- Home
- iSQI Certifications
- CTAL-TA_Syll2012 ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level - Test Analyst [Syllabus 2012] Dumps
Pass iSQI CTAL-TA_Syll2012 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


CTAL-TA_Syll2012 Premium File
- Premium File 60 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Feb 11, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All iSQI CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level - Test Analyst [Syllabus 2012] practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Preparing for ISTQB Test Manager Certification with CTAL-TA_Syll2012
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification represents an advanced level credential for software testing professionals focused on test management. It builds upon foundational knowledge and equips candidates with the expertise required to manage testing projects effectively, align testing activities with organizational goals, and lead teams in delivering high-quality software. The certification is designed to validate skills in planning, monitoring, controlling, and improving test processes across different stages of the software development lifecycle. It is suitable for test managers, senior testers, and professionals aiming to transition into leadership roles within testing environments.
The certification examines not only theoretical knowledge but also the application of that knowledge in real-world scenarios. Candidates are assessed on their ability to develop test strategies, allocate resources efficiently, mitigate risks, and ensure that testing outcomes support both technical and business objectives. By achieving this certification, professionals demonstrate their capacity to handle complex projects, make informed decisions, and drive improvements in software quality management practices.
Exam Structure and Key Details
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 exam consists of 65 multiple-choice questions to be completed within 180 minutes. The passing threshold is 65%, reflecting the advanced nature of the exam. Questions are designed to evaluate candidates across multiple cognitive levels, from basic understanding to higher-order thinking such as analysis, evaluation, and application. Candidates are tested on their ability to integrate testing processes with project management practices, oversee team performance, and make strategic decisions that affect software quality outcomes.
The exam covers several domains including test planning, risk identification, test process monitoring, stakeholder communication, resource allocation, and defect management. It emphasizes real-world applicability, encouraging candidates to consider scenarios that test their ability to balance project constraints, technical challenges, and organizational priorities. The exam evaluates both technical proficiency and managerial skills, ensuring that certified professionals can effectively lead testing initiatives in diverse project environments.
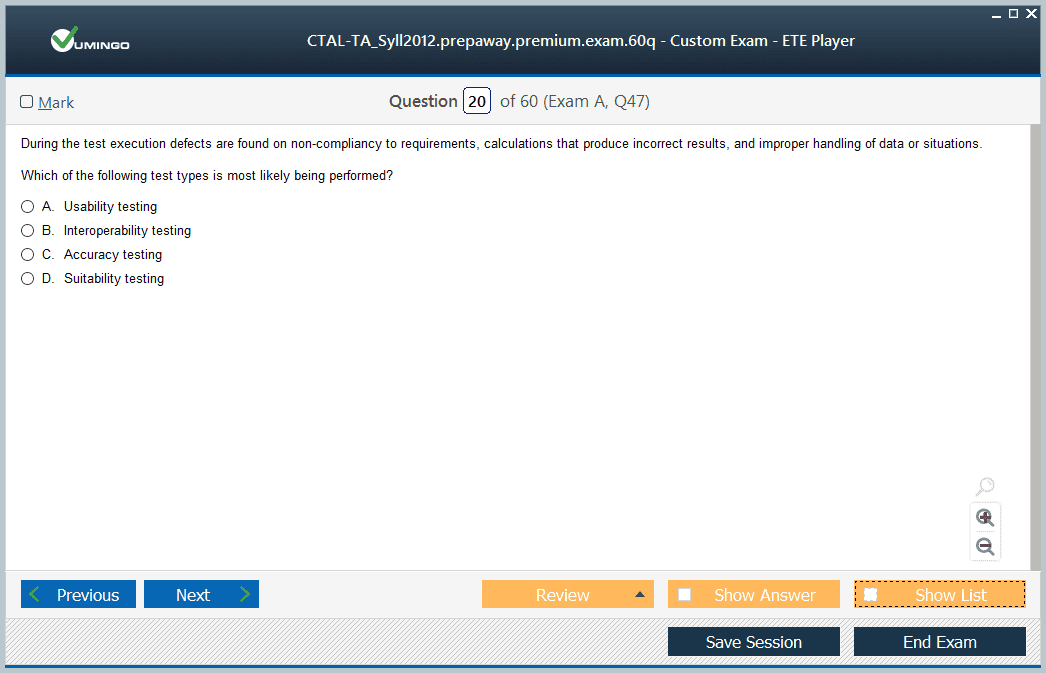
Preparation Strategies for CTAL-TA_Syll2012
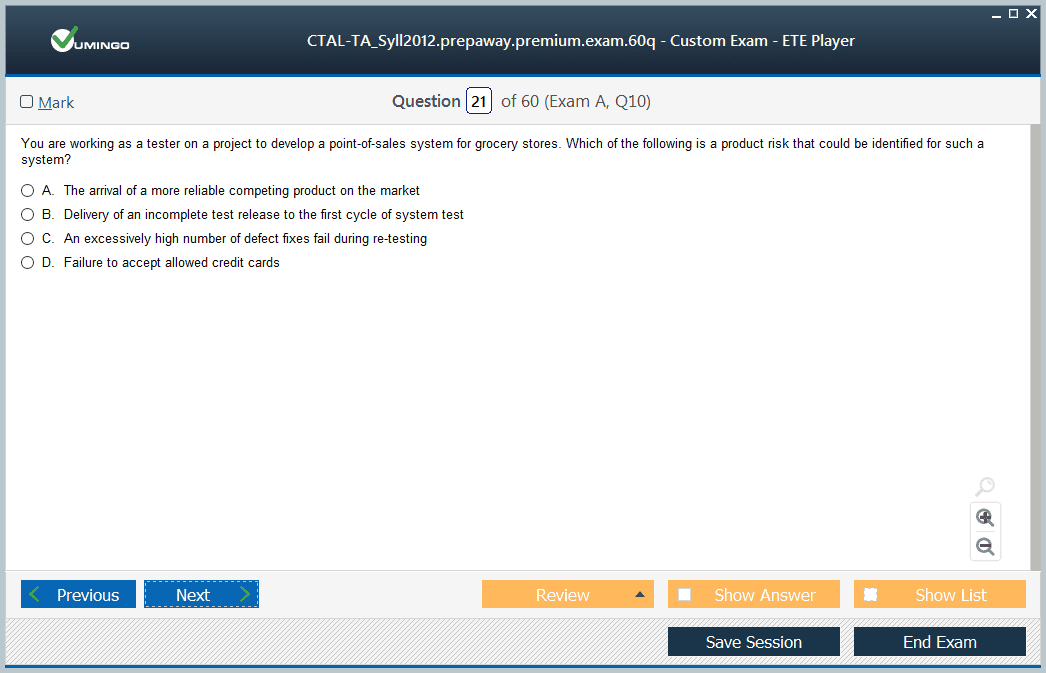
Preparation for the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification requires a combination of structured study and practical experience. Candidates should review the advanced syllabus in detail and ensure a solid understanding of each topic. Scenario-based exercises and case studies help bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. This approach enhances critical thinking and decision-making skills, which are essential for test managers.
Self-assessment plays a crucial role in preparation. Identifying areas of strength and weakness allows candidates to focus on topics that require deeper understanding. Key areas of study include test strategy formulation, risk management, team and resource management, defect lifecycle analysis, and process improvement techniques. Familiarity with organizational policies, project management principles, and quality assurance methodologies enhances the ability to handle complex testing scenarios effectively.
Core Topics and Syllabus Overview
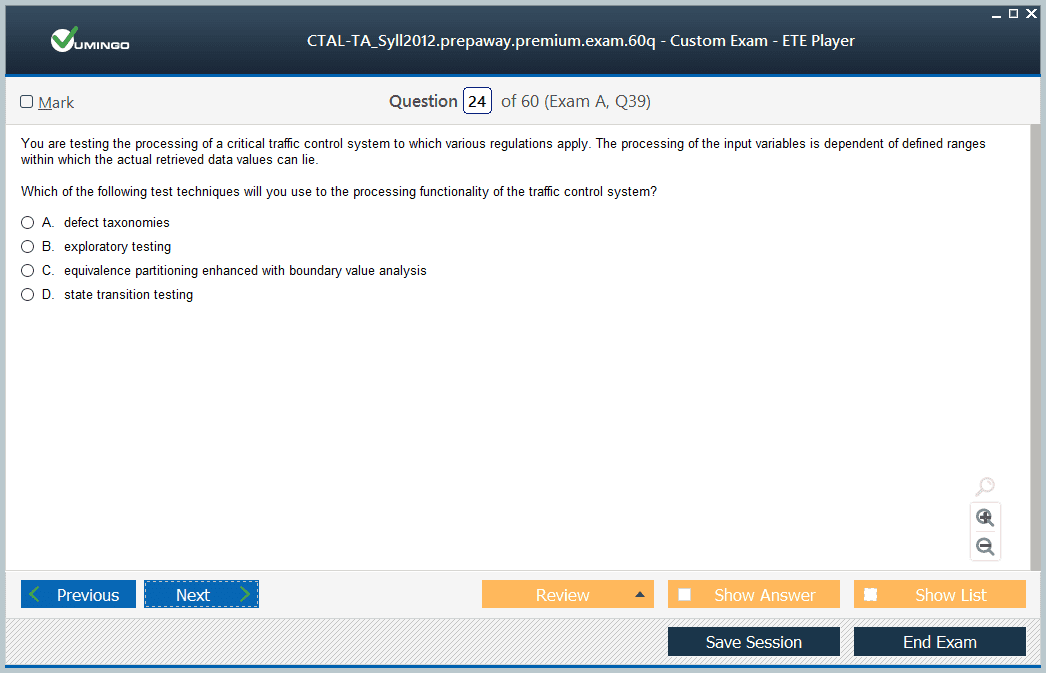
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 syllabus covers ten primary areas that define the competencies of an advanced test manager. These include management of testing projects, organization and identification of risks, creation and implementation of test plans, monitoring and controlling testing activities, reporting to stakeholders, identification of skills and team resources, planning for skill development, proposing business cases with cost-benefit analysis, facilitating communication within the team and stakeholders, and leading process improvement initiatives.
Each topic emphasizes practical application. For instance, risk-based decision-making requires understanding potential project pitfalls and developing mitigation strategies. Test planning focuses on creating comprehensive strategies that align with organizational objectives. Monitoring and control cover progress tracking, issue identification, and adjustment of plans based on project realities. Defect management now emphasizes using defect data to enhance processes and support continuous improvement, moving beyond traditional frameworks.
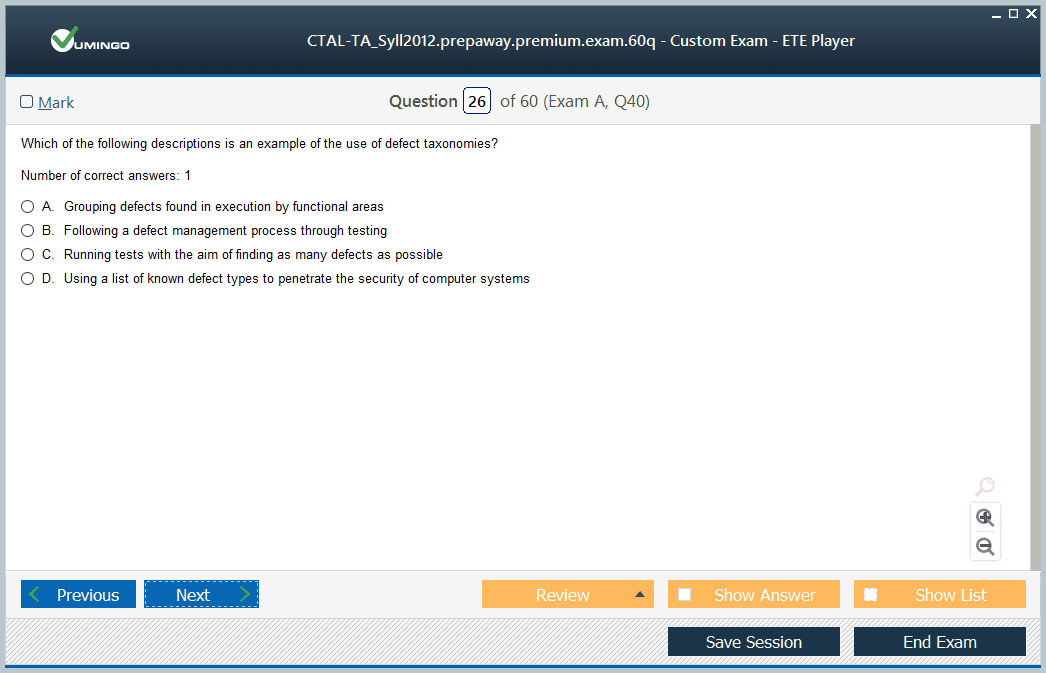
Advanced Practices and Practical Implementation
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes applying knowledge in realistic testing and management scenarios. Certified professionals are expected to lead teams effectively, allocate resources optimally, and communicate with multiple stakeholders. They must demonstrate the ability to analyze project risks, prioritize test activities, and implement strategies that ensure quality deliverables.
Advanced practices include continuous improvement initiatives, process optimization, and leveraging defect data for strategic decisions. Test managers are trained to oversee the integration of automated testing, monitor compliance with standards, and ensure alignment between testing processes and organizational goals. Emphasis is placed on leadership, communication, and analytical skills, enabling candidates to handle high-level responsibilities within testing teams and contribute to organizational success.
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification prepares professionals to transition from operational testing roles to strategic leadership positions, ensuring that they can manage complex testing environments, drive improvements, and achieve high-quality outcomes in software projects.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Test Manager
A test manager plays a crucial role in ensuring that software testing aligns with organizational goals and project requirements. The responsibilities encompass planning, organizing, leading, and controlling all testing activities within a project. Test managers are expected to define objectives, establish priorities, allocate resources, and ensure that testing teams follow standardized processes and best practices. Effective communication with stakeholders, including developers, project managers, and business analysts, is essential to convey testing progress, risks, and outcomes.
Strategic decision-making is a key component of the role. Test managers analyze project risks and determine mitigation strategies to reduce potential impacts on delivery and quality. They must assess team capabilities, identify skill gaps, and plan training or resource allocation accordingly. In addition, they are responsible for developing business cases that demonstrate the value of testing activities, balancing costs, and benefits to ensure that the testing process contributes positively to the overall project.
Test Planning and Strategy
Test planning forms the foundation of effective test management. Developing a test plan requires understanding the project objectives, scope, and constraints. The test manager ensures that all critical areas are covered, including functional and non-functional requirements, integration points, and system dependencies. A comprehensive test strategy identifies priorities, determines test levels, and selects appropriate techniques and tools to achieve testing goals efficiently.
Risk-based test planning is central to advanced test management. By evaluating potential risks related to functionality, performance, security, and usability, the test manager can focus efforts on the areas with the highest impact. This approach optimizes resource utilization and ensures that critical issues are identified and addressed early. Incorporating feedback loops and review checkpoints in the plan enables ongoing assessment of progress and adjustments to maintain alignment with project needs.
Monitoring and Controlling Test Activities
Monitoring and control are vital for maintaining quality and adhering to project timelines. Test managers implement processes to track test execution, detect deviations from the plan, and apply corrective actions when necessary. Metrics and indicators such as defect trends, test coverage, and execution progress provide insight into the effectiveness of testing activities. These measures support informed decision-making and highlight areas requiring attention or adjustment.
Effective monitoring also involves managing dependencies and mitigating risks that may arise during testing. Test managers ensure that teams remain coordinated, resources are available, and any issues affecting progress are resolved promptly. Regular reporting to stakeholders ensures transparency and facilitates early interventions, reducing the likelihood of delays or compromised quality.
Defect Management and Process Improvement
Defect management is a critical area for test managers. The focus has shifted from simply recording and tracking defects to using defect data to drive process improvement. Analyzing defect patterns and trends helps identify weaknesses in development and testing processes, enabling managers to implement targeted improvements. This approach supports the establishment of a continuous improvement cycle, enhancing product quality over time.
Advanced defect management practices include prioritization based on impact, root cause analysis, and feedback loops to inform development teams. By understanding the defect lifecycle and leveraging historical data, test managers can predict potential risks, allocate resources effectively, and improve testing efficiency. Integration of defect management with test planning and execution ensures that issues are addressed systematically, supporting project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
Communication and Leadership in Testing
Leadership and communication are essential for successful test management. Test managers must effectively communicate objectives, plans, and results to both their teams and stakeholders. Facilitating collaboration, resolving conflicts, and motivating team members are critical to maintaining productivity and achieving testing goals. A strong leadership presence ensures that testing activities are aligned with organizational strategy and project requirements.
Test managers are also responsible for advocating best practices, providing guidance, and mentoring team members. Encouraging knowledge sharing, continuous learning, and proactive problem-solving strengthens the testing function and enhances team performance. By fostering an environment of accountability and collaboration, test managers contribute to higher-quality outcomes and increased stakeholder confidence in the testing process.
Advanced Techniques and Tools for Test Management
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes the use of advanced techniques and tools to enhance testing efficiency and effectiveness. Test managers need to understand how to select and implement tools for test design, execution, automation, and reporting. Leveraging technology improves accuracy, reduces manual effort, and supports large-scale testing operations.
Automation tools play a significant role in reducing repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency, and enabling faster feedback cycles. Test managers must evaluate automation feasibility, select appropriate frameworks, and integrate automation into the overall test strategy. Additionally, tools for test data management, defect tracking, and reporting facilitate comprehensive oversight and informed decision-making. Proper utilization of these tools supports process improvement, risk mitigation, and efficient resource utilization.
Integration with Organizational Objectives
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification emphasizes aligning testing activities with organizational goals. Test managers are expected to ensure that testing contributes to business value, supports strategic initiatives, and enhances overall project success. This involves understanding project objectives, stakeholder expectations, and regulatory requirements, and integrating testing practices to meet these needs.
By connecting testing with organizational priorities, test managers provide measurable outcomes and demonstrate the impact of their work. This strategic perspective enables better resource allocation, improved decision-making, and increased recognition of testing as a critical component of project success. The certification ensures that candidates are equipped to manage testing not just as a technical function but as a strategic enabler of quality and value within software projects.
Continuous Improvement and Professional Growth
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 promotes continuous learning and process refinement. Test managers are encouraged to adopt practices that evaluate performance, identify improvement areas, and implement changes to enhance testing effectiveness. This approach ensures that teams remain adaptive, resilient, and capable of meeting evolving project demands.
Professional growth in test management involves staying updated with industry trends, emerging tools, and best practices. By mastering these skills, test managers not only improve project outcomes but also advance their careers. The certification validates expertise in managing complex testing projects, fostering leadership skills, and demonstrating a commitment to excellence in software quality management.
The comprehensive focus of the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 syllabus ensures that certified professionals are well-prepared to handle strategic, operational, and technical aspects of test management, enabling them to lead teams successfully and contribute significantly to software quality and organizational success.
Risk Management and Mitigation in Test Management
Effective test management requires a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact software quality and project timelines. Risk management involves evaluating potential technical, operational, and organizational challenges that may arise during the software development lifecycle. Test managers are responsible for creating risk assessment frameworks that prioritize areas of highest impact, allowing teams to focus their efforts efficiently.
Mitigation strategies are developed based on the identified risks and may include additional testing, resource reallocation, automation, or early engagement with development teams. By addressing risks proactively, test managers ensure that potential defects, delays, or performance issues are minimized. This strategic approach strengthens confidence in the project outcomes and supports decision-making for stakeholders at all levels.
Test Monitoring, Control, and Reporting
Monitoring and controlling test activities are essential to maintain alignment with project objectives and deadlines. Test managers track progress against the test plan, monitor resource utilization, and evaluate test execution effectiveness. Key performance indicators, such as defect discovery rate, test coverage, and execution progress, provide insights into testing quality and efficiency.
Control mechanisms include adjusting schedules, reallocating resources, and implementing additional quality checks where needed. Reporting is critical in this context, as it ensures transparency and informs stakeholders of current project status, risks, and mitigation measures. Clear, structured communication enables prompt decisions and interventions that support project success.
Test Process Improvement and Optimization
Continuous improvement is a cornerstone of advanced test management. Test managers analyze testing processes to identify inefficiencies and implement strategies for process optimization. Leveraging defect data, past project insights, and testing metrics, managers can enhance methodologies, reduce redundant activities, and improve overall testing effectiveness.
Optimization also involves introducing or refining automation, enhancing test planning and execution techniques, and ensuring that testing aligns with both technical and business objectives. Advanced test management requires the integration of lessons learned into future projects, ensuring that improvements are sustainable and contribute to long-term organizational quality goals.
Resource and Team Management
Managing people and resources is a fundamental responsibility for test managers. This includes identifying skill gaps within the team, providing guidance and mentoring, and allocating tasks according to expertise and workload. Proper resource planning ensures that the right skills are available at the right time, minimizing delays and improving testing outcomes.
Test managers also focus on team motivation, communication, and collaboration. By fostering a supportive and productive environment, managers can enhance engagement, reduce errors, and ensure that team members are aligned with project goals. Effective leadership strengthens the testing function and promotes a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
Strategic Alignment with Organizational Goals
Advanced test management goes beyond operational activities to ensure alignment with organizational strategy. Test managers are responsible for integrating testing into broader project objectives, demonstrating how testing contributes to business value, and ensuring that quality goals support overall organizational priorities.
This involves developing test strategies that reflect business needs, communicating the value of testing to stakeholders, and aligning test activities with organizational performance metrics. Strategic alignment ensures that testing is not just a technical task but a critical function that drives project success and customer satisfaction.
Advanced Test Techniques and Tool Utilization
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes the use of advanced test techniques and tools to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of testing processes. Test managers should be skilled in selecting and implementing tools for test design, execution, automation, and reporting. Effective use of technology supports scalability, consistency, and faster feedback loops within the testing process.
Automation tools play a significant role in reducing repetitive tasks, increasing accuracy, and supporting regression and performance testing. Managers must evaluate the suitability of automation frameworks, integrate them with manual testing processes, and ensure that automation contributes to strategic project goals. Additionally, tools for defect tracking, test data management, and reporting improve oversight and facilitate informed decision-making.
Leadership and Decision-Making in Test Management
Strong leadership and decision-making skills are essential for advanced test managers. They are required to make informed decisions about test strategies, risk prioritization, and resource allocation while maintaining transparency with stakeholders. Leadership involves guiding teams, resolving conflicts, and fostering collaboration across multidisciplinary teams to achieve high-quality software outcomes.
Decision-making extends to evaluating testing techniques, selecting appropriate tools, and ensuring that testing aligns with both project and organizational objectives. Effective test managers balance technical knowledge with strategic insight, enabling them to lead complex projects successfully and deliver value to the organization.
Defect Management and Quality Assurance
Defect management in advanced test management focuses on leveraging defect data to improve processes and product quality. Test managers analyze defect patterns, identify root causes, and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence. This approach ensures that defects are addressed systematically, contributing to overall software reliability and stakeholder confidence.
Quality assurance activities are integrated into all stages of the project, ensuring that standards are met and continuous improvement is supported. Test managers play a critical role in defining quality metrics, monitoring compliance, and recommending process enhancements based on empirical data.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification emphasizes the importance of continuous learning for test managers. Staying updated with industry trends, emerging technologies, and evolving testing methodologies is crucial for maintaining expertise and leading teams effectively.
Professional development includes adopting best practices, attending training sessions, and applying lessons learned to improve both individual and team performance. Continuous learning ensures that test managers remain effective in dynamic project environments and are prepared to handle complex challenges, ultimately driving the success of software testing initiatives.
Advanced Test Management
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 equips professionals with the skills to manage testing processes strategically, lead teams efficiently, and ensure alignment with organizational objectives. It emphasizes risk management, process improvement, resource optimization, and leadership, preparing candidates to deliver high-quality software while supporting business goals. Certified professionals are expected to make informed decisions, implement best practices, and continuously enhance testing practices to achieve optimal outcomes in complex project environments.
Advanced Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
In CTAL-TA_Syll2012, understanding and mitigating risks is one of the core responsibilities of a test manager. Test managers need to identify potential project, technical, and business risks that could impact software quality, delivery timelines, and overall project objectives. This requires a systematic approach to assess likelihood, impact, and potential mitigation strategies for each identified risk.
By applying quantitative and qualitative risk assessment methods, test managers can prioritize testing activities and allocate resources effectively. This proactive approach ensures that critical areas of the application are thoroughly tested, reducing the probability of defects reaching production. Additionally, risk assessment provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of potential threats and the strategies in place to manage them.
Resource Management and Team Leadership
Managing resources effectively is crucial for successful test management. Test managers are responsible for assigning tasks based on team members’ skills and experience, monitoring workload distribution, and ensuring that deadlines are met without compromising quality. They must also address skill gaps by implementing training programs and mentoring initiatives to enhance team competency.
Leadership in test management goes beyond task allocation. It involves motivating teams, fostering collaboration, resolving conflicts, and promoting a culture of accountability. A well-led team can adapt to changes in requirements, handle high-pressure situations, and deliver consistent results. Strong leadership ensures that the team remains focused on achieving both testing and project objectives.
Test Planning, Execution, and Reporting
Comprehensive test planning is essential for the success of any testing initiative. CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes creating detailed test plans that outline objectives, scope, test techniques, resource requirements, schedules, and reporting mechanisms. Effective planning provides a roadmap for executing testing activities efficiently and ensures that all critical aspects of the software are evaluated.
Execution of the test plan requires close monitoring of progress, defect detection, and adherence to predefined quality standards. Test managers must adjust the plan dynamically based on project developments, risk assessments, and testing outcomes. Reporting mechanisms, including metrics and dashboards, provide real-time visibility into testing progress, defect status, and overall quality, enabling informed decision-making by stakeholders.
Defect Management and Process Optimization
Defect management is a cornerstone of advanced test management. Test managers establish processes for defect identification, tracking, classification, and resolution. They also analyze defect patterns to identify recurring issues, root causes, and areas for process improvement.
Integrating defect management with continuous process optimization ensures that lessons learned from each project are applied to future testing efforts. By analyzing defect data, test managers can refine test strategies, enhance test coverage, and implement preventive measures to minimize defects in subsequent releases. This approach improves overall software quality and reduces costs associated with post-release defects.
Metrics-Driven Test Management
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes the use of metrics to assess testing effectiveness and efficiency. Test managers monitor key indicators such as test coverage, defect density, defect detection rate, and resource utilization. These metrics provide actionable insights into the performance of testing activities and allow managers to make informed adjustments to improve outcomes.
Metrics also enable test managers to demonstrate the value of testing to stakeholders, providing evidence of testing effectiveness and project risk mitigation. By leveraging data-driven insights, managers can optimize resource allocation, enhance test processes, and ensure that testing contributes strategically to project success.
Non-Functional Testing and Quality Assurance
Non-functional testing is a critical component of the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 syllabus. Test managers oversee performance, security, reliability, maintainability, and usability testing to ensure that software meets user expectations and organizational standards.
Planning non-functional testing involves analyzing requirements, selecting appropriate test techniques, and integrating them into the overall test strategy. Effective management ensures that software not only meets functional specifications but also performs reliably under various conditions, providing a positive user experience.
Continuous Improvement and Strategic Value
Advanced test management requires a focus on continuous improvement. Test managers analyze past projects, defect trends, and testing processes to identify areas for enhancement. Implementing process improvements ensures that testing becomes more efficient, effective, and aligned with organizational goals.
Strategic test management goes beyond operational execution. Test managers contribute to decision-making, provide insights for project planning, and ensure that testing activities support broader business objectives. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations benefit from higher software quality, reduced risks, and enhanced project outcomes.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication is essential for the success of a test manager. CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes clear, concise, and transparent communication with stakeholders, including project managers, developers, business analysts, and clients. This ensures alignment on testing objectives, progress, risks, and results.
Engaging stakeholders proactively helps in managing expectations, addressing concerns, and securing necessary resources. Test managers must balance technical reporting with strategic insights, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions about project priorities, risk management, and quality assurance.
Automation Strategy and Tool Utilization
Test managers in advanced roles leverage automation tools to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and coverage. CTAL-TA_Syll2012 focuses on the strategic selection and implementation of test automation tools based on project needs, complexity, and objectives.
Automation enables repetitive tasks, regression testing, performance evaluation, and continuous integration testing to be executed efficiently. Test managers must assess the cost-benefit of automation, design maintainable scripts, and ensure seamless integration with development pipelines. Proper utilization of tools strengthens testing capabilities and supports the delivery of high-quality software.
Leading Change and Organizational Influence
A key aspect of CTAL-TA_Syll2012 is the test manager’s role in driving organizational change and promoting a culture of quality. Test managers influence process improvements, encourage adoption of best practices, and support knowledge sharing across teams.
By leading change effectively, test managers ensure that testing practices evolve with organizational goals, technology advancements, and industry standards. Their leadership ensures sustainable improvement, better project outcomes, and increased recognition of testing as a strategic function within the organization.
Strategic Planning and Test Governance
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification emphasizes the critical role of strategic planning and governance in effective test management. Beyond simply executing tests, a certified test manager must develop a comprehensive strategy that aligns testing objectives with overall organizational goals. This involves establishing clear governance frameworks that define responsibilities, outline standards, and ensure compliance with industry best practices throughout the software development lifecycle. Governance in test management is not a one-time activity; it requires continuous oversight, monitoring, and evaluation to ensure that all testing activities contribute to the project’s success.
Strategic planning includes anticipating project risks, forecasting potential obstacles, and determining resource requirements well before testing begins. By developing a detailed roadmap, test managers can ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, priorities are balanced appropriately, and critical software components receive adequate coverage. Strategic planning also involves defining key performance indicators that measure the effectiveness of testing activities and track progress against project goals. Proper governance ensures transparency in operations, maintains stakeholder confidence, and provides a structured framework for decision-making during complex projects.
In addition to risk anticipation and resource alignment, strategic planning requires establishing policies that govern test execution, monitoring compliance, and ensuring that deviations from the plan are detected early. Test managers are tasked with aligning testing practices with the organizational culture, ensuring that quality is embedded in both development and operational processes. This proactive approach prevents bottlenecks, minimizes rework, and supports continuous delivery of high-quality software products.
Resource Allocation and Optimization
Resource allocation in advanced test management goes beyond simple task assignment. It requires a nuanced understanding of team dynamics, skill sets, and project demands. Test managers must evaluate the competencies of individual team members, identify skill gaps, and assign responsibilities that maximize efficiency and effectiveness. This includes monitoring workload distribution and adjusting assignments in response to evolving project requirements.
Optimization of resources also involves ensuring that the team remains engaged and productive. Providing targeted training, mentoring, and support allows testers to strengthen their capabilities and perform at their best. Effective resource management ensures that testing objectives are achieved within set timelines without compromising quality. It also enables managers to adapt quickly to changes, manage unforeseen challenges, and maintain team morale.
Advanced resource planning requires balancing short-term project demands with long-term team development goals. Test managers must anticipate future skills requirements, plan for cross-training opportunities, and ensure that team members are prepared to meet upcoming challenges. This strategic allocation and optimization of resources directly impacts testing efficiency, risk mitigation, and the overall success of the project.
Test Lifecycle Management
Test lifecycle management is a core competency assessed by CTAL-TA_Syll2012. It encompasses all phases of testing, from planning and design to execution, monitoring, and closure. Effective test lifecycle management ensures that testing activities are systematically aligned with project milestones and objectives, allowing for efficient use of resources and thorough evaluation of software quality.
Defining clear entry and exit criteria, establishing measurable milestones, and monitoring progress throughout the lifecycle are essential to maintaining control and accountability. Continuous evaluation allows test managers to identify issues early, implement corrective actions, and adjust testing plans dynamically in response to changes in project scope or risks. Holistic management of the test lifecycle ensures that testing contributes meaningfully to project outcomes, mitigates risks, and maintains high-quality standards across all development phases.
Lifecycle management also includes managing dependencies between testing activities and other project functions such as development, deployment, and operations. Integrating testing within the broader project lifecycle promotes early detection of defects, reduces rework, and enhances overall project efficiency. Test managers must ensure that all phases of testing are properly documented, communicated, and reviewed to maintain alignment with project goals and regulatory requirements.
Risk-Based Test Strategy
Developing a risk-based test strategy is a fundamental skill for advanced test managers. This approach prioritizes testing efforts based on the likelihood and impact of potential risks to software quality. By focusing resources on high-risk areas, test managers can maximize defect detection, improve resource efficiency, and provide greater assurance of software reliability.
Risk-based strategies involve identifying potential threats, assessing their probability and severity, and making informed decisions on testing priorities. Both qualitative and quantitative risk assessment methods are employed to evaluate technical, operational, and business risks associated with the software. Effective communication of risk assessments to stakeholders ensures that priorities are understood and that testing activities are aligned with organizational risk tolerance.
A successful risk-based approach also includes continuous reassessment of risks throughout the project lifecycle. Changes in requirements, system architecture, or business priorities can alter risk profiles, and test managers must adjust strategies accordingly. This dynamic and proactive approach to testing ensures that efforts are directed where they are most needed, reducing the likelihood of critical defects reaching production environments.
Metrics and Reporting for Decision Making
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 highlights the importance of metrics and reporting as essential tools for decision-making in test management. Test managers must establish meaningful key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress, and analyze trends in defect detection, test coverage, and resource utilization. These metrics provide actionable insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of testing activities.
Comprehensive reporting allows managers to communicate the status of testing efforts to stakeholders, including project managers, developers, and business leaders. Transparent and timely reporting supports informed decision-making, identifies areas for improvement, and justifies the allocation of resources. Metrics also serve as benchmarks for continuous process improvement, helping managers refine strategies and optimize testing outcomes.
Effective use of metrics requires not only data collection but also interpretation and analysis. Test managers must identify patterns, understand root causes of issues, and develop corrective actions. By integrating metrics into strategic planning, managers can enhance test effectiveness, demonstrate value to stakeholders, and maintain alignment with organizational objectives.
Test Process Improvement
Continuous process improvement is central to advanced test management. Test managers assess past projects, identify recurring issues, and implement changes to enhance the quality and efficiency of testing activities. Process improvement initiatives may involve refining test techniques, updating test documentation, integrating new tools, or adopting innovative methodologies.
Institutionalizing lessons learned from prior projects ensures that best practices are embedded within the organization. Process improvement not only enhances test quality but also reduces defects, shortens testing cycles, and increases stakeholder confidence in software deliverables. Advanced test managers promote a culture of quality, encouraging teams to adopt systematic approaches and continuously seek opportunities for improvement.
Improving the testing process also involves evaluating the effectiveness of test automation, reviewing test coverage, and optimizing test execution strategies. By integrating feedback loops and performance evaluations, test managers ensure that process improvements lead to measurable benefits and sustained enhancements in testing practices.
Communication and Stakeholder Collaboration
Effective communication is crucial for aligning testing activities with project objectives and stakeholder expectations. Test managers must clearly convey goals, risks, and progress to a wide range of stakeholders, including developers, project managers, business analysts, and clients. Transparent communication fosters trust, supports collaborative problem-solving, and ensures that testing contributes to overall project success.
Stakeholder engagement involves regular updates, proactive discussions about risks and issues, and alignment on priorities. Test managers must facilitate cross-functional collaboration, ensuring that all parties understand the implications of testing decisions and the status of software quality. Effective communication enhances decision-making, reduces misunderstandings, and strengthens relationships between testing teams and stakeholders.
Automation Strategy and Implementation
Advanced test managers are responsible for integrating automation strategically into the testing process. This involves evaluating which components are suitable for automation, selecting appropriate tools, and developing maintainable automated test scripts. Automation supports regression testing, performance evaluation, and continuous integration, allowing for rapid and reliable test execution.
Balancing automation benefits against costs and complexity is critical. Test managers must ensure that automation initiatives align with project objectives and deliver measurable improvements in efficiency, coverage, and defect detection. Continuous monitoring and refinement of automated tests are necessary to maintain effectiveness and accommodate changes in software design and requirements.
Quality Assurance and Non-Functional Testing
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 emphasizes non-functional testing as a key responsibility of test managers. This includes evaluating performance, security, reliability, maintainability, and usability. Test managers plan, oversee, and assess these aspects to ensure software meets organizational standards and user expectations.
Non-functional testing requires careful analysis of system requirements, selection of appropriate methodologies, and integration with the overall test strategy. Effective management ensures comprehensive evaluation of both functional and non-functional attributes, contributing to software quality and end-user satisfaction. Test managers also need to prioritize non-functional testing based on risk, criticality, and business impact.
Leadership and Organizational Influence
Test managers are expected to provide leadership beyond project execution. They drive quality initiatives, advocate best practices, and influence organizational processes to foster continuous improvement. Strong leadership ensures that testing remains a strategic function and that teams are motivated and aligned with organizational goals.
Leadership includes mentoring team members, facilitating knowledge sharing, and promoting a culture of quality. Test managers shape organizational attitudes toward testing, encourage innovation, and influence decision-making processes to integrate quality considerations at every stage of software development.
CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification equips test managers with advanced competencies to oversee complex projects, optimize resources, manage risks, and implement effective quality assurance practices. By combining technical expertise, strategic planning, leadership, and continuous improvement, certified test managers ensure that testing activities provide tangible value to organizations. They leverage structured processes, data-driven insights, and proactive stakeholder engagement to deliver high-quality software, minimize project risks, and enhance overall organizational performance. Certified managers play a pivotal role in shaping testing practices, fostering team excellence, and driving continuous enhancement of software quality.
Conclusion
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification represents a comprehensive approach to advanced test management, emphasizing not only technical proficiency but also strategic oversight, leadership, and organizational influence. Achieving this certification demonstrates that a test manager possesses the depth of knowledge and practical skills required to plan, execute, and govern complex testing activities in alignment with organizational goals. It validates the professional’s ability to integrate testing seamlessly into the software development lifecycle while ensuring quality, efficiency, and risk mitigation at all stages.
A central aspect of the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification is its focus on strategic planning and test governance. Advanced test managers are expected to define testing objectives that directly support business goals, establish governance frameworks to regulate processes, and consistently monitor adherence to standards and best practices. Governance is not simply about compliance; it is about ensuring transparency, accountability, and structured decision-making throughout the project. Test managers are tasked with establishing clear roles and responsibilities, maintaining oversight of testing activities, and providing stakeholders with visibility into testing progress and results. By implementing robust governance frameworks, test managers can anticipate risks, allocate resources efficiently, and maintain quality standards throughout the software lifecycle.
Strategic planning extends beyond immediate project execution and requires a forward-looking approach. Test managers must anticipate potential challenges, assess the impact of risks, and develop detailed plans that align testing resources and priorities with project objectives. Effective strategic planning enables test managers to balance short-term operational needs with long-term organizational goals, ensuring that testing efforts are focused on critical areas of the software that carry the highest risk or business impact. By establishing measurable objectives, defining success criteria, and developing comprehensive testing roadmaps, test managers can optimize the allocation of effort and resources while maintaining a clear focus on outcomes that matter most to the organization.
Resource allocation and optimization are critical competencies emphasized in the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 framework. Test managers are responsible for assigning tasks not only based on project requirements but also considering team capabilities, skill levels, and workload distribution. Efficient resource management requires continuous evaluation of team performance, identification of skill gaps, and proactive development of personnel through training or mentoring. Optimizing resources ensures that testing objectives are met without compromising quality or timeline, while also promoting team morale and engagement. This balanced approach allows managers to respond dynamically to changing project demands and ensures that both individual and collective skills are effectively leveraged for project success.
Test lifecycle management is another core area highlighted by the certification. Advanced test managers must oversee all phases of testing, from planning and design through execution and closure, ensuring that testing activities are aligned with overall project timelines and objectives. Managing the test lifecycle involves defining entry and exit criteria, establishing testing milestones, monitoring progress, and making timely adjustments in response to emerging issues. Effective lifecycle management ensures that testing contributes meaningfully to risk mitigation, quality assurance, and project success. It requires coordination with development teams, stakeholders, and other functions to ensure seamless integration and comprehensive coverage of functional and non-functional requirements.
Risk-based test strategy is a fundamental skill assessed by the certification. Test managers are expected to identify potential threats to software quality, evaluate their likelihood and impact, and prioritize testing efforts accordingly. This approach ensures that high-risk areas receive the most attention, maximizing defect detection and optimizing resource utilization. Risk assessment involves both qualitative and quantitative analysis, providing a robust basis for decision-making and enabling managers to communicate risk priorities effectively to stakeholders. Dynamic reassessment of risks throughout the project ensures that testing strategies remain relevant and that resources are directed where they can deliver the greatest impact.
Metrics and reporting are essential tools for informed decision-making in advanced test management. Test managers must establish key performance indicators, track execution progress, and analyze trends in defects, coverage, and resource utilization. Data-driven reporting allows managers to communicate progress, risks, and results clearly to stakeholders, facilitating alignment and informed decision-making. By leveraging metrics, managers can continuously improve processes, refine strategies, and demonstrate the value of testing activities to the organization. Metrics also provide a basis for evaluating the effectiveness of both manual and automated testing efforts, ensuring that testing practices are efficient, reliable, and aligned with business priorities.
Continuous process improvement is a core tenet of CTAL-TA_Syll2012. Test managers are expected to learn from previous projects, identify recurring issues, and implement changes to enhance testing effectiveness. This involves refining methodologies, updating templates and documentation, integrating innovative tools, and embedding lessons learned into organizational practices. Process improvement ensures that testing practices remain efficient, scalable, and adaptable to evolving project and organizational requirements. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and quality enhancement, test managers contribute to long-term excellence in software testing and overall organizational performance.
Communication and stakeholder collaboration are integral to advanced test management. Test managers must clearly convey testing goals, progress, risks, and outcomes to all relevant parties. Effective communication ensures alignment on project objectives, facilitates proactive problem-solving, and fosters collaboration among development teams, business analysts, project managers, and clients. Stakeholder engagement includes transparent reporting, regular updates, and active participation in discussions to ensure that testing efforts support broader organizational goals. Open channels of communication build trust, enhance decision-making, and create a shared understanding of quality expectations across the project lifecycle.
Automation strategy and implementation are increasingly critical in modern testing environments. Test managers must assess the suitability of automation for specific components, select appropriate tools, and ensure that automated test scripts are maintainable and effective. Automation supports regression testing, continuous integration, and rapid feedback loops, improving efficiency and reducing time-to-market. Advanced test managers balance the costs and benefits of automation, ensure proper tool utilization, and continuously monitor the effectiveness of automated testing to achieve optimal results.
Non-functional testing and quality assurance are core areas of responsibility. Test managers oversee testing for performance, security, reliability, maintainability, and usability. These aspects ensure that software meets user expectations and adheres to organizational standards. Non-functional testing requires careful planning, selection of appropriate methods, and integration with functional testing efforts. Advanced managers prioritize non-functional testing based on risk, criticality, and business impact, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of software quality across all dimensions.
Leadership and organizational influence distinguish advanced test managers from others. They are expected to drive quality initiatives, advocate for best practices, mentor teams, and shape organizational processes to foster continuous improvement. Effective leadership promotes collaboration, ensures alignment of testing with business objectives, and establishes a culture of quality within the organization. Test managers influence decision-making, champion innovative practices, and ensure that testing evolves alongside technological advancements and business needs.
Overall, CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification equips test managers with the expertise, strategic insight, and leadership skills required to oversee complex testing projects. It ensures that testing activities are executed efficiently, risks are mitigated proactively, resources are optimized, and quality objectives are consistently achieved. Certified test managers leverage structured methodologies, data-driven insights, and stakeholder collaboration to deliver high-quality software, support organizational performance, and foster continuous improvement in testing practices. The certification validates a professional’s ability to integrate strategic planning, risk management, process optimization, and leadership into a cohesive framework that delivers measurable value and drives organizational success.
This extensive framework makes CTAL-TA_Syll2012 not only a certification but a benchmark of professional excellence in test management. Test managers who achieve this credential are recognized for their comprehensive knowledge, practical skills, and ability to lead testing initiatives that impact software quality and organizational outcomes positively.
iSQI CTAL-TA_Syll2012 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass CTAL-TA_Syll2012 ISTQB Certified Tester Advanced Level - Test Analyst [Syllabus 2012] certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the iSQI certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the iSQI certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 preparation materials for the iSQI certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The CTAL-TA_Syll2012 materials for the iSQI certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my iSQI certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for CTAL-TA_Syll2012. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my CTAL-TA_Syll2012 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my iSQI certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the CTAL-TA_Syll2012 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed CTAL-TA_Syll2012 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!