- Home
- PMI Certifications
- PgMP Program Management Professional Dumps
Pass PMI PgMP Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


PgMP Premium Bundle
- Premium File 623 Questions & Answers. Last update: Feb 04, 2026
- Training Course 58 Video Lectures
- Study Guide 300 Pages
Last Week Results!

Includes question types found on the actual exam such as drag and drop, simulation, type-in and fill-in-the-blank.

Based on real-life scenarios similar to those encountered in the exam, allowing you to learn by working with real equipment.

Developed by IT experts who have passed the exam in the past. Covers in-depth knowledge required for exam preparation.
All PMI PgMP certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the PgMP Program Management Professional practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
PgMP Demystified: Unlocking the Secrets to Program Management Success
The Program Management Professional (PgMP) is a certification that recognizes advanced experience and competency in managing complex programs. It is designed for professionals who oversee multiple related projects that must be coordinated to achieve outcomes that are not attainable if the projects were managed independently. Individuals who pursue this certification typically have significant experience in program management and are responsible for aligning projects with strategic organizational objectives.
A PgMP-certified professional demonstrates the ability to manage resources, risks, and stakeholders across a program, ensuring that the overall initiative delivers maximum value. The certification is awarded through a structured process that includes a detailed application review and a comprehensive exam that tests knowledge, skills, and practical application in program management.
Eligibility and Prerequisites
Candidates for the PgMP exam must possess substantial experience in managing programs. This includes having a record of overseeing multiple projects and achieving outcomes that contribute to strategic goals. Applicants are expected to demonstrate the ability to coordinate cross-functional teams, allocate resources efficiently, and manage program risks.
The eligibility process involves a review of the candidate's professional experience and an assessment of their ability to perform program management responsibilities effectively. The exam evaluates the candidate’s understanding of program management principles, methodologies, and frameworks, as well as their practical application in real-world scenarios.
Program Management Fundamentals
Program management involves managing multiple interrelated projects to achieve benefits that could not be realized by managing each project separately. The program manager must focus on strategic alignment, ensuring that all projects within the program contribute to the organization's overarching objectives. This includes defining program objectives, prioritizing initiatives, and overseeing the integration of individual projects to achieve synergy and efficiency.
Program managers must have a comprehensive understanding of project interdependencies, resource allocation, risk management, and stakeholder engagement. They are responsible for balancing short-term project deliverables with long-term program goals, ensuring that outcomes contribute to organizational success.
Advantages of PgMP Certification
Obtaining the PgMP certification provides several advantages for professionals in program management. It demonstrates advanced knowledge, leadership capabilities, and the ability to handle complex, multi-project environments. Certified program managers are recognized for their strategic decision-making skills and ability to deliver programs that drive organizational value.
One major advantage is enhanced career recognition. Holding the certification signifies a high level of expertise, making individuals more competitive for senior management roles. Certified program managers are also more likely to be entrusted with high-impact initiatives and strategic programs, reflecting their ability to manage complexity effectively.
Resource Management and Optimization
Effective resource management is a core aspect of program management. PgMP-certified professionals are skilled at planning, allocating, and optimizing resources across multiple projects. They assess the resource needs of each project, identify potential conflicts, and implement strategies to ensure that resources are utilized efficiently.
Program managers can allocate resources dynamically, adjusting priorities as program requirements evolve. This approach reduces bottlenecks, enhances productivity, and ensures that program objectives are achieved without overburdening individual teams. Efficient resource management also contributes to cost optimization and improved program performance.
Conflict and Dispute Resolution
Program managers often face conflicts arising from competing priorities, resource constraints, or differing stakeholder expectations. PgMP-certified professionals are equipped to handle these situations proactively. They can identify the root causes of disputes, implement structured resolution mechanisms, and maintain alignment with program objectives.
Establishing governance frameworks and clear decision-making processes allows program managers to address issues efficiently. By resolving conflicts promptly, they ensure that programs remain on track, minimize disruptions, and foster a collaborative working environment.
Strategic Decision-Making
Program management requires the ability to make strategic decisions that align with organizational goals. PgMP-certified professionals are trained to assess risks, evaluate opportunities, and determine the most effective course of action for achieving program objectives.
Strategic decision-making involves analyzing potential outcomes, understanding stakeholder priorities, and considering organizational resources. Tools such as scenario planning, risk assessment, and cost-benefit analysis help program managers make informed decisions. These skills ensure that programs deliver value while mitigating potential risks.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Effective communication is a critical component of program management. PgMP-certified professionals can convey complex information clearly to a wide range of stakeholders, including executives, team members, and external partners. They establish communication plans that provide regular updates on program progress, risks, and key decisions.
Stakeholder engagement is closely linked to communication. Program managers must understand stakeholder expectations, manage their involvement, and maintain trust throughout the program lifecycle. By fostering transparent communication, they create alignment and collaboration across the program.
Risk Management
Program managers must proactively identify, assess, and respond to risks that could impact program success. PgMP-certified professionals have the skills to develop comprehensive risk management plans, monitor risk factors, and implement mitigation strategies.
Risk management involves anticipating potential challenges, evaluating their impact, and taking steps to prevent or reduce negative outcomes. Program managers must also be prepared to adjust strategies as risks evolve, ensuring that the program can continue to meet its objectives.
Quality Management
Quality management is a central responsibility for program managers. PgMP-certified professionals ensure that program deliverables meet defined standards and satisfy stakeholder expectations. They implement quality assurance processes, track performance metrics, and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Maintaining quality across multiple projects requires establishing consistent standards and monitoring outcomes regularly. Program managers must ensure that all projects within the program adhere to agreed-upon quality criteria, resulting in reliable and effective program outcomes.
PgMP Exam Structure and Preparation
The PgMP exam evaluates candidates on a range of program management competencies, including strategic alignment, program lifecycle management, governance, stakeholder engagement, risk and resource management, and benefits realization. The exam format is designed to test both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Effective preparation involves understanding the key program management domains, studying relevant frameworks and methodologies, and practicing scenario-based questions. Developing a structured study plan, allocating dedicated time for review, and applying practical examples from professional experience are essential for success.
Time management is crucial during preparation, as candidates must balance study sessions with professional responsibilities. Practicing exam-style questions under timed conditions can improve familiarity with the format and enhance problem-solving efficiency.
Engaging in peer discussions and study groups provides an opportunity to share insights, clarify complex concepts, and reinforce understanding. Regular review of key concepts, use of summaries, and creating visual aids such as flowcharts can help retain critical information.
Maintaining PgMP Certification
Maintaining the PgMP certification requires ongoing professional development. Program managers must demonstrate continued competency by engaging in activities that enhance their knowledge and skills. This includes participating in professional development initiatives, attending workshops or seminars, and contributing to the program management discipline through practice or mentorship.
Staying current with evolving practices and standards ensures that certified professionals remain effective in managing complex programs. Continuous engagement with the field also supports career growth and reinforces the value of the certification in professional settings.
Career Impact of PgMP Certification
PgMP-certified professionals are recognized for their ability to lead complex programs, manage cross-functional teams, and achieve strategic outcomes. This recognition often translates into greater career opportunities, leadership responsibilities, and the potential for higher compensation.
Employers value certified program managers for their proven expertise, decision-making capabilities, and ability to deliver programs that align with organizational priorities. The certification signals a commitment to excellence in program management, setting certified professionals apart from peers in the field.
Key Areas of Focus for the Exam
The PgMP exam emphasizes several critical areas of program management practice. These include defining program objectives, managing interdependencies among projects, ensuring effective governance, maintaining stakeholder alignment, and achieving benefits realization.
Program managers must also demonstrate expertise in resource allocation, risk management, quality assurance, and communication. The exam tests both theoretical understanding and practical application, requiring candidates to integrate knowledge across multiple domains.
Candidates are assessed on their ability to analyze complex scenarios, propose appropriate solutions, and make decisions that optimize program outcomes. This requires a deep understanding of program management frameworks, methodologies, and best practices.
Preparing for Complex Scenarios
A significant portion of the PgMP exam involves scenario-based questions that simulate real-world program management challenges. Candidates must evaluate situations, identify key issues, and determine effective courses of action.
Preparation for these scenarios involves studying case examples, reflecting on personal experience, and understanding how to apply program management principles in diverse contexts. Analytical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to synthesize information are essential skills for successfully navigating these questions.
Integrating Knowledge and Experience
Success in the PgMP exam relies on both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Candidates must demonstrate an ability to integrate program management concepts with hands-on experience in leading programs.
This includes understanding how to coordinate multiple projects, manage cross-functional teams, engage stakeholders, and deliver measurable outcomes. The ability to translate professional experience into exam responses is critical for demonstrating mastery of program management principles.
Strategic Alignment and Benefits Realization
A central theme of program management is ensuring that all projects contribute to the broader organizational strategy. PgMP-certified professionals are skilled at aligning program objectives with strategic goals, monitoring progress, and measuring benefits realized.
Benefits realization requires defining success criteria, establishing metrics, and tracking performance across the program lifecycle. Program managers must ensure that outcomes deliver tangible value and support long-term organizational priorities.
Governance and Decision-Making
Effective governance is essential for program success. PgMP-certified professionals establish frameworks for oversight, accountability, and decision-making. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting up reporting structures, and implementing controls to ensure alignment with program objectives.
Decision-making within a program context often involves balancing competing priorities, managing risks, and making informed choices that optimize outcomes. Certified program managers are trained to apply structured decision-making processes, ensuring consistency and transparency in managing complex programs.
The PgMP certification represents a high level of expertise in program management, highlighting the ability to coordinate multiple projects, align initiatives with organizational strategy, manage resources, mitigate risks, and deliver measurable benefits. Preparing for the exam requires a structured approach, integrating knowledge of program management frameworks with practical experience. Certified professionals are recognized for their strategic insight, leadership capabilities, and ability to achieve program objectives, making the credential a valuable indicator of advanced program management proficiency.
Understanding the PgMP Exam
The PgMP exam is designed to evaluate the candidate's ability to manage complex programs by applying program management principles, methodologies, and best practices. It tests both knowledge and practical application across various program management domains, including strategic alignment, program life cycle management, stakeholder engagement, governance, risk management, resource management, and benefits realization. The exam requires candidates to demonstrate a deep understanding of how programs operate and the interdependencies that exist among projects within a program.
The exam is structured to assess critical thinking, analytical skills, and the ability to apply program management concepts to real-world scenarios. It includes questions that challenge candidates to interpret complex situations, analyze potential outcomes, and select optimal solutions that align with program objectives and organizational goals. Candidates must show competence in integrating program management processes to achieve successful outcomes.
Key Domains of the Exam
The exam focuses on several core domains that reflect the responsibilities and competencies of a program manager. Strategic program management is one of the primary areas, emphasizing the importance of aligning program objectives with organizational strategies. Candidates are expected to understand the role of program management in achieving long-term goals, creating value, and delivering measurable benefits.
Program life cycle management is another critical domain. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring, controlling, and closing programs effectively. This includes understanding how to manage program transitions, phase gate reviews, and the integration of multiple projects to achieve cohesive outcomes.
Governance and decision-making are tested through questions that require candidates to establish oversight frameworks, define accountability structures, and implement decision-making processes. Exam questions may present scenarios where candidates must resolve conflicts, prioritize initiatives, and make decisions that ensure program success while maintaining stakeholder alignment.
Resource and Risk Management in the Exam
Resource management is an essential aspect of the exam. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to allocate, optimize, and monitor resources across multiple projects. This includes understanding techniques for capacity planning, resource leveling, and conflict resolution to ensure that programs are delivered efficiently. Effective resource management reduces bottlenecks, maximizes utilization, and contributes to achieving program objectives on time and within budget.
Risk management is another heavily emphasized domain. Candidates must be able to identify, assess, and respond to risks that can affect program outcomes. The exam tests knowledge of risk identification techniques, impact analysis, mitigation strategies, and ongoing monitoring. Candidates are expected to integrate risk management into program planning and execution to minimize potential disruptions and enhance the probability of achieving program benefits.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are central to the PgMP exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage expectations, provide timely information, and maintain alignment among all parties involved in a program. The exam includes questions that assess how candidates communicate priorities, escalate issues, and foster collaboration across diverse teams.
Program managers are also evaluated on their ability to influence stakeholders, negotiate competing interests, and build consensus. The exam may present complex scenarios requiring candidates to balance differing priorities while ensuring program objectives remain aligned with strategic goals. Strong communication and engagement skills are critical for maintaining program stability and achieving desired outcomes.
Benefits Realization and Performance Measurement
A critical focus of the PgMP exam is the concept of benefits realization. Candidates must demonstrate understanding of how to define, track, and measure program benefits. This includes setting clear success criteria, establishing performance metrics, and monitoring progress across projects to ensure that programs deliver tangible value.
Performance measurement involves evaluating program outcomes against objectives, identifying deviations, and implementing corrective actions. Candidates are tested on their ability to create frameworks for continuous improvement, monitor program performance, and ensure that benefits are realized in alignment with organizational strategy.
Scenario-Based Questions and Practical Application
A significant portion of the exam consists of scenario-based questions that simulate real-world program management challenges. Candidates must analyze situations, identify key issues, and propose effective solutions. These questions test the ability to apply program management principles to complex, dynamic environments.
Scenario-based questions often require candidates to consider multiple factors, such as resource constraints, stakeholder expectations, risk exposure, and strategic priorities. Successful candidates must demonstrate problem-solving skills, adaptability, and the ability to make informed decisions that optimize program performance and outcomes.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for the PgMP exam requires a structured approach that integrates both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Candidates benefit from creating a study plan that outlines key program management concepts, allocates time for review, and includes practice with scenario-based questions.
Time management is crucial during preparation, as the exam requires candidates to apply knowledge efficiently under timed conditions. Practicing exam-style questions and simulating test scenarios helps candidates become familiar with the format and develop strategies for managing complex problems within the allotted time.
In addition to self-study, collaboration with peers or study groups can enhance understanding of challenging concepts. Discussing program management scenarios, sharing insights, and reviewing different approaches helps reinforce knowledge and improves the ability to think critically under exam conditions.
Integrating Professional Experience
One of the distinguishing features of the PgMP exam is its focus on the practical application of program management experience. Candidates are expected to integrate their professional experience with program management principles, demonstrating their ability to lead complex programs effectively.
This involves drawing on real-world examples of managing interrelated projects, resolving conflicts, optimizing resources, and ensuring stakeholder alignment. Candidates must be able to translate their experience into well-reasoned answers that reflect both understanding and application of program management practices.
Exam Readiness and Knowledge Areas
Candidates must achieve a deep understanding of all knowledge areas related to program management. These include strategic alignment, program governance, stakeholder engagement, resource management, risk management, quality management, and benefits realization. Each knowledge area is tested through questions that evaluate the candidate’s ability to apply principles to practical situations.
Familiarity with program management frameworks and methodologies is essential. Candidates should understand how different components of a program interact and how to coordinate activities to ensure consistent progress toward objectives. This includes knowledge of program structures, reporting mechanisms, and performance measurement techniques.
Challenges in the PgMP Exam
The exam presents several challenges due to its complexity and focus on applied knowledge. Candidates must not only recall theoretical concepts but also demonstrate the ability to integrate them into program management scenarios.
Managing time effectively during the exam is critical, as questions often require analysis of multiple factors before selecting an appropriate solution. Candidates must exercise judgment, prioritize critical issues, and apply program management tools and techniques accurately.
The breadth of content covered in the exam requires comprehensive preparation. Candidates must be well-versed in all aspects of program management, including planning, execution, monitoring, controlling, and closing programs, as well as managing interdependencies among projects.
Applying Frameworks and Methodologies
A strong understanding of program management frameworks is essential for exam success. Candidates must be able to apply methodologies to coordinate projects, manage risks, allocate resources, and achieve program benefits.
Frameworks provide a structured approach to program management, ensuring consistency, accountability, and effective decision-making. Candidates should be familiar with lifecycle stages, governance structures, performance metrics, and reporting requirements. Applying these frameworks in practice allows program managers to navigate complex programs and achieve desired outcomes.
Governance Structures and Decision Making
The exam tests knowledge of governance structures and decision-making processes within program management. Candidates are expected to establish clear roles and responsibilities, implement oversight mechanisms, and ensure that decisions align with program objectives.
Effective governance helps maintain accountability, transparency, and control over program activities. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage decision-making processes, resolve conflicts, and make strategic choices that optimize program performance.
Enhancing Exam Success Through Practice
Regular practice is critical for exam readiness. Candidates should work through sample questions, case studies, and scenario-based exercises to develop confidence and familiarity with exam formats. This practice helps improve analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making speed.
Candidates should also review key program management concepts repeatedly, focusing on areas where they may have less experience. Consistent practice and reinforcement of knowledge increase the likelihood of success by ensuring candidates can respond accurately and efficiently under exam conditions.
Preparing for Complex Programs
Candidates must understand the complexities of managing large programs that involve multiple projects, teams, and stakeholders. The exam assesses the ability to coordinate activities, manage dependencies, and ensure that program objectives are met.
Preparing for the exam includes reflecting on personal experience with complex programs, identifying challenges encountered, and understanding how program management principles can address these challenges. This preparation enhances the ability to apply knowledge in scenario-based questions effectively.
Decision Analysis and Problem Solving
Decision analysis and problem-solving are emphasized throughout the exam. Candidates must evaluate multiple options, consider potential consequences, and select solutions that align with program goals.
The ability to analyze program situations critically, anticipate challenges, and develop effective solutions is essential. Exam questions often simulate real-world decision-making scenarios, requiring candidates to demonstrate analytical thinking, strategic planning, and practical application of program management techniques.
Monitoring and Controlling Programs
The exam tests the ability to monitor and control programs to ensure they remain on track. Candidates must demonstrate knowledge of tracking progress, measuring performance, managing changes, and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
Effective monitoring and control involve assessing program health, identifying variances, and taking proactive measures to address deviations. Candidates should be able to implement performance indicators, review milestones, and ensure that program objectives are achieved efficiently.
Aligning Programs with Organizational Strategy
A fundamental aspect of program management is ensuring that programs support organizational strategy. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to align program objectives with long-term goals, assess strategic impact, and ensure that program outcomes contribute to organizational success.
This involves understanding organizational priorities, evaluating program performance against strategic objectives, and making adjustments to maintain alignment. Candidates must show proficiency in translating strategic goals into actionable program initiatives.
Program Benefits and Value Delivery
Candidates are tested on their ability to define, measure, and deliver program benefits. This includes identifying success criteria, establishing metrics, monitoring progress, and ensuring that programs provide tangible value.
Program managers must demonstrate knowledge of benefits realization frameworks, tracking mechanisms, and performance evaluation. The exam evaluates the ability to ensure that programs deliver measurable outcomes that align with organizational priorities.
Integrating Knowledge Across Domains
The PgMP exam requires candidates to integrate knowledge across multiple program management domains. Candidates must apply principles of governance, stakeholder engagement, resource management, risk mitigation, quality management, and benefits realization in cohesive program strategies.
Integration of knowledge ensures that candidates can manage programs holistically, considering all aspects of project interdependencies, resource allocation, risk management, and strategic alignment. This approach reflects real-world program management practice and is central to exam success.
Exam Mindset and Strategy
Candidates benefit from adopting a strategic mindset for the exam, focusing on understanding program management principles deeply rather than memorizing concepts superficially. Developing the ability to analyze complex scenarios, synthesize information, and make informed decisions is key to success.
Time management during the exam is essential. Candidates should allocate sufficient time to analyze questions, consider options, and select the most appropriate responses. Practicing under simulated exam conditions helps develop efficiency and confidence.
Applying Lessons from Experience
Drawing from professional experience is crucial for the PgMP exam. Candidates should reflect on past program management experiences, identify lessons learned, and consider how these insights apply to scenario-based questions.
Real-world experience enables candidates to approach exam questions with practical understanding, demonstrating the ability to integrate knowledge, anticipate challenges, and propose effective solutions that optimize program outcomes.
Continuous Learning for Exam Readiness
Continuous learning and reflection are important for preparing for the PgMP exam. Candidates should regularly review program management principles, study scenarios, and update their understanding of program management best practices.
Engaging in continuous learning ensures that candidates can approach the exam with a comprehensive perspective, applying both theoretical knowledge and practical experience to answer questions accurately and effectively.
Mastering the PgMP Exam
Achieving success in the PgMP exam requires a combination of theoretical understanding, practical experience, analytical skills, and effective exam strategy. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage complex programs, align initiatives with organizational goals, optimize resources, mitigate risks, engage stakeholders, and deliver measurable benefits.
Thorough preparation, structured study plans, scenario practice, and integration of professional experience are essential components of exam readiness. Candidates who master these elements are well-positioned to succeed and earn recognition for their advanced program management expertise.
Comprehensive Understanding of the PgMP Exam
The PgMP exam is structured to assess advanced program management capabilities, focusing on the integration of multiple projects, strategic alignment, governance, and benefits realization. Candidates are tested on their ability to coordinate interdependent projects, manage complex stakeholder relationships, optimize resources, and mitigate risks across the program lifecycle. The exam evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical application, requiring candidates to demonstrate the skills necessary to lead programs that deliver measurable value to an organization.
The exam emphasizes scenario-based questions that simulate real-world program management situations. Candidates must interpret complex data, identify issues, assess potential outcomes, and select the most effective solutions. This approach ensures that certified professionals have the practical insight and analytical skills necessary to navigate the challenges of large-scale program management.
Program Integration and Coordination
One of the critical aspects assessed in the PgMP exam is the ability to integrate and coordinate multiple projects under a single program. Candidates must demonstrate the capability to align project objectives with program goals, manage interdependencies, and ensure that the collective effort contributes to organizational priorities.
Effective integration requires understanding the relationships between projects, identifying dependencies, and creating a cohesive framework that facilitates collaboration among teams. Program managers are expected to coordinate resources, synchronize schedules, and balance competing priorities to optimize program performance.
Governance and Oversight
The PgMP exam evaluates candidates’ proficiency in establishing governance frameworks and oversight mechanisms for programs. Governance involves defining roles and responsibilities, setting up reporting structures, and implementing decision-making processes that maintain accountability and control.
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to create clear escalation paths, monitor program progress, and ensure adherence to organizational policies and objectives. Governance also includes implementing quality standards, tracking program metrics, and making informed decisions that mitigate risks and optimize outcomes.
Strategic Alignment and Decision-Making
Strategic alignment is a cornerstone of program management and a major focus of the PgMP exam. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to ensure that programs support organizational strategies and deliver intended benefits. This includes evaluating program outcomes against strategic goals and making decisions that enhance overall organizational performance.
Decision-making in program management requires the ability to analyze complex scenarios, consider multiple perspectives, and select courses of action that balance short-term demands with long-term objectives. The exam tests candidates on their ability to make decisions that maximize program value while minimizing risks and conflicts.
Resource Optimization
Resource management is a central domain of the PgMP exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to allocate and optimize resources across projects, ensuring that personnel, budgets, and materials are used efficiently. This involves capacity planning, resource leveling, and conflict resolution to address competing demands.
Program managers are expected to dynamically adjust resource allocation as priorities change and unforeseen challenges arise. Effective resource optimization reduces bottlenecks, increases productivity, and supports the timely delivery of program objectives.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Risk management is another key area assessed in the exam. Candidates must show proficiency in identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and implementing mitigation strategies throughout the program lifecycle. This includes understanding the sources of risks, both internal and external, and developing contingency plans to ensure program stability.
The exam evaluates the ability to integrate risk management into decision-making processes, monitor risk factors, and take proactive steps to minimize negative consequences. Effective risk management enhances program resilience and increases the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Communication and stakeholder engagement are essential for program success and heavily emphasized in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage relationships with diverse stakeholders, communicate program objectives, and maintain alignment across all levels of the organization.
Effective stakeholder engagement involves understanding expectations, addressing concerns, and fostering collaboration. Candidates are tested on their ability to communicate complex ideas clearly, provide status updates, escalate issues appropriately, and influence stakeholders to support program objectives.
Benefits Realization and Value Delivery
A fundamental focus of the PgMP exam is benefits realization. Candidates must demonstrate an understanding of how to define, measure, and track program benefits. This involves setting clear success criteria, establishing performance metrics, and ensuring that programs deliver tangible value aligned with organizational strategy.
Program managers are expected to monitor progress continuously, identify deviations from expected outcomes, and implement corrective actions to ensure benefits are realized. Understanding benefits realization frameworks and integrating them into program planning is critical for exam success.
Scenario-Based Question Analysis
Scenario-based questions constitute a significant portion of the PgMP exam. Candidates must analyze complex program situations, identify critical issues, and propose solutions that optimize program performance. These questions test analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and practical application of program management principles.
Effective preparation for scenario-based questions involves reviewing program management frameworks, reflecting on professional experiences, and practicing problem-solving techniques. Candidates must be able to synthesize information from multiple sources and apply knowledge to make informed decisions.
Program Life Cycle Management
Candidates are evaluated on their understanding of the program life cycle, which includes initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, controlling, and closure. The exam tests knowledge of how to manage program transitions, oversee project integration, and ensure alignment with strategic objectives throughout the program lifecycle.
Program managers must demonstrate the ability to define program objectives, establish governance and oversight, monitor performance, and implement continuous improvement practices. Mastery of the program life cycle ensures that candidates can manage programs effectively from inception to completion.
Quality Management
Quality management is a critical component of program management and is included in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to implement quality assurance processes, monitor program performance, and ensure deliverables meet stakeholder expectations.
Quality management involves establishing standards, tracking metrics, and ensuring that each project within the program adheres to these standards. This contributes to consistent outcomes, stakeholder satisfaction, and overall program success.
Preparing for the Exam
Successful preparation for the PgMP exam requires a combination of structured study, practical experience, and scenario-based practice. Candidates should create a study plan that covers all program management domains, allocates sufficient review time, and includes exercises that simulate exam conditions.
Regular practice with scenario-based questions helps candidates develop analytical thinking and decision-making skills. Reviewing professional experiences and reflecting on program management challenges enhances the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
Time management is an essential aspect of preparation. Candidates must practice answering questions efficiently under timed conditions to ensure they can analyze scenarios and select solutions within the exam constraints.
Applying Professional Experience
Integrating professional experience with program management knowledge is crucial for the PgMP exam. Candidates should draw on past program management experiences to understand how theoretical concepts apply in real-world situations.
Experience with managing multiple projects, coordinating teams, resolving conflicts, optimizing resources, and engaging stakeholders helps candidates approach scenario-based questions effectively. This integration of knowledge and experience demonstrates the practical skills necessary to manage complex programs.
Continuous Review and Reinforcement
Continuous review and reinforcement of program management principles are key to exam readiness. Candidates should revisit critical concepts regularly, practice scenario-based exercises, and analyze case studies to reinforce understanding.
Using visual aids, summaries, and structured notes can help retain complex information. Candidates benefit from reviewing lessons learned from previous program management experiences and applying these insights to exam practice.
Decision-Making Frameworks
Candidates must be familiar with decision-making frameworks and tools used in program management. This includes evaluating alternatives, assessing risks, considering stakeholder impact, and selecting solutions that maximize program benefits.
The exam tests the ability to apply structured decision-making processes in dynamic program environments. Candidates must demonstrate critical thinking, analytical skills, and the capacity to make decisions that align with program objectives and organizational strategy.
Monitoring and Controlling Program Performance
Monitoring and controlling program performance is a core competency tested in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to track progress, identify variances, implement corrective actions, and ensure that program objectives are met efficiently.
This involves using performance metrics, conducting regular reviews, and maintaining oversight across all projects within the program. Candidates are expected to manage deviations proactively and ensure that program outcomes align with strategic goals.
Advanced Risk Assessment
The PgMP exam evaluates candidates’ ability to conduct advanced risk assessments. This includes identifying emerging risks, analyzing potential impacts, prioritizing responses, and implementing mitigation strategies.
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to integrate risk management with program planning and execution. This ensures that programs remain resilient, capable of adapting to changing conditions, and able to deliver intended benefits despite uncertainties.
Strategic Communication
Strategic communication is essential for effective program management and is tested in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to convey program goals, priorities, and progress to stakeholders at all levels.
Communication involves not only providing updates but also influencing decisions, building consensus, and maintaining engagement. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to tailor communication strategies to different audiences, ensuring clarity and alignment with program objectives.
Leveraging Program Management Tools
The exam assesses familiarity with program management tools and techniques that support integration, monitoring, resource management, and risk mitigation. Candidates should understand how to apply tools such as performance dashboards, risk registers, and stakeholder matrices to manage programs effectively.
Proficiency in using these tools allows candidates to analyze data, track progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Effective tool utilization is critical for managing complex programs and achieving desired outcomes.
Exam Mindset and Approach
Adopting the right mindset for the PgMP exam is important for success. Candidates should focus on understanding program management principles deeply, analyzing scenarios critically, and applying knowledge practically.
The exam requires integration of multiple domains, thoughtful evaluation of scenarios, and effective decision-making. Maintaining focus, managing time efficiently, and approaching questions methodically enhances the likelihood of success.
Continuous Professional Development
Preparing for the PgMP exam involves continuous professional development, including expanding knowledge of program management frameworks, reflecting on experiences, and learning from industry practices. Candidates should engage with challenging scenarios, practice problem-solving, and refine decision-making skills.
Continuous learning ensures that candidates can apply program management knowledge effectively during the exam and in professional practice. It reinforces the ability to manage complex programs, address challenges, and deliver value consistently.
Applying Lessons Learned
Candidates benefit from reviewing lessons learned from previous program management experiences. This includes reflecting on successes, identifying areas for improvement, and understanding how different approaches influence outcomes.
Applying these insights to scenario-based questions in the exam allows candidates to demonstrate practical judgment, analytical thinking, and the ability to integrate theoretical knowledge with real-world experience.
Integrating Knowledge Across Programs
The PgMP exam emphasizes the ability to integrate knowledge across multiple programs. Candidates must show how governance, resource management, risk management, quality, benefits realization, and stakeholder engagement work together to achieve program success.
Integration requires understanding interdependencies, aligning objectives, and coordinating projects effectively. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in managing complex programs holistically, balancing competing priorities, and optimizing outcomes.
Exam Preparedness Strategies
Successful exam preparation includes structured study, practice with scenarios, continuous review, and reflection on professional experience. Candidates should focus on understanding concepts deeply, applying them in practice, and developing confidence in decision-making.
Simulation of exam conditions helps candidates develop time management skills and familiarity with question formats. Combining theoretical knowledge with practical application ensures readiness to tackle complex program management challenges during the exam.
Benefits of Certification
PgMP certification validates advanced program management skills, including strategic alignment, governance, risk management, stakeholder engagement, and benefits realization. It demonstrates the ability to lead complex programs, deliver value, and achieve organizational objectives efficiently.
The certification reflects professional competence, practical experience, and mastery of program management principles. It signals to organizations and peers that the certified individual possesses the knowledge, skills, and judgment required to manage multi-project programs effectively.
Achieving Exam Success
Achieving success in the PgMP exam requires a holistic approach that integrates theoretical knowledge, practical experience, analytical thinking, and strategic decision-making. Candidates must be able to manage complex programs, optimize resources, mitigate risks, engage stakeholders, and ensure benefits realization.
Thorough preparation, scenario practice, continuous review, and leveraging professional experience are key to success. Candidates who master these areas demonstrate readiness to lead programs effectively and deliver measurable value to organizations.
Exam Review and Self-Assessment
Candidates are encouraged to conduct self-assessment and review areas of strength and improvement. Identifying knowledge gaps, revisiting challenging concepts, and practicing scenario-based questions strengthens preparedness and confidence for the exam.
Self-assessment also allows candidates to develop strategies for managing exam time, prioritizing critical domains, and approaching questions methodically. This practice reinforces understanding, enhances problem-solving abilities, and increases the likelihood of achieving certification.
Integrating Strategic Perspective
A strategic perspective is essential for exam success. Candidates must understand how programs contribute to organizational goals, evaluate program performance, and make decisions that enhance value delivery.
Integrating strategic thinking with practical program management skills ensures that candidates can approach scenarios thoughtfully, assess implications, and propose solutions that support long-term organizational objectives.
Final Exam Readiness
Comprehensive preparation for the PgMP exam includes mastering program management domains, practicing scenario-based questions, integrating professional experience, and developing strategic decision-making skills. Candidates must be able to manage program complexity, ensure alignment with organizational strategy, mitigate risks, optimize resources, and deliver measurable benefits.
Focused study, practice under simulated conditions, reflection on experiences, and continuous learning provide the foundation for success. Candidates who apply these strategies demonstrate readiness to achieve certification and exemplify advanced program management proficiency.
Overview of the PgMP Exam
The PgMP exam is designed to assess advanced competencies in program management, focusing on the management of complex, interrelated projects that collectively achieve strategic objectives. It evaluates a candidate’s ability to integrate multiple projects, manage program risks, allocate resources effectively, engage stakeholders, and ensure benefits realization. The exam requires candidates to apply program management principles to real-world scenarios, demonstrating both theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
Candidates are tested on their understanding of program life cycles, governance, strategic alignment, stakeholder engagement, risk management, resource optimization, and performance measurement. Scenario-based questions form a significant portion of the exam, requiring candidates to analyze complex situations, evaluate alternatives, and select solutions that maximize program value and outcomes.
Program Life Cycle Management
Understanding the program life cycle is fundamental to the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to manage programs from initiation to closure, integrating multiple projects while maintaining alignment with organizational strategy. This includes defining program objectives, establishing governance structures, managing interdependencies, and monitoring performance throughout the life cycle.
Effective life cycle management involves coordinating projects, ensuring resource allocation aligns with priorities, and mitigating risks that may impact program success. Candidates must be able to demonstrate knowledge of transitions between program phases, tracking progress, and applying corrective actions when necessary.
Governance and Decision-Making
Governance is a core focus of the exam. Candidates must show proficiency in establishing oversight mechanisms, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing decision-making frameworks. Effective governance ensures accountability, transparency, and alignment with organizational objectives.
Decision-making within a program context requires the ability to analyze complex scenarios, weigh potential outcomes, and select options that balance competing priorities. Candidates are expected to demonstrate strategic thinking, problem-solving skills, and the ability to make informed decisions that optimize program performance.
Strategic Alignment and Organizational Impact
The exam evaluates candidates’ ability to align programs with organizational strategies. Program managers must ensure that program objectives support broader business goals and deliver measurable value. This includes evaluating program outcomes, assessing strategic impact, and making decisions that contribute to long-term organizational success.
Strategic alignment involves prioritizing projects, allocating resources effectively, managing risks, and ensuring stakeholder engagement throughout the program lifecycle. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to translate organizational strategy into actionable program initiatives.
Resource Management and Optimization
Effective resource management is a critical domain of the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to allocate, monitor, and optimize resources across multiple projects. This includes managing human resources, budgets, and materials, while addressing conflicts and changing priorities.
Techniques such as capacity planning, resource leveling, and performance monitoring are key components of resource management. Candidates are expected to show proficiency in dynamically adjusting resources to meet program objectives, minimizing bottlenecks, and ensuring efficient utilization.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Risk management is heavily emphasized in the exam. Candidates must identify potential risks, evaluate their impact, and implement mitigation strategies throughout the program lifecycle. This involves proactive planning, continuous monitoring, and adaptive responses to emerging risks.
Candidates are expected to integrate risk management into program planning and execution, ensuring that risks are mitigated without compromising program objectives. Effective risk management enhances program resilience, increases the likelihood of achieving benefits, and supports strategic decision-making.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
The PgMP exam assesses candidates’ ability to manage diverse stakeholders and communicate effectively. Program managers must ensure alignment between stakeholder expectations and program objectives, foster collaboration, and maintain transparency.
Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in developing communication plans, addressing concerns, influencing decisions, and resolving conflicts. Effective stakeholder engagement ensures program stability, promotes trust, and enhances the overall success of program initiatives.
Benefits Realization and Performance Measurement
A central focus of the exam is benefits realization. Candidates must define, track, and measure program benefits to ensure that programs deliver tangible value. This includes establishing success criteria, monitoring performance, and implementing corrective actions to address deviations.
Performance measurement involves evaluating program outcomes against objectives, tracking key metrics, and ensuring that benefits are aligned with organizational strategy. Candidates are expected to demonstrate the ability to apply benefits realization frameworks effectively across all projects within a program.
Scenario-Based Question Analysis
Scenario-based questions form a significant portion of the exam, testing candidates’ ability to analyze complex program situations, identify key issues, and propose optimal solutions. These questions assess problem-solving skills, analytical thinking, and practical application of program management principles.
Candidates are expected to evaluate multiple factors, such as resource constraints, stakeholder priorities, risk exposure, and program dependencies. Successfully answering scenario-based questions requires integrating knowledge from various domains and applying professional experience to make informed decisions.
Program Quality Management
Quality management is an essential component of the PgMP exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to implement quality assurance processes, monitor program performance, and ensure that deliverables meet stakeholder expectations.
This involves establishing consistent standards, tracking progress, and applying continuous improvement practices. Ensuring quality across all projects within a program contributes to stakeholder satisfaction, reduces rework, and enhances the overall effectiveness of program management.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for the PgMP exam requires a structured and disciplined approach. Candidates should develop a study plan covering all program management domains, allocate dedicated review time, and practice scenario-based questions extensively.
Time management is crucial during preparation and exam execution. Practicing under timed conditions helps candidates develop the ability to analyze complex scenarios efficiently and select the most appropriate solutions. Reviewing professional experience and reflecting on lessons learned also supports practical understanding.
Collaboration with peers or study groups can reinforce learning, provide diverse perspectives, and improve problem-solving skills. Discussing challenging scenarios, analyzing solutions, and sharing insights can deepen understanding and enhance exam readiness.
Integrating Professional Experience
Professional experience plays a critical role in preparing for the PgMP exam. Candidates should leverage their experience in managing complex programs, coordinating multiple projects, resolving conflicts, and optimizing resources.
Applying practical knowledge to scenario-based questions allows candidates to demonstrate their ability to integrate theoretical concepts with real-world application. Experience in leading programs provides insight into common challenges and effective strategies, which are valuable for exam success.
Advanced Decision-Making
The exam evaluates advanced decision-making capabilities. Candidates must assess complex scenarios, consider potential outcomes, and select solutions that balance program objectives with organizational priorities.
Effective decision-making requires analytical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to integrate multiple factors, including risks, resources, stakeholder expectations, and strategic goals. Candidates are expected to apply structured approaches to ensure decisions optimize program value and outcomes.
Monitoring and Controlling Program Performance
Monitoring and controlling program performance is a core competency tested in the exam. Candidates must demonstrate the ability to track progress, assess performance against objectives, and implement corrective actions when necessary.
This includes using performance metrics, conducting reviews, managing deviations, and ensuring that projects within the program adhere to planned schedules and budgets. Effective monitoring and control contribute to program stability, efficiency, and successful completion of objectives.
Scenario Analysis Techniques
Scenario analysis is a critical skill for the exam. Candidates must evaluate complex situations, identify interdependencies, and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Techniques for scenario analysis include assessing risks, resource allocation, stakeholder impact, and program priorities. Candidates must integrate knowledge across domains to propose solutions that achieve strategic goals while minimizing negative outcomes.
Integrating Knowledge Across Domains
The PgMP exam requires candidates to demonstrate the ability to integrate knowledge across multiple program management domains. This includes governance, strategic alignment, stakeholder engagement, resource optimization, risk management, benefits realization, and quality management.
Integration involves coordinating projects, managing interdependencies, aligning objectives, and ensuring that program outcomes deliver value. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in applying holistic program management approaches to complex scenarios.
Exam Mindset and Approach
A strategic and analytical mindset is essential for success. Candidates should focus on understanding program management principles deeply, applying knowledge in practical contexts, and analyzing complex scenarios critically.
Approaching questions methodically, managing time efficiently, and considering multiple perspectives enhances performance. Maintaining focus and applying structured thinking are key strategies for navigating challenging exam questions.
Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement
Reviewing lessons learned from professional experience strengthens exam preparation. Candidates should analyze past program management challenges, evaluate outcomes, and understand how different approaches influence results.
Applying these insights to scenario-based questions allows candidates to demonstrate practical judgment, analytical skills, and the ability to integrate knowledge with experience effectively. Continuous improvement and reflection support long-term program management proficiency.
Strategic Perspective
A strategic perspective is crucial for the exam. Candidates must demonstrate how programs align with organizational objectives, contribute to strategic priorities, and deliver measurable value.
Integrating strategic thinking with practical application ensures that candidates can analyze scenarios holistically, assess implications, and make decisions that support organizational goals. Strategic insight enhances both exam performance and professional effectiveness.
Exam Readiness and Self-Assessment
Self-assessment is an important component of preparation. Candidates should evaluate areas of strength and improvement, identify knowledge gaps, and focus on challenging domains to enhance readiness.
Regular practice, scenario exercises, and review of professional experience strengthen confidence and problem-solving ability. Developing a methodical approach to questions, prioritizing critical domains, and managing exam time effectively are key strategies for success.
Applying Frameworks and Methodologies
Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in applying program management frameworks and methodologies. This includes integrating governance, resource management, risk management, stakeholder engagement, and benefits realization into cohesive program strategies.
Frameworks provide structured approaches to program management, ensuring consistency, accountability, and effective decision-making. Candidates are expected to apply these frameworks to complex scenarios, demonstrating their ability to manage programs holistically.
Continuous Professional Development
Preparing for the PgMP exam involves ongoing professional development. Candidates should engage in learning activities, review industry practices, and refine program management skills.
Continuous development ensures candidates can apply knowledge effectively, approach complex scenarios with confidence, and demonstrate advanced program management proficiency. This ongoing learning supports both exam readiness and long-term career growth.
Program Monitoring and Reporting
Candidates must demonstrate the ability to monitor program progress, report on performance, and implement corrective actions as needed. This includes tracking milestones, analyzing metrics, and maintaining oversight across all projects within a program.
Effective monitoring and reporting ensure program alignment with objectives, timely identification of issues, and informed decision-making. Candidates are expected to show proficiency in using performance data to guide program management actions.
Exam Focus on Practical Application
The PgMP exam emphasizes practical application of program management knowledge. Candidates must demonstrate how they would handle complex program situations, coordinate projects, manage risks, allocate resources, and engage stakeholders.
Practical application requires integrating knowledge with professional experience, analyzing scenarios critically, and making informed decisions. The ability to apply concepts in realistic situations is central to achieving certification.
Applying Lessons from Experience
Candidates benefit from reflecting on professional experience, reviewing successes and challenges, and understanding how different approaches influence outcomes.
Applying these insights to scenario-based questions demonstrates analytical thinking, judgment, and the ability to integrate knowledge with experience. Learning from experience supports both exam success and long-term program management proficiency.
Integrating Knowledge Across Program Domains
The exam tests candidates’ ability to integrate knowledge across program management domains. This includes governance, strategic alignment, stakeholder engagement, resource management, risk mitigation, quality management, and benefits realization.
Integration ensures that program activities are coordinated, objectives are aligned, and interdependencies are managed effectively. Candidates are expected to demonstrate proficiency in applying holistic program management approaches to complex scenarios.
Conclusion
The PgMP exam represents a rigorous evaluation of a professional's ability to manage complex programs that span multiple projects, teams, and stakeholders. It is designed not only to test theoretical knowledge but also to measure practical application, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making skills. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency across all domains of program management, including strategic alignment, governance, risk management, resource optimization, stakeholder engagement, quality management, and benefits realization. The exam places a strong emphasis on scenario-based questions, which simulate real-world challenges and require candidates to analyze situations, consider multiple perspectives, and select solutions that maximize program value and outcomes.
Achieving success in the PgMP exam requires a comprehensive understanding of program management principles as well as the ability to apply these principles in complex environments. Candidates must integrate knowledge from multiple domains to ensure that programs are aligned with organizational strategy, deliver measurable benefits, and maintain efficiency and quality across all projects. This integration demands a holistic perspective, where decisions are made not only to meet immediate objectives but also to ensure long-term organizational success. Understanding the program life cycle, from initiation through closure, and being able to manage transitions between phases are essential components of this expertise.
PMI PgMP practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass PgMP Program Management Professional certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- PMP - Project Management Professional
- CAPM - Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100)
- CPMAI - Cognitive project management in AI
- PgMP - Program Management Professional
- PMI-ACP - PMI Agile Certified Practitioner
- PMO-CP - PMO Certified Professional
- PMI-RMP - PMI Risk Management Professional
- PfMP - Portfolio Management Professional
- PMI-PBA - PMI Professional in Business Analysis
- PMI-SP - PMI Scheduling Professional Practice Test
- PMI-CP - PMI Construction Professional
Purchase PgMP Exam Training Products Individually



Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the PMI certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the PgMP test and passed with ease.
Studying for the PMI certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the PgMP exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the PgMP preparation materials for the PMI certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The PgMP materials for the PMI certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the PgMP exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my PMI certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for PgMP. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the PgMP stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my PgMP certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my PMI certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the PgMP were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed PgMP successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

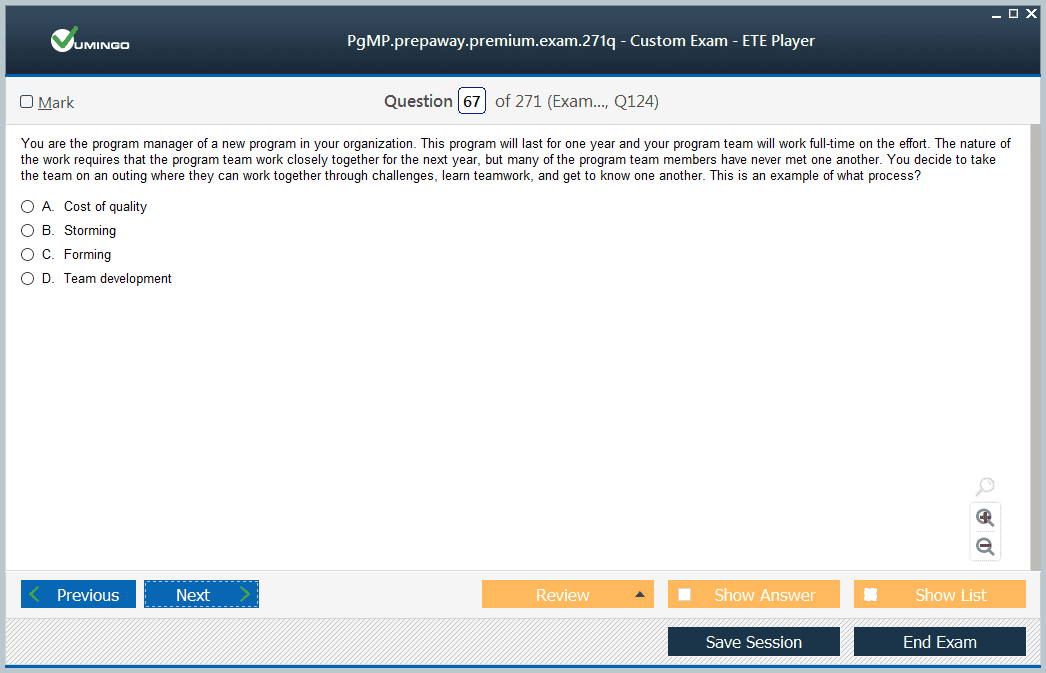
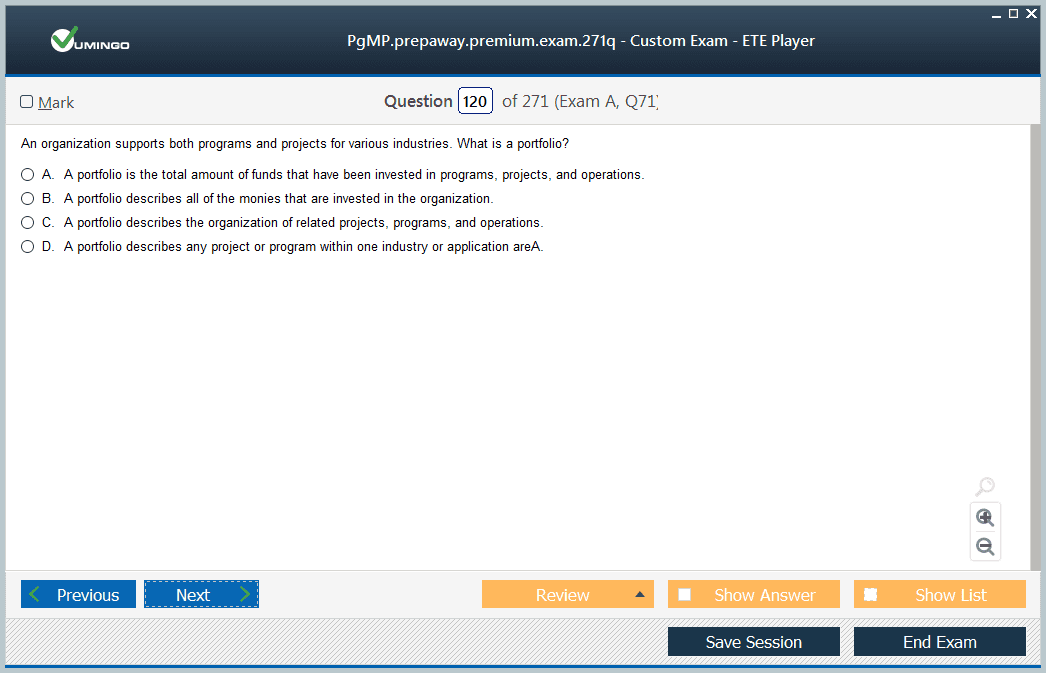
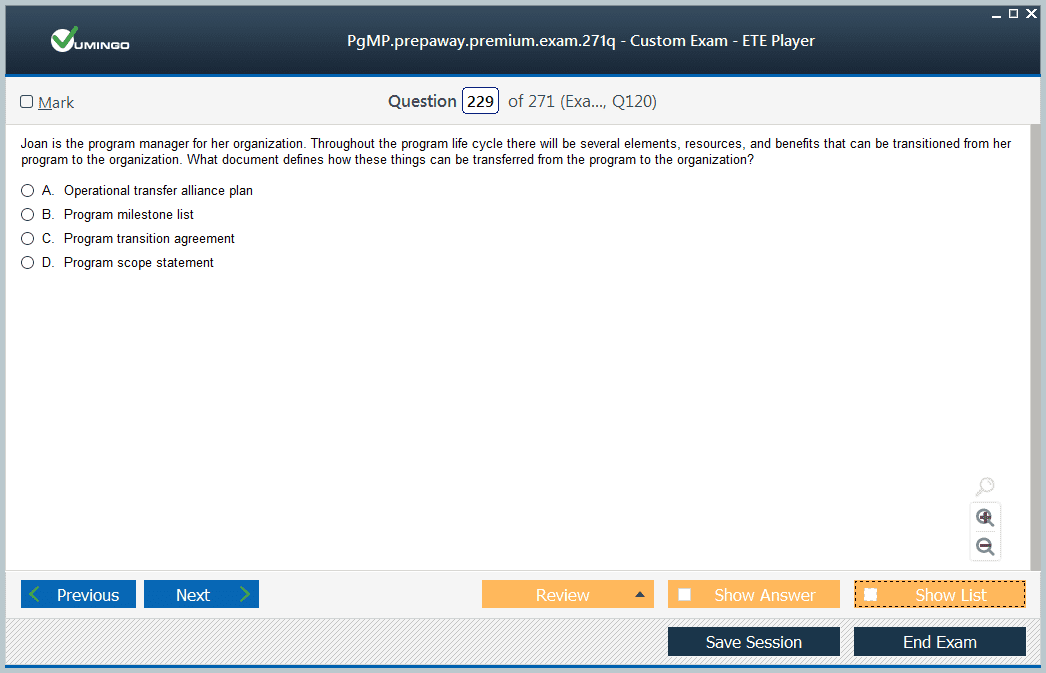
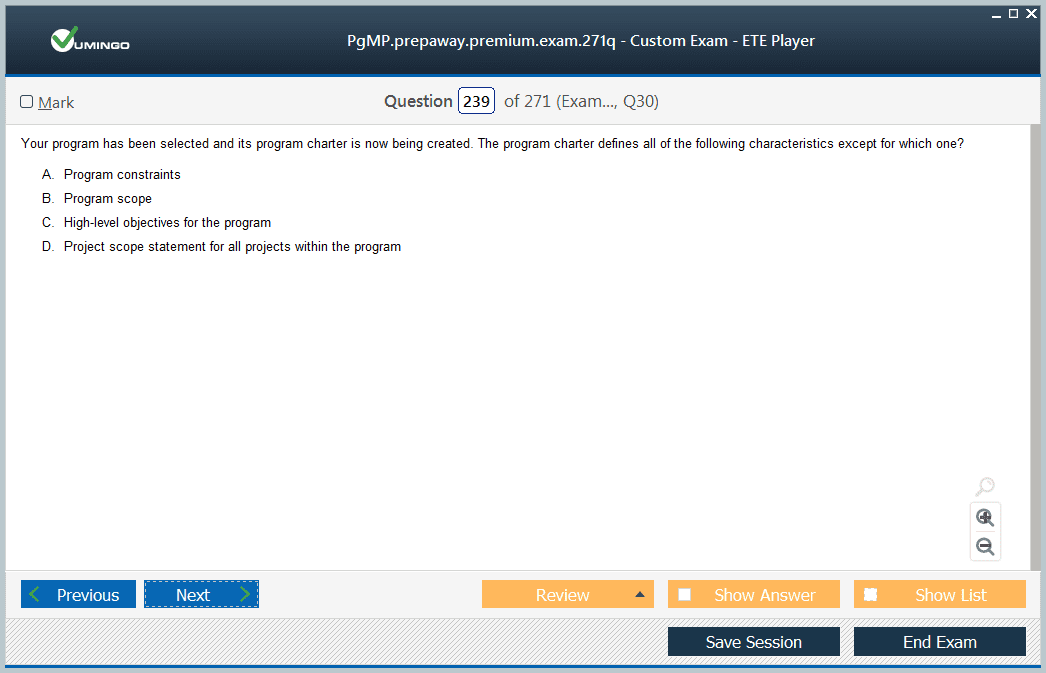








& Exam Questions to study pls.