- Home
- Microsoft Certifications
- 98-364 Database Fundamentals Dumps
Pass Microsoft MTA 98-364 Exam in First Attempt Guaranteed!


98-364 Premium File
- Premium File 140 Questions & Answers. Last Update: Feb 26, 2026
Whats Included:
- Latest Questions
- 100% Accurate Answers
- Fast Exam Updates
Last Week Results!
All Microsoft MTA 98-364 certification exam dumps, study guide, training courses are Prepared by industry experts. PrepAway's ETE files povide the 98-364 Database Fundamentals practice test questions and answers & exam dumps, study guide and training courses help you study and pass hassle-free!
Pass Exam 98-364: Your Complete Microsoft Database Fundamentals Resource
The 98-364 exam assesses foundational knowledge of databases, emphasizing relational systems and their practical applications. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to understand how data is organized, stored, manipulated, and managed within a database environment. A solid grasp of these concepts enables individuals to work effectively with structured data, design efficient databases, and support organizational decision-making. Preparing for this exam involves not only understanding theory but also developing practical skills in database operations, object creation, data management, and basic administration.
Core Concepts of Databases
A strong foundation in database fundamentals begins with understanding what a database is and why it is used. Databases allow organizations to store, retrieve, and manipulate information efficiently. Relational databases organize data into tables, where each table contains rows and columns. The relationships between tables are defined through keys, which maintain data integrity and enable complex queries. Understanding these relationships is essential for performing meaningful analysis and ensuring that data remains consistent across the system.
Data types play a critical role in database design. Each column in a table is assigned a data type that determines the kind of data it can store, such as numbers, text, or dates. Choosing the correct data types ensures efficient storage, accurate calculations, and correct query results. Knowledge of constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and default values ensures that data adheres to business rules and maintains integrity.
Creating Database Objects
Creating database objects is a fundamental skill for anyone preparing for the 98-364 exam. Tables are the primary structures where data is stored, and candidates must understand how to define tables, choose appropriate columns, and apply constraints. Views provide a way to present data in a customized format without modifying the underlying tables. Stored procedures and functions allow repetitive tasks and calculations to be automated, improving efficiency and consistency.
Understanding indexes is also crucial. Indexes improve query performance by allowing the database engine to locate data quickly without scanning the entire table. However, they also add overhead for storage and updates, so candidates must know when and how to apply them effectively. Proper use of indexes, combined with thoughtful table design, ensures optimal performance and maintainability.
Data Manipulation and Querying
Data manipulation is a key domain in the 98-364 exam. Candidates are expected to perform operations such as selecting, inserting, updating, and deleting data using structured query language commands. Mastery of these operations allows individuals to retrieve relevant information efficiently, update records accurately, and maintain data integrity. Understanding query design, including filtering, sorting, and combining data from multiple tables, is essential for producing accurate results.
Candidates must also grasp the differences between data definition language and data manipulation language. Data definition language commands control the structure of database objects, while data manipulation language commands handle the actual data within those structures. Understanding both aspects ensures that candidates can create robust databases and manipulate information safely.
Data Storage and Organization
Effective data storage is vital for performance and integrity. Candidates need to understand normalization, which organizes data to reduce redundancy and improve consistency. Normalization involves dividing data into multiple related tables while maintaining relationships through keys. Knowledge of primary, foreign, and composite keys is essential for linking tables and enforcing relationships.
Understanding indexes and their impact on query performance is also part of data storage knowledge. Candidates should know how clustered and non-clustered indexes work, when to apply them, and how they affect retrieval and modification operations. Proper organization of data, along with effective indexing, ensures that databases can scale efficiently while providing reliable and fast access to information.
Basic Database Administration
The 98-364 exam evaluates knowledge of basic database administration tasks. Security is a critical component, and candidates must understand how to protect data from unauthorized access while ensuring legitimate users can perform necessary operations. Roles, permissions, and authentication methods help enforce security policies and maintain confidentiality.
Backup and recovery procedures are also covered. Candidates must know how to create backups, restore data, and plan for potential failures to ensure business continuity. Basic administrative tasks such as monitoring database performance, managing storage, and maintaining consistency are essential skills that support reliable operation. Understanding these fundamentals prepares candidates to manage a database environment responsibly and respond effectively to operational challenges.
Practical Experience and Hands-On Learning
Practical experience reinforces theoretical knowledge. Candidates are encouraged to practice creating tables, defining relationships, and writing queries to manipulate data. Hands-on exercises allow learners to understand the effects of constraints, keys, and indexes in real-world scenarios. Practicing data insertion, updates, and deletions helps candidates anticipate potential issues and understand how to maintain data integrity.
Exploring different query scenarios, such as joining multiple tables, filtering data with conditions, and aggregating results, strengthens problem-solving skills. Candidates also benefit from experimenting with stored procedures, functions, and views to automate common tasks and enhance efficiency. These exercises provide insight into how databases function in practice and build confidence in managing structured data.
Utilizing Learning Resources
A variety of resources can aid preparation. Study guides, reference books, and tutorials provide detailed explanations of key concepts and practical examples. Structured materials help candidates cover all exam domains systematically and ensure no critical topics are overlooked. Accessing trusted resources ensures accuracy and relevance in preparation.
Online communities, discussion forums, and peer collaboration offer additional benefits. Engaging with others allows candidates to explore alternative solutions, clarify doubts, and deepen their understanding. Learning from diverse perspectives enhances conceptual knowledge and exposes learners to real-world scenarios they might not encounter independently.
Self-Evaluation and Practice Tests
Regular self-evaluation is essential to track progress and identify areas requiring improvement. Practice tests simulate the exam environment and allow candidates to apply their knowledge under timed conditions. Reviewing performance on these exercises helps learners pinpoint weaknesses, refine techniques, and improve accuracy.
Consistent practice of database operations, object creation, query writing, and administrative tasks ensures that candidates are comfortable with all exam domains. Repetition solidifies understanding and builds the ability to respond efficiently to various problem types, improving overall readiness and confidence.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Readiness
Preparing for the 98-364 exam involves integrating theoretical knowledge with practical application. Candidates must understand core concepts, create and manipulate objects, manage data effectively, and perform basic administrative tasks. By combining hands-on practice, structured study materials, community interaction, and self-assessment, learners develop a holistic understanding of database fundamentals.
Mastering these skills equips candidates to approach the exam with confidence. It ensures they are capable of handling real-world database tasks, designing efficient structures, maintaining integrity, and retrieving information accurately. Successful preparation fosters both technical competence and problem-solving ability, forming a solid foundation for future growth in database management and broader IT roles.
Building a Foundation for Future Learning
The 98-364 exam serves as an entry point into the world of database technology. Candidates gain essential skills that are transferable to advanced database studies and practical applications in IT. Understanding relational concepts, data manipulation, storage optimization, and basic administration lays the groundwork for pursuing more complex topics, such as database design, performance tuning, and enterprise-level database management.
By mastering the fundamental principles and practical skills, candidates position themselves to progress confidently in their IT journey. The knowledge acquired through preparation not only enables exam success but also provides practical competencies applicable in professional environments, fostering both technical and analytical capabilities.
Advanced Understanding of Database Objects
A key component of preparing for the 98-364 exam is developing a detailed understanding of database objects and their roles within a relational database. Tables, as the primary storage units, must be designed carefully to ensure efficiency, maintainability, and accuracy. Candidates should be able to define columns with appropriate data types, apply constraints, and enforce relationships between tables through primary and foreign keys. Views provide a mechanism for displaying data in a customized format without altering the underlying structure, allowing users to focus on specific subsets of information. Stored procedures and functions automate repetitive tasks, encapsulate logic, and improve consistency, making them crucial for practical database management.
Indexes are another essential aspect of database objects. They facilitate fast retrieval of data by allowing queries to locate specific records without scanning the entire table. Understanding the difference between clustered and non-clustered indexes, as well as their implications on performance and storage, is vital. Candidates must also know how to use unique indexes and constraints to maintain data integrity while optimizing query performance. Proper application of indexes can significantly enhance database responsiveness, particularly when working with large datasets.
Querying and Data Manipulation
The ability to manipulate and query data effectively is central to the 98-364 exam. Candidates must be proficient in selecting, inserting, updating, and deleting data using structured query commands. Mastery of these operations ensures that users can retrieve accurate information, maintain records, and support business processes. Filtering, sorting, and combining data from multiple tables are essential skills for analyzing datasets and producing meaningful results.
Candidates should also understand join operations, including inner joins, outer joins, and cross joins, to combine information from related tables. Aggregation functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX are frequently applied to summarize data and support reporting. Using conditional logic within queries allows for dynamic calculations and advanced data analysis. These skills demonstrate the ability to extract actionable insights from structured datasets efficiently.
Data Storage and Normalization
Effective data storage strategies are critical for database efficiency and integrity. Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy, eliminate anomalies, and maintain consistency across the database. Candidates must understand normalization rules, including the first, second, and third normal forms, and how they contribute to efficient database design. Proper normalization ensures that updates, deletions, and insertions do not compromise data integrity.
Keys play a central role in connecting tables and enforcing relationships. Primary keys uniquely identify each record within a table, foreign keys link related tables, and composite keys combine multiple columns to create a unique identifier. Candidates must understand how these keys interact to maintain referential integrity. Additionally, knowledge of indexing strategies supports efficient data retrieval, reducing the time required to query large datasets.
Database Security and Access Control
Security is an important domain in the 98-364 exam. Candidates need to understand how to restrict access to sensitive data while allowing authorized users to perform necessary operations. Implementing roles, permissions, and authentication mechanisms ensures that data is protected against unauthorized access. Understanding the principles of least privilege and how to apply them in a database environment is essential for maintaining security without hindering workflow.
Additionally, encryption, both at rest and in transit, can protect data from breaches and unauthorized viewing. Candidates should also be aware of auditing practices that monitor database activity, detect suspicious behavior, and maintain accountability. Security measures, when combined with effective administration, help create a reliable and trustworthy database environment.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
A fundamental aspect of database management is ensuring data durability through backup and recovery strategies. Candidates must know how to perform backups, including full, differential, and transaction log backups. Understanding how to restore databases from backups is essential for recovering from accidental data loss or corruption. Planning for potential failures and implementing recovery procedures ensures continuity of operations and protects critical information.
Candidates should also be familiar with testing backup and recovery processes to verify reliability. This involves simulating failures, restoring data, and checking integrity to ensure that the database can be recovered effectively in real-world scenarios. A well-planned backup strategy is a cornerstone of responsible database administration.
Designing Efficient Queries
Beyond basic operations, candidates must be able to design efficient queries that minimize resource usage and maximize performance. Understanding query execution plans allows candidates to identify bottlenecks and optimize retrieval strategies. Techniques such as indexing, query optimization, and avoiding unnecessary joins or subqueries contribute to faster and more accurate data access.
Efficient query design also includes using functions, conditional logic, and grouping mechanisms to produce concise and meaningful results. Candidates should practice creating queries that address real-world business scenarios, including summarizing sales data, analyzing customer interactions, and producing performance metrics. This practical experience ensures readiness for the exam and real-world applications.
Practical Application of Database Concepts
Hands-on practice is essential for mastering the 98-364 exam objectives. Candidates should create sample databases, define tables, populate data, and experiment with various query scenarios. Practicing the creation of views, stored procedures, and functions helps reinforce understanding of automation and logic encapsulation. Experimenting with constraints, relationships, and indexes allows candidates to see the impact of design decisions on data integrity and performance.
Scenario-based exercises, such as analyzing sales trends, managing employee records, or consolidating customer information, provide context for applying theoretical knowledge. These exercises simulate real-world situations, reinforcing problem-solving skills and the ability to manipulate data effectively.
Utilizing Learning Resources
A structured preparation strategy enhances understanding and retention of database fundamentals. Reference books provide in-depth coverage of database concepts, practical examples, and exercises that align with the exam objectives. Comprehensive guides cover all relevant domains and allow candidates to systematically study each area.
Engaging in online communities and discussion forums provides additional perspectives and clarifies challenging concepts. Collaboration with peers allows candidates to explore different approaches, share solutions, and deepen their understanding of database management. Regular interaction with other learners also encourages the development of problem-solving strategies that are applicable both in exams and professional environments.
Self-Assessment and Practice Exercises
Self-assessment is a critical step in preparation. Candidates should regularly test their knowledge by completing practice exercises and mock exams. This helps identify strengths and areas requiring further study, allowing learners to focus their efforts more effectively. Practicing under timed conditions improves time management and prepares candidates for the pace of the actual exam.
Repetitive practice strengthens familiarity with database structures, query writing, data manipulation, and administration tasks. This repetition ensures that candidates can respond accurately and efficiently to various challenges, enhancing confidence and competence in both exam and practical scenarios.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Success
Successful preparation for the 98-364 exam requires integrating theoretical understanding with practical application. Candidates must be comfortable designing tables, enforcing relationships, manipulating data, and performing basic administrative tasks. Combining hands-on practice with structured study and collaborative learning ensures a comprehensive grasp of database fundamentals.
Mastery of these areas equips candidates to handle realistic scenarios efficiently, design robust databases, and extract meaningful insights from structured data. This holistic approach not only prepares candidates for exam success but also establishes a strong foundation for future learning and professional development in database management and related fields.
Real-World Applications and Career Readiness
The skills developed while preparing for the 98-364 exam are directly applicable to professional environments. Candidates gain the ability to create organized databases, perform data analysis, maintain data integrity, and implement security and backup procedures. These competencies are essential for roles involving data management, reporting, and IT support.
Practical experience with relational databases, querying, and administration enhances problem-solving capabilities and provides confidence in working with structured data. Preparing for this exam fosters both technical knowledge and analytical thinking, equipping learners to contribute effectively in professional settings.
Understanding Relational Database Design
A crucial aspect of preparing for the 98-364 exam is mastering relational database design. Relational databases store data in tables composed of rows and columns, with each table representing an entity and each column representing an attribute. Proper database design ensures data integrity, eliminates redundancy, and facilitates efficient querying. Candidates must understand how to identify entities, define relationships, and establish primary and foreign keys to maintain referential integrity. A solid grasp of normalization principles allows learners to structure data logically and prevent anomalies such as duplication, update, and deletion inconsistencies.
Designing relational databases also involves understanding the trade-offs between normalization and performance. While higher normalization reduces redundancy, it may increase the complexity of queries and joins. Candidates should be able to balance the need for efficient storage with the requirement for rapid access to frequently queried data. By analyzing practical scenarios and determining the optimal structure, learners develop skills that are directly applicable to real-world database management.
Advanced Query Techniques
Querying is at the core of database operations and is heavily tested in the 98-364 exam. Candidates must be adept at writing queries to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data. Beyond basic commands, understanding the use of joins to combine multiple tables is essential. Inner joins extract records with matching keys in both tables, while outer joins include unmatched records from one or both tables. Cross joins produce Cartesian products, and candidates should know when such operations are useful and how to handle large results efficiently.
Candidates must also be skilled in filtering data with conditions, using logical operators, and applying aggregate functions like SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX. Grouping and having clauses allow for summarization and conditional filtering of aggregated data. Subqueries enable nested queries that provide dynamic results based on related datasets. Mastery of these techniques allows candidates to construct efficient queries that meet complex requirements while minimizing computational overhead.
Implementing Data Integrity
Ensuring data integrity is a major focus for exam preparation. Candidates must understand constraints, including primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, check constraints, and default values. These mechanisms enforce rules on the data, ensuring consistency and preventing invalid entries. Referential integrity ensures that relationships between tables remain accurate, and constraints are applied consistently to avoid orphaned records or duplication.
Triggers and stored procedures can be used to enforce business rules programmatically. Candidates should understand when and how to apply these tools to automate validation, maintain integrity, and reduce the risk of errors during data manipulation. Learning to balance integrity constraints with performance requirements is essential for designing functional and reliable database systems.
Data Storage Optimization
Data storage and optimization techniques are critical for efficient database management. Indexes improve query performance by enabling rapid access to data, but they also add overhead during insertions, updates, and deletions. Candidates must understand clustered and non-clustered indexes, their use cases, and the trade-offs involved. Proper indexing strategies ensure that frequently accessed data can be retrieved quickly without excessive resource consumption.
Normalization, as a storage optimization strategy, reduces redundancy and improves consistency. However, candidates must also consider denormalization in certain scenarios to improve query performance for reporting or analysis. Partitioning tables and managing storage allocation are additional techniques that can enhance scalability and responsiveness in larger databases. Understanding these strategies allows candidates to optimize both performance and reliability.
Database Security Practices
Securing a database is a fundamental skill tested in the 98-364 exam. Candidates must understand user authentication, access control, and permission management to restrict unauthorized access while enabling legitimate use. Roles and permissions allow administrators to assign appropriate levels of access based on job functions, enforcing the principle of least privilege.
Encryption, both at rest and in transit, protects sensitive data from exposure. Candidates should understand how to implement security measures and audit database activity to monitor access patterns and detect anomalies. Effective security practices prevent data breaches, maintain confidentiality, and ensure compliance with organizational or regulatory requirements. Security knowledge also encompasses backup protection and controlled restoration processes to prevent data loss or tampering.
Backup and Recovery Procedures
Candidates must understand backup strategies and recovery procedures to ensure data durability and business continuity. Different types of backups, such as full, differential, and transaction log backups, serve distinct purposes and offer varying recovery options. Knowing when and how to perform each type of backup allows administrators to maintain an up-to-date copy of data and minimize downtime in case of failure.
Restoration involves recovering the database to a consistent state, which may include point-in-time recovery using transaction logs. Candidates should practice planning recovery strategies, testing restoration procedures, and documenting processes to ensure reliability. Understanding how to manage storage requirements, verify backups, and execute recovery plans reinforces practical skills critical for database maintenance.
Developing Efficient Queries and Reporting
Efficient query development is essential for performance and accuracy. Candidates must learn to construct queries that minimize unnecessary computations, use proper indexing, and avoid excessive joins or subqueries that can slow performance. Optimization techniques include analyzing query execution plans, understanding data access paths, and refining queries to retrieve only the required data.
Creating reports and aggregations based on queries is another practical application. Candidates should understand how to summarize data, generate calculated fields, and present results in a clear, actionable format. Learning to combine queries with views or stored procedures allows for reusable, maintainable reporting solutions that support decision-making and operational efficiency.
Hands-On Exercises for Skill Reinforcement
Practical exercises enhance understanding and retention of database concepts. Candidates should design sample databases, define tables and relationships, and populate data to practice real-world scenarios. Working on queries that involve multiple tables, aggregate functions, and conditional logic helps reinforce learning.
Implementing views, stored procedures, and functions provides insight into automating repetitive tasks and encapsulating business logic. Experimenting with constraints, keys, and indexing allows candidates to observe how design choices affect integrity and performance. Scenario-based exercises such as managing sales records, customer databases, or inventory data provide context for practical application and reinforce problem-solving skills.
Utilizing Structured Learning Materials
Organized study resources help candidates systematically cover all exam domains. Comprehensive guides explain core concepts, provide examples, and include exercises to strengthen understanding. Structured materials ensure no essential topic is overlooked and help learners progress logically from basic principles to more advanced applications.
Engaging with learning communities and forums supplements study materials by providing additional perspectives and solutions. Peer discussions allow candidates to clarify doubts, explore alternative approaches, and gain insight into practical challenges. Collaborative learning fosters deeper understanding and encourages the development of problem-solving techniques applicable both in exams and professional work.
Practice Testing and Self-Evaluation
Self-assessment is a critical component of exam preparation. Candidates should work through practice exercises and mock scenarios to evaluate their knowledge and identify areas requiring further study. Timed exercises help develop efficiency, accuracy, and familiarity with the structure and flow of typical exam questions.
Consistent practice reinforces technical skills and builds confidence in executing tasks under exam-like conditions. By repeatedly applying database concepts to various scenarios, candidates improve their problem-solving ability, strengthen understanding of query logic, and enhance their ability to manage data effectively.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Readiness
Preparation for the 98-364 exam requires combining theoretical understanding with practical application. Candidates must demonstrate competence in designing tables, enforcing relationships, performing queries, and managing basic administrative tasks. Hands-on practice, structured study materials, community engagement, and self-evaluation create a comprehensive learning experience.
This integration of knowledge equips candidates to handle real-world database tasks efficiently. It ensures they can create organized structures, maintain integrity, optimize performance, and secure data effectively. Holistic preparation fosters technical proficiency, analytical thinking, and problem-solving capabilities that are essential for both exam success and professional application.
Real-World Applications of Exam Skills
The skills acquired during preparation for this exam extend beyond the test itself. Candidates develop the ability to manage relational databases, design efficient structures, manipulate data accurately, and implement security and backup procedures. These competencies are valuable in professional settings, enabling individuals to contribute effectively to data management, analysis, and reporting tasks.
Practical application of knowledge gained ensures candidates are ready to handle scenarios such as monitoring performance, optimizing queries, securing sensitive information, and supporting organizational decision-making. Mastering these fundamentals provides a strong foundation for advancing to more complex database tasks and expanding career opportunities in IT and data management fields.
Advanced Data Modeling Concepts
A critical part of preparing for the 98-364 exam is understanding advanced data modeling concepts. Effective database design requires a clear understanding of entities, attributes, and relationships. Candidates should be able to identify how different entities interact and determine the most suitable type of relationship for each scenario, whether one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many. Proper modeling ensures data integrity, prevents redundancy, and facilitates accurate and efficient queries. Understanding these principles allows candidates to design databases that are scalable, maintainable, and aligned with organizational needs.
Normalization remains a central aspect of database modeling. It involves structuring tables to reduce duplication and enhance consistency. Candidates must understand the different normal forms and know how to apply them in practice. While higher normalization improves data integrity, it can also increase the complexity of queries. Balancing normalization with practical performance considerations is essential for designing effective databases. In some cases, denormalization may be applied to optimize read performance, particularly for reporting and analytical purposes.
Designing and Implementing Tables
Creating tables is a fundamental task in database management, and exam candidates must master this process. Each table should be defined with appropriate columns, data types, and constraints to ensure accurate and reliable storage. Constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and check constraints enforce rules that maintain data consistency and prevent errors. Candidates must also understand default values and nullability to control the behavior of columns effectively.
The process of table creation is not limited to individual tables but also includes designing relationships among multiple tables. Properly linked tables enable complex queries, reporting, and data manipulation without compromising integrity. Understanding how indexes affect table performance is equally important, as they can dramatically improve query speed while adding overhead to data modification operations. Strategic index placement helps optimize database efficiency for both transactional and analytical tasks.
Writing Complex Queries
Complex queries are a major focus of the 98-364 exam. Candidates must be able to retrieve data from single and multiple tables using join operations, subqueries, and nested queries. Inner joins return records with matching keys in both tables, while outer joins include unmatched records from one or both tables. Cross joins produce all possible combinations of rows between tables. Mastery of these join types enables candidates to extract relevant information efficiently from relational datasets.
Filtering and sorting data are also essential skills. Candidates should use conditional logic and operators to refine query results and apply aggregation functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX to summarize information. Grouping and having clauses allow for filtering of aggregated results, while functions such as string manipulation, date calculation, and conversion support dynamic and precise data analysis. Practicing these operations enhances problem-solving skills and prepares candidates for real-world database tasks.
Maintaining Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is a fundamental principle in database management. Candidates must understand how to implement and enforce constraints that govern the behavior of data. Primary keys ensure uniqueness, foreign keys enforce relationships, and check constraints validate data according to business rules. Understanding cascading updates and deletes helps maintain consistent relationships between tables and prevents orphaned records.
Triggers and stored procedures provide additional mechanisms for enforcing business logic automatically. Candidates must know when to use these tools to maintain consistency, validate inputs, and automate repetitive tasks. Proper implementation of these mechanisms ensures data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable across the database environment.
Optimizing Data Storage and Performance
Data storage optimization is critical for effective database management. Candidates should understand how to use indexes, partitioning, and other performance-enhancing techniques. Indexes allow for faster retrieval of records but can increase storage requirements and slow data modification operations. Candidates must balance the use of indexes with the need for efficient inserts, updates, and deletions.
Partitioning tables can improve performance by dividing large datasets into manageable segments, allowing queries to access relevant portions of data quickly. Efficient storage strategies also involve selecting appropriate data types, optimizing table structure, and minimizing unnecessary duplication. Understanding the trade-offs between storage efficiency, performance, and complexity ensures that databases remain both effective and manageable.
Security and Access Control
Securing a database is a key area of focus. Candidates must understand how to implement authentication, authorization, and access control to protect sensitive data. Roles and permissions allow administrators to grant specific access rights to users based on their responsibilities. The principle of least privilege ensures that users have only the access necessary to perform their tasks.
Encryption protects data both at rest and in transit, preventing unauthorized access and enhancing confidentiality. Candidates should also understand how auditing can be used to monitor database activity, detect anomalies, and maintain accountability. Security considerations are essential not only for protecting data but also for supporting regulatory compliance and ensuring trustworthiness of the database system.
Backup and Recovery Planning
Backup and recovery strategies are essential for maintaining database availability and reliability. Candidates must be familiar with different backup types, including full, differential, and transaction log backups. Knowing when and how to apply these backups ensures that data can be restored accurately in case of failure.
Restoring a database requires careful planning, including point-in-time recovery using transaction logs. Candidates should practice performing restoration tasks to ensure reliability and accuracy. Regular testing of backups and recovery procedures helps identify potential issues and prepares candidates to respond effectively in real-world scenarios. Proper backup and recovery practices safeguard data and support continuous operations.
Practical Application and Hands-On Experience
Hands-on experience is critical for understanding and applying database concepts. Candidates should create sample databases, define tables and relationships, and populate them with realistic data. Practicing queries that involve joins, aggregation, and conditional logic strengthens problem-solving skills.
Implementing views, stored procedures, and functions allows candidates to automate tasks and encapsulate logic. Experimenting with constraints, keys, and indexes demonstrates the impact of design choices on performance and integrity. Scenario-based exercises, such as managing customer information, sales data, or inventory records, provide context for applying theoretical knowledge and reinforce practical skills.
Utilizing Learning Resources
Structured learning materials help candidates systematically cover all exam domains. Reference guides, tutorials, and exercises provide detailed explanations, examples, and practice opportunities. Comprehensive resources allow candidates to progress logically from basic concepts to advanced applications.
Participation in online communities and forums offers additional perspectives and collaborative learning opportunities. Engaging with peers allows candidates to clarify doubts, share strategies, and explore alternative approaches. Collaborative learning enhances understanding, supports problem-solving, and provides insight into practical challenges encountered in database management.
Self-Assessment and Practice
Regular self-assessment is essential for exam readiness. Candidates should complete practice exercises, mock exams, and scenario-based tasks to evaluate their knowledge. Identifying strengths and areas for improvement enables focused study and efficient preparation.
Practicing under timed conditions helps candidates develop time management skills and become familiar with exam structure. Repeated application of database concepts in practice scenarios reinforces technical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and confidence. This preparation ensures candidates are equipped to handle both the exam and real-world database tasks efficiently.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Success
Success in the 98-364 exam requires combining theoretical understanding with practical application. Candidates must demonstrate competence in designing tables, managing relationships, executing complex queries, ensuring data integrity, and performing basic administrative tasks. Structured study, hands-on practice, community engagement, and self-evaluation create a comprehensive preparation strategy.
By integrating these elements, candidates develop the skills necessary to manage databases effectively, optimize performance, maintain security, and provide reliable data for decision-making. This holistic preparation supports exam success and lays the foundation for advanced database learning and professional growth.
Applying Skills in Real-World Scenarios
The knowledge and skills acquired while preparing for the 98-364 exam are directly applicable in professional environments. Candidates learn to manage relational databases, design efficient structures, manipulate and analyze data, and implement security and backup procedures. These abilities are valuable for roles that involve database administration, reporting, and IT support.
Practical experience with data modeling, querying, integrity enforcement, and performance optimization ensures that candidates are prepared to handle real-world database challenges. Mastery of these fundamentals enhances analytical thinking, problem-solving skills, and technical competence, providing a strong foundation for ongoing career development in database management and information technology.
Designing Efficient Database Structures
A critical aspect of preparing for the 98-364 exam is the ability to design efficient and scalable database structures. Candidates must understand how to define tables, choose appropriate data types, and establish relationships that maintain data integrity. Identifying entities and attributes, and determining the correct type of relationship for each scenario, ensures that databases are organized logically and can handle both transactional and analytical workloads. Effective design reduces redundancy, prevents anomalies, and supports the accuracy and reliability of the data stored within the system.
Candidates should also understand the principles of normalization and denormalization. Normalization eliminates redundancy by organizing data into related tables, whereas denormalization may be applied strategically to improve query performance for reporting or analytical purposes. A balance between normalization for integrity and denormalization for performance is necessary to create functional and efficient databases.
Advanced Query Development
Developing advanced queries is a core skill tested in the 98-364 exam. Candidates must be able to retrieve, manipulate, and summarize data efficiently using structured query commands. Queries often involve joining multiple tables to combine related information. Understanding inner joins, outer joins, and cross joins allows candidates to select appropriate operations for various scenarios.
Using aggregate functions such as SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX helps summarize information for decision-making and reporting purposes. Candidates should also practice using grouping and conditional logic to refine results and produce meaningful insights. Subqueries and nested queries enable dynamic retrieval of data based on related information and provide solutions to more complex requirements.
Maintaining and Enforcing Data Integrity
Data integrity ensures the reliability and accuracy of information stored in databases. Candidates must understand constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and check constraints. These mechanisms enforce rules that prevent duplication, invalid entries, and inconsistent data. Proper application of keys ensures that relationships between tables remain accurate and reliable.
Triggers and stored procedures offer additional ways to enforce business rules automatically. Candidates must know how to use these tools to validate data, maintain consistency, and automate repetitive processes. Understanding the interplay between constraints, triggers, and procedural logic helps maintain a robust and trustworthy database environment.
Optimizing Database Performance
Database performance is influenced by design, indexing, and query efficiency. Candidates must understand how indexes, partitioning, and data types affect performance. Clustered and non-clustered indexes allow for rapid retrieval of records but can increase storage requirements and slow modification operations. Effective indexing strategies improve response times for frequently accessed data while minimizing overhead.
Partitioning large tables into smaller segments enhances performance by allowing queries to access only the relevant portions of data. Efficient storage design, including appropriate data types and optimized table structures, also contributes to better performance. Candidates should practice analyzing query execution plans to identify bottlenecks and implement optimization techniques that enhance efficiency.
Database Security and Access Control
Protecting data is an essential component of database management. Candidates must understand authentication, authorization, and access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access while allowing legitimate users to perform necessary tasks. Assigning roles and permissions based on user responsibilities ensures that access is controlled according to the principle of least privilege.
Encryption techniques safeguard data both at rest and in transit, while auditing provides insight into user activity and potential anomalies. Understanding how to secure backups, implement role-based access, and monitor database activity is critical for maintaining a safe and reliable environment. Security considerations also encompass disaster recovery planning and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
Ensuring data availability through backups and recovery planning is a fundamental aspect of database management. Candidates must be familiar with full, differential, and transaction log backups, and understand the scenarios in which each type is appropriate. Knowledge of how to restore databases from backups, including point-in-time recovery, ensures that operations can continue in the event of data loss or corruption.
Testing backup and recovery procedures is an important practice to verify that restoration processes are reliable. Candidates should develop skills in planning, performing, and documenting backup and recovery tasks. Understanding how to manage storage, monitor backup success, and verify restored data strengthens practical database management capabilities.
Practical Application Through Hands-On Experience
Hands-on practice reinforces theoretical knowledge and prepares candidates for real-world database tasks. Candidates should create sample databases, define tables and relationships, and populate them with realistic data. Practicing queries that include joins, aggregations, conditional logic, and subqueries develops problem-solving skills and builds familiarity with relational data operations.
Implementing views, stored procedures, and functions enhances understanding of automation and encapsulation of logic. Candidates should also experiment with constraints, keys, and indexing strategies to observe their impact on data integrity and performance. Scenario-based exercises, such as managing sales records, tracking inventory, or analyzing customer information, provide practical experience and contextualize learning for exam success.
Utilizing Structured Study Materials
Effective preparation requires structured study materials that cover all exam domains systematically. Reference guides and tutorials provide detailed explanations of key concepts, examples, and exercises. Comprehensive resources allow candidates to progress logically from foundational knowledge to more complex topics, ensuring that no critical area is overlooked.
Participation in online communities and discussion forums provides additional learning opportunities. Interacting with peers allows candidates to clarify doubts, exchange strategies, and explore alternative approaches to problem-solving. Collaborative learning enhances understanding and prepares candidates to handle diverse scenarios in both exams and practical database management tasks.
Self-Evaluation and Practice Tests
Regular self-assessment is essential for exam readiness. Candidates should complete practice exercises, mock scenarios, and timed tests to evaluate their knowledge and proficiency. Identifying areas of strength and weakness enables focused study and efficient preparation.
Repeated practice under realistic conditions reinforces technical skills, strengthens confidence, and improves problem-solving abilities. Candidates develop familiarity with the types of tasks and questions likely to appear on the exam, ensuring they can respond efficiently and accurately. Self-evaluation also highlights gaps in understanding that can be addressed through targeted study.
Integrating Knowledge for Exam Readiness
Preparation for the 98-364 exam requires the integration of theoretical concepts with practical skills. Candidates must demonstrate competence in designing tables, defining relationships, writing complex queries, maintaining data integrity, securing databases, optimizing performance, and performing basic administrative tasks. Hands-on experience, structured study, community engagement, and self-assessment form a comprehensive preparation strategy.
This integrated approach equips candidates to manage real-world databases effectively. It ensures that they can retrieve and manipulate data accurately, enforce security, optimize performance, and provide reliable information for decision-making. Holistic preparation fosters technical proficiency, analytical thinking, and problem-solving capabilities, all of which are critical for success in the exam and professional practice.
Real-World Application of Skills
The competencies gained through preparing for the 98-364 exam are directly applicable in professional environments. Candidates acquire the ability to design and maintain relational databases, execute queries, ensure data integrity, implement security measures, and manage backups and recovery. These skills are valuable in roles involving database administration, data analysis, IT support, and reporting.
Hands-on experience with scenario-based exercises, practical problem-solving, and query optimization ensures candidates are prepared for challenges encountered in professional settings. Mastery of database fundamentals enhances analytical thinking and technical expertise, providing a strong foundation for advanced studies and career development in database management and information technology.
Advanced Data Modeling Techniques
Preparing for the 98-364 exam requires an in-depth understanding of advanced data modeling techniques. Candidates should be able to identify entities and relationships in complex datasets and determine how to represent these relationships accurately within a relational database. One-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships must be implemented effectively to ensure data integrity and support query efficiency. Understanding entity-relationship diagrams and translating them into well-structured tables is a critical skill. Proper data modeling reduces redundancy, prevents inconsistencies, and ensures that the database can scale to accommodate growing datasets while maintaining performance.
Normalization is a fundamental principle of data modeling. Candidates must understand first, second, and third normal forms and how to apply them to organize data logically. Normalized structures eliminate redundant data and maintain consistency, but excessive normalization may lead to complex joins and potential performance issues. In practice, some degree of denormalization can improve query efficiency for reporting or analytical operations. Candidates should be able to make informed decisions about when and how to apply normalization and denormalization techniques based on specific database requirements.
Table Design and Implementation
Designing and implementing tables effectively is a core skill for the 98-364 exam. Each table must be carefully structured with appropriate columns, data types, and constraints to store data accurately and efficiently. Primary keys uniquely identify records, foreign keys establish relationships, and unique constraints prevent duplicate values. Check constraints and default values enforce rules and control column behavior, maintaining the integrity of the data stored.
Relationships between tables are crucial for executing accurate queries and maintaining data integrity. Candidates should understand how to define one-to-many and many-to-many relationships and implement junction tables when necessary. Properly designed tables, along with thoughtful index placement, contribute to optimal performance and facilitate efficient data retrieval in both transactional and analytical scenarios.
Query Development and Optimization
Querying is a central aspect of the 98-364 exam, requiring candidates to retrieve, manipulate, and summarize data efficiently. Complex queries often involve combining information from multiple tables using joins. Inner joins return records with matching keys, outer joins include unmatched records, and cross joins produce all possible row combinations. Candidates must understand the implications of each join type and know when to use them.
Filtering data with conditional logic and using aggregate functions such as COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX allows candidates to summarize and analyze datasets effectively. Grouping and having clauses refine aggregated results, and subqueries enable nested operations that support dynamic and flexible data retrieval. Candidates should practice optimizing queries by analyzing execution plans, minimizing unnecessary joins, and using indexes strategically to improve performance while maintaining accuracy.
Data Integrity and Constraints
Maintaining data integrity is essential for reliable database operations. Candidates must understand constraints such as primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, check constraints, and default values. These mechanisms enforce rules that prevent invalid or duplicate data and maintain consistency across related tables. Cascading updates and deletes help maintain referential integrity by automatically updating or removing dependent records.
Triggers and stored procedures can enforce business rules and automate repetitive tasks. Candidates should understand when and how to use these tools to validate data and maintain consistency. Combining constraints, triggers, and procedural logic ensures a robust environment where data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable, supporting both operational and analytical needs.
Indexing and Performance Optimization
Indexes play a critical role in optimizing query performance. Candidates should understand the differences between clustered and non-clustered indexes, their applications, and their impact on both read and write operations. While indexes improve data retrieval speed, they also increase storage requirements and can slow insert, update, and delete operations. Effective index placement balances performance improvements with system resource considerations.
Partitioning large tables enhances performance by dividing data into manageable segments, allowing queries to access only relevant portions. Choosing appropriate data types, structuring tables efficiently, and avoiding unnecessary redundancy further optimize storage and performance. Candidates should practice using indexing and partitioning strategies to ensure efficient query execution and maintain system responsiveness.
Security and Access Management
Database security is a key component of exam preparation. Candidates must understand authentication, authorization, and role-based access control to ensure data is protected while allowing legitimate operations. The principle of least privilege should guide permission assignments, granting users only the access required to perform their tasks.
Encryption protects sensitive data at rest and in transit, while auditing monitors user activity and identifies potential security breaches. Understanding how to secure backups and implement monitoring mechanisms ensures a reliable and secure database environment. Candidates should also be aware of best practices for protecting data during migrations and backups, maintaining both integrity and confidentiality.
Backup, Recovery, and Continuity
Backup and recovery strategies are essential for maintaining database availability and durability. Candidates must be familiar with full, differential, and transaction log backups and understand their appropriate use cases. Restoring databases accurately, including point-in-time recovery using transaction logs, is critical for minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity.
Testing backup and recovery procedures validates their reliability and prepares candidates for real-world scenarios. Proper documentation of processes, monitoring of storage, and verification of restored data are crucial practices for maintaining operational readiness. Candidates should understand the balance between backup frequency, storage requirements, and recovery objectives to design robust strategies.
Hands-On Practice and Scenario-Based Learning
Practical experience reinforces theoretical knowledge. Candidates should create sample databases, define tables and relationships, and populate them with realistic datasets. Practicing queries involving joins, aggregations, and conditional logic strengthens analytical and problem-solving skills.
Implementing views, stored procedures, and functions allows candidates to automate repetitive tasks and encapsulate logic for consistent application. Experimenting with constraints, keys, and indexes demonstrates their effects on performance and integrity. Scenario-based exercises, such as managing employee records, inventory tracking, or customer information analysis, provide context and deepen understanding of practical database operations.
Structured Study Approaches
Systematic study of all exam domains ensures comprehensive coverage. Reference guides and tutorials offer detailed explanations, examples, and exercises that build knowledge progressively from foundational concepts to advanced applications. Comprehensive materials help candidates approach the exam with confidence, reducing the risk of overlooked topics.
Engaging in discussion forums and online communities allows candidates to explore diverse perspectives, clarify doubts, and exchange problem-solving strategies. Collaborative learning reinforces understanding, introduces practical insights, and encourages effective approaches to challenging tasks, enhancing both exam preparation and professional competence.
Self-Evaluation and Practice Testing
Self-assessment is essential for measuring progress and identifying knowledge gaps. Candidates should work through practice exercises, scenario-based tasks, and mock exams to evaluate their skills. Timed practice builds familiarity with the exam format and improves efficiency in responding to questions.
Repeated practice reinforces query writing, table design, integrity enforcement, indexing, and security skills. Self-assessment highlights areas that require additional focus, allowing candidates to refine their preparation strategy and gain confidence. This iterative process ensures readiness for the exam and strengthens practical database management abilities.
Integration of Knowledge for Exam Mastery
Success in the 98-364 exam requires integrating theoretical concepts with practical skills. Candidates must be proficient in designing tables, defining relationships, writing queries, maintaining data integrity, securing databases, optimizing performance, and performing administrative tasks. Hands-on practice, structured learning, community engagement, and self-assessment combine to create a thorough preparation framework.
This integrated approach equips candidates to manage real-world databases effectively, ensuring accurate data retrieval, secure operations, and efficient performance. Holistic preparation supports both exam success and practical application in professional database environments, fostering analytical thinking, problem-solving skills, and technical expertise.
Applying Skills in Professional Contexts
The skills acquired through 98-364 exam preparation are directly applicable in professional settings. Candidates gain the ability to design and maintain relational databases, implement complex queries, enforce integrity, optimize performance, manage security, and conduct backups and recovery. These competencies are valuable for roles in database administration, IT support, data analysis, and reporting.
Hands-on experience with scenario-based exercises, practical problem-solving, and performance tuning ensures candidates are equipped to tackle challenges in real-world database management. Mastery of these fundamentals strengthens analytical abilities, technical knowledge, and professional confidence, providing a strong foundation for continued growth and advanced database learning.
Comprehensive Database Design Strategies
Effective preparation for the 98-364 exam requires a comprehensive understanding of database design strategies. Candidates must be able to conceptualize data structures, define entities and attributes, and determine how these elements interact within a relational system. Accurately representing one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships ensures logical organization and supports efficient data retrieval. Understanding entity-relationship modeling and converting these diagrams into functional tables is crucial for creating databases that are maintainable, scalable, and capable of supporting both operational and analytical requirements.
Candidates should be adept at applying normalization principles to reduce redundancy and maintain data consistency. They should also recognize scenarios where denormalization may improve query performance without compromising data integrity. A strong grasp of these strategies allows candidates to design databases that balance efficiency with reliability, meeting both technical and business needs.
Advanced Query Construction
Mastering advanced queries is essential for the 98-364 exam. Candidates must be able to retrieve, filter, and manipulate data using structured query operations. This includes combining multiple tables using joins, such as inner, outer, and cross joins, to produce meaningful datasets. Proper use of joins ensures accurate data representation and efficient information retrieval.
Aggregate functions like SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX allow candidates to summarize large datasets and extract actionable insights. Grouping and conditional clauses refine the output, enabling advanced reporting and analysis. Subqueries and nested queries provide dynamic data access, allowing candidates to solve complex scenarios effectively. Practicing query optimization techniques, including indexing, filtering, and analyzing execution plans, ensures queries run efficiently and deliver accurate results.
Enforcing Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is a central theme in database management. Candidates must understand how to implement primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, and check constraints to prevent duplication and enforce consistency. Cascading updates and deletes help maintain accurate relationships across tables, preventing orphaned or inconsistent records.
Triggers and stored procedures provide automated mechanisms to enforce business rules and maintain consistency. Candidates should know how to apply these tools effectively to validate inputs, enforce constraints, and automate routine database operations. Ensuring data integrity through these mechanisms safeguards the reliability and accuracy of database systems, which is critical for both the exam and real-world applications.
Indexing and Optimization Techniques
Optimizing database performance involves understanding indexing strategies and other optimization techniques. Candidates should differentiate between clustered and non-clustered indexes and recognize their impact on data retrieval and modification operations. Effective indexing improves query performance but also introduces storage and maintenance considerations that must be balanced.
Partitioning large tables enhances performance by allowing queries to focus on relevant subsets of data, reducing processing time. Candidates must also be able to select appropriate data types and structure tables efficiently to optimize storage and improve system responsiveness. Practicing these techniques ensures candidates can design databases that support high-performance operations while maintaining data integrity.
Security and Access Management
Database security is a critical component of effective database administration. Candidates must understand authentication and authorization mechanisms, implementing role-based access control to limit user privileges according to responsibilities. Adhering to the principle of least privilege ensures that users have only the access necessary to perform their tasks.
Encryption techniques protect sensitive data during storage and transmission, while auditing and monitoring track user activity and identify potential security threats. Candidates should also understand best practices for securing backups and maintaining compliance with organizational policies. Mastery of these concepts ensures that databases remain secure, reliable, and compliant with operational standards.
Backup and Recovery Planning
Backup and recovery strategies are essential for database reliability. Candidates should be familiar with full, differential, and transaction log backups and understand the appropriate application for each. Restoring databases effectively, including point-in-time recovery, ensures operational continuity in the event of failure or data corruption.
Testing backup and recovery procedures is a key practice to verify reliability and identify potential issues. Candidates should document processes, monitor storage requirements, and validate restored data. Understanding how to design and implement effective backup strategies ensures that databases remain resilient, supporting both exam preparation and practical management scenarios.
Scenario-Based Hands-On Practice
Practical experience is crucial for mastering concepts required in the 98-364 exam. Candidates should create sample databases, define tables and relationships, and populate them with realistic datasets. Performing queries that involve joins, aggregation, conditional logic, and subqueries strengthens problem-solving abilities and reinforces theoretical knowledge.
Implementing views, stored procedures, and functions allows candidates to automate tasks and encapsulate business logic. Experimenting with constraints, keys, and indexes demonstrates their impact on integrity and performance. Scenario-based exercises, such as managing customer data, tracking sales, or monitoring inventory, provide practical context and prepare candidates for real-world applications of database concepts.
Structured Learning and Reference Materials
Systematic study using structured resources ensures comprehensive coverage of exam objectives. Reference guides, tutorials, and exercises provide detailed explanations and examples that progress logically from foundational concepts to advanced practices. Utilizing these materials ensures candidates address all relevant topics and develop confidence in their abilities.
Engaging with peers through online communities enhances learning by allowing candidates to share strategies, discuss challenges, and explore alternative solutions. Collaborative learning deepens understanding, encourages problem-solving, and provides practical insights that are valuable both for the exam and professional application.
Self-Assessment and Practice Evaluation
Self-assessment is an essential component of exam readiness. Candidates should complete practice exercises, mock scenarios, and timed tests to measure their understanding and identify areas needing improvement. Regular practice under exam-like conditions builds familiarity with question formats and strengthens time management skills.
Repeated practice reinforces technical skills in query writing, table design, data integrity enforcement, indexing, and security. Evaluating performance allows candidates to refine study strategies, focus on weak areas, and gain confidence. This iterative approach ensures a well-rounded preparation and equips candidates to handle both exam questions and practical database challenges effectively.
Integration of Knowledge for Exam Success
Preparation for the 98-364 exam requires integrating theoretical knowledge with practical skills. Candidates must demonstrate competence in designing tables, establishing relationships, writing queries, enforcing data integrity, optimizing performance, implementing security measures, and performing basic administrative tasks. Hands-on practice, structured study, peer engagement, and self-assessment collectively form a robust preparation strategy.
This integrated approach ensures that candidates can manage databases effectively in real-world scenarios. It fosters the ability to retrieve and manipulate data accurately, secure operations, optimize performance, and maintain reliable backups. Holistic preparation enhances analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and technical expertise, laying the groundwork for success in both the exam and professional database management roles.
Application in Professional Environments
The skills gained through 98-364 exam preparation are directly applicable in professional contexts. Candidates learn to design, maintain, and query relational databases, enforce data integrity, optimize performance, implement security protocols, and manage backups. These competencies are essential for roles involving database administration, IT support, data analysis, and reporting.
Scenario-based practice prepares candidates for challenges encountered in workplace environments. Developing proficiency in handling complex queries, performance tuning, security management, and disaster recovery strengthens practical problem-solving skills. Mastery of these fundamentals builds a solid foundation for continued learning, advanced database tasks, and career development in information technology and database management.
Conclusion
The preparation for the 98-364 exam involves a thorough understanding of foundational database concepts, practical implementation skills, and the ability to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. This exam emphasizes not only the technical aspects of relational databases but also the importance of logical thinking, problem-solving, and effective data management practices. Candidates must be able to design efficient database structures, create tables and relationships, and implement constraints that ensure data integrity. These skills form the foundation of any relational database system and are critical for maintaining accuracy and consistency across datasets.
Advanced query development is a significant component of exam preparation. Candidates are required to retrieve and manipulate data using complex queries, including joins, subqueries, and aggregate functions. The ability to filter, sort, and summarize information enables professionals to extract meaningful insights and supports informed decision-making. Developing proficiency in query optimization, such as understanding indexing strategies and analyzing execution plans, ensures that data retrieval is not only accurate but also efficient, which is essential for handling large-scale databases in practical environments.
Maintaining data integrity and implementing security measures are fundamental for any database professional. Candidates must understand how to enforce rules using primary and foreign keys, unique constraints, and triggers, as well as manage user access through role-based permissions and authentication protocols. These skills protect data from corruption, unauthorized access, and inconsistencies, ensuring reliability and compliance with organizational policies. Additionally, understanding backup and recovery strategies is crucial to prevent data loss and maintain continuity in the event of failures or unexpected incidents.
Hands-on practice and scenario-based exercises play an important role in reinforcing knowledge. Creating sample databases, performing queries, implementing stored procedures, and experimenting with constraints and indexes provide candidates with practical experience. These exercises help translate theoretical knowledge into actionable skills that can be applied in professional settings. Structured learning through guides, tutorials, and reference materials ensures that candidates cover all exam objectives systematically while online discussions and peer interaction provide additional perspectives and problem-solving strategies.
Self-assessment and practice testing allow candidates to evaluate their understanding, identify areas of improvement, and refine their preparation strategy. Regular testing under realistic conditions builds familiarity with exam formats, strengthens confidence, and enhances time management skills. This iterative process ensures candidates are fully prepared for the challenges of the 98-364 exam and capable of applying their knowledge effectively in practical database management scenarios.
Ultimately, preparing for the 98-364 exam equips candidates with the essential skills required to design, manage, and manipulate relational databases successfully. It fosters analytical thinking, technical proficiency, and problem-solving capabilities, laying a strong foundation for advanced learning and career growth in database administration and information technology. Mastery of these concepts ensures candidates can work efficiently, make informed decisions, and contribute effectively to organizational data management efforts.
The 98-364 exam serves as both a benchmark of knowledge and a practical guide for professional skill development, preparing candidates to meet real-world database challenges with confidence and competence.
Microsoft MTA 98-364 practice test questions and answers, training course, study guide are uploaded in ETE Files format by real users. Study and Pass 98-364 Database Fundamentals certification exam dumps & practice test questions and answers are to help students.
Exam Comments * The most recent comment are on top
- AZ-104 - Microsoft Azure Administrator
- AI-900 - Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals
- AI-102 - Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution
- AZ-305 - Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions
- DP-700 - Implementing Data Engineering Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- PL-300 - Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst
- MD-102 - Endpoint Administrator
- AZ-900 - Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- MS-102 - Microsoft 365 Administrator
- AZ-500 - Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
- SC-300 - Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator
- SC-200 - Microsoft Security Operations Analyst
- SC-401 - Administering Information Security in Microsoft 365
- DP-600 - Implementing Analytics Solutions Using Microsoft Fabric
- AZ-700 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- AZ-204 - Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure
- SC-100 - Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect
- PL-200 - Microsoft Power Platform Functional Consultant
- AZ-400 - Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- PL-400 - Microsoft Power Platform Developer
- AZ-140 - Configuring and Operating Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
- AZ-800 - Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure
- SC-900 - Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals
- PL-600 - Microsoft Power Platform Solution Architect
- GH-300 - GitHub Copilot
- DP-300 - Administering Microsoft Azure SQL Solutions
- MS-900 - Microsoft 365 Fundamentals
- AZ-801 - Configuring Windows Server Hybrid Advanced Services
- MS-700 - Managing Microsoft Teams
- PL-900 - Microsoft Power Platform Fundamentals
- MB-280 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Experience Analyst
- MB-330 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
- MB-800 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Functional Consultant
- DP-900 - Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
- AB-730 - AI Business Professional
- MB-310 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance Functional Consultant
- DP-100 - Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure
- MB-820 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central Developer
- MB-230 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service Functional Consultant
- MS-721 - Collaboration Communications Systems Engineer
- MB-700 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Solution Architect
- PL-500 - Microsoft Power Automate RPA Developer
- MB-500 - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer
- GH-900 - GitHub Foundations
- MB-335 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management Functional Consultant Expert
- GH-200 - GitHub Actions
- GH-500 - GitHub Advanced Security
- DP-420 - Designing and Implementing Cloud-Native Applications Using Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- MB-240 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Field Service
- AB-100 - Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect
- GH-100 - GitHub Administration
- AB-731 - AI Transformation Leader
- MB-910 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Customer Engagement Apps (CRM)
- SC-400 - Microsoft Information Protection Administrator
- AZ-120 - Planning and Administering Microsoft Azure for SAP Workloads
- MB-920 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Finance and Operations Apps (ERP)
- DP-203 - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- 62-193 - Technology Literacy for Educators
- AZ-303 - Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
- MO-100 - Microsoft Word (Word and Word 2019)
- MO-300 - Microsoft PowerPoint (PowerPoint and PowerPoint 2019)
- MB-210 - Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Sales
- 98-383 - Introduction to Programming Using HTML and CSS
Why customers love us?
What do our customers say?
The resources provided for the Microsoft certification exam were exceptional. The exam dumps and video courses offered clear and concise explanations of each topic. I felt thoroughly prepared for the 98-364 test and passed with ease.
Studying for the Microsoft certification exam was a breeze with the comprehensive materials from this site. The detailed study guides and accurate exam dumps helped me understand every concept. I aced the 98-364 exam on my first try!
I was impressed with the quality of the 98-364 preparation materials for the Microsoft certification exam. The video courses were engaging, and the study guides covered all the essential topics. These resources made a significant difference in my study routine and overall performance. I went into the exam feeling confident and well-prepared.
The 98-364 materials for the Microsoft certification exam were invaluable. They provided detailed, concise explanations for each topic, helping me grasp the entire syllabus. After studying with these resources, I was able to tackle the final test questions confidently and successfully.
Thanks to the comprehensive study guides and video courses, I aced the 98-364 exam. The exam dumps were spot on and helped me understand the types of questions to expect. The certification exam was much less intimidating thanks to their excellent prep materials. So, I highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for this certification exam.
Achieving my Microsoft certification was a seamless experience. The detailed study guide and practice questions ensured I was fully prepared for 98-364. The customer support was responsive and helpful throughout my journey. Highly recommend their services for anyone preparing for their certification test.
I couldn't be happier with my certification results! The study materials were comprehensive and easy to understand, making my preparation for the 98-364 stress-free. Using these resources, I was able to pass my exam on the first attempt. They are a must-have for anyone serious about advancing their career.
The practice exams were incredibly helpful in familiarizing me with the actual test format. I felt confident and well-prepared going into my 98-364 certification exam. The support and guidance provided were top-notch. I couldn't have obtained my Microsoft certification without these amazing tools!
The materials provided for the 98-364 were comprehensive and very well-structured. The practice tests were particularly useful in building my confidence and understanding the exam format. After using these materials, I felt well-prepared and was able to solve all the questions on the final test with ease. Passing the certification exam was a huge relief! I feel much more competent in my role. Thank you!
The certification prep was excellent. The content was up-to-date and aligned perfectly with the exam requirements. I appreciated the clear explanations and real-world examples that made complex topics easier to grasp. I passed 98-364 successfully. It was a game-changer for my career in IT!

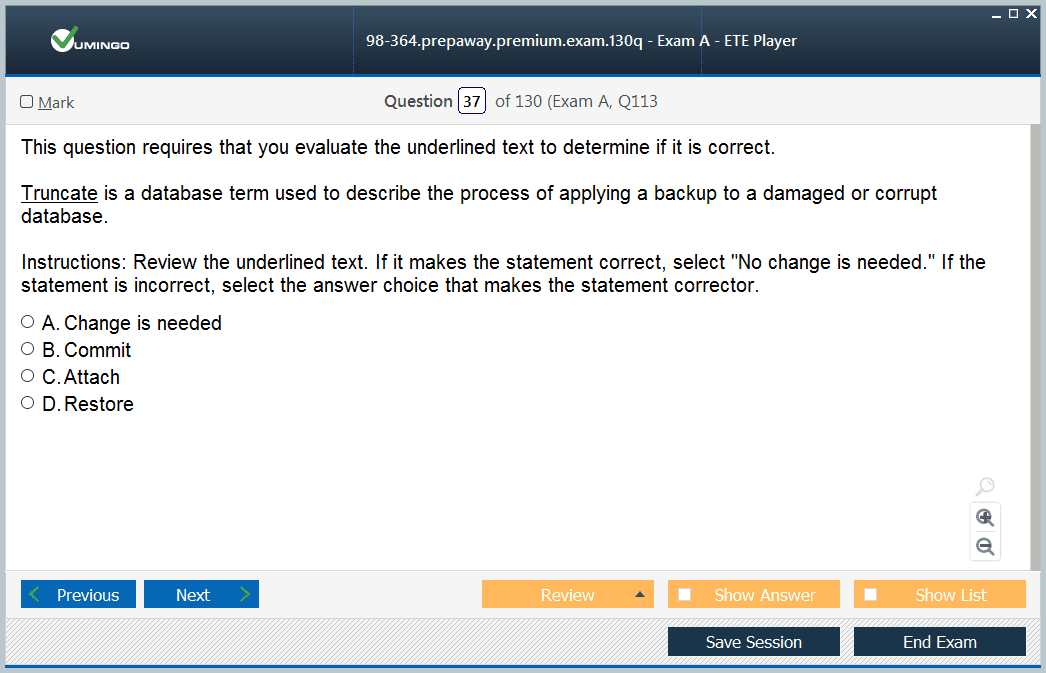
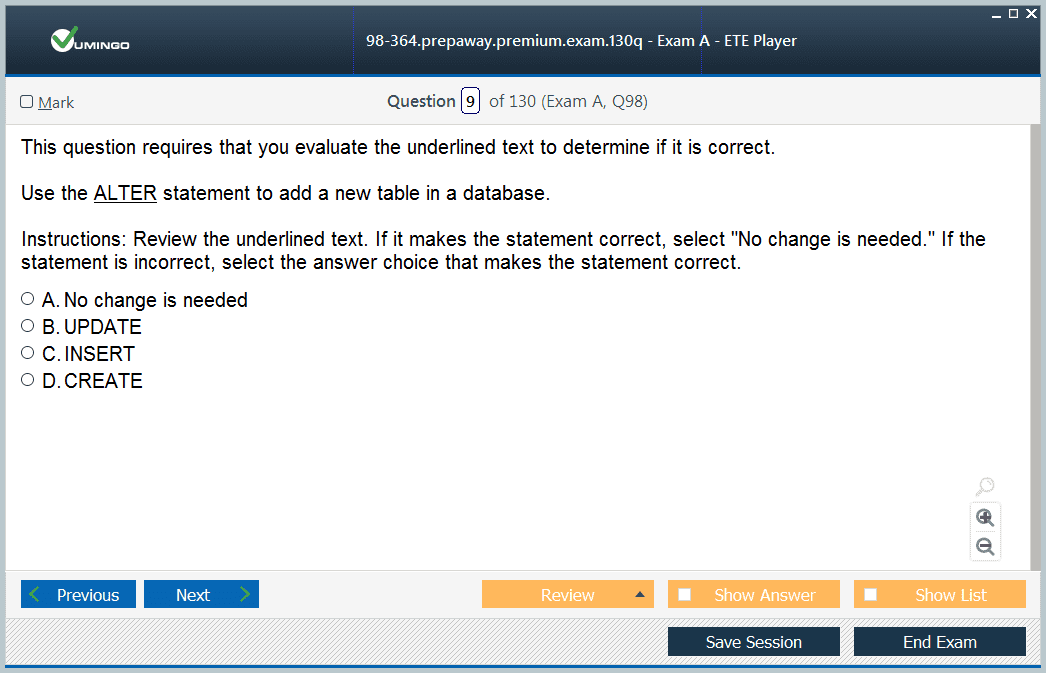
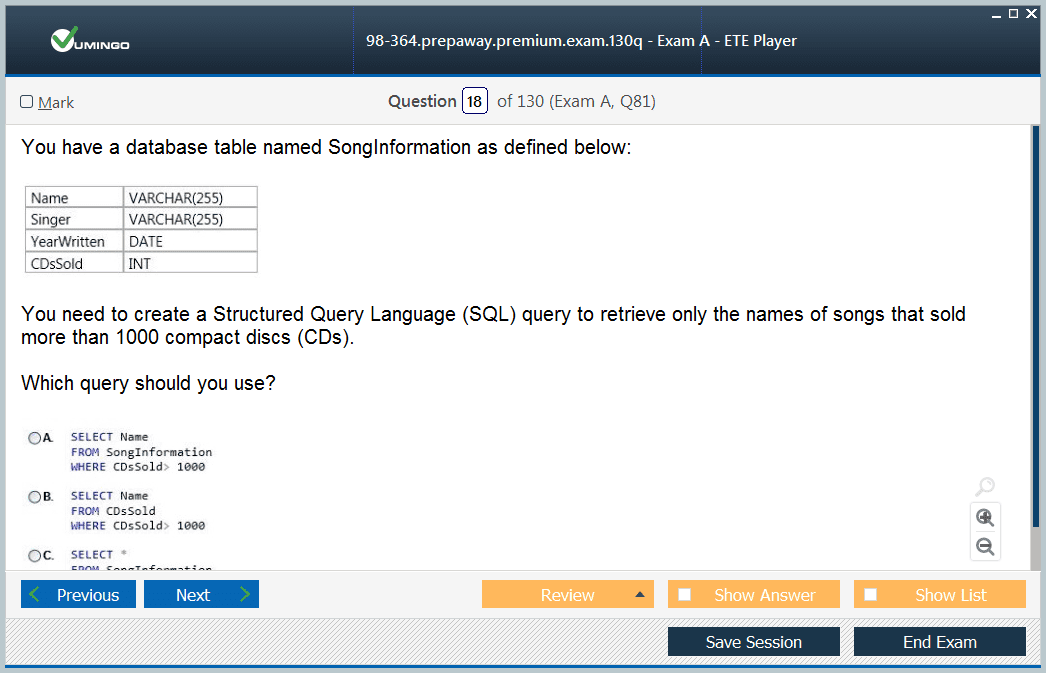
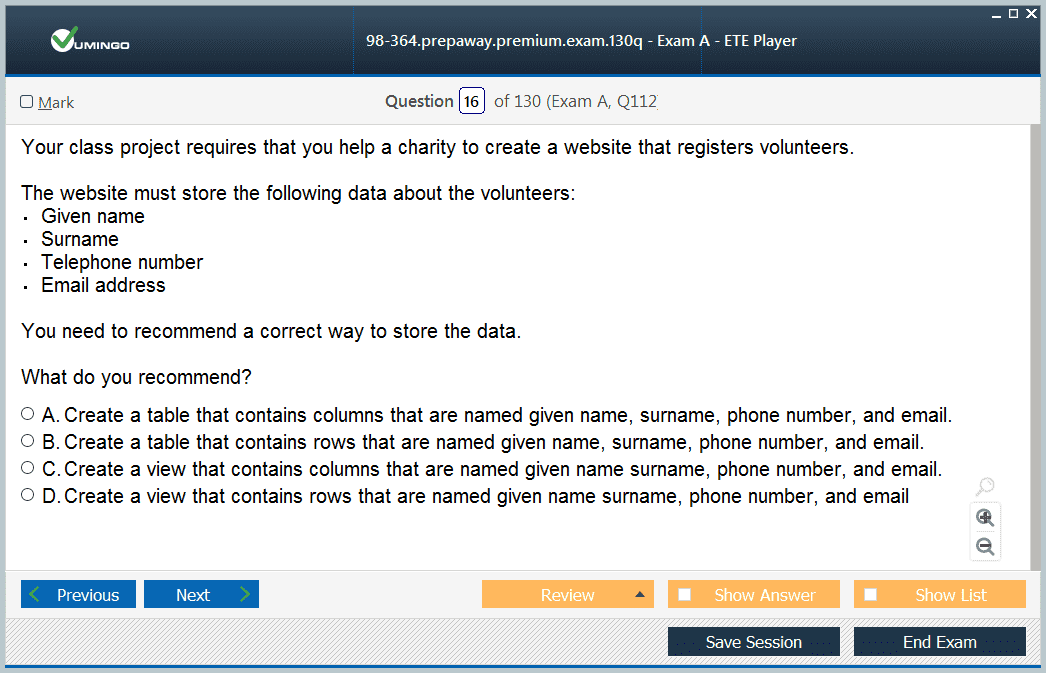








What is the minimum passing score for the 98-364 exam?
Thx