- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 98-368 Mobility and Devices Fundamentals Dumps
Pass Microsoft Mobility 98-368 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!
Get 100% Latest Exam Questions, Accurate & Verified Answers to Pass the Actual Exam!
30 Days Free Updates, Instant Download!


98-368 Premium File
- Premium File 66 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Feb 15, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Microsoft Mobility 98-368 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 98-368 Mobility and Devices Fundamentals practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Mobility and Device Fundamentals: How the Microsoft MTA 98-368 Shapes IT Foundations
The MTA Mobility and Devices Fundamentals exam provides a comprehensive introduction to the essential knowledge and skills required for managing and configuring devices in modern IT environments. As organizations increasingly adopt mobile-first strategies and embrace cloud technologies, the ability to configure, secure, and manage Windows devices becomes vital. This exam is positioned as an entry-level certification that validates foundational knowledge in device management, enterprise mobility, and the use of Microsoft technologies to support business operations.
Unlike advanced certifications, this exam is designed for individuals starting their journey in IT. It covers practical and theoretical areas that build the groundwork for further learning, ensuring candidates can move confidently into more specialized areas such as systems administration, cloud infrastructure, and advanced security. By preparing for and taking this exam, learners gain exposure to the critical areas of device and mobility fundamentals that reflect real-world business needs.
Significance of Device Configurations in Modern IT
Device configuration is a major component of the exam because it reflects one of the most frequent responsibilities of IT professionals. When a new device is introduced into an organization, it must be properly set up to ensure that it functions as required while also aligning with company policies. This includes configuring system options, setting up accounts, applying desktop settings, and ensuring device encryption is in place. Each of these tasks ensures that devices are both user-friendly and secure.
System options configuration involves adjusting key features such as display settings, sound, and performance preferences to match organizational standards. These tasks may seem simple, but in enterprise environments, consistency across devices is critical for reducing support issues and ensuring compatibility with business applications.
Desktop settings are also important, as they directly affect the user experience. Configuring profiles, group policies, and shortcuts ensures that employees can access the resources they need quickly and securely. The exam places emphasis on understanding how to configure these settings effectively, because poor configuration can lead to decreased productivity or even vulnerabilities.
Device options such as power management, accessibility features, and connectivity settings are also tested. Candidates should understand how to enable and configure these options to meet the diverse needs of users while maintaining efficiency. For example, properly configuring power settings can extend battery life in mobile devices, which is essential for employees who rely on laptops or tablets while working remotely.
The Role of Drive Encryption and File Security
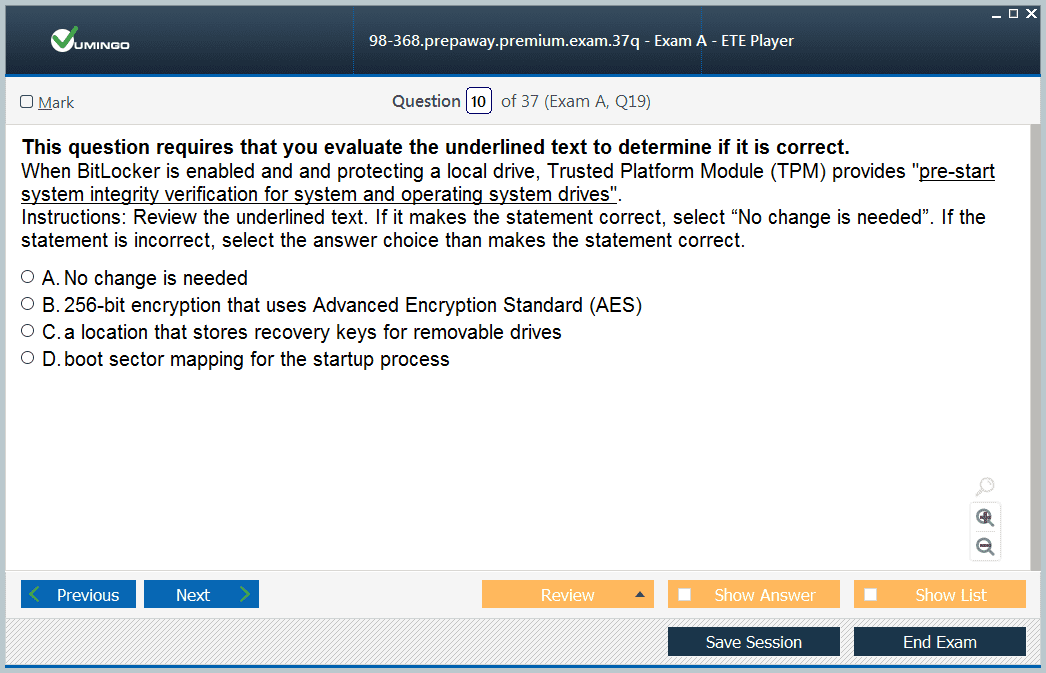
One of the critical aspects of device configuration is ensuring that data stored on devices is protected. The exam focuses heavily on encryption methods such as BitLocker, which is Microsoft’s built-in solution for encrypting entire drives. By requiring candidates to understand how to configure BitLocker and prepare systems for file encryption, the exam ensures that future IT professionals can safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Drive encryption is more than just a theoretical concept. In real-world environments, laptops and mobile devices are frequently lost or stolen. Without encryption, the data on these devices could be accessed easily by malicious actors. BitLocker provides a practical solution by ensuring that data remains inaccessible unless the correct authentication is provided. Candidates preparing for the exam must understand how to enable and manage such encryption, including features like BitLocker To Go for removable drives.
The exam also addresses the encrypting file system (EFS), another important feature that allows individual files and folders to be encrypted rather than entire drives. This enables more granular control over data protection. Understanding the differences between drive-level encryption and file-level encryption is critical for implementing the appropriate security strategy in different scenarios.
System Updates and Patch Management
Another fundamental responsibility covered in the exam is managing system updates. Candidates are expected to describe and configure Windows Update, as well as understand how app updates and device system updates are applied. Updates are critical for maintaining both security and functionality, as they patch vulnerabilities and introduce performance improvements.
In enterprise environments, updates must be managed carefully. Automatic updates may not always be appropriate because they could disrupt critical operations. Instead, administrators often configure update policies that ensure devices are updated during scheduled maintenance windows. The exam requires knowledge of how these updates are configured, ensuring that candidates understand the balance between security and operational continuity.
Application updates are another area of focus, as applications must be kept up to date to prevent exploitation of vulnerabilities. Candidates should understand how Windows manages app updates through the Microsoft Store and other mechanisms. Knowledge of system update processes, including service packs and cumulative updates, ensures that candidates are prepared to handle the lifecycle management of devices.
Data Access and File Management
The exam also emphasizes knowledge of data access and file management. IT professionals must understand how to configure and manage both local and cloud storage solutions to ensure that data is available, secure, and efficiently managed. This involves knowledge of different file systems, storage spaces, and permissions that govern access to resources.
Candidates are required to understand the differences between file systems such as FAT, FAT32, NTFS, and ReFS. NTFS, for example, supports advanced features such as permissions and encryption, making it more suitable for enterprise environments than FAT32, which has limitations on file sizes and lacks security features. ReFS, or Resilient File System, is designed to provide greater reliability and is often used in environments requiring high data integrity.
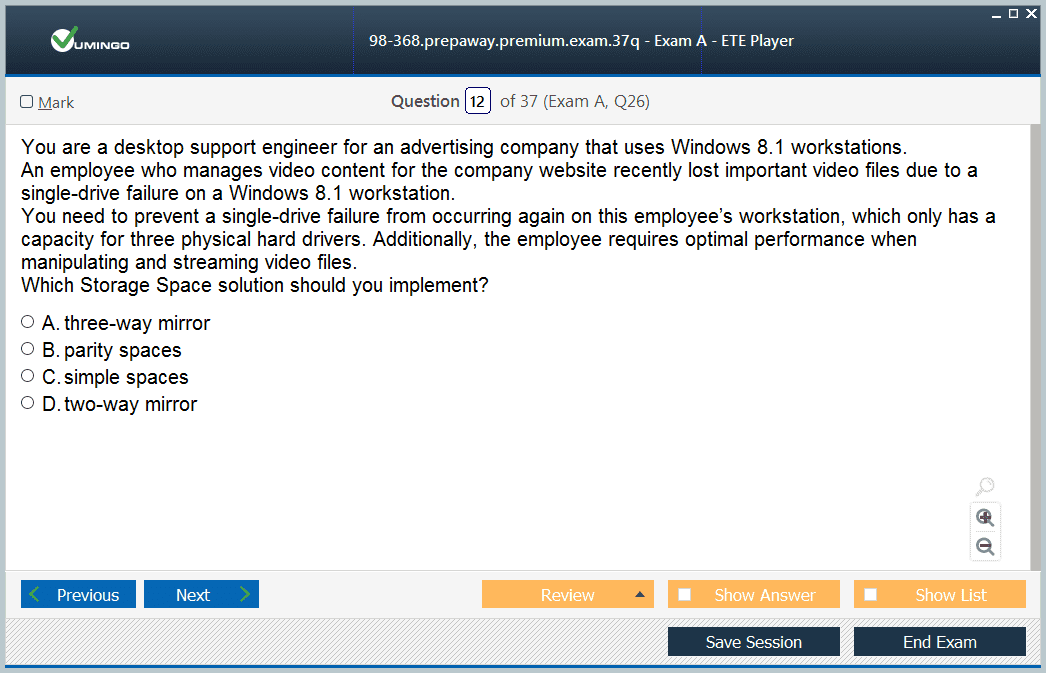
Storage spaces and storage pools provide another important capability, allowing administrators to combine physical disks into logical storage pools. This enables flexible management of storage resources and supports features like redundancy. Candidates must understand how these technologies work and how they can be applied in enterprise scenarios.
File and print sharing is another crucial topic. Candidates must understand how to configure permissions, create different types of shares, and manage access to shared resources. Misconfigured file sharing can result in unauthorized access or data leaks, so mastering this area is critical for ensuring both security and efficiency in collaborative environments.
Security and User Authentication
The exam gives special attention to device security and authentication, recognizing that these are critical for protecting organizational resources. Candidates must understand different authentication methods, including passwords, smart cards, multifactor authentication, and biometrics. Each of these methods provides varying levels of security, and the exam requires candidates to recognize their strengths and limitations.
For example, passwords remain the most common form of authentication but are also highly vulnerable to attacks such as phishing and brute force. Multifactor authentication enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a password combined with a mobile device code. Smart cards and biometrics offer additional layers of security, reducing reliance on weak or reused passwords.
Candidates must also understand how Windows Rights Management Services and Active Directory Federation Services support authentication and identity management. These technologies allow organizations to manage access to resources more effectively, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
Permissions are another critical aspect of security. Understanding basic and advanced permissions, how they are inherited, and how they are applied when files are moved or copied is central to ensuring proper access control. Misconfigured permissions can lead to either unnecessary restrictions or unintended access, both of which can disrupt operations and expose data to risks.
Malware and Threat Protection
Another area emphasized in the exam is malware and threat protection. Candidates must understand the differences between viruses, Trojan horses, spyware, and adware, as well as strategies for defending against them. This includes implementing antivirus software, configuring firewalls, and maintaining best practices for device security.
Malware represents one of the greatest threats to enterprise environments. A single infected device can compromise an entire network, leading to data breaches or downtime. The exam ensures that candidates understand how to recognize different types of malware and how to configure protective measures to mitigate risks.
Firewalls are another essential part of threat protection. They act as barriers between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, controlling traffic based on predefined rules. Candidates must understand how to configure and manage firewalls to protect devices without interfering with legitimate business activities.
By mastering these areas, candidates not only prepare for the exam but also build skills that will be directly applicable in their future roles. Security knowledge is universally relevant, and the topics covered in this exam lay the foundation for more advanced security certifications and responsibilities.
Understanding Cloud Services in the Context of Mobility
Cloud services play a significant role in modern enterprise environments, and this is why the exam dedicates coverage to them. Understanding cloud-based solutions enables candidates to recognize how organizations manage devices, applications, and user data more effectively. For candidates sitting the exam, familiarity with productivity services, storage services, and communication platforms is essential, as these are now integral parts of daily IT operations.
The exam focuses on helping learners identify different types of cloud services. Productivity services such as Office 365 applications support collaboration and efficiency across multiple devices. Storage services, like OneDrive and Azure Storage, ensure that data is accessible from any location while maintaining strong security measures. Communication services, including platforms integrated with Microsoft technologies, demonstrate how organizations can support remote and distributed teams without losing efficiency.
The importance of cloud services extends beyond access and convenience. They provide scalability, allowing organizations to expand resources based on demand. They also enable high availability and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring business continuity even in unexpected circumstances. By testing knowledge of cloud service types, the exam ensures candidates are prepared for environments where these solutions form the backbone of IT infrastructure.
Exploring Microsoft Intune Capabilities
Microsoft Intune is highlighted as a central technology in the exam because of its ability to manage devices and applications in a cloud-driven environment. Intune provides administrators with tools to enforce security policies, configure applications, and protect organizational data across mobile devices, desktops, and tablets. Understanding Intune is critical for anyone preparing for the exam, as it directly supports enterprise mobility.
One of Intune’s most important capabilities is mobile device management, often referred to as MDM. Through Intune, administrators can remotely configure device settings, enforce compliance rules, and monitor device health. This ensures that all devices connecting to the organization’s network meet security and policy standards. For example, Intune can require that devices have encryption enabled or block access to company data on devices that are not compliant.
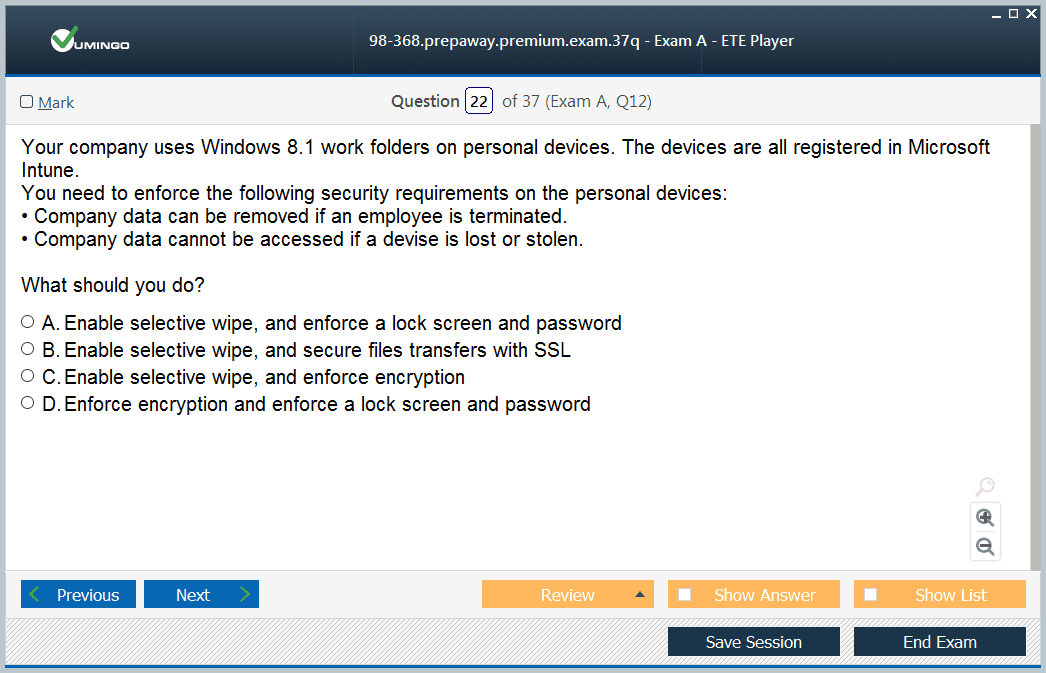
Another valuable feature is application management. Intune allows administrators to deploy applications directly to devices and manage them throughout their lifecycle. It supports app protection policies that help control how data is used within managed apps, preventing sensitive information from being copied or shared inappropriately. For the exam, candidates must understand how Intune supports selective wipe capabilities, where only organizational data is removed from a device, leaving personal data intact.
The exam also assesses knowledge of Intune’s role in supporting remote work and bring your own device scenarios. Intune provides the flexibility for employees to use personal devices while maintaining a high level of security, which aligns with the modern workplace trend toward mobility and flexibility.
Introduction to Microsoft Azure Services
Microsoft Azure is another crucial area tested in the exam because of its importance in enterprise cloud solutions. Azure provides a wide range of services, including virtual machines, storage, networking, and advanced features such as disaster recovery and redundancy. Understanding the basics of Azure is essential for candidates because it demonstrates how organizations leverage cloud platforms to extend their IT capabilities.
Virtual machines are a foundational service in Azure. They allow organizations to create and run operating systems in the cloud, supporting testing, development, or production environments without the need for physical hardware. Candidates preparing for the exam should understand the role of virtual machines and how they contribute to flexibility and scalability.
High availability and redundancy are key concepts within Azure. These ensure that applications and services remain operational even in the event of hardware failures or outages. Disaster recovery solutions within Azure provide additional resilience by replicating services across different geographical regions. By mastering these concepts, candidates demonstrate their ability to understand how businesses use Azure to guarantee reliability and minimize downtime.
Azure services also extend into identity and access management, which connects closely with enterprise mobility. Azure Active Directory, for example, provides centralized identity services that integrate with on-premises Active Directory. Candidates should understand the importance of this service in enabling secure sign-in and access management across multiple platforms.
Identity Services in Enterprise Mobility
Identity services are critical for managing access to organizational resources in enterprise environments. The exam tests knowledge of technologies such as Windows Server Active Directory, Azure Active Directory, Microsoft accounts, and federation services. Understanding these services allows candidates to recognize how organizations authenticate users and control access across devices and applications.
Windows Server Active Directory provides centralized management of users, groups, and devices within on-premises environments. It enables administrators to enforce policies and manage permissions consistently across an organization. Azure Active Directory extends these capabilities into the cloud, supporting single sign-on and enabling integration with thousands of third-party applications.
Federation services further enhance identity management by enabling trust relationships between different systems or organizations. This allows users to access resources across domains without needing multiple sets of credentials. For exam preparation, it is important to understand not only the technical definitions of these services but also their practical applications in managing modern enterprise mobility.
By mastering identity services, candidates demonstrate their readiness to support secure and efficient access to resources, which is increasingly important in workplaces where employees use a variety of devices to perform their roles.
Business Data Access and Remote Solutions
Managing access to business data is a vital skill for IT professionals, and the exam ensures candidates are equipped with knowledge of the tools and technologies that support this responsibility. Business data access must balance availability with security, ensuring that employees can retrieve necessary information without compromising sensitive resources.
The exam highlights technologies such as Work Folders, Company Portal, and Azure RemoteApp. Work Folders allow users to access work files from personal or corporate devices while maintaining synchronization and encryption. This enables employees to work from different locations without losing productivity.
Company Portal, often integrated with Microsoft Intune, provides employees with a centralized location to access organizational applications and resources. It helps streamline the user experience while giving administrators better visibility and control over device and app usage.
Azure RemoteApp is another solution tested in the exam, offering the ability to deliver Windows-based applications from the cloud to various devices. This allows users to run full-featured applications on devices that might not support them natively, expanding flexibility and mobility within the enterprise.
These tools collectively demonstrate the importance of enabling secure access to data and applications in a mobile-first world. For exam preparation, candidates should understand how these technologies work and how they fit into broader strategies for enterprise mobility.
Bring Your Own Device and its Implications
Bring Your Own Device, or BYOD, is an important concept in the exam because it reflects real-world practices that many organizations have adopted. BYOD policies allow employees to use their personal devices for work purposes, increasing flexibility and potentially reducing hardware costs for the organization. However, BYOD also introduces challenges in terms of security, compliance, and management.
Candidates are expected to understand how BYOD policies shift the focus from device-centric to people-centric IT. Instead of controlling every aspect of the device, administrators focus on protecting data and ensuring compliance regardless of where the data is accessed. This often involves using technologies such as Intune and Azure Active Directory to enforce policies and secure data access.
Desktop virtualization is another relevant topic, as it allows organizations to deliver a consistent work environment to users regardless of the device they are using. Dynamic Access Control policies also play a role in BYOD environments, allowing organizations to apply conditional access rules based on user identity and device compliance.
Windows Rights Management is another tool that supports BYOD by enabling organizations to control how data is used, even after it leaves the organization’s network. By mastering these topics, candidates demonstrate their understanding of how organizations implement BYOD strategies without compromising security or productivity.
Preparing for the Exam
Preparation for the exam requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical knowledge. Candidates should spend time familiarizing themselves with device configuration, security features, and cloud-based solutions through hands-on practice. Working with tools such as Windows devices, Intune, and Azure will provide the necessary experience to reinforce theoretical concepts.
Understanding the exam objectives is essential. Candidates should ensure they can describe and configure device settings, understand storage and file systems, manage permissions, configure encryption, and implement updates. Equally important is the ability to explain how cloud services, identity management, and enterprise mobility solutions function in practice.
Candidates should also practice applying these concepts in scenarios that reflect real-world environments. For example, configuring a group of devices to meet organizational standards, setting up BitLocker encryption, or deploying policies through Intune can reinforce understanding and build confidence.
The exam does not require advanced expertise but expects candidates to have foundational knowledge and some practical exposure to Windows devices, networking, and security concepts. By focusing on both the theoretical and practical aspects of the exam objectives, candidates can position themselves for success and establish a strong foundation for further certifications and career progression.
Configuring Device Settings in Modern Environments
Device configuration is one of the fundamental areas covered in the exam because it sets the foundation for usability, security, and efficiency. Configuring desktop settings, system options, and device preferences ensures that an organization can standardize user experiences while maintaining security and operational control. Candidates must understand how to manage the Start menu, display preferences, user profiles, and shortcuts. These settings may seem basic but are critical for ensuring consistency across multiple devices in enterprise environments.
Managing device options involves adjusting system configurations that influence performance and functionality. This includes understanding how to configure power options to balance performance with energy efficiency, managing device drivers to ensure hardware compatibility, and configuring accessibility settings for inclusive use. For exam preparation, candidates should be able to explain how these settings are applied, how they impact device usability, and how administrators enforce them across an enterprise network.
Another important aspect is Control Panel configuration. Even though newer versions of Windows increasingly emphasize Settings, the Control Panel remains relevant for managing advanced system options, user accounts, and hardware preferences. Knowing the differences between the two interfaces and when to use each is a point of focus. Understanding how administrators apply policies to standardize configurations also aligns with real-world enterprise practices.
Drive Encryption and Data Protection
The exam requires candidates to demonstrate understanding of drive encryption technologies such as BitLocker and BitLocker To Go. These features are critical in securing data at rest, preventing unauthorized access in cases where devices are lost or stolen. BitLocker integrates with Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware to provide strong encryption and ensure the integrity of system files.
Candidates should know how to enable BitLocker on supported devices, configure recovery keys, and understand the importance of key management. Recovery keys allow authorized users to regain access to encrypted drives in cases where credentials are lost, ensuring that security measures do not lock out legitimate users. The exam emphasizes not only the technical setup but also the broader implications of encryption in enterprise environments.
BitLocker To Go extends encryption to external drives such as USB devices. This is particularly relevant in mobile environments where users frequently transfer data between devices. Candidates must understand how this feature supports compliance requirements by ensuring that sensitive data cannot be accessed if removable media is misplaced.
Encrypting File System, or EFS, is another topic included in the exam. While BitLocker encrypts entire drives, EFS focuses on encrypting individual files and folders. Candidates should know when to use EFS, how it impacts file sharing and movement, and how it works alongside certificate services.
File Systems and Storage Management
A strong understanding of file systems and storage structures is essential for success in the exam. Candidates must differentiate between file systems such as FAT, FAT32, NTFS, and ReFS, each of which has unique characteristics and use cases.
FAT and FAT32 are older file systems that provide compatibility across multiple platforms but lack advanced features such as file permissions and large file support. NTFS, by contrast, offers features such as file-level security, compression, and support for large volumes, making it the default file system for modern Windows environments. ReFS, or Resilient File System, is designed for fault tolerance and data integrity, providing advantages in environments requiring high reliability.
Understanding how to manage storage spaces and storage pools is another focus area. Storage Spaces allow administrators to combine multiple physical drives into a single logical volume, improving redundancy and performance. Candidates must be able to describe how storage pools work and how they can be configured to support organizational needs.
File and print sharing also plays an important role in enterprise device management. Candidates should be able to describe how NTFS and share permissions work, the difference between basic and advanced sharing options, and how effective permissions are calculated when multiple permission sets overlap. Understanding print driver management and creating shared printers are additional skills relevant to the exam.
Device Security and Authentication Practices
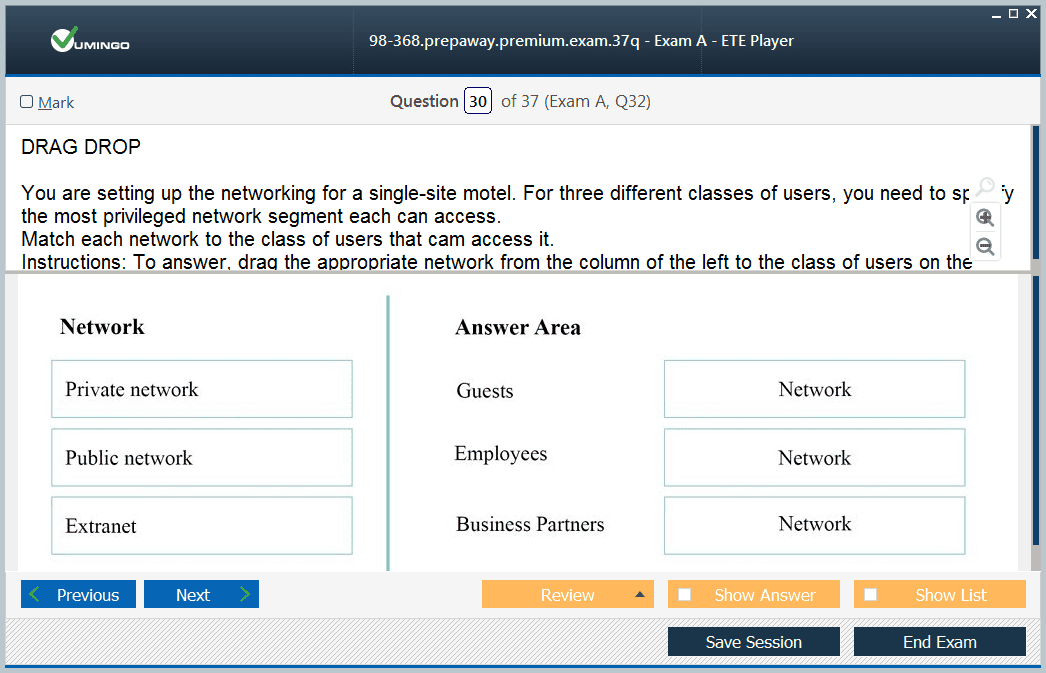
Security is central to enterprise mobility, and the exam evaluates understanding of how organizations protect devices and data. Candidates must recognize the differences between the Internet, intranets, and extranets, and understand how private and public networks influence device configuration and security measures.
User authentication is a key concept. The exam emphasizes knowledge of methods such as multifactor authentication, smart cards, biometrics, and password policies. Multifactor authentication combines two or more factors, such as something the user knows, something the user has, and something the user is, to strengthen security. Smart cards and biometrics provide additional layers of identity verification, while strong password policies reduce vulnerabilities to unauthorized access.
Windows Rights Management Services (RMS) are also covered, enabling organizations to protect sensitive data by controlling how files can be accessed, shared, or printed. Understanding RMS is essential for candidates because it demonstrates the ability to secure data beyond basic authentication.
Permissions management is another focus area. Candidates must understand how to configure file and share permissions, how ownership and delegation work, and how resultant permissions are calculated. This knowledge ensures that users can access only the resources they are authorized to use, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious data exposure.
Malware and Protective Strategies
The exam requires candidates to demonstrate an understanding of common malware types, including viruses, Trojans, spyware, and adware. Each type of malware poses unique threats, and recognizing their characteristics is essential for implementing effective defenses.
Viruses attach themselves to files or applications and spread when those files are shared. Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software but deliver malicious payloads once installed. Spyware operates silently to collect sensitive information such as login credentials, while adware generates unwanted advertisements and can degrade performance.
Protecting devices against malware requires a combination of strategies. Candidates should understand how antivirus and antimalware tools function, how firewalls provide perimeter protection, and how regular updates mitigate vulnerabilities. They should also be familiar with best practices such as user education, which plays an essential role in preventing malware infections by reducing risky behavior.
Managing Updates and System Reliability
Keeping devices up to date is a critical element of system management. The exam tests knowledge of Windows Update, application updates, and system firmware updates. Each type of update plays a role in ensuring security, stability, and performance.
Windows Update provides patches for operating system vulnerabilities and improvements to system features. Application updates ensure that productivity software and business tools function correctly and securely. Device system updates, including drivers and firmware, maintain compatibility and hardware performance.
Candidates should understand how updates can be managed manually, through group policies, or via centralized tools such as Intune. They must also recognize the importance of balancing update schedules with business continuity, ensuring that updates are applied promptly without disrupting operations.
Networking Considerations for Mobility
Networking concepts are also central to the exam, as mobile devices rely heavily on network connectivity. Candidates must understand how private and public networks function, and how security measures such as firewalls protect devices in different environments.
Knowledge of wireless networking is particularly relevant. Candidates should be familiar with standards such as Wi-Fi, understand how to configure secure wireless connections, and know the importance of protocols such as WPA2 and WPA3. Virtual private networks, or VPNs, are another important concept, enabling secure communication between remote devices and organizational networks.
Candidates should also be able to explain the role of network ports, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems in securing devices. By mastering these networking fundamentals, they can demonstrate the ability to support mobile devices in diverse environments.
Enterprise Mobility Scenarios and Real-World Application
One of the goals of the exam is to prepare candidates for real-world scenarios where enterprise mobility is critical. This includes supporting distributed workforces, managing hybrid environments, and ensuring secure access to applications and data.
Candidates must understand how technologies such as Intune, Azure Active Directory, and BitLocker work together to support mobility strategies. For example, an organization may implement Intune to manage device compliance, Azure Active Directory to authenticate users, and BitLocker to protect data at rest. Together, these technologies create a comprehensive approach to enterprise mobility.
Another scenario involves bring your own device strategies, where personal devices connect to organizational resources. In these cases, administrators must ensure that sensitive data remains protected without restricting employee flexibility. This often involves configuring policies that enforce encryption, restrict data sharing, and allow selective wipe capabilities.
By practicing and applying these scenarios, candidates preparing for the exam can connect theoretical knowledge to practical enterprise challenges. This ensures they not only pass the exam but also develop the skills required to support mobility in modern organizations.
Identity Management in Mobility Environments
Identity management is a critical component of the 98-368 exam because it directly influences security, user experience, and organizational control. Devices used in mobile environments often connect from multiple locations and networks, requiring strong identity solutions to ensure that the right individuals gain access to the right resources. Windows Server Active Directory and Azure Active Directory are the primary tools tested in the exam, as they provide the backbone for identity services.
Active Directory has long been used in enterprise environments to manage users, groups, and computers within a domain. It enables administrators to enforce policies, manage permissions, and create a consistent security framework. Azure Active Directory extends these capabilities to the cloud, supporting mobility by allowing users to authenticate across devices and services, regardless of their location. Exam candidates need to understand the differences between on-premises Active Directory and Azure Active Directory, including scenarios where federation services are used to bridge the two environments.
Another aspect of identity management involves single sign-on, which simplifies user access to multiple applications while reducing password fatigue. Candidates must understand how single sign-on works, how it is implemented using Azure Active Directory, and how it contributes to both security and productivity. Federation services extend single sign-on by allowing authentication across organizational boundaries, making it possible for users in one enterprise to securely access resources in another without maintaining multiple sets of credentials.
Business Data Access in Enterprise Mobility
The 98-368 exam evaluates understanding of how organizations manage access to business data in mobile environments. This includes services like Company Portal, Work Folders, and Azure RemoteApp, which support secure and seamless data access.
Company Portal allows users to install approved applications, access resources, and manage devices under organizational policies. For exam preparation, candidates must know how the Company Portal interacts with Intune and Azure Active Directory to provide secure access while maintaining user flexibility.
Work Folders enable users to synchronize work files across devices while storing the data securely on organizational servers. This ensures that employees have access to important files whether they are in the office or working remotely, while administrators maintain control over storage and permissions. Candidates should be familiar with how Work Folders integrate with encryption and data protection measures to safeguard information.
Azure RemoteApp extends business applications to remote devices without requiring full installations. This approach supports bring your own device strategies by allowing applications to run on personal devices while keeping business data contained within controlled environments. For the exam, candidates must understand the benefits of RemoteApp in terms of security, resource management, and mobility.
Bring Your Own Device Strategies
Bring your own device, or BYOD, is increasingly relevant as organizations adapt to flexible working models. The exam emphasizes the importance of understanding how BYOD affects security, identity management, and access controls.
In BYOD environments, devices are often personally owned but used to access business resources. This introduces challenges because the organization must secure its data without infringing on personal usage. The exam covers strategies such as desktop virtualization, dynamic access control, and rights management services to address these challenges.
Desktop virtualization enables business applications and desktops to run in controlled environments while being accessed remotely. This ensures that sensitive data never leaves the organization’s infrastructure, even though the user may be working on a personal device.
Dynamic Access Control provides policies that adjust access rights based on user attributes, device compliance, and resource sensitivity. For example, a user might be allowed to access confidential documents only when connecting from a compliant, encrypted device.
Windows Rights Management further protects data by controlling how files are used. Even if a file leaves the organization’s network, rights management can prevent unauthorized sharing, printing, or editing. This feature is important in BYOD environments where data may travel across unmanaged devices.
Cloud Services for Mobility
Cloud services are at the center of enterprise mobility, and the 98-368 exam requires a clear understanding of their types, functions, and benefits. Candidates must be able to differentiate between productivity, storage, communication, and search services, as well as explain how Microsoft solutions like Intune and Azure provide mobility support.
Productivity services, such as cloud-hosted applications, allow users to work collaboratively across devices and locations. Storage services, like OneDrive and Azure storage, provide secure repositories for files with synchronization capabilities. Communication services, including email and instant messaging platforms, support collaboration, while search services enhance accessibility of information across distributed systems.
Microsoft Intune is especially relevant to the exam because it enables centralized management of mobile devices, applications, and policies. Candidates must understand how Intune supports selective wipe, enforces compliance policies, and integrates with Azure Active Directory to ensure secure access. Intune’s role in mobile application management is also critical, as it allows organizations to protect data within applications without restricting personal use of devices.
Azure services, on the other hand, extend enterprise mobility through virtual machines, redundancy, high availability, and disaster recovery solutions. Candidates must be able to explain how Azure contributes to enterprise resilience and supports scenarios where employees require constant access to resources.
Virtual Private Networks in Mobile Security
Virtual private networks, or VPNs, are central to secure communication in mobile environments. The 98-368 exam requires candidates to understand how VPNs encrypt traffic, protect data integrity, and provide secure tunnels between remote devices and organizational resources.
VPNs are especially important when devices connect to public networks, such as coffee shop Wi-Fi, where the risk of data interception is high. Candidates should be able to explain the differences between types of VPNs, including point-to-point tunneling, secure socket tunneling, and IPsec.
Understanding how VPNs integrate with identity management systems and encryption technologies is also crucial. For example, a VPN may require multifactor authentication for access, ensuring that only authorized users can establish secure connections. VPNs often work alongside BitLocker and EFS, ensuring that both communication channels and stored data remain protected.
Security Policies for Mobile Devices
Organizations implement security policies to protect devices and data in mobility scenarios. The 98-368 exam emphasizes knowledge of how policies are configured and enforced across devices.
Security policies may cover areas such as password complexity, device encryption, update requirements, and application controls. Candidates must understand how group policies, Intune policies, and local device policies interact to enforce compliance. For example, an organization may require all devices to enable BitLocker before they can access sensitive data through the Company Portal.
Application control is another important policy area. Administrators may restrict installations to approved applications, reducing the risk of malware. Candidates should know how application whitelisting works, how mobile device management tools enforce it, and how it supports enterprise security.
Compliance reporting is also relevant, as organizations need visibility into device status. Intune provides dashboards that display compliance levels, allowing administrators to take corrective action when devices fall out of compliance. Candidates must understand the importance of monitoring and how it ensures that security policies remain effective.
Encryption Beyond the Device
While drive encryption protects data at rest, mobile environments require encryption of data in transit and in use. The exam evaluates knowledge of technologies like secure sockets layer, or SSL, and transport layer security, or TLS. These protocols secure web traffic and application communication, ensuring that sensitive data cannot be intercepted during transmission.
Certificate services play a key role in encryption. Candidates must understand how certificates are issued, validated, and revoked, and how they enable secure communication between devices and services. Certificates are especially important in scenarios where devices connect to corporate Wi-Fi or VPNs, as they authenticate devices and users while encrypting data.
Encryption of email and messaging is another focus area. Mobile users often exchange sensitive information through communication platforms, and encryption ensures that this data remains confidential. The exam requires candidates to describe how encryption methods integrate with authentication and rights management to form a comprehensive security approach.
Preparing for Real-World Application
The exam does not only test technical knowledge but also evaluates how candidates apply it in real-world mobility scenarios. This involves understanding the balance between usability and security, the challenges of supporting distributed workforces, and the strategies for maintaining compliance across diverse devices.
For example, a mobile workforce may require access to cloud applications, file storage, and internal systems. Administrators must configure identity management to allow seamless access while applying policies that ensure devices remain encrypted and updated. They must also prepare for potential incidents such as lost devices, ensuring that selective wipe and recovery processes are in place.
Candidates must also demonstrate the ability to plan for scalability. As organizations grow, mobility solutions must accommodate more users, more devices, and more complex policies. Understanding how Azure and Intune scale to meet these demands is essential for exam success.
Device Management in Distributed Workforces
One of the central themes of the 98-368 exam is the ability to manage devices in environments where employees operate across multiple locations and platforms. Distributed workforces require administrators to create management structures that maintain consistency while still allowing flexibility. Candidates need to be aware of how tools such as Group Policy, Intune, and device management frameworks interact to maintain organizational control without disrupting productivity.
Group Policy remains a foundational element for on-premises environments, allowing administrators to configure settings such as password policies, desktop restrictions, and update requirements. These policies can be applied across domains, ensuring that every device that joins the domain complies with organizational standards. For exam preparation, it is important to understand how policies cascade, how conflicts are resolved, and how administrators can enforce restrictions even on remote machines connected via VPN.
Intune adds another layer of management, especially important in mobile and cloud-first environments. Intune policies can be applied to devices that may not always connect to the internal domain, ensuring that compliance is maintained regardless of location. Intune also supports cross-platform device management, meaning organizations can apply consistent standards across Windows, iOS, and Android devices. This flexibility is crucial for mobile workforces where employees often use a mix of personal and organizational devices.
Application Deployment in Mobile Environments
The 98-368 exam emphasizes understanding how applications are deployed and managed in mobile environments. Traditional application deployment strategies are not always sufficient for mobile devices, as users may not have consistent access to organizational networks or may be using personal hardware.
Windows Store applications represent one deployment method, where users install applications directly from the store. Administrators can manage access to these applications through Intune or Group Policy, ensuring only approved applications are installed. Candidates must understand how application whitelisting works and how it prevents the installation of unapproved or potentially harmful applications.
Another method is centralized deployment, where administrators push applications to devices through management systems. This allows organizations to maintain control over which versions of software are installed, reducing security risks from outdated or vulnerable applications. For exam purposes, candidates need to recognize how centralized deployment supports enterprise mobility while maintaining security.
Virtual application delivery is also relevant, as it allows users to run applications hosted in controlled environments. This method is often used in BYOD scenarios, ensuring that applications can run on personal devices without compromising organizational security. Understanding how virtual application delivery works and how it integrates with cloud services is a key aspect of the exam.
Data Protection Across Devices
Data protection is one of the most critical areas of the 98-368 exam, as mobile devices are particularly vulnerable to loss, theft, or unauthorized access. Candidates must understand how multiple layers of protection come together to safeguard data.
Encryption is the foundation of data protection. BitLocker provides full-disk encryption, while BitLocker To Go extends protection to removable drives. Encrypting File System allows for file-level encryption, ensuring that even individual documents remain secure. Exam candidates must be able to explain how each encryption method works, when it should be used, and how it integrates with user authentication.
Authentication itself plays a key role in data protection. Multifactor authentication requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a smart card or biometric factor. Candidates should be able to explain how multifactor authentication enhances security in mobile environments where devices are at greater risk of compromise.
Remote wipe is another critical concept, allowing administrators to erase organizational data from lost or stolen devices without affecting personal content. This feature supports BYOD strategies while ensuring sensitive data does not fall into the wrong hands. For the exam, candidates should understand how selective wipe works in Intune and why it is preferable to full-device wipes in certain scenarios.
Networking in Mobile Contexts
Networking concepts are heavily tested in the 98-368 exam, as mobile devices rely on connectivity for access to resources. Candidates must understand the differences between private, public, and enterprise networks, as well as the role of firewalls in protecting communications.
Private networks, such as home or corporate networks, typically provide controlled environments where administrators can configure security policies. Public networks, such as those in airports or coffee shops, pose greater risks due to open access. Candidates should be able to describe how device firewalls and VPNs mitigate these risks by filtering traffic and encrypting communication.
Extranets are also relevant, as they allow organizations to share resources with external partners while maintaining security boundaries. Understanding how extranets differ from intranets and public networks is important for exam scenarios where organizations collaborate with external stakeholders.
Candidates must also understand basic networking hardware such as switches, routers, and access points, as well as their roles in supporting mobile devices. Network ports and protocols are another focus area, with candidates expected to describe how ports are used in communication and why closing unused ports reduces attack surfaces.
File and Print Services in Mobility
File and print services remain essential in enterprise environments, even in mobile contexts. The 98-368 exam tests understanding of how permissions, shares, and print services are configured and secured.
File sharing involves creating shares that users can access across the network. Candidates must know the differences between basic and advanced shares, as well as how to map drives for easier access. Understanding the differences between NTFS permissions and share permissions is crucial, as both layers determine the final access rights.
Effective permissions can become complex, as they depend on multiple factors such as group memberships, inherited permissions, and explicit denies. For the exam, candidates should be able to calculate effective permissions in various scenarios and explain how ownership transfer affects access control.
Print services also play a role in mobility, especially when employees use mobile devices to print documents in corporate environments. Candidates should know how print drivers are deployed, how printer access is controlled, and how to manage print queues.
Malware Protection in Mobile Scenarios
The 98-368 exam requires knowledge of malware types and strategies for protecting devices against them. Malware can affect mobile devices just as easily as traditional desktops, making this an important area of study.
Viruses, Trojan horses, spyware, and adware represent common categories of malware. Candidates must be able to describe how each operates and what risks they present. For example, spyware may capture login credentials from a mobile device, while adware may disrupt productivity with unwanted pop-ups.
Antivirus and antimalware tools provide primary protection, but candidates must also understand how layered defenses improve resilience. Firewalls block malicious traffic, intrusion detection systems identify suspicious behavior, and patch management reduces vulnerabilities. The exam evaluates knowledge of how these measures work together to protect devices in mobile environments.
User awareness is another important aspect of malware protection. Many infections occur due to phishing emails or unsafe downloads, so organizations must educate users on safe practices. Candidates should understand how training and awareness programs complement technical defenses to create comprehensive protection strategies.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery
High availability and disaster recovery strategies ensure that enterprise mobility remains functional even during failures. The 98-368 exam covers these concepts to evaluate understanding of resilience in IT infrastructures.
High availability focuses on designing systems that remain accessible despite hardware or software failures. This may involve redundancy, clustering, and load balancing. Candidates should know how Azure services provide high availability through geographically distributed data centers and failover capabilities.
Disaster recovery involves restoring services after significant disruptions, such as natural disasters or cyberattacks. Candidates must understand the role of backups, replication, and recovery procedures. For exam purposes, it is important to explain how recovery objectives are defined, such as recovery time objective and recovery point objective, and how they influence disaster recovery planning.
Integrating Mobility with Enterprise Strategy
Enterprise mobility is not just a technical challenge but also a strategic one. The 98-368 exam requires candidates to demonstrate understanding of how mobility integrates with broader organizational goals.
Mobility strategies must balance security, productivity, and cost efficiency. For example, implementing BYOD policies may reduce hardware expenses but requires stronger security measures to protect data. Cloud services may increase flexibility but require planning to avoid unnecessary costs.
Administrators must also align mobility strategies with compliance requirements, such as data protection regulations. Candidates should understand how encryption, auditing, and monitoring contribute to compliance in mobile environments.
Ultimately, mobility strategies should support business objectives by enabling employees to work efficiently from any location without compromising security. The exam assesses not only technical knowledge but also the ability to apply it in ways that support organizational success.
Conclusion
The Microsoft MTA Mobility and Devices Fundamentals exam provides a comprehensive overview of the essential skills needed to manage Windows devices and enterprise mobility in modern organizations. Candidates are expected to demonstrate understanding across multiple domains, including device configuration, security, identity management, networking, application deployment, data protection, and cloud services. Mastery of these areas ensures that professionals can effectively support mobile workforces, safeguard data, and maintain reliable access to organizational resources.
Device configuration forms the foundation of enterprise mobility management. Understanding desktop settings, system options, drive encryption, and update processes allows administrators to create standardized, secure environments across multiple devices. Encryption technologies such as BitLocker and Encrypting File System protect sensitive data, while authentication mechanisms, including multifactor authentication and smart cards, ensure that only authorized users gain access. Knowledge of file systems, storage management, and sharing permissions further supports secure and efficient operations.
Security is a recurring focus throughout the exam, emphasizing the importance of malware protection, firewall configurations, and rights management. Candidates must understand how these protections integrate into enterprise mobility strategies, particularly in bring your own device environments where personal and organizational use converge. Understanding VPNs, network segmentation, and cloud-based identity solutions like Azure Active Directory ensures that mobile devices remain protected when accessing corporate resources across diverse networks.
Enterprise mobility also requires expertise in application deployment, cloud services, and data access. Candidates must understand how to use Intune for device and application management, configure secure access to OneDrive and other storage solutions, and apply selective wipe or remote wipe processes when necessary. High availability and disaster recovery concepts, along with monitoring and compliance considerations, round out the knowledge needed to support resilient and efficient mobile environments.
Preparation for the 98-368 exam ensures that candidates not only acquire technical skills but also develop the ability to apply them in real-world scenarios. The exam emphasizes practical understanding, problem-solving, and the integration of multiple technologies to create secure, accessible, and scalable mobile environments. Achieving this certification equips professionals to manage enterprise mobility effectively, safeguard organizational data, and contribute to broader IT strategy, making it a critical stepping stone for careers in IT and technology.
Microsoft Mobility 98-368 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 98-368 Mobility and Devices Fundamentals certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MO-300 - Microsoft PowerPoint (PowerPoint and PowerPoint 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 98-368 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 98-368 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 98-368 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 98-368 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 98-368 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 98-368. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 98-368 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 98-368 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 98-368 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 98-368 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!