- Home
- Scrum Certifications
- PSM I Professional Scrum Master I Dumps
Pass Scrum PSM I Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


PSM I Premium Bundle
- Premium File 255 Questions & Answers. Last update: Jan 20, 2026
- Training Course 30 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 98 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All Scrum PSM I certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the PSM I Professional Scrum Master I practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
PSM I Scrum Certification Journey: Key Lessons, Tips, and Best Practices
The Professional Scrum Master I certification is a globally recognized credential that validates your knowledge and skills in Scrum. For many professionals, earning the PSM I certification marks an important milestone in their Agile journey. Scrum is one of the most widely used frameworks for Agile project management, emphasizing collaboration, iterative development, and delivering value in short cycles. By obtaining this certification, individuals not only demonstrate their understanding of Scrum principles but also enhance their credibility in managing teams, facilitating Scrum events, and implementing Scrum practices in real-world projects.
This certification is designed for professionals at various stages of their careers, from those just starting in Agile to experienced practitioners looking to formalize their knowledge. While some certifications require mandatory training, the PSM I offers the flexibility to prepare independently, allowing candidates to study at their own pace. This flexibility makes the certification accessible to professionals worldwide who are motivated to master Scrum concepts and apply them effectively in their organizations. We will explore the significance of the PSM I certification, its structure, preparation strategies, and essential resources to help candidates approach the exam with confidence.
Why the PSM I Certification Matters
The PSM I certification is widely recognized and valued by organizations globally. Earning this certification signals a solid understanding of Scrum principles and demonstrates the ability to apply them in various project scenarios. Professionals with this certification are often considered for roles such as Scrum Master, Agile Coach, or Product Owner. These roles require a deep understanding of team dynamics, Scrum events, and artifacts to ensure efficient project delivery.
Beyond career advancement, preparing for the PSM I exam helps professionals gain a comprehensive understanding of Scrum principles. The knowledge acquired is applicable in daily team operations, from conducting effective sprint planning to facilitating productive retrospectives. Candidates also develop the ability to handle real-world challenges, such as managing stakeholder expectations, resolving team conflicts, and maintaining transparency within the Scrum framework.
The certification also reflects a commitment to continuous learning and professional development. Organizations increasingly value employees who actively pursue recognized certifications, as they demonstrate dedication to adopting best practices and improving project outcomes.
Eligibility and Exam Overview
One of the advantages of the PSM I certification is its accessible eligibility requirements. There is no prerequisite training, although candidates are expected to have a solid understanding of the Scrum Guide. This guide serves as the foundation for all exam content, covering the Scrum framework, its roles, events, artifacts, and associated principles. Familiarity with the Scrum Guide is crucial for successfully navigating exam questions and understanding practical applications of Scrum practices.
The PSM I exam is structured as an online assessment consisting of 80 multiple-choice or true/false questions. Candidates have 60 minutes to complete the exam, and a score of 85% or higher is required to pass. The exam can be taken from anywhere, allowing professionals to choose a comfortable environment that supports focused thinking and minimal distractions. Once the exam is purchased, it does not expire, providing flexibility in scheduling the attempt.
The online format is convenient but requires self-discipline. Candidates must manage their time effectively, maintain focus, and understand how to approach questions strategically. Familiarity with the exam structure and question types is a key component of preparation.
Preparing for the PSM I Certification
Effective preparation for the PSM I exam involves a structured approach that combines reading, practice assessments, and optional training resources. The first step is a thorough review of the Scrum Guide, which provides a concise but comprehensive overview of the framework. Reading the guide multiple times helps candidates internalize key concepts, understand Scrum roles, and become familiar with essential terminology.
Taking notes while reviewing the Scrum Guide is a helpful practice. Candidates should jot down unfamiliar terms, important definitions, and practical examples. This process reinforces learning and creates a reference material for later review. Notes also assist in retaining information and quickly revisiting complex concepts when needed.
Practice assessments are another critical component of preparation. Scrum.org provides open assessments that simulate the exam environment and allow candidates to test their knowledge under timed conditions. Regularly taking these assessments helps identify areas of weakness and strengthens understanding of Scrum principles. Consistent practice can also increase confidence and reduce anxiety on the day of the exam.
Study Strategies for Success
Successful PSM I candidates often use a combination of techniques to prepare efficiently. Structured study sessions with a clear plan can help ensure consistent progress. Allocating specific daily or weekly study periods allows candidates to cover all aspects of the Scrum Guide without feeling overwhelmed. Breaking down study sessions into smaller sections, such as focusing on roles one day and events the next, can improve retention and comprehension.
Using practical examples and real-world scenarios enhances understanding. For instance, candidates can consider how Scrum events like sprint planning or retrospectives function in their current workplace. Visualizing these processes in context makes theoretical concepts more concrete and easier to remember during the exam.
Flashcards are another useful tool. They help reinforce key concepts, definitions, and Scrum terminology. Candidates can review flashcards daily, which aids in memorization and improves recall. Additionally, discussing Scrum principles with peers or participating in online forums can provide new perspectives and clarify doubts. Engaging in discussions also reinforces knowledge and exposes candidates to different approaches to applying Scrum.
Training Resources and Tools
While formal training is optional, several online resources can significantly enhance preparation. Udemy courses, for example, provide structured lessons that include video lectures, practice questions, and case studies. These courses are designed to complement the Scrum Guide and offer insights into real-world Scrum applications. Candidates can use these resources to deepen their understanding of complex concepts and practice answering questions similar to those on the exam.
Scrum Open Assessments remain a core tool for exam preparation. They allow candidates to experience the format, question types, and timing constraints of the actual exam. Analyzing the explanations for incorrect answers is critical for understanding the reasoning behind correct solutions. This reflective approach ensures that mistakes become learning opportunities, reinforcing knowledge and improving problem-solving skills.
In addition to online courses and open assessments, candidates can benefit from discussion groups, study communities, and webinars. Engaging with others who are preparing for the exam provides support, motivation, and practical insights. Sharing experiences and strategies can help candidates identify effective study techniques and avoid common pitfalls.
Personal Insights and Lessons Learned
From my preparation journey, several key lessons emerged. First, consistent effort is more important than cramming. Studying a little each day builds steady knowledge retention and reduces stress. Second, practice is crucial. Taking multiple open assessments not only tests knowledge but also helps candidates become comfortable with exam timing and question formats.
Using two monitors during practice was particularly helpful. One screen allowed me to take practice assessments, while the other provided quick access to notes and reference material. This approach improved efficiency, enabling me to cross-check concepts and clarify doubts in real time.
Time management during the exam is essential. It is important to move past difficult questions, make an informed guess, and return later if time permits. This strategy ensures that all questions are addressed and prevents spending too much time on a single challenging question. Staying calm and confident throughout the exam also contributes significantly to success. Understanding that a perfect score is not required helps reduce pressure and allows candidates to focus on applying their knowledge effectively.
Key Concepts to Focus On
To excel in the PSM I exam, candidates must focus on understanding core Scrum concepts rather than memorizing details. These include the definition of Scrum as a lightweight framework designed to deliver value through adaptive solutions, the five Scrum values that guide team behavior, and the principles of empiricism and lean thinking that underpin Scrum practices.
Scrum roles are fundamental to exam success. Candidates should understand the responsibilities of the Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Developers. The Scrum Master facilitates events, removes impediments, and supports the team in achieving its goals. The Product Owner is responsible for managing the Product Backlog and maximizing product value. Developers are accountable for delivering high-quality increments, planning work, and collaborating effectively to meet sprint objectives.
Understanding Scrum events is also essential. Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective each serve a specific purpose within the Scrum framework. Candidates should be able to explain the objectives of each event, the participants involved, and the expected outcomes.
Scrum artifacts, including the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment, along with their respective commitments, form another critical area of focus. Candidates should understand the purpose of each artifact, how they are maintained, and how they contribute to transparency, focus, and progress measurement.
Applying Knowledge to the Exam
When preparing for the exam, it is important to approach questions analytically. Understanding the “why” behind each concept is more valuable than memorizing definitions. Practice assessments are useful for applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, reinforcing comprehension, and developing problem-solving strategies.
Time management is key during the exam. Candidates should pace themselves, allocate time for reviewing difficult questions, and avoid rushing. Staying calm and maintaining focus helps in selecting the most accurate answers. Remember, the goal is to achieve the passing score, not perfection, which allows candidates to approach the exam with confidence and clarity.
Enhancing Exam Readiness
To enhance readiness, candidates should regularly review the Scrum Guide, practice assessments, and notes. Repeated exposure to questions and scenarios builds familiarity and improves the ability to recall information quickly. Engaging in discussions with peers or mentors can also help clarify doubts and deepen understanding of complex concepts.
Creating a study plan that covers all aspects of Scrum ensures balanced preparation. Allocating time for roles, events, artifacts, and exam-focused concepts prevents gaps in knowledge. Combining reading, practice, and discussion provides a comprehensive approach that maximizes the likelihood of passing the exam.
Understanding Scrum Roles
Scrum defines three essential roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Developers. Each role has distinct responsibilities, and understanding these differences is vital for both the exam and practical application.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is a facilitator, coach, and servant leader for the Scrum Team. Their primary responsibility is to ensure that Scrum practices are understood and followed. This includes coaching team members in self-management and cross-functionality, helping the team focus on high-value work, and removing obstacles that may impede progress.
Scrum Masters also serve the Product Owner by assisting with effective backlog management, facilitating clear communication of goals, and ensuring empirical product planning in complex environments. In addition, they support the organization by promoting Scrum adoption, guiding teams, and removing barriers between teams and stakeholders.
A key point to understand for the exam is that the Scrum Master is not a traditional manager. They do not assign tasks or control team members. Instead, they empower the team to self-organize, make decisions, and deliver value independently.
Product Owner
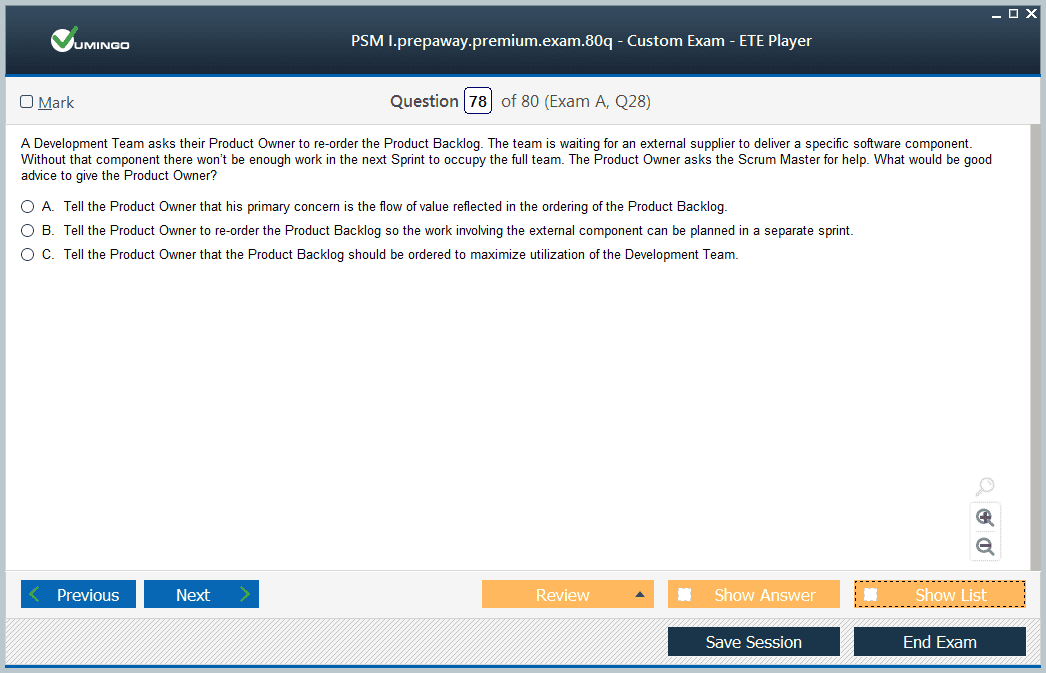
The Product Owner is responsible for maximizing the value of the product resulting from the Scrum Team’s work. This includes managing the Product Backlog, clearly defining product goals, creating and prioritizing backlog items, and ensuring transparency for all stakeholders.
The Product Owner may delegate certain tasks but remains accountable for the overall outcomes. They act as the voice of stakeholders, balancing requirements and priorities to ensure that the team delivers the most valuable increments. Candidates should understand that a Product Owner is a single individual, not a committee, and that collaboration with the Scrum Master and Developers is essential for success.
Developers
Developers are the members responsible for delivering potentially shippable increments during each sprint. They collaborate on planning the sprint, creating the Sprint Backlog, ensuring quality according to the Definition of Done, and adapting daily to achieve sprint goals.
Developers are self-organizing, which means they collectively decide how to accomplish the work rather than having tasks assigned by others. Each Developer does not need to possess all skills individually, but the team collectively must have the capabilities necessary to deliver the product increment.
Developers are also accountable for estimating work, managing risks, resolving conflicts, and maintaining quality standards. This role emphasizes collaboration, accountability, and professionalism within the Scrum Team.
Detailed Overview of Scrum Events
Scrum events provide structure and consistency to the workflow. Each event has a specific purpose, expected participants, and a time-boxed duration. Mastery of these events is crucial for both the exam and effective Scrum practice.
Sprint
The Sprint is the core time-boxed iteration in Scrum, typically lasting one month or less. It provides a consistent rhythm for planning, delivering, and reviewing work. Every sprint begins immediately after the conclusion of the previous one, ensuring continuous progress.
During the sprint, no changes should endanger the Sprint Goal, and quality must be maintained. The Product Backlog can be refined as needed, and scope adjustments are possible through negotiation with the Product Owner. Only the Product Owner has the authority to cancel a sprint, which is rare and typically occurs when the sprint goal becomes obsolete.
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning defines what will be delivered during the sprint and how it will be achieved. The event addresses three key questions: why the sprint is valuable, what can be done during the sprint, and how the work will be completed.
The Sprint Goal, selected Product Backlog items, and the plan for delivering them together form the Sprint Backlog. Sprint Planning is time-boxed to eight hours for a one-month sprint, with shorter durations for shorter sprints. Candidates should understand that planning is a collaborative effort involving the entire Scrum Team.
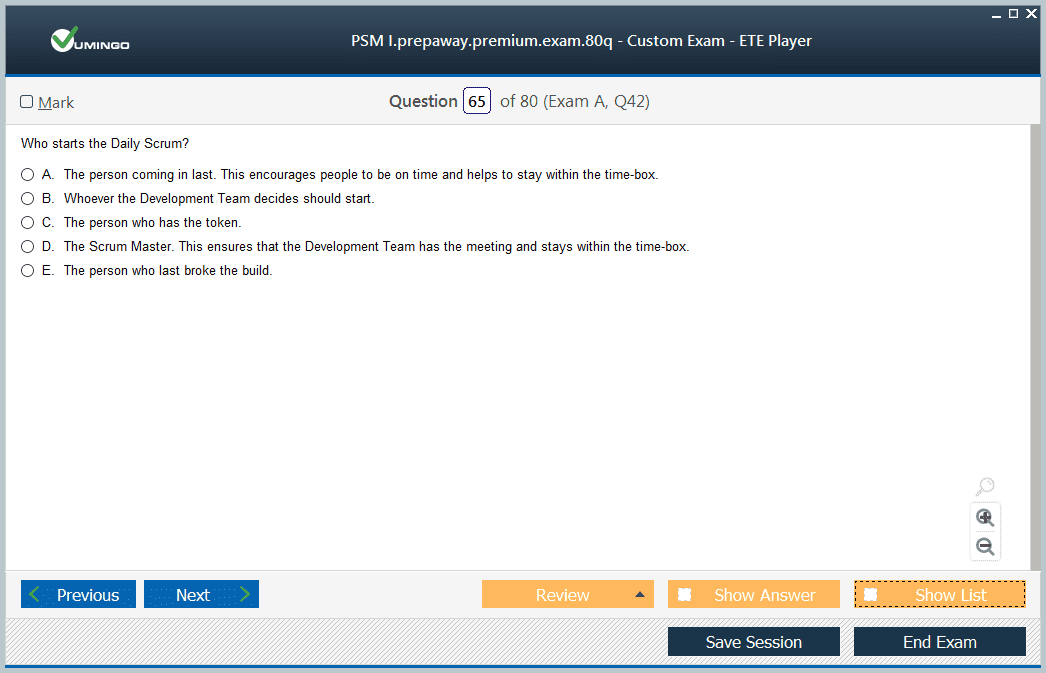
Daily Scrum
The Daily Scrum is a 15-minute event for inspecting progress toward the Sprint Goal and adapting the Sprint Backlog as necessary. Developers determine the best time for this meeting, while the Scrum Master ensures regularity and consistency.
The structure of the Daily Scrum is flexible, allowing teams to use any format or techniques that enhance focus and self-management. Participation by Product Owners or Scrum Masters occurs only if they are actively working on sprint items. The purpose is to create transparency, promote accountability, and facilitate adaptive planning.
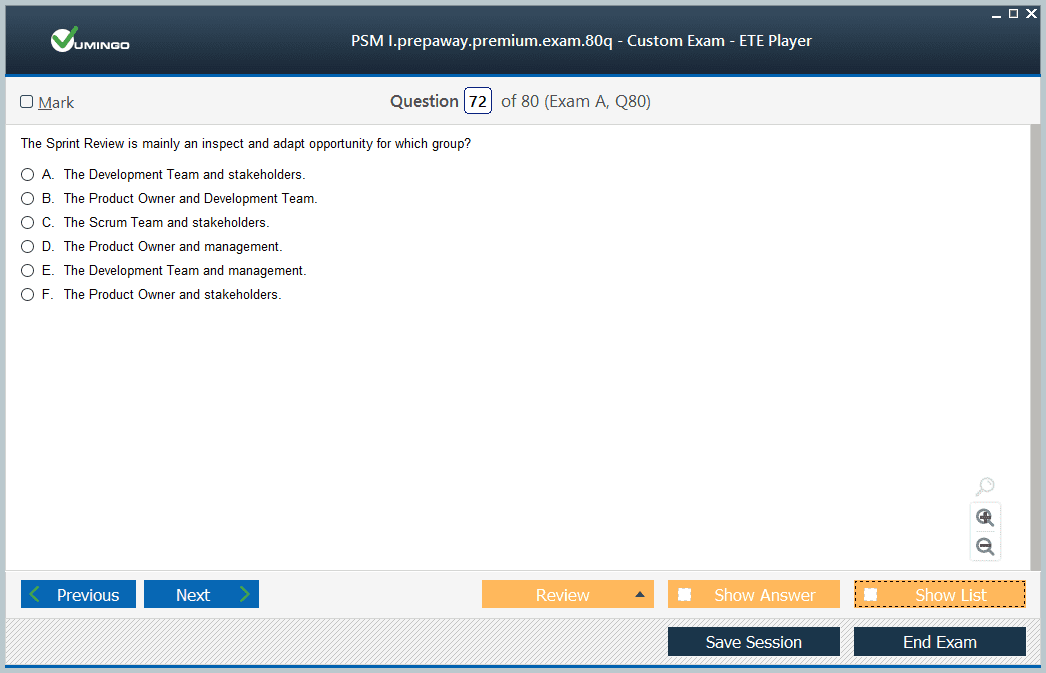
Sprint Review
The Sprint Review inspects the outcome of the sprint and identifies potential adaptations for future work. The Scrum Team collaborates with stakeholders to review completed work, assess changes in the environment, and adjust the Product Backlog as necessary.
This event is time-boxed to four hours for a one-month sprint, shorter for shorter sprints. Candidates should recognize that the Sprint Review focuses on product inspection and feedback, not formal approval or project closure.
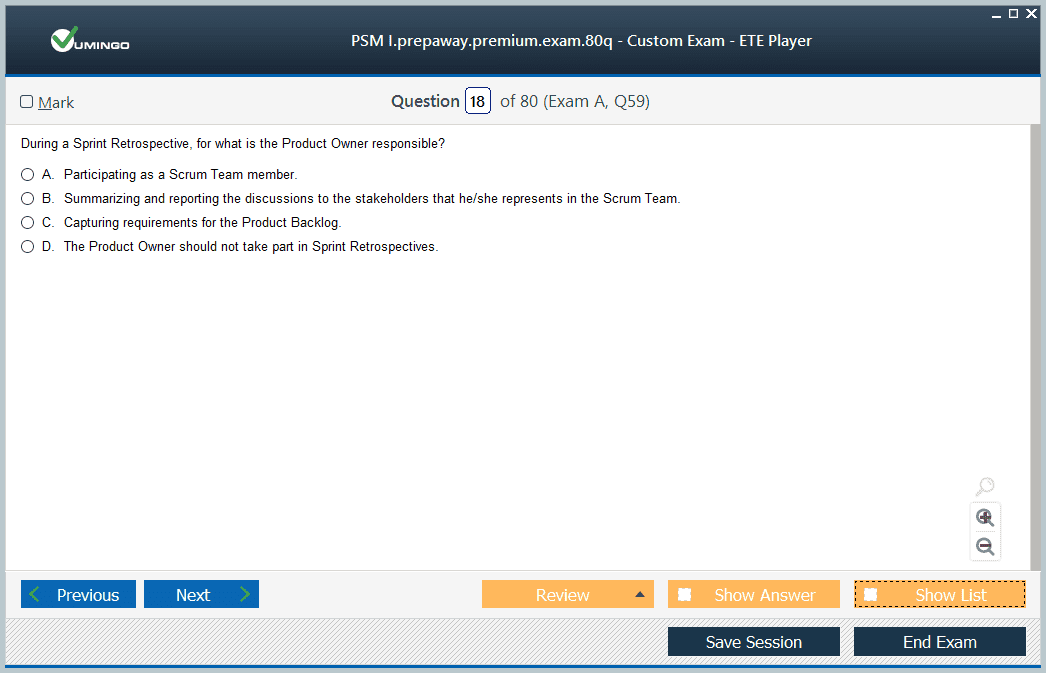
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective concludes the sprint by reflecting on processes, interactions, and outcomes. The Scrum Team identifies improvements to increase effectiveness in future sprints.
Time-boxed to three hours for a one-month sprint, the retrospective emphasizes continuous improvement. Teams may include identified changes in the next sprint backlog, ensuring iterative enhancement of workflows and collaboration.
Understanding Scrum Artifacts
Scrum artifacts provide transparency, focus, and measurement against progress. Each artifact has an associated commitment to ensure its effectiveness.
Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is an ordered, emergent list of items needed to improve the product. It evolves as new requirements, opportunities, or market changes arise. The Product Goal serves as the commitment for the Product Backlog, guiding planning and decision-making.
Sprint Backlog
The Sprint Backlog includes the Sprint Goal, selected Product Backlog items, and an actionable plan to deliver the increment. It evolves throughout the sprint as more information is learned, allowing teams to inspect and adapt their progress in real time.
Increment
The Increment represents a concrete step toward the Product Goal, combining all completed backlog items that meet the Definition of Done. Each increment must be potentially releasable, providing measurable value to stakeholders.
Definition of Done
The Definition of Done is a formal description of the state of an increment when it meets required quality standards. It ensures transparency and shared understanding within the team. Any backlog item that does not meet the Definition of Done cannot be considered complete and may be returned for further refinement.
Understanding these artifacts, their commitments, and their role in creating transparency and focus is essential for exam success.
Integrating Roles, Events, and Artifacts
A key part of mastering Scrum is understanding how roles, events, and artifacts interact. The Scrum Team works together to plan sprints, execute work, and deliver increments of value. The Scrum Master facilitates, the Product Owner guides prioritization, and Developers implement and adapt plans. Events structure the workflow, while artifacts provide transparency and measurable progress.
Exam questions often focus on scenarios that test understanding of these interactions. Candidates should practice applying Scrum theory to practical situations, such as handling scope changes, managing team conflicts, or adjusting sprint priorities. This approach ensures readiness for both the exam and real-world application.
Preparing for Exam Scenarios
Beyond memorizing definitions, candidates must be able to analyze situations and apply Scrum principles appropriately. Practice assessments are valuable for simulating such scenarios. Candidates should focus on the reasoning behind answers, not just the correct choice. Reviewing wrong answers and identifying knowledge gaps strengthens understanding and prepares candidates for complex questions.
Time management, calmness under pressure, and familiarity with Scrum terminology contribute to exam success. It is important to pace oneself, make informed decisions, and use strategic approaches for challenging questions.
Practical Tips for Deep Understanding
To fully grasp Scrum concepts, candidates should consider practical application in their work or projects. Participating in Scrum events, facilitating backlog refinement, or simulating sprint planning exercises can provide real experience. Using tools such as task boards, burndown charts, and backlog management software helps solidify theoretical knowledge through practical implementation.
Engaging with peers, mentors, or online communities can also provide alternative perspectives, clarify doubts, and reinforce learning. Discussion-based learning complements individual study and exposes candidates to different interpretations of Scrum principles.
Study Techniques for Exam Mastery
Organizing a comprehensive study plan is essential. Candidates should allocate time for reading the Scrum Guide, practicing assessments, and revising key concepts. Breaking down topics into manageable sections, such as focusing on one role, event, or artifact per session, ensures balanced coverage.
Using visual aids, flowcharts, and diagrams can enhance retention and comprehension. Recording questions from practice tests and reviewing them periodically helps maintain familiarity with exam-style scenarios. Consistent review and reflection on learning progress are key to retaining knowledge and boosting confidence before the exam.
Setting Up for Exam Success
Preparation for the PSM I exam begins with creating a conducive study environment. A quiet, distraction-free space is essential for focus during both study sessions and the actual exam. Candidates may also benefit from using two monitors: one for accessing the exam and another for referencing the Scrum Guide or notes. This setup allows for efficient navigation and quick verification of concepts without disrupting concentration.
Time management is a critical factor. With 80 questions to answer in 60 minutes, candidates must allocate less than a minute per question on average. Practicing under timed conditions familiarizes candidates with the pace required and reduces anxiety on exam day. Developing a personal strategy for handling challenging questions, such as marking them for review and returning later, ensures all questions receive attention without consuming excessive time.
Staying calm and maintaining confidence is equally important. Understanding that a score of 85% is sufficient to pass reduces pressure and encourages candidates to focus on applying knowledge rather than striving for perfection. Mindfulness techniques, short breaks during study sessions, and adequate rest before the exam contribute to optimal performance.
Practice Assessments and Mock Exams
Practice assessments are among the most effective preparation tools for the PSM I exam. Scrum.org offers open assessments that mirror the structure and question types of the actual exam. Regularly taking these assessments helps candidates identify knowledge gaps, test understanding of key concepts, and build confidence.
Analyzing mistakes is crucial. For every incorrect answer, candidates should review the related section of the Scrum Guide and understand why the correct answer is preferred. This reflective approach converts errors into learning opportunities and ensures a deeper understanding of Scrum principles.
Mock exams can simulate real testing conditions, including time constraints and question sequencing. Treating these assessments seriously, as if taking the actual exam, helps candidates manage time, reduce stress, and develop a strategic approach to answering questions. Repeating mock exams until high scores are consistently achieved is a proven technique for improving performance.
Exam Strategy and Question Handling
The PSM I exam presents a combination of multiple-choice and true/false questions, some of which may be scenario-based. Candidates should approach each question methodically. Reading questions carefully, identifying keywords, and understanding the context are essential steps.
For complex or unfamiliar questions, a practical strategy is to select the most reasonable answer, mark the question for review, and continue with others. This prevents time from being consumed disproportionately by a single question. Once all questions have been addressed, candidates can return to the marked items with remaining time.
It is important to avoid overthinking or second-guessing answers. The Scrum Guide provides clear guidance for most questions, and relying on studied principles often leads to the correct choice. Confidence in preparation and familiarity with Scrum terminology and practices are key to effective decision-making under exam conditions.
Managing Time During the Exam
Time management is one of the biggest challenges for candidates. With an average of 45 seconds per question, pacing is essential. Candidates should quickly assess question difficulty, answer straightforward items immediately, and allocate extra time for more challenging questions.
Using the navigation tools provided by the exam platform can enhance efficiency. Candidates can jump directly to specific questions, skip difficult items temporarily, and revisit them strategically. Maintaining a steady pace throughout the exam reduces the risk of rushing toward the end and ensures all questions are addressed.
Focus Areas for Exam Preparation
Certain concepts are emphasized in the PSM I exam and should receive focused attention. Understanding Scrum values, including commitment, focus, openness, respect, and courage, is fundamental. These values underpin team behavior and decision-making in practical scenarios.
Candidates should also be comfortable with Scrum theory, including empiricism and lean thinking. Understanding how these principles guide decision-making and adaptive planning is essential for answering scenario-based questions.
Scrum roles require detailed knowledge. Candidates must know the responsibilities of Scrum Masters, Product Owners, and Developers, their interactions, and their accountabilities. Similarly, mastery of Scrum events, including Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, is crucial. Candidates should understand the purpose, timing, participants, and expected outcomes of each event.
Scrum artifacts are another key focus area. Candidates must be able to explain the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment, and Definition of Done, along with their commitments. Understanding how artifacts provide transparency, track progress, and support decision-making is critical for both exam and real-world application.
Real-World Application of Scrum Principles
Passing the PSM I exam is not solely about theoretical knowledge. Applying Scrum principles in professional environments reinforces understanding and prepares candidates for practical challenges. Participating in Scrum events, facilitating backlog refinement, and collaborating on sprint planning exercises provide hands-on experience.
Teams can use visual management tools, such as task boards, burndown charts, or Kanban boards, to track progress and visualize workflow. These tools enhance transparency and help team members stay aligned with sprint objectives. By applying Scrum in real-world contexts, candidates can observe how principles translate into actionable practices, improving both learning and team outcomes.
Handling Common Scrum Scenarios
During both preparation and real-world application, candidates may encounter common challenges. Managing scope changes, addressing team conflicts, and adapting to evolving requirements are frequent situations. Understanding the Scrum framework provides structured approaches to handle these challenges effectively.
For example, if a change arises during a sprint that threatens the Sprint Goal, the Product Owner evaluates its impact and negotiates adjustments with the team. Developers adapt their plan, while the Scrum Master ensures the process remains smooth and impediments are addressed. Candidates should be familiar with such scenarios, as exam questions often mirror these real-world situations.
Study Techniques for Effective Retention
Active engagement with study materials enhances retention. Techniques such as summarizing the Scrum Guide in personal words, creating mind maps, or developing flashcards can reinforce knowledge. Reviewing notes regularly and revisiting challenging concepts strengthens memory and understanding.
Collaborative learning also adds value. Discussing concepts with peers, mentors, or online study groups provides alternative perspectives, clarifies doubts, and deepens comprehension. Candidates can simulate Scrum events, role-play scenarios, or analyze case studies to enhance practical understanding and reinforce theoretical knowledge.
Building Confidence Through Practice
Confidence is a key factor in exam success. Repeated practice, whether through open assessments, mock exams, or scenario-based exercises, builds familiarity and reduces anxiety. Candidates should aim to consistently achieve high scores in practice tests before attempting the actual exam.
Reflecting on progress, identifying weak areas, and systematically addressing them ensures readiness. Candidates who combine practice with active learning techniques and practical application are more likely to perform well under exam conditions.
Leveraging Online Resources
The internet offers a wealth of resources for PSM I preparation. Video tutorials, practice quizzes, discussion forums, and study guides provide diverse learning opportunities. Udemy courses, for instance, offer structured lessons with practice questions and real-world examples. Candidates can use these resources to reinforce learning, clarify difficult concepts, and explore different approaches to Scrum implementation.
Participating in online communities allows candidates to engage with peers worldwide, share experiences, ask questions, and access advice from certified professionals. This interaction broadens understanding, exposes candidates to varied perspectives, and provides practical insights that complement formal study materials.
Maintaining a Consistent Study Routine
Consistency is vital for mastering Scrum principles. Candidates should establish a regular study schedule, allocating dedicated time each day or week for reading, practice, and review. Breaking down topics into smaller sections, such as focusing on a specific role, event, or artifact in each session, ensures comprehensive coverage.
Tracking progress, setting milestones, and periodically assessing understanding help maintain motivation and accountability. Incorporating review sessions into the routine reinforces memory and strengthens confidence.
Applying Scrum Beyond the Exam
Earning the PSM I certification opens doors to applying Scrum in real-world projects. Knowledge of Scrum roles, events, and artifacts enables professionals to facilitate effective sprint planning, manage backlogs efficiently, and deliver high-quality increments.
In practice, certified professionals can guide teams toward self-organization, continuous improvement, and collaborative problem-solving. They contribute to creating high-performing Agile teams capable of adapting to changing requirements and delivering value consistently. By integrating Scrum principles into daily workflows, professionals ensure that certification knowledge translates into tangible organizational benefits.
Exam-Day Preparation Tips
On the day of the exam, preparation extends beyond technical knowledge. Candidates should ensure a stable internet connection, a quiet environment, and readiness to reference materials efficiently if needed. A brief review of notes and key concepts before starting helps refresh memory and focus attention.
Managing stress and maintaining calm is critical. Candidates should approach questions methodically, trust their preparation, and use the navigation and review features of the exam platform strategically. Allocating time for each question, prioritizing easier items first, and returning to challenging ones ensures complete coverage and reduces the risk of errors due to rushed answers.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Certain mistakes can undermine exam performance. Over-reliance on memorization rather than understanding, neglecting practice assessments, or failing to manage time effectively are common pitfalls. Candidates should focus on comprehension, repeated practice, and strategic question handling.
Another potential issue is neglecting scenario-based questions. These require applying Scrum principles to real-world situations rather than simply recalling definitions. Engaging in practical exercises, case studies, and discussion forums can help candidates develop the analytical skills needed for these questions.
Conclusion
Earning the PSM I certification is a rewarding milestone that validates both your understanding of Scrum principles and your ability to apply them in practical settings. Success requires a combination of thorough study, consistent practice, and strategic preparation. By mastering Scrum roles, events, and artifacts, and by understanding how they interact in real-world scenarios, candidates not only enhance their exam readiness but also improve their effectiveness as Agile practitioners.
Key takeaways for achieving the PSM I certification include staying confident, regularly practicing with assessments and mock exams, focusing on understanding rather than memorization, and applying Scrum principles in daily work. Leveraging study resources, maintaining a structured preparation routine, and engaging with the Scrum community further strengthen knowledge and build real-world competence.
Ultimately, the PSM I certification is more than an exam—it is an investment in your Agile career. With dedication, practice, and a clear grasp of Scrum theory and practice, passing the PSM I exam is entirely achievable, opening doors to new opportunities and enabling you to drive value and collaboration in your organization.
Scrum PSM I practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass PSM I Professional Scrum Master I certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
Purchase PSM I Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Scrum certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the PSM I test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Scrum certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the PSM I exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the PSM I preparation materials for the Scrum certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The PSM I materials for the Scrum certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the PSM I exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Scrum certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for PSM I. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the PSM I stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my PSM I certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Scrum certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the PSM I were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed PSM I successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!