evaluate how changes in one lifecycle stage affect others and apply methods to maintain performance, reliability, and value delivery. Holistic understanding enables effective management of services, optimized resource utilization, and proactive problem-solving.
Advanced Process Assessment
The ITILFND exam emphasizes evaluating processes for efficiency, effectiveness, and alignment with organizational objectives. Candidates study metrics to assess incident resolution, change success, service request handling, and problem recurrence. Evaluating process maturity and performance identifies areas for improvement, informs decision-making, and supports optimization initiatives. Candidates develop skills to implement changes that enhance service delivery, operational efficiency, and overall value to the organization.
Optimizing Services with Technology and Automation
Technology and automation are integral to optimizing service management. Candidates study how tools support process execution, monitoring, reporting, and problem resolution. Automation reduces errors, standardizes workflows, and improves efficiency. Candidates learn to select, implement, and evaluate tools to enhance performance and maintain consistent service quality. Effective use of technology ensures organizations can deliver high-quality services while optimizing resource utilization and operational capabilities.
Collaboration, Team Dynamics, and Leadership
Collaboration and leadership are critical for effective service management. Candidates examine methods for coordinating roles, sharing knowledge, resolving conflicts, and aligning team efforts with organizational objectives. Leadership skills include guiding teams, making strategic decisions, and motivating staff to achieve performance goals. Effective collaboration ensures efficient incident management, change implementation, and service improvement. Candidates learn to foster teamwork that enhances service quality, operational efficiency, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Practical Application of Continual Service Improvement
Candidates apply CSI principles to identify performance gaps, implement improvements, and monitor outcomes. Techniques include analyzing operational metrics, assessing process maturity, and integrating stakeholder feedback. Practical application ensures that services evolve to meet business needs, achieve measurable improvements, and maintain alignment with organizational objectives. Developing practical CSI skills equips candidates to implement changes effectively and maintain high-quality service delivery.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparation for the ITILFND exam requires structured study, scenario-based practice, and review of core concepts. Candidates analyze the syllabus, allocate time based on topic complexity, and prioritize areas requiring deeper understanding. Practice exercises reinforce knowledge, improve time management, and build confidence. Reviewing lifecycle stages, processes, roles, and improvement methodologies ensures comprehensive coverage. Combining theoretical study with practical application prepares candidates to approach the exam with clarity and demonstrate applied competence.
Developing Professional Competence
The ITILFND exam evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical application. Candidates integrate processes, roles, technology, and improvement initiatives to deliver effective IT services. Professional competence includes assessing service quality, optimizing operations, managing risks, and implementing enhancements. Applying ITIL principles in practical scenarios ensures candidates can contribute strategically to service management and support organizational objectives effectively.
Commitment to Continuous Development
ITILFND emphasizes ongoing professional growth. Candidates are trained to reflect on experiences, analyze performance, and implement continuous improvements. Continuous development enhances adaptability, decision-making, and problem-solving skills. Candidates develop the ability to maintain high service quality, optimize processes, and support innovation. A commitment to continuous learning ensures long-term effectiveness in service management roles and contributes to sustained organizational value.
Conclusion
The ITILFND exam equips candidates with in-depth knowledge of IT service management, covering strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Candidates develop expertise in process assessment, operational efficiency, risk management, technology integration, collaboration, and performance measurement. Scenario-based exercises reinforce practical application and prepare candidates for real-world service management challenges. Mastery of ITIL principles enables candidates to deliver high-quality IT services, align operations with organizational goals, and contribute strategically to overall success
The ITILFND exam provides a detailed understanding of IT service management, covering strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement. Candidates develop skills in process evaluation, operational efficiency, risk management, technology integration, collaboration, and performance measurement. Scenario-based exercises reinforce applied knowledge and prepare candidates for real-world service management challenges. Mastery of ITIL principles enables candidates to deliver high-quality IT services, align with business objectives, and contribute strategically to organizational success
ITIL ITILFND practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass ITILFND ITIL Foundation certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- ITILFND V4 - ITIL 4 Foundation
- ITIL 4 Specialist Create Deliver and Support - ITIL 4 Specialist Create, Deliver and Support
- ITIL 4 Leader Digital and IT Strategy
- ITIL4 Specialist - Monitor and Support and Fulfil - ITIL4 Specialist: Monitor, Support and Fulfil
- ITIL 4 Specialist High-Velocity IT
- ITIL 4 Specialist Collaborate Assure and Improve - ITIL 4 Specialist: Collaborate, Assure and Improve
- ITIL 4 BRM - ITIL 4 Specialist Business Relationship Management (BRM)
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the ITIL certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the ITILFND test and passed with ease.
Studying for the ITIL certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the ITILFND exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the ITILFND preparation materials for the ITIL certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The ITILFND materials for the ITIL certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the ITILFND exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my ITIL certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for ITILFND. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the ITILFND stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my ITILFND certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my ITIL certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the ITILFND were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed ITILFND successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

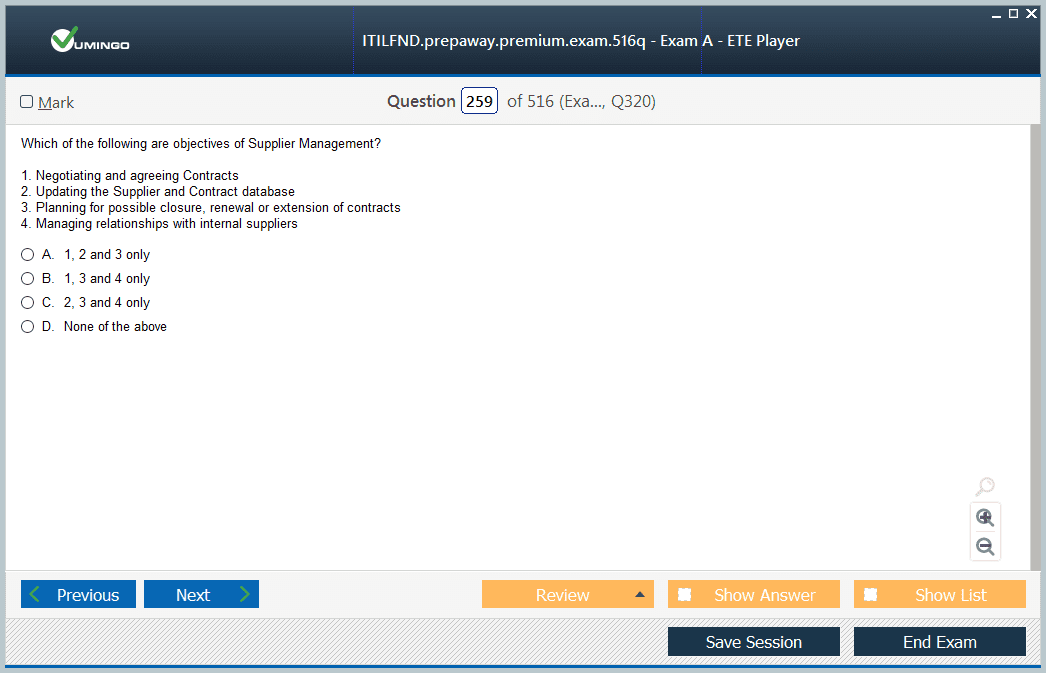
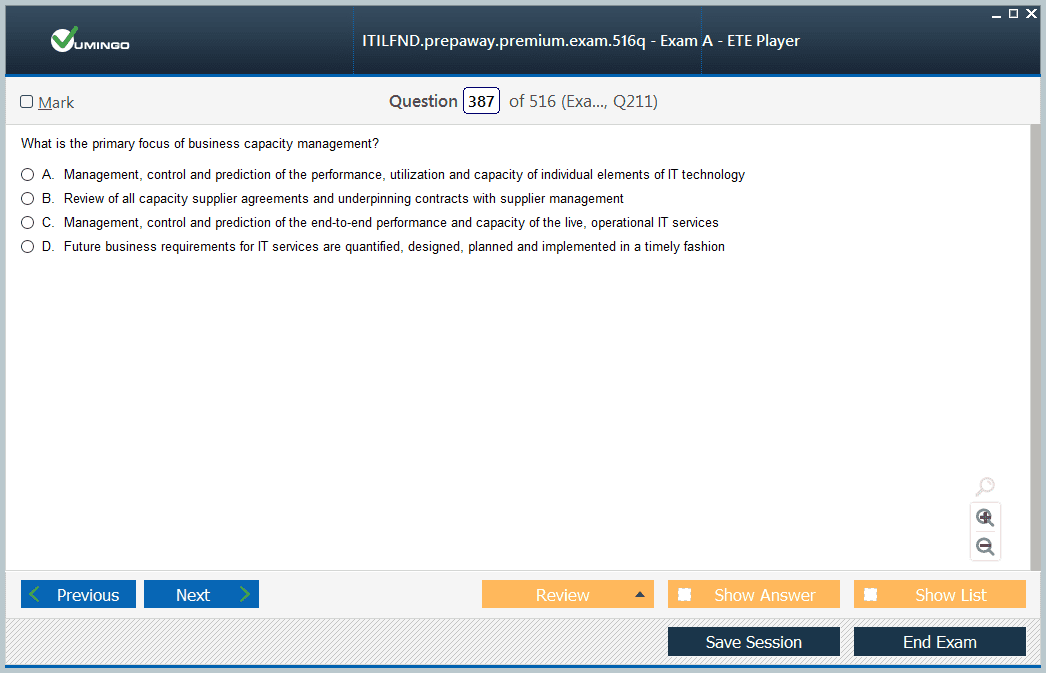
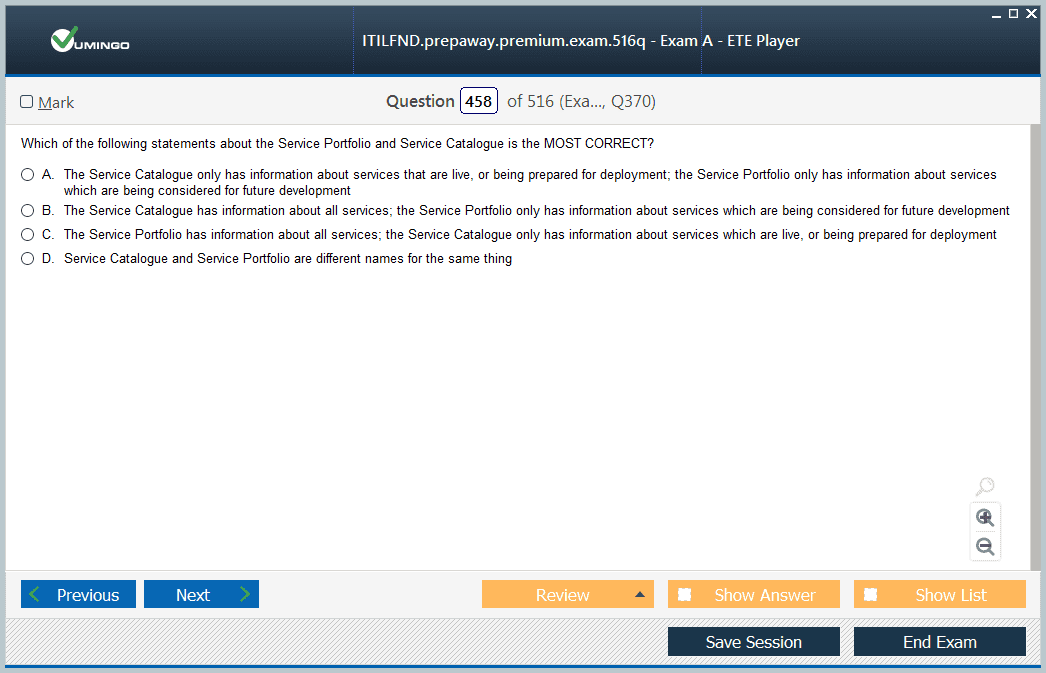
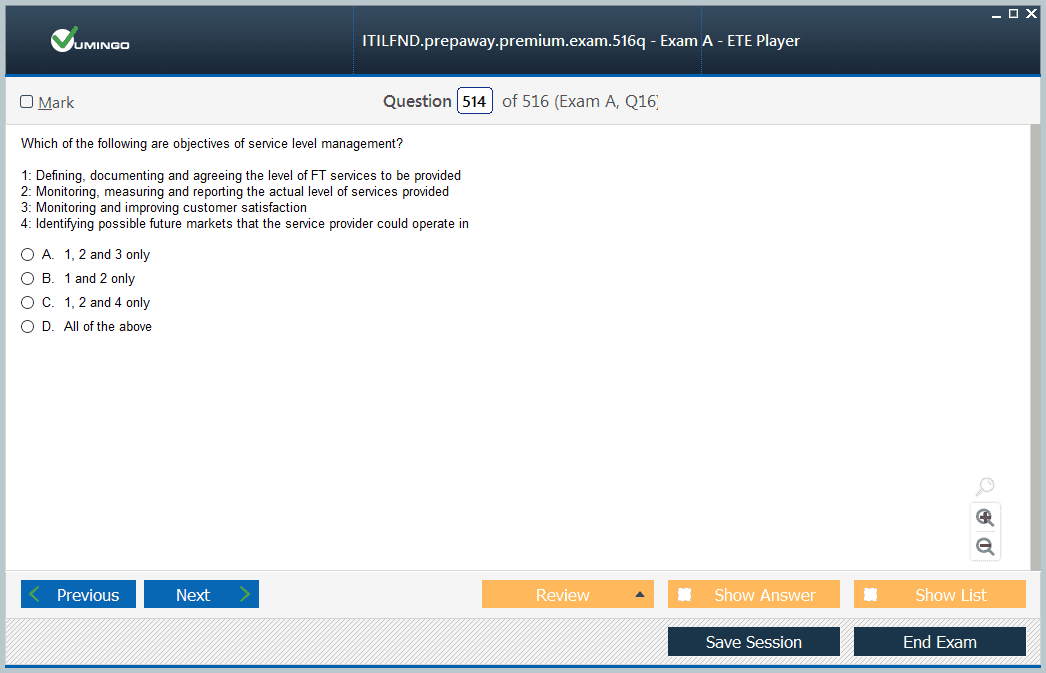








PS: those who’s gonna take the exam soon,pay attention to the guiding principles of ITIL, Service Management, and review concepts of DevOps, Agile, and Lean! I thought these won’t be tough but alas..